Professional Documents
Culture Documents
14 15
14 15
Uploaded by
aleeza.vargas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
14-15
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pages14 15
14 15
Uploaded by
aleeza.vargasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
1. Give and explain the major activities of 2.
What is meant by “off-balance-sheet”
banks for the last 5 decades activities of commercial banks?
Traditional Banking Services (1970s-1980s): Off-balance-sheet activities refer to financial
transactions that do not appear on a bank's
Deposits and Loans: Banks primarily focused on
balance sheet but can impact its financial
taking deposits and providing loans to
position. Examples include loan commitments,
individuals and businesses.
letters of credit, and derivatives. These activities
Payment Services: Offering payment services, allow banks to manage risk and provide
such as check clearing and wire transfers. additional services without directly affecting
their balance sheet ratios.
Deregulation and Expansion (1980s-1990s):
Diversification: Banks started diversifying their
services, including insurance and investment 3. Why are investment banks considered
products. engaged in “shadows banking”?
Global Expansion: Increased international Investment banks are considered engaged in
presence and operations. "shadow banking" due to their involvement in
activities outside traditional banking
Technological Advances (1990s-2000s): regulations. Shadow banking involves financial
Digital Banking: Introduction of online banking, intermediaries facilitating credit creation and
ATMs, and other technological innovations. liquidity outside the traditional banking system.
Investment banks engage in activities like
Risk Management: Enhanced risk management securitization, money market funds, and
practices due to increased financial complex financial products, operating in the
complexities. shadows of traditional banking regulations.
Financial Crisis and Regulatory Changes (2008-
2010s):
4. What are sources of income of
Regulatory Reforms: Stringent regulations post investment banks?
the 2008 financial crisis to enhance stability.
Underwriting Fees: Earnings from underwriting
Focus on Risk Management: Greater emphasis new securities issuances.
on risk management and compliance.
Trading and Sales: Profits from buying and
Digital Transformation (2010s-Present): selling financial instruments.
Fintech Collaboration: Collaboration with Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A): Advisory fees
fintech firms for innovation and digital services. for facilitating mergers and acquisitions.
Cybersecurity: Heightened focus on Asset Management: Management fees for
cybersecurity due to increased digitalization. handling investment portfolios.
Advisory Services: Fees for providing financial
advice to clients.
5. Distinguish between the industry 1. Indicators of Improvement in the
coverage groups and financial services Philippine Banking System:
group within the organization of
Capital Adequacy: Higher capital adequacy
investment banks
ratios signify a strengthened financial position,
Industry Coverage Groups: Focus on specific ensuring banks can absorb potential losses and
industries (e.g., technology, healthcare) and maintain stability.
provide specialized financial services tailored to
the needs of those industries.
Asset Quality: Improvements in asset quality,
Financial Services Group: Covers a range of
with a lower ratio of non-performing loans
financial products and services, including
(NPLs) to total loans, reflect effective risk
mergers and acquisitions, restructuring, and
management.
capital raising, not limited to a specific industry.
6. Enumerate / describe the classification
of firms engaged in investment banking Profitability: Rising return on assets (ROA) and
according to size. return on equity (ROE) indicate that banks are
generating healthy profits from their operations.
Bulge Bracket Firms: Large, globally recognized
investment banks with extensive capabilities
and services.
Liquidity Position: Adequate liquidity, reflected
Middle Market Firms: Medium-sized in favorable loan-to-deposit ratios and liquid
investment banks that focus on mid-sized asset holdings, ensures banks can meet short-
companies, often regionally or sector-specific. term obligations.
Boutique Firms: Small, specialized firms that
provide niche services, such as M&A advisory in
specific industries. Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to
regulatory standards, such as Basel III
Regional/Local Firms: Smaller banks that requirements, demonstrates a commitment to
operate within a specific region or locality, financial stability.
offering a range of financial services.
Technological Adoption: Implementation of
innovative technologies and digital banking
services shows adaptability to evolving
customer needs.
Governance and Risk Management:
Strengthened governance practices and robust
risk management frameworks contribute to the
overall stability of the banking sector.
Financial Inclusion: Efforts to enhance access to 3. Major Forces Leading to the Growth of
financial services for underserved populations the Philippine Banking System:
contribute to a more inclusive banking system.
Economic Expansion: A growing economy
creates demand for banking services,
encouraging the expansion of the banking
2. Importance of the Banking Sector in the
sector.
Philippine Economy:
The banking sector is considered a key anchor of
the country's growing economy for several Financial Inclusion Initiatives: Government
reasons: efforts to promote financial inclusion increase
the reach and impact of the banking system.
Financial Intermediation: Banks facilitate the
flow of funds between savers and borrowers, Regulatory Reforms: Regulatory changes aimed
supporting economic activities and investments. at enhancing governance, risk management,
and compliance contribute to a more robust
banking sector.
Credit Provision: Banks provide loans to
businesses and individuals, fostering
entrepreneurship, job creation, and economic Technological Advancements: Adoption of
development. modern technologies and digital banking
solutions enhances efficiency and broadens
service offerings.
Payment and Settlement Systems: Efficient
banking systems facilitate smooth and secure
transactions, promoting trade and commerce. Globalization: Increased integration with global
financial markets exposes Philippine banks to
international opportunities and fosters
Capital Mobilization: Banks play a crucial role in competitiveness.
mobilizing and allocating capital, channeling
funds to sectors with growth potential.
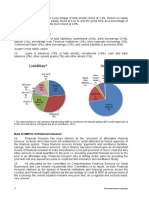
4. Unfavorable Effects of COVID-19 on the
Philippine Banking and Insurance Industries (as
Risk Management: Banks help manage financial of Q2 2021):
risks, contributing to overall economic stability.
a. Philippine Banking Industry:
Monetary Policy Transmission: The banking
Asset Quality Deterioration: Economic
sector acts as a conduit for monetary policy
uncertainties led to an increase in non-
implementation, influencing interest rates and
performing loans.
liquidity in the economy.
Provisions and Reserves: Banks had to allocate
higher provisions for potential loan losses.
Liquidity Challenges: Some sectors faced
liquidity constraints due to disruptions in
business operations.
b. Philippine Insurance Industry:
Claims and Underwriting Challenges: Increased
claims and underwriting difficulties due to the
pandemic's impact on health and business
activities.
Investment Portfolio Volatility: Market volatility
affected the value and returns of insurance
companies' investment portfolios.
Operational Disruptions: Operational challenges
arose, impacting the seamless delivery of
insurance services.
Both industries experienced challenges related
to economic uncertainties, business disruptions,
and the need to adapt to new operating
conditions during the pandemic. The severity of
these effects varied across sectors and
companies.
You might also like
- CFA Sector Analysis BankingDocument10 pagesCFA Sector Analysis BankingTai NguyenNo ratings yet
- TB Chapter02Document54 pagesTB Chapter02Dan Andrei BongoNo ratings yet
- Dow TheoryDocument7 pagesDow TheoryChristopher Michael Quigley100% (4)
- Commercial Banks: Functions and Present PositionDocument22 pagesCommercial Banks: Functions and Present Positionraghvendragaur22No ratings yet
- IFS Notes 1Document43 pagesIFS Notes 1Tejas NagulwarNo ratings yet
- Overview of Indian Financial SystemDocument17 pagesOverview of Indian Financial SystemKIng KumarNo ratings yet
- Marketing of Financial ServicesDocument20 pagesMarketing of Financial ServicesVirendra Choudhry100% (2)
- Financial ServicesDocument4 pagesFinancial Serviceschakki737603No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Financial Services: An Introduction: ObjectivesDocument19 pagesUnit 3 Financial Services: An Introduction: ObjectivesKashif UddinNo ratings yet
- Financial Services Unit IVDocument19 pagesFinancial Services Unit IVghoshpreetu11No ratings yet
- IMChap 1Document10 pagesIMChap 1babar zahoor100% (1)
- Unit1 Financial Services 1 PDFDocument6 pagesUnit1 Financial Services 1 PDFRoshan SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment Commercial Banking System (Vaani Khurana)Document20 pagesAssignment Commercial Banking System (Vaani Khurana)dhawalbaria7No ratings yet
- Fs Unit 1Document17 pagesFs Unit 1lokiloki0916No ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument22 pagesFinancial ServicessonuNo ratings yet
- Banking 424Document17 pagesBanking 424Sumaiya AfrinNo ratings yet
- ICWIM - 001 The Financial ServicesDocument25 pagesICWIM - 001 The Financial ServicesMaher G. BazakliNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Financial ServicesDocument24 pagesAssignment of Financial ServicesBALPREET_SVIETNo ratings yet
- FM 11-2Document5 pagesFM 11-2Romzor ArecilNo ratings yet
- Issues Faced by Banks in Global Markets (Case Study) : MADHAV LUTHRA (1520468)Document2 pagesIssues Faced by Banks in Global Markets (Case Study) : MADHAV LUTHRA (1520468)Madhav LuthraNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banking System and Role of RBI PG QP JUNE 2024 PDFDocument4 pagesCommercial Banking System and Role of RBI PG QP JUNE 2024 PDFBalamuralikrishna YadavNo ratings yet
- Sana DessertationDocument80 pagesSana DessertationNaghul KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Financial Services SectorDocument2 pagesFinancial Services SectorVineet PatilNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Banking 302 Ch.Document158 pagesFundamentals of Banking 302 Ch.davidsmith.1242.comNo ratings yet
- MFS NotesDocument139 pagesMFS NotesSHANAT BENNYNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument27 pagesFinancial ServicesPoonam100% (1)
- FMS Chapter 3 NDocument27 pagesFMS Chapter 3 NcoolartncraftsNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument182 pagesFinancial ServicesVivek KuchhalNo ratings yet
- Financial Services Notes - Jeganraj - 2020Document23 pagesFinancial Services Notes - Jeganraj - 2020jeganrajraj100% (1)
- Wa0013.Document11 pagesWa0013.Merlyn MartinNo ratings yet
- Banking Challenges 09AC31 PsgimDocument10 pagesBanking Challenges 09AC31 Psgimscribd09ac31No ratings yet
- As Per Section 6a5Document7 pagesAs Per Section 6a5vasimahmad20No ratings yet
- BANK3014 Week 13 Tutorial Suggested Solutions - Week 12 MaterialDocument3 pagesBANK3014 Week 13 Tutorial Suggested Solutions - Week 12 Materialdarcy whiteNo ratings yet
- Fims CiaDocument15 pagesFims Cia17.Krisha JogiNo ratings yet
- Retail BankingDocument5 pagesRetail Bankingpayal guravNo ratings yet
- Functions of Financial ServicesDocument15 pagesFunctions of Financial ServicesAshutosh Pandey67% (9)
- Definition of Financial ServicesDocument25 pagesDefinition of Financial ServicesShailesh SoniNo ratings yet
- Sharath Chandra.M.S. Vinoth Babu Vinoth Arumugam Avudaipan Ramiah Dinesh MuthuDocument27 pagesSharath Chandra.M.S. Vinoth Babu Vinoth Arumugam Avudaipan Ramiah Dinesh MuthuAvudaiappan RamNo ratings yet
- Value Chain FinancingDocument2 pagesValue Chain FinancingAvdhesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Macauro: Emerging Trends in Banking - Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesMacauro: Emerging Trends in Banking - Challenges and Opportunitiesrk_rkaushikNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document15 pagesAssignment 1Jhilik PradhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Commercial BanksDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Commercial BanksAtharva AlokNo ratings yet
- 45 NBFC PDFDocument109 pages45 NBFC PDFTushar JainNo ratings yet
- Report 24 PDFDocument56 pagesReport 24 PDFGopi SKNo ratings yet
- Blackbook FinalDocument86 pagesBlackbook Finalgunesh somayaNo ratings yet
- RBI Circulars March 2023Document8 pagesRBI Circulars March 2023Udya singhNo ratings yet
- Nature and Characteristics of Financial ServicesDocument51 pagesNature and Characteristics of Financial Servicesnaveen6018No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1AliansNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial Services PDFDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Financial Services PDFudayachari907No ratings yet
- The Triangle of Microfinance-EdDocument29 pagesThe Triangle of Microfinance-EdAdela Miranti YuniarNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Credit Risk ManagementDocument3 pagesDissertation On Credit Risk ManagementShahbazHasanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Model For Assessing NBFCsAsset FiDocument11 pagesRisk Assessment Model For Assessing NBFCsAsset FiNishit RelanNo ratings yet
- Embeded WealthDocument36 pagesEmbeded WealthEzam0% (1)
- Session 3-4Document43 pagesSession 3-4jaitik nagpalNo ratings yet
- Role NBFC PDFDocument3 pagesRole NBFC PDFAGN YaNo ratings yet
- Report From Lars - IBFED-OW - Report - FinalDocument56 pagesReport From Lars - IBFED-OW - Report - FinalSabina vlaicuNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Management in BanksDocument53 pagesCredit Risk Management in Banksrahulhaldankar100% (1)
- Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesExecutive SummaryyogeshramachandraNo ratings yet
- Tobeina Competitive Edge:: Perils of Innovation Rosita ChongDocument28 pagesTobeina Competitive Edge:: Perils of Innovation Rosita Chongranj19869No ratings yet
- Bank Lending EnvironmentDocument7 pagesBank Lending EnvironmentMoses OlabodeNo ratings yet
- Black Book ShubhamDocument82 pagesBlack Book ShubhamShubham GaikarNo ratings yet
- Bank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingFrom EverandBank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Midterm 3Document1 pageMidterm 3aleeza.vargasNo ratings yet
- Deficit. This Budget Balance Is Commonly Used inDocument8 pagesDeficit. This Budget Balance Is Commonly Used inaleeza.vargasNo ratings yet
- 8 9Document9 pages8 9aleeza.vargasNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument9 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionsaleeza.vargasNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument1 pageFormulaaleeza.vargasNo ratings yet
- Into To Treasury & Risk Management - FinalDocument21 pagesInto To Treasury & Risk Management - FinalGaurav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- AFOWERK FINAL laundry-CBE LOANDocument54 pagesAFOWERK FINAL laundry-CBE LOANAbel GetachewNo ratings yet
- Domino's Pizza Enterprises LTDDocument14 pagesDomino's Pizza Enterprises LTDemmacahillNo ratings yet
- Bear Bull Power Indicator ExplainedDocument11 pagesBear Bull Power Indicator ExplainedMin Than Htut0% (1)
- Oberoi Realty Limited - Red Herring ProspectusDocument452 pagesOberoi Realty Limited - Red Herring ProspectusShyam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Fundamental Accounting Principles 22nd Edition Wild Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Fundamental Accounting Principles 22nd Edition Wild Solutions Manualzax.algerian.tco4gNo ratings yet
- 1 2 Types of Organisation PDFDocument3 pages1 2 Types of Organisation PDFGermanRobertoFongNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and Markets - Foreign Exchange MarketsDocument19 pagesFinancial Institutions and Markets - Foreign Exchange MarketsSiddhartha saiNo ratings yet
- STCBL Financial AnalysisDocument33 pagesSTCBL Financial AnalysisSonam K Gyamtsho67% (3)
- Corporate Finance PDFDocument56 pagesCorporate Finance PDFdevNo ratings yet
- Are The 100 Best Better by Fulmer Citado Por S RobbinsDocument29 pagesAre The 100 Best Better by Fulmer Citado Por S RobbinsJONEL ANTONY MAYHUA CHUCHONNo ratings yet
- International Finance NoteDocument35 pagesInternational Finance Noteademoji00No ratings yet
- Define A Corporation.: Activity For Module 7Document4 pagesDefine A Corporation.: Activity For Module 7Jeselle BagsicanNo ratings yet
- Accounting CH 14Document34 pagesAccounting CH 14Juan JohnNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Return On Incremental Capital Investments - Saber Capital ManagementDocument9 pagesCalculating The Return On Incremental Capital Investments - Saber Capital ManagementAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Special Topics in Financial ManagementDocument16 pagesModule 2 Special Topics in Financial Managementkimjoshuadiaz12No ratings yet
- Annexure 2Document13 pagesAnnexure 2Shalini SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation AssignmentDocument1 pageIncome Taxation AssignmentHannah MeranoNo ratings yet
- Entrep Week 7Document13 pagesEntrep Week 7Pantz Revibes PastorNo ratings yet
- Guide To Moving Averages: The UltimateDocument23 pagesGuide To Moving Averages: The UltimateShakar RajNo ratings yet
- Overview of Finance: Addison-Wesley. All Rights Reserved. 9-1Document25 pagesOverview of Finance: Addison-Wesley. All Rights Reserved. 9-1Hamza KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Binary OptionsDocument24 pagesBinary Optionssamsa7No ratings yet
- Beige Brown Minimal Organic Creative Project Presentation PDFDocument17 pagesBeige Brown Minimal Organic Creative Project Presentation PDFAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- ACC104 - Fundamentals of Product and Service CostingDocument7 pagesACC104 - Fundamentals of Product and Service CostingZACARIAS, Marc Nickson DG.No ratings yet
- Financial Management Course OutlineDocument4 pagesFinancial Management Course OutlineRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Group # 1: Company: LocationDocument4 pagesGroup # 1: Company: LocationFria Mae Aycardo AbellanoNo ratings yet
- 04P Other Components of Shareholders EquityDocument7 pages04P Other Components of Shareholders EquityjulsNo ratings yet
- Ansoff MatrixDocument4 pagesAnsoff MatrixNeeraja KesavarajNo ratings yet