Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Artapp Notes
Artapp Notes
Uploaded by
Christine Dapun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesArt appreciation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentArt appreciation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesArtapp Notes
Artapp Notes
Uploaded by
Christine DapunArt appreciation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
ARTAPP NOTES (Midterm) NATURE OF ART EUROPEAN (MIDDLE AGE) Constantinople) and in various areas that
came under its influence.
ART – from the Latin word Ars which Expression/Communication – King Louis XIV (17th Century)
means ability or skill; everything made by express feelings and thousands In this era, we begin by considering the
people of stories Established French Royal production and consumption of art from
Creation – skills and ability Academy the Crusades through to the period of
Tangible – paintings, sculpture the Catholic Reformation.
Intangible – play, literature RESPONSES: 19TH CENTURY – Victorians introduced
art in grade school The period witnessed the slow erosion of
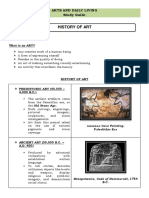
VISUAL ARTS – oldest form of art SENSORY – delighted or joy, the crusader states in the Holy Land,
CRITERIA TO BE CALLED AN ARTIST:
feelings finally relinquished in 1291, and of the
TWO CLASSIFICATIONS OF ART: EMOTIONAL – recognition of a You must have a talent. Greek Byzantine world until
1. Functional Art – has a familiar situation or relate to it You must have skills. Constantinople fell to the Ottomans in
purpose, can be used INTELLECTUAL – inspire You must have creativity. 1453.
2. Non-Functional Art –
Why is Art Important: Columbus made his voyage to the
decorative DEFINING ART FROM THE MEDIEVAL
Americas in 1942.
Valuable source of inspiration PERIOD TO THE RENAISSANCE
ARTIST – make nonfunctional art
Commemorate situations or The Dark Ages is a term for the Early
ARTISAN- make functional art past events Middle Ages, or occasionally the entire
Middle Ages, in Western Europe after the
FORMS – appearance of the art ART PROCESS:
fall of the Western Roman Empire that
ELEMENTS OF ART: 1. Topic characterizes it as marked by economic,
2. Idea Generation intellectual, and cultural decline.
1. Medium – material used 3. Explore
2. Colors – give life, dimensions, In the year 476 A.D., the great civilization
4. Refine (Enhance)
and sets the mood of Rome collapsed, thus bringing Europe
5. Output/Final Piece
PRIMARY – nonmixing into a time of “darkness”. 476 A.D.
6. Evaluate
colors, Red, Blue, marked the fall of Ancient Rome, the
Yellow SUPPORT NETWORK – inspiration; great civilization that ruled most of
helps you create your art Europe until its fall. Trade, diplomacy, and conquest
SECONDARY –
connected Christendom to the wider
combination of primary This collapse was limited to Western
TWO PLACES WHERE ART IS FOUND: world, which in turn had a great impact
colors Rome, which the Byzantine Empire, on art.
COMPLEMENTARY Commercial Art Galleries – also referred to as the Eastern Roman
3. Line – provides dimension sell and buy art Empire or Byzantium, was the Artists traveled both within and between
4. Texture – rough, smooth, hard, Museum – for viewing art only; continuation of the Roman Empire in its countries and on occasion, even
soft preserving art eastern provinces during Late Antiquity between continents.
5. Content – subject matter and the Middle Ages, when its capital city
CRITICS – people who evaluate/judge was Constantinople as the actual seat of Such mobility was facilitated by the
AESTHETIC – philosophy of beauty the art if it is good or bad; make network of the European courts which
ancient Rome.
judgments were instrumental in the rapid spread of
LIPP’S THEODOR – describes Aesthetic the Italian Renaissance.
Eastern Rome, was centered on
as the science of beauty; attracts ART DIRECTOR – an artist who has an Constantinople and continued to exist for
attention apprentice many more centuries. Byzantine art,
architecture, paintings, and other visual
arts were produced in the Middle Ages in
the Byzantine Empire (centered at
MEDIEVAL PERIOD ROMANESQUE ARCHITECTURE (11TH Paintings are symmetrical - An Italian polymath of the High
CENTURY) (balanced on both sides) Renaissance period and is
Characteristics of Medieval Art: active as a painter, engineer,
Semi-circular arches, heavy Forms of Art: sculptures, murals, sculptor, architect, and theorist.
Subjects mostly religious stone walls, and stable drawings, paintings He serves as the role model
Figures look flat and stiff with little construction in monasteries and applying the scientific method to
real movement churches marked the growth of Purposes: to show the importance of
every aspect of life, including art
Important figures are large the European City. people and nature, not just religion
and music.
Fully clothes, draped in deeply - Monalisa and The Last Supper
GOTHIC STYLE (12TH CENTURY) 3 MAJOR PERIODS OF
carved, still-looking clothes
RENAISSANCE ART:
Faces are solemn with little MICHELANGELO
Was developed as a result of
emotion Proto-Renaissance
the French Monarchy - Michelangelo di Lodovico
Paintings use vibrant colors Early Renaissance Art
Menacing gargoyles and flying Buonarroti Simoni known as
Flat, two-dimensional painted High Renaissance
buttresses in Gothic Cathedral Michelangelo was an Italian
figures
sculptor, painter, architect, and
Backgrounds a single color, often FAMOUS ARTIST OF MEDIEVAL PROTO-RENAISSANCE ART (1300-
poet of the High Renaissance
gold, with no interest in creating a PERIOD 1400)
period.
realistic space
Duccio di Bouninsegna, It refers to the Renaissance in - The frescoes on the ceiling of
The church forbids displaying the naked Italy, their activities that the Sistine Chapel
founder of the Sienese School
human body. painting, was one of the pioneered “figurative realism”.
RAFFAELLO SANZIO DA URBINO
greatest Italian painters It is the foundation of what was
Forms of Art: stained-glass windows, considered the period of the
Maesta has been recognized as - Known as Raphael was an
sculptures, illuminated manuscripts, Italian Renaissance.
the greatest of all his works. Italian painter, sculptor, and
paintings, and tapestries
architect of the High
RENAISSANCE PERIOD In the early Renaissance, one of the
Purposes: to teach religion to people Renaissance period
principal characteristics is humanism. It
who cannot read or write - He was known and admired for
Renaissance art is marked by the is a term that refers to revived classical
his clarity of form, ease of
gradual shift from the abstract forms of antiquity, meaning its concern is with the
3 MAJOR PERIODS OF MEDIEVAL composition, and visual idea of
the medieval period to the studies of human – that is grammar,
ART: human grandeur (it means high
representational forms of the 15th century. history poetry, and even philosophy.
rank or importance).
Early Christian Characteristics of Renaissance Art: “I wonder lonely as a cloud.” – William
Romanesque
Shakespeare
Gothic Both religious and nonreligious
scenes HIGH RENAISSANCE (1500-1600)
EARLY CHRISTIAN AGE (350 C.E) Figures look idealized, perfect
Bodies may look active, moving It is the period of the most exceptional
The Catholic Church had two artistic production of masterpiece in the
main centers of power: Rome Bodies may be nude or clothed
Italian state. It is the period of the best-
and Constantinople Real people doing real tasks of
known paintings, sculptures, and
Medieval art was popular in daily life
architecture.
houses of worship and was Faces express what people are
used as decoration for the thinking Some of the Famous Artists of the
public’s appreciation. Colors respond to the light that Renaissance Period
falls on them
Interest in nature, lots of natural LEONARDO DA VINCI
details
You might also like
- History of Western ArchitectureDocument9 pagesHistory of Western ArchitectureYham ValdezNo ratings yet
- Grewe Domesticated MadonnasDocument12 pagesGrewe Domesticated Madonnasquis_ut_deusNo ratings yet
- CONTEMPREVIEWERDocument6 pagesCONTEMPREVIEWERjamilaranedNo ratings yet
- Art Lesson 1 2 CriticismDocument4 pagesArt Lesson 1 2 CriticismdexieNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument5 pagesArt AppreciationblainechloeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8 - Art of Emerging EuropeDocument3 pagesLESSON 8 - Art of Emerging EuropeCM Pailago86% (7)
- Lesson 8 Art of Emerging Europe - CompressDocument4 pagesLesson 8 Art of Emerging Europe - CompressAivee SumulongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Arts-9Document7 pagesLesson Plan in Arts-9LOURD GINA JUANICONo ratings yet
- Final Cpar NotesDocument12 pagesFinal Cpar NotesKylee Pedro NgaloyNo ratings yet
- G9 3rd Q ARTS REVIEWERDocument2 pagesG9 3rd Q ARTS REVIEWERCyra50% (2)
- Lesson 1 (Part 3) - History of Visual ArtsDocument26 pagesLesson 1 (Part 3) - History of Visual ArtsMac FortichNo ratings yet
- Art Movements: Art Appreciation Reviewer 2019Document3 pagesArt Movements: Art Appreciation Reviewer 2019Jazzy MercadoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Art Application: Sunflowers, Irises, at Eternity's GateDocument4 pagesReviewer Art Application: Sunflowers, Irises, at Eternity's GateAngelica Delos santosNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentMarjorie Salvador ValleNo ratings yet
- Twentieth Century Art MovementsDocument83 pagesTwentieth Century Art MovementsSonny ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 3rd QDocument2 pagesReviewer 3rd QjakelaurencevanoNo ratings yet
- CPAR ReviewerDocument10 pagesCPAR ReviewerDiane CruzNo ratings yet
- MX4 Mapeh Final 1Document3 pagesMX4 Mapeh Final 1jumboNo ratings yet
- Notes in Arts 9 and English 9Document3 pagesNotes in Arts 9 and English 9Jave Clark Diziel UnayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet g9 - ARTS - Week 3 4Document14 pagesWorksheet g9 - ARTS - Week 3 4shie ann castillanesNo ratings yet
- Arts of The Neoclassic AND Romantic PeriodDocument20 pagesArts of The Neoclassic AND Romantic PeriodAirynna (Yan)No ratings yet
- Explore - ArtsDocument2 pagesExplore - ArtsMarnel Puso SumagpangNo ratings yet
- Cpar ReviewerDocument3 pagesCpar Reviewerysha maiiNo ratings yet
- Hand Out 2nd Grading G9Document4 pagesHand Out 2nd Grading G9Kean CardenasNo ratings yet
- Saint Ferdinand College: "Art Appreciation"Document4 pagesSaint Ferdinand College: "Art Appreciation"Kryza CastilloNo ratings yet
- ELT 313 2nd Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesELT 313 2nd Exam Reviewerkylamendiola543No ratings yet
- ADL Study GuideDocument14 pagesADL Study GuideFlorgelita Noble RequirmeNo ratings yet
- Cpar ReviewerDocument12 pagesCpar Reviewerfranzkafka978No ratings yet
- Pre Final HandoutsDocument1 pagePre Final Handoutsjdj robertoNo ratings yet
- Pre Colonial To Contemporary Art: PresentDocument2 pagesPre Colonial To Contemporary Art: PresentMISSY BETH VILLONESNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument12 pagesArt AppreciationChristaniel LangerNo ratings yet
- CPARDocument23 pagesCPARMara MayoNo ratings yet
- ART 002 ReviewerDocument8 pagesART 002 ReviewerClarence ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Beige and Grey Vintage Illustrative Archeology History Report Project PresentationDocument32 pagesBeige and Grey Vintage Illustrative Archeology History Report Project Presentationka3rine2022No ratings yet
- Twentieth Century Art MovementsDocument42 pagesTwentieth Century Art MovementsRaven O-oNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2Julie Pearl OberioNo ratings yet
- Art HistoryDocument13 pagesArt HistoryJhoann Kim TingNo ratings yet
- CPAR Q1 W1 VariousArtFormsV1Document39 pagesCPAR Q1 W1 VariousArtFormsV1bert jacob tropicalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 PP - 431-436 - PPTDocument11 pagesChapter 15 PP - 431-436 - PPTBook WormNo ratings yet
- Art 002 p1Document6 pagesArt 002 p1Ariane Grace Hiteroza MargajayNo ratings yet
- g5 Art of Emerging EuropeDocument32 pagesg5 Art of Emerging Europecute cuteNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsDocument4 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsLouielyn AbellaNo ratings yet
- The Encyclopedia of Visual Art Vol. 07Document200 pagesThe Encyclopedia of Visual Art Vol. 07Pedro FanoNo ratings yet
- Art 002 ReviewerDocument5 pagesArt 002 Reviewerpaopao.backup1No ratings yet
- Art Appre MOD 3 4Document20 pagesArt Appre MOD 3 4Jastine Miguel EGUIANo ratings yet
- 12 CparDocument17 pages12 CparKiel LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Las Q3 Arts 1Document4 pagesLas Q3 Arts 1Kay Cee0025No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Appreciating History of ArtDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Appreciating History of ArtRochelle Ann Ido AcebuNo ratings yet
- Pabello, Rhaiza P. WS 10:30 AM - 12:00 NN HUM SEPTEMBER 14, 2019 Artistic Periods A. Ancient ArtDocument3 pagesPabello, Rhaiza P. WS 10:30 AM - 12:00 NN HUM SEPTEMBER 14, 2019 Artistic Periods A. Ancient ArtRhaiza PabelloNo ratings yet
- What Is Art?: Power of Canons and Elitist Belief SystemsDocument9 pagesWhat Is Art?: Power of Canons and Elitist Belief SystemsAlahna Marie SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Marjan ReortDocument3 pagesMarjan ReortElizamy BayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 ContempDocument4 pagesLesson 2 ContempAtasha ValdezNo ratings yet
- GR 9 MAPEH ReviewerDocument7 pagesGR 9 MAPEH ReviewerDenise CanlasNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument9 pagesArt AppreciationKimberly PuddefootNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Art of Emerging Europe: CoverageDocument8 pagesTopic 1: Art of Emerging Europe: CoverageSarah GgNo ratings yet
- Art App ReviewerDocument3 pagesArt App ReviewerAIAH RIZPAH SOLIVANo ratings yet
- Arts 3QDocument10 pagesArts 3QTim DarvisNo ratings yet
- All Sub ReviewersDocument34 pagesAll Sub ReviewersLouie MagbojosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8Document27 pagesChapter-8ken balandraNo ratings yet
- Black LadyDocument58 pagesBlack LadyHans Ioan SpirescuNo ratings yet
- ExpressionismDocument11 pagesExpressionismanabelenopia3No ratings yet
- MAPEH 1st Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesMAPEH 1st Quarter ExamRheaMaePagaranOnyotNo ratings yet
- Migration of Ideas: From The Italian Futurism To The Romanian IntegralismDocument8 pagesMigration of Ideas: From The Italian Futurism To The Romanian IntegralismEmmaNo ratings yet
- Ludwig Mies Van Der RoheDocument10 pagesLudwig Mies Van Der RoheNancy TessNo ratings yet
- Saul Steinberg 2018 Catalogue-1Document36 pagesSaul Steinberg 2018 Catalogue-1Nunta de Vis100% (1)
- IV. Vietnamese Arts From 1945 To PresentDocument104 pagesIV. Vietnamese Arts From 1945 To PresentThảo NgânNo ratings yet
- WLP g10 q1 First Week 5 Music 10Document4 pagesWLP g10 q1 First Week 5 Music 10Uricca Mari Briones SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Cpar - Art of Graffiti - Furio, Balbalosa & BerbaDocument7 pagesCpar - Art of Graffiti - Furio, Balbalosa & BerbaJohnmar FortesNo ratings yet
- Carol Hepper: 9 East Broadway, New York, NY. 10038Document7 pagesCarol Hepper: 9 East Broadway, New York, NY. 10038carolhepper1No ratings yet
- Grade 08 Art & Handwork Materials ListDocument4 pagesGrade 08 Art & Handwork Materials Listmanoja hiroshiniNo ratings yet
- D&PIII Doherty SituationDocument4 pagesD&PIII Doherty SituationJulieta PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Backtothefuture ClairedohertyDocument7 pagesBacktothefuture ClairedohertycchangNo ratings yet
- Grva ReviewerDocument2 pagesGrva Reviewersandara sorianoNo ratings yet
- MichelangeloDocument11 pagesMichelangeloSolomon UwaNo ratings yet
- STANGOS by LYNTON - ExpressionismDocument10 pagesSTANGOS by LYNTON - ExpressionismJs Ls GuijarroNo ratings yet
- Art Deco NotesDocument13 pagesArt Deco NotesSameer MohammedNo ratings yet
- Pietro AnnigoniDocument5 pagesPietro Annigonipaulina R.No ratings yet
- 2o Ano - 4o BimestreDocument21 pages2o Ano - 4o BimestremhyxewNo ratings yet
- Modern Still LifeDocument243 pagesModern Still LifepakoliviaxxNo ratings yet
- Different Contemporary Art Techniques and PerformanceDocument30 pagesDifferent Contemporary Art Techniques and PerformanceAoi BaraNo ratings yet
- GROUP-9 - Historical Development of ArtDocument9 pagesGROUP-9 - Historical Development of ArtDianna Lynn MolinaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture: Semester 6Document24 pagesHistory of Architecture: Semester 6Ashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- CPAR Lesson 3Document46 pagesCPAR Lesson 3Shaila DelatorreNo ratings yet
- Matisse and Room 7Document134 pagesMatisse and Room 7Carlo Roa100% (1)
- Filipino ArtistsDocument6 pagesFilipino ArtistsMary jane SisonNo ratings yet
- Noche ClaraDocument11 pagesNoche ClaraFabe Marie RiegoNo ratings yet
- Beauford Delaney: The Abstract Expressionism of OthernessDocument12 pagesBeauford Delaney: The Abstract Expressionism of OthernessChristian WeaverNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Ver 2Document39 pagesLesson 1 Ver 2史朗EzequielNo ratings yet