Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radio Network Temporary Identifyer
Radio Network Temporary Identifyer
Uploaded by
Dereje FelekeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Radio Network Temporary Identifyer
Radio Network Temporary Identifyer
Uploaded by
Dereje FelekeCopyright:
Available Formats
RNTI :- Radio Network Temporary Identifier
1. RA-RNTI :-Random Access Radio Network Temporary Identifier
Used to identify random access response.
2. (C-RNTI) Cell Radio Network Temporary Identifier (C-RNTI):- temporary identifier for a User
Equipment (UE) or mobile device within a specific cell.
When a UE initiates a connection with an eNodeB or enters a cell, it needs a temporary
identifier before a permanent identity, such as the International Mobile Subscriber Identity
(IMSI), can be established and verified.
The C-RNTI serves as a temporary, cell-specific identifier for the UE during this initial
connection phase.
3. SPS-C-RNTI : Semi persistance Scheduling C-RNTI :- In the case of Dynamic Scheduling,
the UE can get scheduling assignments/grants in every subframe. This gives the
network full flexibility in assigning the resources to the UE at the cost of transmission
of resource allocation information on PDCCH in every subframe. This also gives the
flexibility of varying the resource allocation based on the reported channel conditions
4. Paging RNTI (P-RNTI) is an essential component of the Long Term Evolution (LTE) and
5G wireless communication systems. It plays a crucial role in managing the paging
process, which is responsible for notifying a mobile device about incoming calls, text
messages, and other system events while the device is in an idle or standby mode. In
this explanation, we will delve into the details of P-RNTI, its purpose, functions, and
significance in the overall operation of the cellular network.
5. SI-RNTI, System Information Radio Network Temporary Identifier, is a specific Radio
Network Temporary Identifier used in LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and 5G wireless
communication systems. It is a unique identifier assigned to user equipment (UE) to
receive system information from the base station or evolved NodeB (eNodeB) in LTE, or
the gNB (Next Generation NodeB) in 5G.
UE ID in NAS layer
A unique International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) shall be allocated to each mobile
subscriber in the GSM/UMTS/EPS system.
MCC -Mobile Country Code
MNC -Mobile Network Code
MSIN-Mobile Subscriber Identity Number
NMSI-National Mobile Subscriber Identity
There is a one-to-one mapping between TMSIs and IMSIs within a VLR. The TMSI is allocated
by the MSC or VLR, and will be reallocated if routing information is updated.
P-TMSI :- Packet -Temporary Mobile The P-TMSI is allocated by the SGSN, and is valid only
within a routing area. It will be reallocated during an RAU. The P-TMSI consists of 3 octets
SAE Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity: - The S-TMSI is similar in format to the P-TMSI. It is
used to protect the subscribers IMSI during NAS interaction as well as identifying the MME (Mobility
Management Entity) or MME pool that is responsible for the UE. The S-TMSI is constructed from the
MMEC (MME Code) and the M-TMSI.
GUTI is the Globally Unique Temporary ID
GUTI plays a crucial role in ensuring user privacy and security during communication with the network.
Purpose of GUTI:
1. Privacy: To ensure that user activities are not easily traceable, especially
in scenarios where passive eavesdropping or active attacks might
compromise user privacy.
2. Security: To provide a temporary identifier that is not easily linked to
the long-term identity of the subscriber (like the IMSI - International
Mobile Subscriber Identity).
How GUTI Works:
initial Attach Procedure: When a user device (UE - User Equipment) initiates
a connection to the 4G network, it starts with an attach procedure. During this
process, the UE communicates with the network's access and core
components.
Temporary Identifiers: Initially, the UE provides its IMSI to the network.
However, to prevent the IMSI from being exposed frequently (which
could be exploited for tracking), the network allocates a temporary
identifier called the Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI).
Allocation of GUTI: Once the TMSI is allocated, the network can
generate a GUTI. The GUTI comprises two parts:
I. GUMMEI (Globally Unique MME Identifier): This identifies
the Mobility Management Entity (MME) that serves the UE.
II. M-TMSI (Mapped TMSI): This is the TMSI mapped to the UE
within the MME context.
Using GUTI for Communication: For subsequent communications between
the UE and the network, the UE uses its GUTI instead of its IMSI. This way, the
long-term identity (IMSI) remains concealed, and only the GUTI is used for
session management and mobility procedures.
You might also like
- Instruction Manual: AH-250H Automatic Hitch Feed Metal Cutting Band Saw (415V) 280 X 250mm (W X H) RectangleDocument134 pagesInstruction Manual: AH-250H Automatic Hitch Feed Metal Cutting Band Saw (415V) 280 X 250mm (W X H) Rectanglemaicon sulivanNo ratings yet
- 03 - LTE-EPS Mobility & Session ManagementDocument0 pages03 - LTE-EPS Mobility & Session ManagementSonal Singh100% (1)
- MMMACNS2017 MjolsnesOlimidDocument12 pagesMMMACNS2017 MjolsnesOlimidDref DryerNo ratings yet
- A Minimum Feature Set of Ims Is Required To Support Voip Over LteDocument7 pagesA Minimum Feature Set of Ims Is Required To Support Voip Over LteInstructor Tx LabNo ratings yet
- 5G Identifiers SUPI and SUCIDocument8 pages5G Identifiers SUPI and SUCIOscar DazaNo ratings yet
- IMSI, TMSI and GUTI - How They Are Created - LTE and BEYOND - Tech-Blog On 4G - LTE and Beyond.Document5 pagesIMSI, TMSI and GUTI - How They Are Created - LTE and BEYOND - Tech-Blog On 4G - LTE and Beyond.TitusNo ratings yet
- Volte White Paper by Spirent From NetDocument9 pagesVolte White Paper by Spirent From NetPushpendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Making of Imsi CatcherDocument11 pagesMaking of Imsi CatcherAwass100% (1)
- A Simplified Learning DocumentDocument50 pagesA Simplified Learning DocumentPoojaNo ratings yet
- AdrianDabrowski IMSI Catcher Catcher ACSAC2014 Preprint 20140820Document11 pagesAdrianDabrowski IMSI Catcher Catcher ACSAC2014 Preprint 20140820Björn HellerNo ratings yet
- GSM and GPRS SecurityDocument12 pagesGSM and GPRS Securityphandaka100% (5)
- LTE Numbering & AddressingDocument3 pagesLTE Numbering & AddressingVishwaNo ratings yet
- Volte Architecture: Abdulsalam Maher Cellqual CompanyDocument22 pagesVolte Architecture: Abdulsalam Maher Cellqual CompanyAbdulsalam MaherNo ratings yet
- What Is IUBDocument17 pagesWhat Is IUBtuyambaze jean claudeNo ratings yet
- VOLTE Network ArchitectureDocument9 pagesVOLTE Network ArchitectureShrikant SinghNo ratings yet
- If6i-Wmn-Unit 1 NotesDocument14 pagesIf6i-Wmn-Unit 1 Notes514 Vaibhavi PawarNo ratings yet
- Archtecture of GSMDocument8 pagesArchtecture of GSMMjrtMQNo ratings yet
- DoS Attacks Exploiting Signaling in UMTS and IMSDocument20 pagesDoS Attacks Exploiting Signaling in UMTS and IMSzaffsanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication ProblemsDocument4 pagesMobile Communication ProblemsIshan DixitNo ratings yet
- Second Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsDocument40 pagesSecond Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsMd. Golam Sarwar JoyNo ratings yet
- IP Multimedia Subsystem - WikipediaDocument10 pagesIP Multimedia Subsystem - Wikipediajeanne_85No ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsDocument25 pagesLecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsOpilaStephen100% (1)
- Name-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationDocument21 pagesName-Suvajit Mondal. Stream-E.C.E. Roll No.-3047. Semester-8 - Subject-3G PresentationSubir MaityNo ratings yet
- Procedures: UMTS System OverviewDocument45 pagesProcedures: UMTS System OverviewRock DolphinNo ratings yet
- Mobility and Roaming - T3.10Document42 pagesMobility and Roaming - T3.10acajahuaringaNo ratings yet
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDocument13 pages2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555No ratings yet
- Securing Authentication For Mobile Networks A Survey On 4G Issues and 5G AnswersDocument8 pagesSecuring Authentication For Mobile Networks A Survey On 4G Issues and 5G AnswersSharique A MNo ratings yet
- GSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioDocument5 pagesGSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioImen DjebliNo ratings yet
- 22 VoLTE Call Steps FiDocument309 pages22 VoLTE Call Steps FiSri KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Forensics and The GSM Mobile Telephone System: International Journal of Digital Evidence Spring 2003, Volume 2, Issue 1Document17 pagesForensics and The GSM Mobile Telephone System: International Journal of Digital Evidence Spring 2003, Volume 2, Issue 1BEALogicNo ratings yet
- Mc all questions papers answersDocument62 pagesMc all questions papers answersmihirgt21hcompeNo ratings yet
- Ims (Ip Multimedia Subsystem) PDFDocument31 pagesIms (Ip Multimedia Subsystem) PDFRoberto TR100% (1)
- LTE Identities-FinalDocument5 pagesLTE Identities-FinalArun BaidyaNo ratings yet
- Ik1330lab2 (KTH)Document7 pagesIk1330lab2 (KTH)Mehdi RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Signaling-Oriented Dos Attacks in Umts Networks: AbstractDocument10 pagesSignaling-Oriented Dos Attacks in Umts Networks: AbstractTareq BakrNo ratings yet
- Global System Mobility (GSM)Document28 pagesGlobal System Mobility (GSM)Zain ABNo ratings yet
- Future Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFuture Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)No ratings yet
- Mobile Node Correspondent Node Home Network Foreign Network Foreign Agent Home Agent Care - of AddressDocument3 pagesMobile Node Correspondent Node Home Network Foreign Network Foreign Agent Home Agent Care - of AddressMustafa Troy TroyNo ratings yet
- IP Multimedia SubsystemDocument8 pagesIP Multimedia SubsystemWewe SlmNo ratings yet
- Look Then The: Two IsDocument4 pagesLook Then The: Two IsHarjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- 4G and 5G Cellular Hacking PDFDocument17 pages4G and 5G Cellular Hacking PDFAutomotriz BriceñoNo ratings yet
- LTEDocument57 pagesLTEarvindsarvesh207645No ratings yet
- Enhancing User Identity Privacy in LTEDocument9 pagesEnhancing User Identity Privacy in LTEJakub ObetkoNo ratings yet
- How We Make A CallDocument4 pagesHow We Make A CallAbuzarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Mobile Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Secand Dev NotesDocument28 pagesMobile Secand Dev Notesnahid.nuri03No ratings yet
- Mobile Communication SystemsDocument136 pagesMobile Communication SystemsJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Telecom AssignmentDocument5 pagesTelecom Assignmentikra khanNo ratings yet
- GSM Data CompleteDocument12 pagesGSM Data CompleteAdeel TajNo ratings yet
- 52 Deb 99Document48 pages52 Deb 99Lục VânNo ratings yet
- Call Setup in A GSM NetworkDocument6 pagesCall Setup in A GSM NetworkluvdembadNo ratings yet
- LTE IdentificationDocument15 pagesLTE Identificationanuj tripathi 12No ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For MobileDocument16 pagesOverview of The Global System For MobilevenkateshmukharjiNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 ECE4009 ETH VL2023240102914 2023-10-04 Reference-Material-IDocument24 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 ECE4009 ETH VL2023240102914 2023-10-04 Reference-Material-IPraneshNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document61 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)VyomNo ratings yet
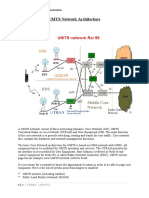
- UMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationDocument11 pagesUMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationNuces LahoreNo ratings yet
- Gs Interface DescriptionDocument38 pagesGs Interface Descriptionramilo caluagNo ratings yet
- 3G - Basic KPIs CountersDocument3 pages3G - Basic KPIs CountersDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- Target Area - Serving SitesDocument2 pagesTarget Area - Serving SitesDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- SD AdjustmentDocument3 pagesSD AdjustmentDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- Indoor DT Thresholds Report FormatDocument17 pagesIndoor DT Thresholds Report FormatDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- ENodeB Parameter ReferenceDocument11,382 pagesENodeB Parameter ReferenceDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- 4G /LTE (Long Term Evolution) : 1. FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)Document6 pages4G /LTE (Long Term Evolution) : 1. FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)Dereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- 4G /LTE (Long Term Evolution) : 1. FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)Document6 pages4G /LTE (Long Term Evolution) : 1. FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access)Dereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- 4G ParameterReferenceDocument16 pages4G ParameterReferenceDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- Design and Demonstration of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Relay MultipliersDocument4 pagesDesign and Demonstration of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Relay MultipliersDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- LED DesignDocument39 pagesLED DesignDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- Digitata Networks - Business Case and Use Cases (May 2017)Document31 pagesDigitata Networks - Business Case and Use Cases (May 2017)Dereje Feleke100% (1)
- Jawwal PDFDocument13 pagesJawwal PDFDereje FelekeNo ratings yet
- 331952.public Speaking AnxietyDocument9 pages331952.public Speaking AnxietydewiNo ratings yet
- The Legend of Daragang Magayon: by Merito B. EspinasDocument1 pageThe Legend of Daragang Magayon: by Merito B. EspinasReu Amor AmorgandaNo ratings yet
- Oyster Mushroom Cultivation: Non-Sterilized Wheat StrawDocument0 pagesOyster Mushroom Cultivation: Non-Sterilized Wheat StrawEdu Ar DoNo ratings yet
- Bride For SaleDocument3 pagesBride For SalePrince SamsonNo ratings yet
- Syracuse Solitary Final SignedDocument42 pagesSyracuse Solitary Final SignedPatLohmannNo ratings yet
- Scholarship FormDocument3 pagesScholarship FormHammad Yousaf100% (6)
- 2018 AFR Local Govt Volume IIDocument528 pages2018 AFR Local Govt Volume IIJericho VillalonNo ratings yet
- Effective Project Management Traditional, Agile, E... - (Appendix C Case Study Pizza Delivered Quickly (PDQ) )Document1 pageEffective Project Management Traditional, Agile, E... - (Appendix C Case Study Pizza Delivered Quickly (PDQ) )Arnaldo Jonathan Alvarado RuizNo ratings yet
- Sahali Vs COMELECDocument11 pagesSahali Vs COMELECDaley CatugdaNo ratings yet
- Kunal Bindra: "Believe in Delivering Superior Results"Document3 pagesKunal Bindra: "Believe in Delivering Superior Results"Kunal BindraNo ratings yet
- 001 Nokia 810 Contacts Sync Instruction GuideDocument6 pages001 Nokia 810 Contacts Sync Instruction GuideJuan Ramón MartínezNo ratings yet
- Contoh Data PurchasingDocument4 pagesContoh Data PurchasingNonton NontonNo ratings yet
- BABOK - Techniques by KADocument1 pageBABOK - Techniques by KABenhar Masahod BLM-VLOGNo ratings yet
- Make KiljuDocument2 pagesMake KiljuslamonNo ratings yet
- Crowding Risk in Smart Beta StrategiesDocument32 pagesCrowding Risk in Smart Beta StrategiesRogerio Monaco SimõesNo ratings yet
- Farinas Vs Exec SecretaryDocument10 pagesFarinas Vs Exec SecretarySharmila AbieraNo ratings yet
- VAN FRAASSEN Scientific Representation: Paradoxes of PerspectiveDocument4 pagesVAN FRAASSEN Scientific Representation: Paradoxes of Perspectivethemostatomikrat100% (1)
- Middle Ages - Ged104-A7Document2 pagesMiddle Ages - Ged104-A7KleyrNo ratings yet
- Fusion Applications: Co-Existence and SSO - Overview and ImplementationDocument14 pagesFusion Applications: Co-Existence and SSO - Overview and Implementationnitinjain2020No ratings yet
- Fixed Income Portfolio ManagementDocument81 pagesFixed Income Portfolio ManagementYamila VallejosNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in Reading 2018-2019Document2 pagesAction Plan in Reading 2018-2019Es Jey NanolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1U2104004 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Mustafa Barakat CV 2 - 2020Document6 pagesMustafa Barakat CV 2 - 2020Musa BaraNo ratings yet
- Hoa Election ProtestDocument2 pagesHoa Election Protestmaycil ambagNo ratings yet
- IELTS Listening Task Type 2 (Matching) Activity (1) - Teacher's NotesDocument8 pagesIELTS Listening Task Type 2 (Matching) Activity (1) - Teacher's NotesmohsenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug Study - LosartanCath Bril50% (2)
- Awareness and Practices On Solid Waste Management Among Elementary Pupils Implications or Makakalikasan Core ValueDocument13 pagesAwareness and Practices On Solid Waste Management Among Elementary Pupils Implications or Makakalikasan Core ValueAPJAET JournalNo ratings yet
- JavascriptDocument15 pagesJavascriptRajashekar PrasadNo ratings yet
- Waterfront Boundaries For Grants of Public Crown Lands - MNR - E000074 - 2001Document3 pagesWaterfront Boundaries For Grants of Public Crown Lands - MNR - E000074 - 2001Sen HuNo ratings yet