Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11th Chemistry Chapter 11 Notes
11th Chemistry Chapter 11 Notes
Uploaded by
sharafatzadranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11th Chemistry Chapter 11 Notes
11th Chemistry Chapter 11 Notes
Uploaded by
sharafatzadranCopyright:
Available Formats
More Notes, Books for Class, 9, 10, 11, 12 Visit TaleemCorner.
com
1st Year Chemistry
Chapter 11
Lecture-1
HESS’S LAW
Statement
It states that the enthalpy change in a chemical reaction is same whether the
reaction takes place in a single step or in several steps.
Explanation
Enthalpy is a state function; therefore, enthalpy change in a chemical
reaction in going from some initial state to some final state is independent
of the path followed by the reaction.
Thus in going from a particular set of reactant to a particular set of
products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes
place in one step or in many steps.
More Notes, Books for Class, 9, 10, 11, 12 Visit TaleemCorner.com
This principle is known as Hess’s law.
Mathematical Form
∑ ∆𝐻 (𝑐𝑦𝑐𝑙𝑒) = 0
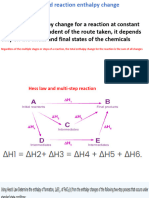
General Representation
Suppose a reactant A changes into the product B in one step and enthalpy
change in this step is ∆𝐻.
Now suppose this change takes place in three steps, involving a change
from A to C, C to D, and finally D to B.
If ∆𝐻1, ∆𝐻2 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ∆𝐻3 are enthalpy changes in these steps, then according
to the Hess’s Law;
∆𝐻 = ∆𝐻1 + ∆𝐻2 + ∆𝐻3
Example: Formation of CO2
Path-1
Combustion of C to CO2 evolves 393.5 KJ of energy
It is direct formation of CO2 from the reaction of C and O2
More Notes, Books for Class, 9, 10, 11, 12 Visit TaleemCorner.com
Path-2
It is indirection path;
C first changes to CO, it releases – 110.52 kJ
1
𝐶 + 𝑂 → 𝐶𝑂 ∆𝐻𝑜 = - 110.52 kJ
(𝑠) 2(g) (g) 1
2
CO then change to CO2, it releases – 282.98 KJ
1
𝐶𝑂 + 𝑂 → 𝐶𝑂 ∆𝐻𝑜 = - 282.98 KJ
(g) 2(g) 2(g) 2
2
Net release in path-2 is – 393.50 KJ
1
𝐶 + 𝑂 → 𝐶𝑂 ∆𝐻𝑜 = - 110.52 kJ
(𝑠) 2(g) (g) 1
2
1
𝐶𝑂 + 𝑂 → 𝐶𝑂 ∆𝐻𝑜 = - 282.98 KJ
(g) 2(g) 2(g) 2
2
𝐶(𝑠) + 𝑂2(g) → 𝐶𝑂(g) ∆𝐻𝑜 = - 393.50 kJ
Conclusion
Enthalpy change in path-1 and enthalpy change in path-2 is same.
You might also like
- Modul 2Document2 pagesModul 2Aditya Whisnu Heryudhanto0% (1)
- Rate of Chemical ChangesDocument3 pagesRate of Chemical ChangesAhmad Taufiq Mohd ZaidNo ratings yet
- Stereoselective and Stereospecific ReactionsDocument20 pagesStereoselective and Stereospecific ReactionsHunzalaNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument35 pagesEnergeticsRodaine BaileyNo ratings yet
- 2 Lluhd SFX Og WL0 Yqh HVSDocument31 pages2 Lluhd SFX Og WL0 Yqh HVSsagarshivnathsingh18818No ratings yet
- 8 - Thermodynamics - Lecture 8Document19 pages8 - Thermodynamics - Lecture 8Ramy MaamounNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Chemistry Questions With SolutionsDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Chemistry Questions With SolutionsHARSH RoopejaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 F I Cal - 1 - 1 - 1 Cal Cal - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1Document3 pages1 - 1 - 1 - 1 F I Cal - 1 - 1 - 1 Cal Cal - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1Andrea LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Enthalpy of Chemical Reactions and Hess's LawDocument15 pagesExperiment 2 Enthalpy of Chemical Reactions and Hess's LawUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Hukum HessDocument4 pagesHukum HessLys HopeNo ratings yet
- Energetics - Summary: Exothermic EndothermicDocument7 pagesEnergetics - Summary: Exothermic EndothermicKiara LimNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy and ThermochemistryDocument12 pagesEnthalpy and ThermochemistryMollin SiwellaNo ratings yet
- 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument176 pages7 Chemical EnergeticsUng Hie HuongNo ratings yet
- Name - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawDocument4 pagesName - Honors Chemistry - / - / - Hess's LawGunjee GunjeeNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: QuestionsDocument32 pagesThermochemistry: QuestionsBe like BruhNo ratings yet
- Final Initial: Products ReactantsDocument14 pagesFinal Initial: Products ReactantsAlisa DowningNo ratings yet
- 6.9 Hesss Law StudentDocument3 pages6.9 Hesss Law StudentRemasa BakraibaNo ratings yet
- Energy 2Document27 pagesEnergy 2Diana ToroNo ratings yet
- Hesss Law Awesome Ib Packet Questions OnlyDocument6 pagesHesss Law Awesome Ib Packet Questions OnlyEmmanuel JoyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics (As) 2023 With AnswersDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics (As) 2023 With AnswersNurli SallehNo ratings yet
- 10 Thermodynamics (S)Document8 pages10 Thermodynamics (S)Mr TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Lecture Worksheet 2: RXN 1: Use As Is RXN 2: Reverse, Muliply by 2 Add (Multiply K'S)Document2 pagesChapter 9 - Lecture Worksheet 2: RXN 1: Use As Is RXN 2: Reverse, Muliply by 2 Add (Multiply K'S)MoiMoi P.S.No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Edition Steven S Zumdahl Susan A ZumdahlDocument31 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Edition Steven S Zumdahl Susan A ZumdahlJenniferLarsonpsdc100% (52)
- Topic 15Document41 pagesTopic 15api-485190482No ratings yet
- Section - 2 Hess'S Law and Its Applications: 2 (Graphite) + 2Document31 pagesSection - 2 Hess'S Law and Its Applications: 2 (Graphite) + 2api-3728411No ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionDocument31 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionChristianGonzalezsrybm100% (93)
- Hess's LawDocument7 pagesHess's Lawjax stykerNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry 10th by ZumdahlDocument33 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry 10th by ZumdahlAmandaHarrissftia100% (98)
- EnergrticsDocument31 pagesEnergrticsnaeem mushtaqNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument35 pagesHess LawMARYAM AHMED MOHAMED HAMEDNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics PDFDocument11 pagesChemical Energetics PDFJoanne75% (4)
- Lecture-Unit 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument5 pagesLecture-Unit 7 Chemical EnergeticsKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ThermochemistryDocument13 pagesIntroduction To ThermochemistryLumamba ChiyabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12. Reactive SystemsDocument9 pagesLecture 12. Reactive SystemsHirun ManujayaNo ratings yet
- Section 3 EnergeticsDocument47 pagesSection 3 Energeticsapi-3734333No ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Module 1Document9 pagesThermochemistry Module 1PavithiranNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument6 pagesThermonivrutiverma1234No ratings yet
- BOND ENERGIES - Entropy-Free EnergyDocument3 pagesBOND ENERGIES - Entropy-Free EnergyOluwatosin OsisanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument43 pagesChemical EquilibriumRick Allen RamirezNo ratings yet
- 5.6: Hess's Law: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pages5.6: Hess's Law: Learning ObjectivesDhaba AberaNo ratings yet
- Energy Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesEnergy Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDanise NicoleNo ratings yet
- 2011 Final AnswerDocument8 pages2011 Final Answerxuan1002No ratings yet
- Energetics by Abhishek JaguessarDocument10 pagesEnergetics by Abhishek Jaguessarreedoye21No ratings yet
- Chem 1-8Document43 pagesChem 1-8Cabacungan, John VinceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and HeatDocument37 pagesChemical Reactions and HeatDamir BalmassovNo ratings yet
- 7 Thermochemistry Short Question and Answers PDFDocument8 pages7 Thermochemistry Short Question and Answers PDFMARITIM GEOFFREY KIPLANGAT100% (2)
- Heat Energy Is Absorbed And: Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed But Can Be Converted From One Form To AnotherDocument12 pagesHeat Energy Is Absorbed And: Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed But Can Be Converted From One Form To AnotherAeyyjayyNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of Reaction and Hess' LawDocument4 pagesEnthalpy of Reaction and Hess' LawJbreNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 2 PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 2 PDFwelp100% (1)
- Thermochemistry XIDocument18 pagesThermochemistry XIletmeuseinternetNo ratings yet
- Example Problems For Lecture 15: Umass Boston Chem 115 Spring 2009 Prof. SevianDocument4 pagesExample Problems For Lecture 15: Umass Boston Chem 115 Spring 2009 Prof. Seviankamal touilebNo ratings yet
- 2022w-Chem154-Unit+9+ (Student) 2022-11-23 21 - 25 - 22Document29 pages2022w-Chem154-Unit+9+ (Student) 2022-11-23 21 - 25 - 22Jaswinder BrarNo ratings yet
- Review Questions - Solutions: Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesReview Questions - Solutions: Multiple ChoiceMarikNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of ReactionDocument22 pagesEnthalpy of ReactionPatricia CadacioNo ratings yet
- Handout No. in General Chemistry 2Document7 pagesHandout No. in General Chemistry 2Portgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- Hess LawDocument24 pagesHess Lawactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Chemical Thermodynamics Important Questions With AnswersDocument15 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 Chemical Thermodynamics Important Questions With AnswersMinato NamikazeNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy AsDocument9 pagesEnthalpy AsA LEVEL TOPNo ratings yet
- CHM 152 - Thermodynamics (Ch. 16) Spontaneity: False eDocument7 pagesCHM 152 - Thermodynamics (Ch. 16) Spontaneity: False eQueenQiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Entropy - Lecture PDFDocument37 pagesThermodynamics - Entropy - Lecture PDFFrancinne MartinNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 10 QDocument7 pages10 QsharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 12th Computer Chapter 3 NotesDocument54 pages12th Computer Chapter 3 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 12th Computer Chapter 8 NotesDocument37 pages12th Computer Chapter 8 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Physics Chapter 13 NotesDocument63 pages10th Class Physics Chapter 13 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Ch14 Sindh Board NotesDocument30 pages11th Biology Ch14 Sindh Board NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Ch8 Sindh Board NotesDocument14 pages11th Biology Ch8 Sindh Board NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Ch12 Sindh Board NotesDocument27 pages11th Biology Ch12 Sindh Board NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Ch9 Sindh Board NotesDocument27 pages11th Biology Ch9 Sindh Board NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Ch11 Sindh Board NotesDocument19 pages11th Biology Ch11 Sindh Board NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 NotesDocument8 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotesDocument38 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Chapter 12 NotesDocument31 pages11th Chemistry Chapter 12 NotessharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Atomic StructureDocument44 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Atomic StructuresharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Notes 2024 Physics CH 3Document17 pages11th Class Notes 2024 Physics CH 3sharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Notes 2024 Physics CH 1Document10 pages11th Class Notes 2024 Physics CH 1sharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Notes 2024 Physics CH 7Document16 pages11th Class Notes 2024 Physics CH 7sharafatzadranNo ratings yet
- Sigmatropic ReactionDocument14 pagesSigmatropic ReactionAatir HashmiNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Efficacy Viz. Product Yield, Turnover Number (TON), Space-Time Yield EtcDocument12 pagesCatalyst Efficacy Viz. Product Yield, Turnover Number (TON), Space-Time Yield EtcdackoNo ratings yet
- Meldrum's AcidDocument14 pagesMeldrum's AcidDianasfoNo ratings yet
- Unit-V: Reactions of Synthetic Importance Bp401T: Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-Iii Metal Hydride Reduction (Nabh 4 and Lialh 4)Document15 pagesUnit-V: Reactions of Synthetic Importance Bp401T: Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-Iii Metal Hydride Reduction (Nabh 4 and Lialh 4)Kartik RajpootNo ratings yet
- Lecture 30 - Enamine and Iminium OrganocatalysisDocument22 pagesLecture 30 - Enamine and Iminium OrganocatalysisDênisPiresdeLimaNo ratings yet
- CET 2 - Chemical Reaction EquilibriumDocument46 pagesCET 2 - Chemical Reaction EquilibriumMihir ParekhNo ratings yet
- Hidrotreating PDFDocument10 pagesHidrotreating PDFM Fariz YasminNo ratings yet
- Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Halogenation 0Document3 pagesHell-Volhard-Zelinsky Halogenation 0Bhargav SinghaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Xu - JMolCatA - Dihydrochalcones Via The AlCl3 CynamoylDocument9 pages12 - Xu - JMolCatA - Dihydrochalcones Via The AlCl3 Cynamoyllenggah purwandariNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of AlkenesDocument2 pagesHydrogenation of AlkenesNur FarahinNo ratings yet
- 9 Edition, Global Edition L. G. Wade, JR.: Organic ChemistryDocument60 pages9 Edition, Global Edition L. G. Wade, JR.: Organic ChemistryRoma Blaise G FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Reaction Kinetics McqsDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Reaction Kinetics McqsshahidkakaNo ratings yet
- "Master Organic Chemistry": Anti-Markovnikoff BH H Syn AdditionDocument1 page"Master Organic Chemistry": Anti-Markovnikoff BH H Syn AdditionMoncef AbbesNo ratings yet
- AnggitWijaya 5213420048 QUIZ1Document6 pagesAnggitWijaya 5213420048 QUIZ1Anggit WijayaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 1Document114 pagesChemical Kinetics 1Ashish KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Activity Number 2Document9 pagesActivity Number 2Mariella SingsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsDocument18 pagesLecture 1 - The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionsGenevive S. de VeraNo ratings yet
- NEET-JEE Academy: Chemical Kinetics-TestDocument2 pagesNEET-JEE Academy: Chemical Kinetics-TestdillipNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Organometallic CompoundsDocument44 pagesSynthesis of Organometallic CompoundsJimmy Boone100% (1)
- Lab Chem 3 :kinetics-Factor Affecting Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesLab Chem 3 :kinetics-Factor Affecting Rate of ReactionNadiah Matarsim60% (5)
- Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesChemical Kineticsnur hashimahNo ratings yet
- Reactants Products: Double Lined Boxes Are Conversion Factors To Convert From One Quantity To AnotherDocument5 pagesReactants Products: Double Lined Boxes Are Conversion Factors To Convert From One Quantity To AnotherfaltriqueraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5Document3 pagesChemistry Form 5alliey75% (8)
- MCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Document7 pagesMCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Sanjeev Chaudhary100% (1)
- Michaelis-Menten DerivationDocument7 pagesMichaelis-Menten Derivationaneesaahmed1991No ratings yet
- Recent Advances in The Hydrosilylation of AlkynesDocument4 pagesRecent Advances in The Hydrosilylation of AlkynesjavasoloNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Reaction KineticsDocument142 pages1.0 Reaction KineticsKhairul Aswari Ab RahmanNo ratings yet