Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Machines Tutorial Sheet #5 (2024)
Machines Tutorial Sheet #5 (2024)
Uploaded by
atulsinha803115Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Machines Tutorial Sheet #5 (2024)
Machines Tutorial Sheet #5 (2024)
Uploaded by
atulsinha803115Copyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Machines Tutorial Sheet #5 (2024)
1. a) A three phase, 16 pole synchronous generator has a star connected winding with 144 slots and
10 conductors per slot. The coils are full pitched. The flux per pole is 0.03 Wb, sine distributed. The
rotational speed is 375 RPM. Find RMS induce phase and line voltages and also the frequency of the
induced voltage.
b) A three phase 10 pole star connected alternator runs at 600 RPM. It has 120 stator slots
with 8 conductors per slot. The conductors of each phase are series connected forming full pitch
coils. The flux per pole is 56 mWb. Determine the phase and line induced voltages. What harmonics
due to the slots may appear in the phase and line induced voltages?
2. A 3 phase 8 pole 50 Hz synchronous generator is designed such that the ratio of the fundamental
RMS phase induced voltage to the fundamental flux per pole (in mWb) is 48.5. The third harmonic
induced phase voltage is 25% of the fundamental induced phase voltage while the third harmonic
flux per pole is 19.93% of the fundamental flux per pole. The stator phase winding coils are short
corded to eliminate the fifth harmonic induced phase voltage. The phase spread of the stator coils is
600 (electrical). Find out
(a) The coil span of the stator coils in degrees (electrical).
(b) Total number of slots in the machines
(c) The number of conductors per slot
3. A 2 pole 3 phase synchronous machine (working as a motor) has the following mechanical
dimensions and winding particulars. Air gap length = 1.3mm, mean air gap diameter = 22 cm, axial
length = 41 cm, Total field series turns = 880, rotor winding factor = 0.965, stator slots / pole / phase
= 3, stator conductors / slot = 12. Field current = 4 A, peak air gap flux density = 1.35T, Find the
following
a. Peak rotor ampere-turns.
b. Torque and Power developed (Tdev, Pdev) as functions of the rotor angle (δ).
c. Maximum values of Tdev and Pdev.
4. A 460-V, 50-kW, 60-Hz, three-phase synchronous motor has a synchronous reactance of Xs =
4.15 Ω and negligible stator resistance. The motor is operating at rated terminal voltage and an input
power of 40 kW. Calculate the magnitude and phase angle of the line-to neutral generated voltage
Eaf when the motor is operating at (i) 0.85 power factor lagging, (ii) unity power factor, and (iii)
0.85 power factor leading.
5. Consider a two-pole, 60-Hz, 13.8-kV, 10-MVA synchronous generator which achieves rated open-
circuit armature voltage at a field current of 842 A. It achieves rated armature current into a three-
phase terminal short circuit for a field current of 226 A.
a. Calculate the per-unit synchronous reactance.
Consider the situation in which this generator is connected to a 13.8 kV distribution feeder of
negligible impedance and operating at an output power of 8.75 MW at 0.9 pf lagging.
Neglect armature resistance. Calculate:
b. the reactive-power output in MVA, and the rotor angle for this operating condition.
c. the rotor angle and reactive-power output in MVA if the field current is reduced to 842 A
while the shaft-power supplied by the prime mover to the generator remains constant.
6. A three phase 2.5 MVA, 6.6 kV synchronous generator gave the following data for OCC at the
synchronous speed.
If (A) 16 20 25 32 45
Voc (L-L, V) 4400 5500 6600 7700 8800
With the armature short circuited and full load current flowing, the field current is 18 A. When the
machine is supplying full load current at zero pf at the rated voltage, the field current required is 45
A. Determine the leakage reactance per phase of the machine in Ω and the full load armature reaction
in terms of equivalent field amperes. Also find the field current and voltage regulation when the
machine is supplying full load at 0.8 pf lagging at the rated voltage. Neglect armature resistance.
You might also like
- Eee52 - Electrical Machines - Ii - Fast Track 2019Document4 pagesEee52 - Electrical Machines - Ii - Fast Track 2019Preethi Sinha100% (2)
- DC Generator NumericalsDocument2 pagesDC Generator NumericalsSumanjumanji0% (1)
- Tutorial Sheet 04Document5 pagesTutorial Sheet 04Abhishek ThakurNo ratings yet
- Assignments 1, 2, 3Document7 pagesAssignments 1, 2, 3Mude Kishore NaikNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document104 pagesQuiz 1ianguieb60% (5)
- Synchronous Generators - SheetDocument3 pagesSynchronous Generators - Sheetahmed1422zhNo ratings yet
- Emassignment 1Document3 pagesEmassignment 1Pushkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Exercises)Document10 pagesProblem Set (Exercises)John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument28 pagesAssignmentsaly.abdulghafarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems Synchronous MachinesDocument3 pagesNumerical Problems Synchronous MachinestusharNo ratings yet
- EM 2 AssignmentDocument3 pagesEM 2 AssignmentSagar VermaNo ratings yet
- EENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Document4 pagesEENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Jamil NahraNo ratings yet
- Sheet EEx73Document3 pagesSheet EEx73mohamedsabah22No ratings yet
- Assignmentsolutionselected 150208132823 Conversion Gate02Document30 pagesAssignmentsolutionselected 150208132823 Conversion Gate02apelokayaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 oDocument2 pagesExam 2 opollobNo ratings yet
- Phase: SemisterDocument5 pagesPhase: SemisterMuhammad TausiqueNo ratings yet
- Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering: Electromechanical Engineering Sheet 1 (Synchronous Machine)Document5 pagesAlexandria University Faculty of Engineering: Electromechanical Engineering Sheet 1 (Synchronous Machine)Mahmoud EltawabNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 Ac Otplusbook-1Document37 pagesQuiz1 Ac Otplusbook-1ianguieb0% (1)
- Final ELEC3130 S2 2010 CAL CompleteDocument5 pagesFinal ELEC3130 S2 2010 CAL CompletedeNo ratings yet
- pb04: A 3600 RPM, 60 HZ, 13.8 KV Synchronous Generator Has A Synchronous Reactance of 20Document3 pagespb04: A 3600 RPM, 60 HZ, 13.8 KV Synchronous Generator Has A Synchronous Reactance of 20Hamid BentarziNo ratings yet
- Tutorials On Synchronous Generators - 091421Document2 pagesTutorials On Synchronous Generators - 091421geraldinkougoum04No ratings yet
- Synchronous MachineDocument3 pagesSynchronous MachineAvishek0% (1)
- End of SemDocument2 pagesEnd of SemyaaNo ratings yet
- GATE Lectures by KN Rao: Machines Problem Set - Synchronous MachinesDocument8 pagesGATE Lectures by KN Rao: Machines Problem Set - Synchronous MachinesGUJJALA TARUN MANIKYA KIRANNo ratings yet
- 1 0 1 1 0 2 0 Rot OssDocument2 pages1 0 1 1 0 2 0 Rot OssEmerging TubeNo ratings yet
- Engineering ContentDocument5 pagesEngineering ContentVikas ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- EECE 370 Problems From Similar/Previous ExamsDocument4 pagesEECE 370 Problems From Similar/Previous ExamsKent Martin D. CartagenaNo ratings yet
- Important Question Em2Document4 pagesImportant Question Em2Dinesh PeterNo ratings yet
- Finals Machines Ot 2 Lab PDFDocument18 pagesFinals Machines Ot 2 Lab PDFWenzy BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDocument1 pageAssignment 1 Question On DC MachinesDeepti MishraNo ratings yet
- Syncronous Machine TUTDocument6 pagesSyncronous Machine TUTClaudioNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Tutorial Questions On Induction MachineDocument2 pagesElectrical Machines Tutorial Questions On Induction Machinejosenit1787No ratings yet
- 16 Mark Questions - BEEEDocument5 pages16 Mark Questions - BEEEVignesh GNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Synch - MachinesDocument3 pagesPractice Problems - Synch - MachinesBea DucaoNo ratings yet
- Important Questions 4Document1 pageImportant Questions 4sneha thiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- AC Rotating Machine MO'08Document5 pagesAC Rotating Machine MO'08Ank A DigItNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument1 pageQuestion BankMaheswariRVNo ratings yet
- Machines Tutorial Sheet #6 (2024) Answer KeysDocument3 pagesMachines Tutorial Sheet #6 (2024) Answer KeysmechanicsstudentNo ratings yet
- Machines SheetsDocument7 pagesMachines SheetsSammy BrioNo ratings yet
- ELE3114 Tutorial April 2022Document6 pagesELE3114 Tutorial April 2022Sahiil MauriceNo ratings yet
- Question 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound CompoundDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound Compoundالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.gokulchandruNo ratings yet
- DC MOTOR - EnerconDocument19 pagesDC MOTOR - EnerconJoanna Fabricante100% (1)
- EE 321 Assignment No. 1 Finals SY23 24Document3 pagesEE 321 Assignment No. 1 Finals SY23 24johnpaulshobayanNo ratings yet
- Short Questions ECDDocument7 pagesShort Questions ECDNanda Kishore RayNo ratings yet
- Assignment (DC Motors and Measurement)Document1 pageAssignment (DC Motors and Measurement)RoronoaNo ratings yet
- Serie de Sincronas 2013-2Document5 pagesSerie de Sincronas 2013-2Manuel MartínezNo ratings yet
- EEE 43 Final 2017Document3 pagesEEE 43 Final 2017Emman Joshua BustoNo ratings yet
- ELP-850 Assignment 5Document2 pagesELP-850 Assignment 5bathula pavanchandNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2ShabihNo ratings yet
- UIU EC-II Lecture#9Document18 pagesUIU EC-II Lecture#9Montosh RoyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010Document9 pagesExercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010Suleman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument5 pagesQuestion BankAASTHA KIETNo ratings yet
- Assignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Document1 pageAssignment I EEE 2214 ELECTRICAL MACHINES I Feb 2023 (2) (Original)Jimmy MachariaNo ratings yet
- Written QuestionsDocument18 pagesWritten QuestionsGokul RajNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Foundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsFrom EverandFoundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Picoturbine Windmill Kit V2Document9 pagesPicoturbine Windmill Kit V2Vinil RadhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Popular Woodworking 2000-11 No. 118Document69 pagesPopular Woodworking 2000-11 No. 118Miguel A. Ramirez100% (1)
- Elon Musks NEW HairPin Motor SHOCKS Entire IndustryDocument11 pagesElon Musks NEW HairPin Motor SHOCKS Entire IndustrySirin AktarNo ratings yet
- Construction & Working of AlternatorDocument14 pagesConstruction & Working of AlternatorBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine DesignDocument29 pagesElectrical Machine DesignMahmoud Fawzi100% (1)
- Q3 Science 5 Module 6Document16 pagesQ3 Science 5 Module 6Cecilia Guevarra DumlaoNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument65 pagesProjectSrinath Chary KajanaNo ratings yet
- 1885 35-VocabularyDocument49 pages1885 35-Vocabularycrazy devilNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Eff of CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Eff of CurrentR K SharmaNo ratings yet
- US768413 Tattoo GunDocument4 pagesUS768413 Tattoo GunEl GrandeNo ratings yet
- EMAC 2 Modified 2023 Single Phase WK 6 7 8 Module .Docx.1Document22 pagesEMAC 2 Modified 2023 Single Phase WK 6 7 8 Module .Docx.1alinsasaguinjoyNo ratings yet
- Batch - 14 - Protection Scheme of Busbars and Transmission LinesDocument26 pagesBatch - 14 - Protection Scheme of Busbars and Transmission LinesYugendran KumaravelNo ratings yet
- Vaj CortecDocument6 pagesVaj CortecvenkateshbitraNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering NotesDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering NotesAnas AnsariNo ratings yet
- DC Machine & Ac MachineDocument19 pagesDC Machine & Ac MachineSankara nathNo ratings yet
- Super Elex 4Document10 pagesSuper Elex 4Charles Adrian CNo ratings yet
- 3.proiectare Transformator Retea Mica Putere PDFDocument9 pages3.proiectare Transformator Retea Mica Putere PDFAlexandra FlorentinaNo ratings yet
- WWW Studyrankers Com 2017 08 Notes of CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument17 pagesWWW Studyrankers Com 2017 08 Notes of CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentVikas KashyapNo ratings yet
- DPP 3 PhysicsDocument2 pagesDPP 3 PhysicsSanjay VermaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 5: Simple Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument21 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 5: Simple Electric Motor and GeneratorMark PandilNo ratings yet
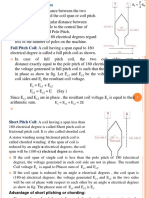
- Full Pitch Coil:: C P P PDocument12 pagesFull Pitch Coil:: C P P PAkashman ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Marine Electrical Engineering: TransformersDocument35 pagesMarine Electrical Engineering: TransformersMugilrajan DevarajanNo ratings yet
- EP1446862B1 Meg Tom Bearden 2Document22 pagesEP1446862B1 Meg Tom Bearden 2Mihai Daniel100% (1)
- 362-RCm2 FuellessEngineM2 Plans Part8Document15 pages362-RCm2 FuellessEngineM2 Plans Part8Leonardo Eladio Vergara67% (3)
- Electrical Machines 1: Prepared By-Mohammad Zohurul IslamDocument13 pagesElectrical Machines 1: Prepared By-Mohammad Zohurul IslamNabil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Gate Drive TrafoDocument4 pagesGate Drive Trafobenygiurgiu100% (1)
- KSH International Brochure CoverDocument4 pagesKSH International Brochure CoverkshintlNo ratings yet
- Dubar Christian IMPDocument81 pagesDubar Christian IMPakhilnandanNo ratings yet