Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Mighty Nucleus
The Mighty Nucleus
Uploaded by
Senio, Lexis Jan A.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesprotons vs. neutrons
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentprotons vs. neutrons
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThe Mighty Nucleus
The Mighty Nucleus
Uploaded by
Senio, Lexis Jan A.protons vs. neutrons
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
The Mighty Nucleus: Protons vs.
Neutrons
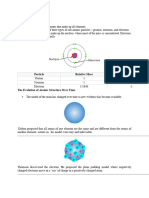
Let's talk about the building blocks of atoms, protons and
neutrons! These tiny particles live in the center of an atom,
called the nucleus, and they are what define an element's
identity. But how are they different, and what role do they
play?
Proton Power:
Charge: Protons are the party animals of the nucleus, sporting
a positive (+) electrical charge. This positive charge attracts
the negatively charged electrons that zip around the outside of
the atom, creating the stable atomic structure we know and
love.
Identity Theft: The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is
its atomic number. This number is like a fingerprint for each
element on the periodic table. Hydrogen, for example, always
has 1 proton, while helium has 2.
The Stable Force: Protons like to stick together, but they also
repel each other because of their positive charges. This
creates a balancing act in the nucleus.
Neutron Neutrality:
The Chill Broker: Neutrons, on the other hand, are the calming
influence in the nucleus. They have no electrical charge
(hence the name "neutrons"), acting as neutral peacekeepers
between the positively charged protons.
The Heavyweight: Neutrons have a mass similar to protons,
around 1 atomic mass unit (amu). This mass contributes
significantly to the overall weight of an atom, also known as
its atomic mass.
Isotope Innovation: The number of neutrons in an atom can
vary. These variations are called isotopes of the same
element. For instance, carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6
neutrons, while carbon-14 (used in radiocarbon dating) has 6
protons and 8 neutrons.
You might also like
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNo ratings yet
- Victoria Catholic School: Submitted By: Jessica V. MarceloDocument4 pagesVictoria Catholic School: Submitted By: Jessica V. MarceloEric CastilloNo ratings yet
- What Is Radioactivity?Document27 pagesWhat Is Radioactivity?Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Properties of The AtomDocument9 pagesStructure and Properties of The AtomenesNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesAtomic StructureJessica BeasleyNo ratings yet
- IG Chem - Nuclear MatterDocument1 pageIG Chem - Nuclear MatterRyno BredenkampNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StabilityDocument7 pagesNuclear StabilityWaqas SaeedNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNo ratings yet
- Atoms Ni JohannDocument1 pageAtoms Ni JohannRACHELLE MAE LLAGASNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument14 pagesNuclear Physics NotesJonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory & Structure: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitDocument52 pagesAtomic Theory & Structure: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnithendraprimaNo ratings yet
- 1.nuclear PharmacyDocument40 pages1.nuclear PharmacySheetal MeeniaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Synthesis of New Elements, Nuclear ReactionDocument58 pagesAtomic Number and Synthesis of New Elements, Nuclear ReactionJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument2 pagesAtomsJullienne Noreen AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Strand Notes 3Document1 pageChemistry Strand Notes 3Mazuba ChibbelaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number and Atomic MassDocument8 pagesAtomic Number and Atomic MassManasvi KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry 20-10-2020Document16 pagesNuclear Chemistry 20-10-2020Manohar MaripeNo ratings yet
- Simple Atomic StructureDocument1 pageSimple Atomic StructureSamartha RVNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument2 pagesThe Structure of The Atomapi-666588628No ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements: Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtoms and Elements: Atomic StructureJohn Rey Siwala EduqueNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear AtomDocument4 pagesThe Nuclear AtomMantiki QhobosheaneNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Phy Lecture1Document11 pagesNuclear Phy Lecture1foyshall foraejeeNo ratings yet
- 160 Nuclear ChemistryDocument32 pages160 Nuclear ChemistryMaria Rayappan S.No ratings yet
- Nuclear StructureDocument2 pagesNuclear Structureapi-237070241No ratings yet
- Basic Rad Phy1Document99 pagesBasic Rad Phy1Rashmi RajanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure.Document2 pagesAtomic Structure.shadnawazkhanNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument12 pagesAtomatgimale.comNo ratings yet
- About AtomsDocument2 pagesAbout AtomsnaivaanNo ratings yet
- Atomic NucleusDocument10 pagesAtomic NucleusKristiyan GeorgievNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL TERMS 1st Lesson WordDocument5 pagesTECHNICAL TERMS 1st Lesson Wordmhariz encinasNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument19 pagesAtomic Structuregoh benNo ratings yet
- Atomic ParticlesDocument3 pagesAtomic Particlesanas subhanNo ratings yet
- Atom and The Location of Its Major ComponentsDocument11 pagesAtom and The Location of Its Major ComponentsAldenramosNo ratings yet
- Element Builder VocabDocument2 pagesElement Builder VocabLashaunnie LawsonNo ratings yet
- Element Builder VocabDocument2 pagesElement Builder VocabMadhu Santosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 AtomsDocument22 pagesUnit 3 AtomsmaryNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: Electricity-Ohm's Law - Law of ResistanceDocument8 pagesBasic Concepts: Electricity-Ohm's Law - Law of ResistanceBSMK60No ratings yet
- A Water Molecule Consists of An Oxygen Atom and Two Hydrogen Atoms, Which Are Attached at An Angle of 105°Document20 pagesA Water Molecule Consists of An Oxygen Atom and Two Hydrogen Atoms, Which Are Attached at An Angle of 105°Kunal LunawatNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TablecalimagandaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - 1Document61 pagesNuclear Physics - 1Rose MusariraNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ModelDocument11 pagesNuclear Modelzeamayf.biasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The AtomDocument4 pagesChapter 2: The Structure of The AtomSalma FatymhNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Atoms and ElementsDocument18 pagesAtoms and ElementsJACK CAMPBELLNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Theory 20-28Document9 pagesAtomic Structure - Theory 20-28tc2brmg4mkNo ratings yet
- GenPhy2 - Lesson 4.2 - Atomic and Nuclear PhenomenaDocument12 pagesGenPhy2 - Lesson 4.2 - Atomic and Nuclear PhenomenaKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- Element Builder VocabDocument3 pagesElement Builder Vocabjovona seideNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR01x 2016 1.2 The Atomic Model-TranscriptDocument2 pagesNUCLEAR01x 2016 1.2 The Atomic Model-TranscriptArnoldo DanielNo ratings yet
- CHAP#2Document2 pagesCHAP#2Seema MemonNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics Atom and Its StructureDocument13 pagesModern Physics Atom and Its StructureRAHUL CHOUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Nucleus and Its Characterstics: Prof - Arun Bharti Department of Physics University of JammuDocument41 pagesNucleus and Its Characterstics: Prof - Arun Bharti Department of Physics University of JammuSurbhi guptaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2101 Lecture 1 (Atomic Structure)Document4 pagesCHEM 2101 Lecture 1 (Atomic Structure)Asif UddinNo ratings yet
- What Is Atomic Structure?: ProtonsDocument22 pagesWhat Is Atomic Structure?: ProtonsCaleb MukaviNo ratings yet
- Note For EJUDocument18 pagesNote For EJUmr.draungnaingwinNo ratings yet
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2From EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- Is Nuclear Energy Safe? -Nuclear Energy and Fission - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandIs Nuclear Energy Safe? -Nuclear Energy and Fission - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet