Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Popplet
Popplet
Uploaded by
DaniellaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Popplet
Popplet
Uploaded by
DaniellaCopyright:
Available Formats
*entre 500.000 y 1,5 *200.000-500.
000 habitantes
millones de habitantes
*Madrid y Barcelona Metrópolis
Metropolis regionales subregionales
Centros subregionales 50.000-200.000
*medium-sized city habitantes
with fewer urban
*state capital or another large city with functions
considerable international influence
Metrópolis nacionales
Jerarquía
Regional city Capitales comarcales 10.000-50.000
habitantes
National city
*area of influence is
provincial or regional Small city or town
Cities in rich countries Cities in poor countries
*small
*dispersed or concentrates activities related with primary sector:
*in villages *agriculture
*livestock farming
ESPACIO ESPAÑOL
URBANO
HIERARCHY OF CITIES
Global city *bigger size
*cities
*city with international *more number of inhabitants
power and influence
URBAN LADSCAPES
ALL OVER THE Rural settlements:
WORLD
Problemática
Activities related with industry and tertiary sector
*eliminación de residuos
Industrial *contaminación
Commercial and *exceso de tráfico
financial *presión espacio urbano sobre rural Urban settlements
Residential Urban a rural
Settlements
URBAN FUNCTIONS
Cultural
*number of inhabitants
*economic activity
Politics *compact shape
*high density of population
*built spaces
criteria to definde a
*succession of city
conurbations and megacity
metropolitan areas Militar
WHAT IS A CITY?
*several scattered
cities and towns that
are close together
urban region URBANISM center of power,
concentration of
activities and functions creativity and chance
The concept of city
THE URBAN
TIPOLOGY
Classification of cities
metropolitan area
*cosmopolitan
*big city merges with *tolerant
other smaller cities and *dynamic
towns fast way of life *anonymous
Conurbation
Historic centre
URBANISATION
PROCESS
Expansion zone
THE URBAN
*nearby cities of similar MORPHOLOGY
importance expand Geometry of the city
and merge together The postindustrial city
Urban layout *developed and developing countries
*space for services sector and house
*industrial activities outside the city
*more dispersed settlements
*outside residential areas
*higher price of urban space
*facilities on means of transport
Outskirts
Urban layouts
The industrial city
Regular The preindustrial city
Radial
Irregular
*emerge with Industrial Revolution
*factories and railways
*cities ned more space
*new residential areas: for workers and for the bourgeois
*new means of transport and connection
Medieval cities
Greek cities Roman cities
Modern era cities
You might also like
- UEENEEI157A+Inotech Controls+Handbook - V2 - 3Document142 pagesUEENEEI157A+Inotech Controls+Handbook - V2 - 3Kim N Lewis100% (3)
- Dietplan Type2B Balanceddiet PDFDocument5 pagesDietplan Type2B Balanceddiet PDFMario The Coach100% (2)
- Plan Amsterdam Magazine 03-2018Document36 pagesPlan Amsterdam Magazine 03-2018Kamila HidalgoNo ratings yet
- South Sudan MapDocument1 pageSouth Sudan MaplasudeneNo ratings yet
- Population: Million MillionDocument1 pagePopulation: Million MillionNynNo ratings yet
- Mapa Capacidad de Uso Mayor de Suelos: BrasilDocument1 pageMapa Capacidad de Uso Mayor de Suelos: BrasilCarlos Augusto Navas ArmasNo ratings yet
- GTS Chapter 8 WSDocument135 pagesGTS Chapter 8 WSM.NABILAH ABRORNo ratings yet
- Camp Hill Official Zoning MapDocument1 pageCamp Hill Official Zoning MapSean SauroNo ratings yet
- SrnmapfrontDocument1 pageSrnmapfrontsaurav kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Exe Summary Ss-12Document1 pageExe Summary Ss-12RagavanNo ratings yet
- Different Situations: - Ground Zero - New York, USA - Curitiba - Brazil - Downtown Core - SingaporeDocument1 pageDifferent Situations: - Ground Zero - New York, USA - Curitiba - Brazil - Downtown Core - SingaporeMeitar KeshetNo ratings yet
- Kota Malang PDFDocument1 pageKota Malang PDFPheby Cintha CliquersNo ratings yet
- 10 - Principles of Sustainable Transport SystemDocument1 page10 - Principles of Sustainable Transport SystemJawadRanaNo ratings yet
- Phl-Ocha-R4b Profile-A3 Final 0Document1 pagePhl-Ocha-R4b Profile-A3 Final 0Jerald P MancillaNo ratings yet
- 5G Poster 3-28-16 Lowres No StampDocument1 page5G Poster 3-28-16 Lowres No StampEduardo Javier100% (1)
- MT700D Interactive WiringDocument7 pagesMT700D Interactive WiringAndrás FehérNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHYDocument1 pageGEOGRAPHYphamhongnhung7858357No ratings yet
- Ab MapDocument8 pagesAb Mapmetalign198No ratings yet
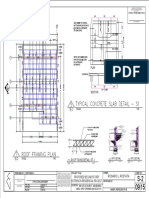
- Sheet 4 - GF-Roof Beam DrawingDocument1 pageSheet 4 - GF-Roof Beam DrawingBãlã Ð Chøçølãtě Røměø0% (1)
- 101 Plano GeneralDocument1 page101 Plano GeneralKenia Sofia MartínezNo ratings yet
- Catella Infographic Micro-LivingDocument1 pageCatella Infographic Micro-LivingAz RaNo ratings yet
- MEUK-TW-001-DRAWS-1-2016-28-01 Rev DDocument1 pageMEUK-TW-001-DRAWS-1-2016-28-01 Rev DbgygNo ratings yet
- RPA Region 7Document1 pageRPA Region 7John Lloyd AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Indicative Card Scheme Fee Rates: RomaniaDocument1 pageIndicative Card Scheme Fee Rates: RomaniaVáclav NěmecNo ratings yet
- Niger Carte Ref Niger PDFDocument1 pageNiger Carte Ref Niger PDFJesus AntonioNo ratings yet
- NIgerDocument1 pageNIgerIgor SemenovNo ratings yet
- NIgerDocument1 pageNIgerIgor SemenovNo ratings yet
- Is Regionalism An Increasing Feature of The World Economy?: Richard PomfretDocument25 pagesIs Regionalism An Increasing Feature of The World Economy?: Richard PomfretTanweer AlamNo ratings yet
- Block Sujanpur-IIIDocument147 pagesBlock Sujanpur-IIIashok kumarNo ratings yet
- Mapa SNT Septiembre 2021 A1Document1 pageMapa SNT Septiembre 2021 A1Jairo DumanNo ratings yet
- Eastern Border Zone Covid 19 NSW Border Entry Permit 2Document1 pageEastern Border Zone Covid 19 NSW Border Entry Permit 2Elspeth KerneboneNo ratings yet
- CBLN 19061017 0006Document1 pageCBLN 19061017 0006Aidel BelamideNo ratings yet
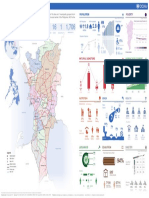
- AllWards StatisticsDocument1 pageAllWards StatisticsCHMLNo ratings yet
- Blossom City BrochureDocument5 pagesBlossom City BrochureParbancha AmitNo ratings yet
- 002 Article A004 enDocument20 pages002 Article A004 enCamilo BlancoNo ratings yet
- Roof Truss Detail: Rt-1: Office of The Building OfficialDocument1 pageRoof Truss Detail: Rt-1: Office of The Building OfficialJesusAntonioJugosNo ratings yet
- Kjaer Global Trends 2020Document11 pagesKjaer Global Trends 2020João JönkNo ratings yet
- Amhara MapDocument1 pageAmhara MapJoseph Thompson100% (1)
- ZS Resort STP Project 2Document1 pageZS Resort STP Project 2Jake Ariel Partosa ElmidoNo ratings yet
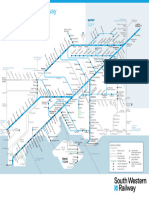
- SWR Station Toilet Map May 2022Document1 pageSWR Station Toilet Map May 2022dreareyNo ratings yet
- Arif Karim-1Document1 pageArif Karim-1Arif KarimNo ratings yet
- Gobierno Regional Huánuco: Pip "Desarrollo de Capacidades para El Ordenamiento Territorial en La Región Huánuco"Document1 pageGobierno Regional Huánuco: Pip "Desarrollo de Capacidades para El Ordenamiento Territorial en La Región Huánuco"Rikrdo Vargas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Existing Future Expansion: A. P. Garcia & AssociatesDocument1 pageExisting Future Expansion: A. P. Garcia & AssociatesDominic Robiso DatuinNo ratings yet
- (Proposed Renovation) Existing: A. P. Garcia & AssociatesDocument1 page(Proposed Renovation) Existing: A. P. Garcia & AssociatesDominic Robiso DatuinNo ratings yet
- Mercados Campesinos PDFDocument21 pagesMercados Campesinos PDFtoton2No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Accounting, Finance and Operations (Responses)Document3 pagesChapter-4 Accounting, Finance and Operations (Responses)Santanu MukherjeeNo ratings yet
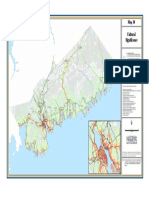
- Map10 CulturalSignificance PDFDocument1 pageMap10 CulturalSignificance PDFcarmenNo ratings yet
- Population Population: Natural DisastersDocument1 pagePopulation Population: Natural DisastersJohn Marco AciertoNo ratings yet
- WD Drawing 3.01 & 3.02 BA19ARC005Document2 pagesWD Drawing 3.01 & 3.02 BA19ARC005BA19ARC009 Deepali BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Citadis Spirit - Brochure - enDocument6 pagesCitadis Spirit - Brochure - enLuca Marius CristianNo ratings yet
- What Is Affordable Housing?Document3 pagesWhat Is Affordable Housing?PierulisNo ratings yet
- Perspective A: KarevDocument1 pagePerspective A: KarevJohn Paul GutierrezNo ratings yet
- JacksonChan SampleDocument1 pageJacksonChan SampleerniE抖音 AI Mobile Phone Based MovieNo ratings yet
- Wholesale Retail - Main PanelDocument1 pageWholesale Retail - Main PanelMuhammad Amri IdrisNo ratings yet
- Arabian Construction Company: Projected Cash FlowDocument8 pagesArabian Construction Company: Projected Cash FlowJule LobresNo ratings yet
- Hard Rock Cafe Location Strategy PDFDocument3 pagesHard Rock Cafe Location Strategy PDFpuesyo666No ratings yet
- RC Wall LayoutDocument1 pageRC Wall LayoutDINESH M.NNo ratings yet
- MaharashtraDocument1 pageMaharashtraManju BirjeNo ratings yet
- DWG Cscec D01 DD El PW 03 GF C1 0000 01Document1 pageDWG Cscec D01 DD El PW 03 GF C1 0000 01Mostafa AsemNo ratings yet
- CE 567 Public Mass Transportation: Course ContentsDocument148 pagesCE 567 Public Mass Transportation: Course ContentsEng Muhammad Afzal AlmaniNo ratings yet
- Astm A313 2003Document7 pagesAstm A313 2003ArefkhanNo ratings yet
- Pensamento Do Design Urbano Contemporâneo - Roggema RobDocument340 pagesPensamento Do Design Urbano Contemporâneo - Roggema RobLuana LuNo ratings yet
- 50420231021331792nav.2 Module 5Document2 pages50420231021331792nav.2 Module 5joeNo ratings yet
- Microsoft For Startups Deck 19Document20 pagesMicrosoft For Startups Deck 19Rajni Kant Sinha100% (1)
- POWER SYSTEM NUTRAL GRND FundamentalDocument21 pagesPOWER SYSTEM NUTRAL GRND FundamentalAbhay ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Cadence Vol 23Document38 pagesCadence Vol 23api-3709957No ratings yet
- 360rsw05 WKB Ca09 Ak PDFDocument50 pages360rsw05 WKB Ca09 Ak PDFErnesto Rodriguez67% (3)
- My Hell Vol.4 - Janez DrnovšekDocument6 pagesMy Hell Vol.4 - Janez DrnovšekAleksandar JankuloskiNo ratings yet
- Factoring Flow Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesFactoring Flow Sheet PDFReginald LopezNo ratings yet
- Oodp Unit 1Document30 pagesOodp Unit 1Amp RajasriNo ratings yet
- Personal Nutrition 9th Edition Boyle Solutions ManualDocument32 pagesPersonal Nutrition 9th Edition Boyle Solutions Manualthoabangt69100% (29)
- Action Plan LIPAWAN ESDocument3 pagesAction Plan LIPAWAN ESJo RieNo ratings yet
- Hamza Afzal Lab 5Document17 pagesHamza Afzal Lab 5ahmad riazNo ratings yet
- Unit I: The Writing Process: Reading To Write: Becoming A Critical Reader Brent Staples. "Cutting and Pasting: A Senior Thesis" (BothDocument3 pagesUnit I: The Writing Process: Reading To Write: Becoming A Critical Reader Brent Staples. "Cutting and Pasting: A Senior Thesis" (Bothghaji hdjkajNo ratings yet
- Implement A Verilog Model and Display The Output For A Set of Sample Data Together With The Wave Form Obtained For The Problems Given BelowDocument6 pagesImplement A Verilog Model and Display The Output For A Set of Sample Data Together With The Wave Form Obtained For The Problems Given Belowlilly pushparaniNo ratings yet
- To Study The Consumer Attitude Towards Domestic Solar Power Energy - by Tanisha RajpotDocument8 pagesTo Study The Consumer Attitude Towards Domestic Solar Power Energy - by Tanisha RajpotDeepak SoniNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis School of Banking and Finance (SSBF)Document20 pagesSymbiosis School of Banking and Finance (SSBF)bkniluNo ratings yet
- Kao LC - Portafolio de ProductosDocument2 pagesKao LC - Portafolio de ProductosBadri Rached100% (1)
- ESP Standard SizingDocument131 pagesESP Standard Sizingmohamed gamal100% (2)
- Aktu Result 2 Yr PDFDocument2 pagesAktu Result 2 Yr PDFprashantNo ratings yet
- OS101 ReviewerDocument3 pagesOS101 ReviewerMimi DamascoNo ratings yet
- Ijbd Vol1 No2Document469 pagesIjbd Vol1 No2Shaun StevensNo ratings yet
- Windows Server ChecklistDocument116 pagesWindows Server Checklistravichandran_mcpNo ratings yet
- Project - Portugal An Unlikely Empire - Student GuideDocument5 pagesProject - Portugal An Unlikely Empire - Student GuideBeanieNo ratings yet
- Engineers Syndicate Company ProfileDocument17 pagesEngineers Syndicate Company ProfileSakshi NandaNo ratings yet
- Osek Os: Session Speaker Deepak VDocument60 pagesOsek Os: Session Speaker Deepak VDaour DiopNo ratings yet
- List of IP Reference Substances Available at IPC, Ghaziabad List of ImpuritiesDocument4 pagesList of IP Reference Substances Available at IPC, Ghaziabad List of ImpuritiesUrva VasavadaNo ratings yet
- Berkeleyme - CIMA Executive ProgramDocument22 pagesBerkeleyme - CIMA Executive ProgramMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet