Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsJas DJ DJF BJV
Jas DJ DJF BJV
Uploaded by
cojos36357Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- MECP Exam ContentsDocument11 pagesMECP Exam Contentsedd toroNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document5 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document17 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document17 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument17 pagesBasic ElectronicsDevikaNo ratings yet
- Photodiode - WikipediaDocument15 pagesPhotodiode - WikipediaIKENNANo ratings yet
- Discoveries and Early DevicesDocument18 pagesDiscoveries and Early DevicesRamkumarNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument8 pagesSemiconductorsKathleen cheyenne EbajanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Technology ResearchDocument7 pagesElectronics Technology ResearchInigo PanesNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose Diodes: Engr. Mark Eullysis D. AlzagaDocument30 pagesSpecial Purpose Diodes: Engr. Mark Eullysis D. Alzagaroi constantineNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument3 pagesDiodeslitrakhanNo ratings yet
- A Photo Diode Is A Type of Photo Detector Capable of Converting Light Into Either Current or Voltage Repaired)Document14 pagesA Photo Diode Is A Type of Photo Detector Capable of Converting Light Into Either Current or Voltage Repaired)vikassist1024No ratings yet
- Photodiode: Sahil Bansal Sahil ChhabraDocument13 pagesPhotodiode: Sahil Bansal Sahil Chhabrashankarshiv010No ratings yet
- Group - 10-Solar Power Projects in Andhra PradeshDocument30 pagesGroup - 10-Solar Power Projects in Andhra PradeshScribd Dot ComNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaratannsNo ratings yet
- 5 - Special-Purpose DiodesDocument6 pages5 - Special-Purpose DiodesAdham Aboul KheirNo ratings yet
- Tuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2Document7 pagesTuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2melenyo tuqueroNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Applied Physic22Document9 pagesAssignment For Applied Physic22Saad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Automatic Room Light Controller: Bharat Institute of Technology SonipatDocument53 pagesAutomatic Room Light Controller: Bharat Institute of Technology SonipatParveen DahiyaNo ratings yet
- ASH Physics Project FinalDocument16 pagesASH Physics Project Finalrishabh tripathiNo ratings yet
- IP 2 DiodeDocument6 pagesIP 2 DiodeRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- Light Emitting Diode: Made By: Gurjeet Singh (BSC Physics - Iii - 1901721083028)Document27 pagesLight Emitting Diode: Made By: Gurjeet Singh (BSC Physics - Iii - 1901721083028)GURJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument10 pagesDiodefewpew LumanglasNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistance Project Report PhysicsDocument23 pagesLight Dependent Resistance Project Report Physicsapi-342687563100% (1)
- Physic Project LDRDocument18 pagesPhysic Project LDRaPP bOssNo ratings yet
- Schottky DiodeDocument3 pagesSchottky DiodeYenNo ratings yet
- LED - Device Performance CharacteristicsDocument52 pagesLED - Device Performance CharacteristicsMehjabin Abdurrazaque100% (1)
- Semiconductor DeviceDocument6 pagesSemiconductor DeviceGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- KVS Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesKVS Physics ProjectLokesh MaliNo ratings yet
- Diode CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesDiode CharacteristicsCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- The Junction DiodeDocument29 pagesThe Junction Diodeapi-3717843No ratings yet
- Photoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument32 pagesPhotoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamNo ratings yet
- I 2Document10 pagesI 2ankit gautamNo ratings yet
- Ali AsignmentDocument10 pagesAli AsignmentMuhammad Zain YousafNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - PHOTONICSDocument35 pagesModule 5 - PHOTONICSHarith PES 2020No ratings yet
- Diodes: Rectifying Property. The Most Common Function ofDocument8 pagesDiodes: Rectifying Property. The Most Common Function oframeshNo ratings yet
- PN Junction DiodesDocument18 pagesPN Junction DiodesPulkitNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument85 pagesUnit IbalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics Basics: Advantages of Optoelectronic DevicesDocument44 pagesOptoelectronics Basics: Advantages of Optoelectronic DevicesrafiNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication SystemDocument42 pagesOptical Communication SystemProf.Vidya KeshwaniNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument11 pagesZener Diodeusama saleemNo ratings yet
- Electronics Indivisual AssignmentDocument9 pagesElectronics Indivisual AssignmentYordanos TadeleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lecture 1Document43 pagesUnit 1 Lecture 1Shamil GadaNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronic Devices: Industrial ElectronicsDocument21 pagesOptoelectronic Devices: Industrial ElectronicsImadeadwriter WPNo ratings yet
- Reverse Direction) - Thus, The Diode Can Be Thought of As An Electronic Version of ADocument14 pagesReverse Direction) - Thus, The Diode Can Be Thought of As An Electronic Version of AVaron MirandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2.1Document16 pagesLecture 2.2.1Shubham JadhavNo ratings yet
- Group 5 MembersDocument29 pagesGroup 5 MembersedwardNo ratings yet
- A Semiconductor Device Is An Electronic Component That Exploits The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialDocument10 pagesA Semiconductor Device Is An Electronic Component That Exploits The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialPrakhar Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - L-12 - Characteristics of LED, Photodiode, and LDRDocument9 pagesUnit-2 - L-12 - Characteristics of LED, Photodiode, and LDRwebip33713No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Metal DetectorDocument16 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Metal Detectorred snapperNo ratings yet
- BEEE - Batch 6Document22 pagesBEEE - Batch 6Neo TarunNo ratings yet
- BY-Anagha R.Anjana Chandana.MDocument30 pagesBY-Anagha R.Anjana Chandana.MManjula S DevasurNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Optoelectronic Devices: 1. Describe The Working of Photo DiodeDocument7 pagesUnit-Iv Optoelectronic Devices: 1. Describe The Working of Photo DiodeVijay GNo ratings yet
- Children's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- IncinfenfnfDocument1 pageIncinfenfnfcojos36357No ratings yet
- JbdwibeibfifibefDocument1 pageJbdwibeibfifibefcojos36357No ratings yet
- InfinwifnifnfiDocument1 pageInfinwifnifnficojos36357No ratings yet
- EibhicebifhefhDocument1 pageEibhicebifhefhcojos36357No ratings yet
- AibdiscabsfefbfhDocument1 pageAibdiscabsfefbfhcojos36357No ratings yet
- Ojshfohc 9 Oifh 9 FHWFHFWHF 9 HDocument1 pageOjshfohc 9 Oifh 9 FHWFHFWHF 9 Hcojos36357No ratings yet
- Iehfnihnciebhf 8 IhefihfiefhnfDocument1 pageIehfnihnciebhf 8 Ihefihfiefhnfcojos36357No ratings yet
- Turn AroundDocument1 pageTurn Aroundcojos36357No ratings yet
- DfibfifebDocument1 pageDfibfifebcojos36357No ratings yet
- Euabhf 8 Ihe 8 HF 8 FG 8Document1 pageEuabhf 8 Ihe 8 HF 8 FG 8cojos36357No ratings yet
- IcshichDocument1 pageIcshichcojos36357No ratings yet
- MoneoniebcDocument1 pageMoneoniebccojos36357No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Mahishadal Raj CollegeDocument27 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Mahishadal Raj Collegeanon_703852302No ratings yet
- Infineon IRLB3036 DataSheet v01 01 enDocument9 pagesInfineon IRLB3036 DataSheet v01 01 enDavid BedoyaNo ratings yet
- IGBT Testing - A Technical OverviewDocument2 pagesIGBT Testing - A Technical OverviewGalco IndustrialNo ratings yet
- Probset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Document2 pagesProbset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Ralph Jayson SilangNo ratings yet
- MV103 - BZV86-2V0 PDFDocument5 pagesMV103 - BZV86-2V0 PDFgastone zanchettaNo ratings yet
- LM2695 High Voltage (30V, 1.25A) Step Down Switching RegulatorDocument14 pagesLM2695 High Voltage (30V, 1.25A) Step Down Switching RegulatorYoyok CahyonoNo ratings yet
- SMD 3apowerDocument104 pagesSMD 3apowerGregory LevantNo ratings yet
- The First Schedule: List of Exempted CommoditiesDocument89 pagesThe First Schedule: List of Exempted CommoditiesMohnishNo ratings yet
- Tester LPS04 LabManualDocument17 pagesTester LPS04 LabManualSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Overview of Silicon Carbide Technology: Device, Converter, System, and ApplicationDocument20 pagesOverview of Silicon Carbide Technology: Device, Converter, System, and ApplicationBhawna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Control of HydroponicsDocument88 pagesOptimization and Control of HydroponicsDeepak KNo ratings yet
- E66 B2 04 SummaryDocument3 pagesE66 B2 04 SummarySteven J. SelcukNo ratings yet
- Dummy LoadDocument6 pagesDummy LoadJorge Eduardo Iriart BidartNo ratings yet
- Automatic Water Level Controller Using NDocument15 pagesAutomatic Water Level Controller Using Nsaadahmedkalidaas100% (2)
- 6N60Document7 pages6N60HadeedAhmedSherNo ratings yet
- Car Jack Control System With RemoteDocument72 pagesCar Jack Control System With RemoteMaximilian SylvesterNo ratings yet
- GKU B Tech Civil SyllabusDocument60 pagesGKU B Tech Civil SyllabustajudeenNo ratings yet
- Bosch Rexroth Coils Conectors RE18325-90Document20 pagesBosch Rexroth Coils Conectors RE18325-90Luka Borna100% (1)
- 13N06L FairchildSemiconductorDocument9 pages13N06L FairchildSemiconductorfahmy najibNo ratings yet
- Monitor Sony Cpd-101vsDocument28 pagesMonitor Sony Cpd-101vspepitito22No ratings yet
- STTH812Document11 pagesSTTH812rolando ojedaNo ratings yet
- Radio and Hobbies 1965 01Document116 pagesRadio and Hobbies 1965 01MarcosGuitar1928No ratings yet
- Inverter Commutation CircuitsDocument7 pagesInverter Commutation Circuitskanor1991No ratings yet
- of Expt 3 & 4Document34 pagesof Expt 3 & 4DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument27 pagesPDFThunder IasdfwNo ratings yet
- Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesDiode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- MDI5N40/MDD5N40: N-Channel MOSFET 400V, 3.4 A, 1.6Document7 pagesMDI5N40/MDD5N40: N-Channel MOSFET 400V, 3.4 A, 1.6Francisco RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP2761I-HDocument4 pagesAdvanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP2761I-HAbelito JesusNo ratings yet
- 220 JBT Info TestreportsDocument5 pages220 JBT Info TestreportsC.H. WEENo ratings yet
Jas DJ DJF BJV
Jas DJ DJF BJV
Uploaded by
cojos363570 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesOriginal Title
jas dj djf bjv
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views5 pagesJas DJ DJF BJV
Jas DJ DJF BJV
Uploaded by
cojos36357Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
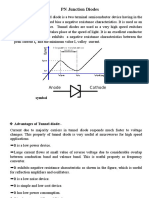
Introduction
▪ A diode is a two-terminal electronic
component that
conducts current primarily in one
direction (asymmetric conductance). It
has low (ideally zero) resistance in one
direction, and high (ideally infinite)
resistance in the other.
▪ A semiconductor diode, the most
commonly used type today, is
a crystalline piece
of semiconductor material with a p–n
junction connected to two electrical
terminals.[4] It
has an exponential current–voltage
characteristic. Semiconductor diodes
were the first semiconductor
electronic devices. The discovery of
asymmetric electrical conduction
across the contact between a
crystalline mineral and a metal was
made by German physicist Ferdinand
Braun in 1874.
TYPES OF DIODES
• There are many types of diodes. Ja scu
ujs cu su cub auc ajc ja ciu auc
jabcubaucibusacb
• Light-Emitting Diode
• An LED produces light when electricity
flows through it. It is a longer lasting and
more efficient way of creating light
than incandescent light bulbs.
• Depending on how it was made, the LED
can make different colors. LEDs were
first used in the 1970's. The light-
emitting diode may eventually replace
the light bulb as developing technology
makes it brighter and cheaper (it is
already more efficient and lasts longer).
In the 1970's the LEDs were used to
show numbers in appliances such as
calculators, and as a way to show the
power was on for larger appliances.
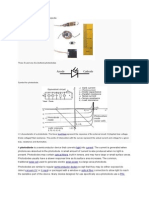
PHOTODIODE
• A photodiode is a light-sensitive
semiconductor diode.[1] It produces
current when it absorbs photons.
• The package of a photodiode allows
light (or infrared or ultraviolet
radiation, or X-rays) to reach the
sensitive part of the device. The
package may include lenses or optical
filters. Devices designed for use
specially as a photodiode use a PIN
junction rather than a p–n junction,
to increase the speed of response.
Photodiodes usually have a slower
response time as their surface area
increases. A photodiode is designed
to operate in reverse bias.[2] A solar
cell used to generate electric solar
power is a large area photodiode.
PRINCIPLE OF
OPERATION
• A photodiode is a PIN structure or p–
n junction. When a photon of
sufficient energy strikes the diode, it
creates an electron–hole pair. This
mechanism is also known as the
inner photoelectric effect. If the
absorption occurs in the
junction's depletion region, or one
diffusion length away from it, these
carriers are swept from the junction
by the built-in electric field of the
depletion region. Thus holes move
toward the anode, and electrons
toward the cathode, and
a photocurrent is produced. The total
current through the photodiode is the
sum of the dark current (current that
is generated in the absence of light)
and the photocurrent, so the dark
current must be minimized to
maximize the sensitivity of the device.
You might also like
- MECP Exam ContentsDocument11 pagesMECP Exam Contentsedd toroNo ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document5 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document17 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document21 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Presentation 4Document17 pagesPresentation 4xoranek474No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument17 pagesBasic ElectronicsDevikaNo ratings yet
- Photodiode - WikipediaDocument15 pagesPhotodiode - WikipediaIKENNANo ratings yet
- Discoveries and Early DevicesDocument18 pagesDiscoveries and Early DevicesRamkumarNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument8 pagesSemiconductorsKathleen cheyenne EbajanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Technology ResearchDocument7 pagesElectronics Technology ResearchInigo PanesNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose Diodes: Engr. Mark Eullysis D. AlzagaDocument30 pagesSpecial Purpose Diodes: Engr. Mark Eullysis D. Alzagaroi constantineNo ratings yet
- DiodesDocument3 pagesDiodeslitrakhanNo ratings yet
- A Photo Diode Is A Type of Photo Detector Capable of Converting Light Into Either Current or Voltage Repaired)Document14 pagesA Photo Diode Is A Type of Photo Detector Capable of Converting Light Into Either Current or Voltage Repaired)vikassist1024No ratings yet
- Photodiode: Sahil Bansal Sahil ChhabraDocument13 pagesPhotodiode: Sahil Bansal Sahil Chhabrashankarshiv010No ratings yet
- Group - 10-Solar Power Projects in Andhra PradeshDocument30 pagesGroup - 10-Solar Power Projects in Andhra PradeshScribd Dot ComNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaratannsNo ratings yet
- 5 - Special-Purpose DiodesDocument6 pages5 - Special-Purpose DiodesAdham Aboul KheirNo ratings yet
- Tuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2Document7 pagesTuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2melenyo tuqueroNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Applied Physic22Document9 pagesAssignment For Applied Physic22Saad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Automatic Room Light Controller: Bharat Institute of Technology SonipatDocument53 pagesAutomatic Room Light Controller: Bharat Institute of Technology SonipatParveen DahiyaNo ratings yet
- ASH Physics Project FinalDocument16 pagesASH Physics Project Finalrishabh tripathiNo ratings yet
- IP 2 DiodeDocument6 pagesIP 2 DiodeRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- Light Emitting Diode: Made By: Gurjeet Singh (BSC Physics - Iii - 1901721083028)Document27 pagesLight Emitting Diode: Made By: Gurjeet Singh (BSC Physics - Iii - 1901721083028)GURJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument10 pagesDiodefewpew LumanglasNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistance Project Report PhysicsDocument23 pagesLight Dependent Resistance Project Report Physicsapi-342687563100% (1)
- Physic Project LDRDocument18 pagesPhysic Project LDRaPP bOssNo ratings yet
- Schottky DiodeDocument3 pagesSchottky DiodeYenNo ratings yet
- LED - Device Performance CharacteristicsDocument52 pagesLED - Device Performance CharacteristicsMehjabin Abdurrazaque100% (1)
- Semiconductor DeviceDocument6 pagesSemiconductor DeviceGilberto ManhattanNo ratings yet
- KVS Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesKVS Physics ProjectLokesh MaliNo ratings yet
- Diode CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesDiode CharacteristicsCarryl BaerNo ratings yet
- The Junction DiodeDocument29 pagesThe Junction Diodeapi-3717843No ratings yet
- Photoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument32 pagesPhotoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamNo ratings yet
- I 2Document10 pagesI 2ankit gautamNo ratings yet
- Ali AsignmentDocument10 pagesAli AsignmentMuhammad Zain YousafNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - PHOTONICSDocument35 pagesModule 5 - PHOTONICSHarith PES 2020No ratings yet
- Diodes: Rectifying Property. The Most Common Function ofDocument8 pagesDiodes: Rectifying Property. The Most Common Function oframeshNo ratings yet
- PN Junction DiodesDocument18 pagesPN Junction DiodesPulkitNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument85 pagesUnit IbalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronics Basics: Advantages of Optoelectronic DevicesDocument44 pagesOptoelectronics Basics: Advantages of Optoelectronic DevicesrafiNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication SystemDocument42 pagesOptical Communication SystemProf.Vidya KeshwaniNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument11 pagesZener Diodeusama saleemNo ratings yet
- Electronics Indivisual AssignmentDocument9 pagesElectronics Indivisual AssignmentYordanos TadeleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lecture 1Document43 pagesUnit 1 Lecture 1Shamil GadaNo ratings yet
- Optoelectronic Devices: Industrial ElectronicsDocument21 pagesOptoelectronic Devices: Industrial ElectronicsImadeadwriter WPNo ratings yet
- Reverse Direction) - Thus, The Diode Can Be Thought of As An Electronic Version of ADocument14 pagesReverse Direction) - Thus, The Diode Can Be Thought of As An Electronic Version of AVaron MirandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2.1Document16 pagesLecture 2.2.1Shubham JadhavNo ratings yet
- Group 5 MembersDocument29 pagesGroup 5 MembersedwardNo ratings yet
- A Semiconductor Device Is An Electronic Component That Exploits The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialDocument10 pagesA Semiconductor Device Is An Electronic Component That Exploits The Electronic Properties of Semiconductor MaterialPrakhar Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - L-12 - Characteristics of LED, Photodiode, and LDRDocument9 pagesUnit-2 - L-12 - Characteristics of LED, Photodiode, and LDRwebip33713No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Metal DetectorDocument16 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Metal Detectorred snapperNo ratings yet
- BEEE - Batch 6Document22 pagesBEEE - Batch 6Neo TarunNo ratings yet
- BY-Anagha R.Anjana Chandana.MDocument30 pagesBY-Anagha R.Anjana Chandana.MManjula S DevasurNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Optoelectronic Devices: 1. Describe The Working of Photo DiodeDocument7 pagesUnit-Iv Optoelectronic Devices: 1. Describe The Working of Photo DiodeVijay GNo ratings yet
- Children's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren's Encyclopedia Electronics & Communications: The World of KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- IncinfenfnfDocument1 pageIncinfenfnfcojos36357No ratings yet
- JbdwibeibfifibefDocument1 pageJbdwibeibfifibefcojos36357No ratings yet
- InfinwifnifnfiDocument1 pageInfinwifnifnficojos36357No ratings yet
- EibhicebifhefhDocument1 pageEibhicebifhefhcojos36357No ratings yet
- AibdiscabsfefbfhDocument1 pageAibdiscabsfefbfhcojos36357No ratings yet
- Ojshfohc 9 Oifh 9 FHWFHFWHF 9 HDocument1 pageOjshfohc 9 Oifh 9 FHWFHFWHF 9 Hcojos36357No ratings yet
- Iehfnihnciebhf 8 IhefihfiefhnfDocument1 pageIehfnihnciebhf 8 Ihefihfiefhnfcojos36357No ratings yet
- Turn AroundDocument1 pageTurn Aroundcojos36357No ratings yet
- DfibfifebDocument1 pageDfibfifebcojos36357No ratings yet
- Euabhf 8 Ihe 8 HF 8 FG 8Document1 pageEuabhf 8 Ihe 8 HF 8 FG 8cojos36357No ratings yet
- IcshichDocument1 pageIcshichcojos36357No ratings yet
- MoneoniebcDocument1 pageMoneoniebccojos36357No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Mahishadal Raj CollegeDocument27 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Mahishadal Raj Collegeanon_703852302No ratings yet
- Infineon IRLB3036 DataSheet v01 01 enDocument9 pagesInfineon IRLB3036 DataSheet v01 01 enDavid BedoyaNo ratings yet
- IGBT Testing - A Technical OverviewDocument2 pagesIGBT Testing - A Technical OverviewGalco IndustrialNo ratings yet
- Probset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Document2 pagesProbset in Semiconductor Theory Diodes and Application Topics 2 March 2019Ralph Jayson SilangNo ratings yet
- MV103 - BZV86-2V0 PDFDocument5 pagesMV103 - BZV86-2V0 PDFgastone zanchettaNo ratings yet
- LM2695 High Voltage (30V, 1.25A) Step Down Switching RegulatorDocument14 pagesLM2695 High Voltage (30V, 1.25A) Step Down Switching RegulatorYoyok CahyonoNo ratings yet
- SMD 3apowerDocument104 pagesSMD 3apowerGregory LevantNo ratings yet
- The First Schedule: List of Exempted CommoditiesDocument89 pagesThe First Schedule: List of Exempted CommoditiesMohnishNo ratings yet
- Tester LPS04 LabManualDocument17 pagesTester LPS04 LabManualSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Overview of Silicon Carbide Technology: Device, Converter, System, and ApplicationDocument20 pagesOverview of Silicon Carbide Technology: Device, Converter, System, and ApplicationBhawna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Optimization and Control of HydroponicsDocument88 pagesOptimization and Control of HydroponicsDeepak KNo ratings yet
- E66 B2 04 SummaryDocument3 pagesE66 B2 04 SummarySteven J. SelcukNo ratings yet
- Dummy LoadDocument6 pagesDummy LoadJorge Eduardo Iriart BidartNo ratings yet
- Automatic Water Level Controller Using NDocument15 pagesAutomatic Water Level Controller Using Nsaadahmedkalidaas100% (2)
- 6N60Document7 pages6N60HadeedAhmedSherNo ratings yet
- Car Jack Control System With RemoteDocument72 pagesCar Jack Control System With RemoteMaximilian SylvesterNo ratings yet
- GKU B Tech Civil SyllabusDocument60 pagesGKU B Tech Civil SyllabustajudeenNo ratings yet
- Bosch Rexroth Coils Conectors RE18325-90Document20 pagesBosch Rexroth Coils Conectors RE18325-90Luka Borna100% (1)
- 13N06L FairchildSemiconductorDocument9 pages13N06L FairchildSemiconductorfahmy najibNo ratings yet
- Monitor Sony Cpd-101vsDocument28 pagesMonitor Sony Cpd-101vspepitito22No ratings yet
- STTH812Document11 pagesSTTH812rolando ojedaNo ratings yet
- Radio and Hobbies 1965 01Document116 pagesRadio and Hobbies 1965 01MarcosGuitar1928No ratings yet
- Inverter Commutation CircuitsDocument7 pagesInverter Commutation Circuitskanor1991No ratings yet
- of Expt 3 & 4Document34 pagesof Expt 3 & 4DEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument27 pagesPDFThunder IasdfwNo ratings yet
- Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesDiode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- MDI5N40/MDD5N40: N-Channel MOSFET 400V, 3.4 A, 1.6Document7 pagesMDI5N40/MDD5N40: N-Channel MOSFET 400V, 3.4 A, 1.6Francisco RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP2761I-HDocument4 pagesAdvanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP2761I-HAbelito JesusNo ratings yet
- 220 JBT Info TestreportsDocument5 pages220 JBT Info TestreportsC.H. WEENo ratings yet