Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsCommon Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Common Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Uploaded by
sspsangitaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument56 pagesContinuity and DifferentiabilityAvirup Ray100% (1)
- 2024 3 (Updated)Document20 pages2024 3 (Updated)a.emera22No ratings yet
- Continuity: Lim LimDocument8 pagesContinuity: Lim LimKainat Komal KhanNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument21 pagesContinuityParthav MashruNo ratings yet
- Continuity SheetDocument20 pagesContinuity SheetHJNo ratings yet
- Continuity 413Document69 pagesContinuity 413ChuyiyaNo ratings yet
- Maths Project FileDocument13 pagesMaths Project FileArt GalleryNo ratings yet
- Continuity Exe SheetDocument31 pagesContinuity Exe SheetSarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- 3 ContinuityDocument16 pages3 ContinuitySupawit FuntipNo ratings yet
- m100 Chapter1 Part3Document26 pagesm100 Chapter1 Part3Vongola SunNo ratings yet
- Exempler Chapter 5Document31 pagesExempler Chapter 5King of DonsNo ratings yet
- Definition of Continuous at A Point:) (X ) (Lim ) (Lim ) (LimDocument3 pagesDefinition of Continuous at A Point:) (X ) (Lim ) (Lim ) (LimtemkimleangNo ratings yet
- C&D SynopsisDocument7 pagesC&D SynopsisprekshithreddygattlaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and It's ApplicationDocument7 pagesDifferentiation and It's ApplicationKirti Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument29 pagesContinuity and Differentiabilitynitish21012006No ratings yet
- Laws of Continuous FunctionsDocument1 pageLaws of Continuous FunctionsRafi MohammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 (Continuity and Differentiability)Document31 pagesUnit 5 (Continuity and Differentiability)Siddharth DubeyNo ratings yet
- Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument31 pagesContinuity and DifferentiabilityKavyaNo ratings yet
- 1703589281Document28 pages1703589281Vince 0pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Applications of DifferentiationDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Applications of Differentiation祈翠No ratings yet
- Mathematics Mathematics: Continuity ContinuityDocument170 pagesMathematics Mathematics: Continuity ContinuitySatyajeet Mohanty100% (1)
- Lecture-6, Continuous Functions, Cal-1 IBADocument15 pagesLecture-6, Continuous Functions, Cal-1 IBAOrochi ScorpionNo ratings yet
- Calculus2014 Lecturenote 10 23Document9 pagesCalculus2014 Lecturenote 10 23盧思宇No ratings yet
- Calculus: Mrs. Dougherty's ClassDocument66 pagesCalculus: Mrs. Dougherty's ClassAbdullah SoomroNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Analysis - ApostoleDocument22 pagesMathematical Analysis - ApostoleVelliyangiriNo ratings yet
- Math 2400 Lecture Notes: Differentiation: Pete L. ClarkDocument33 pagesMath 2400 Lecture Notes: Differentiation: Pete L. ClarkEGE ERTENNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.3 Finding The Derivative of An Inverse Function-1Document5 pagesLesson 3.3 Finding The Derivative of An Inverse Function-1Hazen D'AuroraNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - ContinuityDocument16 pagesSheet - 01 - ContinuityNoob Game PlayNo ratings yet
- AppsDiff3c RemovedDocument9 pagesAppsDiff3c RemovedMuskan ParveenNo ratings yet
- Leep 205Document31 pagesLeep 205Ujjwal Singh sainiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Continuity & DifferentiationDocument31 pagesNCERT Continuity & Differentiationmastermohit1No ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiability - Crash CourseDocument104 pagesContinuity and Differentiability - Crash CourseSarvjeet Singh Kalsi100% (1)
- 2.3. Sự liên tục hàm sốDocument31 pages2.3. Sự liên tục hàm sốDo Phuong NamNo ratings yet
- 8 - Applications of Derivatives PDFDocument15 pages8 - Applications of Derivatives PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- TheoremsDocument6 pagesTheoremsMickey BoyNo ratings yet
- MA10001 (Advanced Calculus) : C NahakDocument19 pagesMA10001 (Advanced Calculus) : C NahakSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 05 MonotonicFunctionshhDocument1 page05 MonotonicFunctionshhRaja KushwahNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Continuity NJ - 247Document16 pagesSheet - 01 - Continuity NJ - 2471qerfdNo ratings yet
- Integral Inequalities 2014Document6 pagesIntegral Inequalities 2014Taniya SahaNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis LectureDocument21 pagesReal Analysis Lectureruchi21july25% (4)
- Continuous FunctionDocument9 pagesContinuous FunctionNur AmaninaNo ratings yet
- IOSR JournalsDocument2 pagesIOSR JournalsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- F.Y.B.Sc.C.S - Semester-Ii Paper-5: Calculus Unit - 1: Derivatives and Its Applications DefinitionsDocument8 pagesF.Y.B.Sc.C.S - Semester-Ii Paper-5: Calculus Unit - 1: Derivatives and Its Applications Definitionspreksha dixitNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Notes9Document3 pagesReal Analysis Notes9MathsisCoolV1No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Continuity of A FunctionDocument4 pagesLesson 5 - Continuity of A FunctionLewis PharmaceuticalsNo ratings yet
- 1371 EmvtDocument6 pages1371 EmvtAhmed SudanNo ratings yet
- Ch.6 Applications of Differentiation (6.1-6.2)Document16 pagesCh.6 Applications of Differentiation (6.1-6.2)hinchosyNo ratings yet
- Continuity: 1. Definition 3. The Intermediate Value TheoremDocument11 pagesContinuity: 1. Definition 3. The Intermediate Value TheoremShivam SoniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 6. Application of DerivativesDocument14 pagesMathematics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 6. Application of DerivativesDeepak kumar KanojiyaNo ratings yet
- Rolle's, Langrage's and Cauchy's Theorem Numeric NotationDocument5 pagesRolle's, Langrage's and Cauchy's Theorem Numeric Notationchauhangoli2425No ratings yet
- Continuty and DifferentibilyDocument7 pagesContinuty and DifferentibilythinkiitNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mean Value TheoremDocument5 pages3.2 Mean Value TheoremHimal BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- CH 3. Continuity Differentiability - Differentiation (Math +2)Document68 pagesCH 3. Continuity Differentiability - Differentiation (Math +2)Sajag GargNo ratings yet
- Lecature Real16Document3 pagesLecature Real16عبدالرحمن هشامNo ratings yet
- MTH165 Unit 3Document154 pagesMTH165 Unit 3RahulNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesPart 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionmercyNo ratings yet
- Continuity fs01Document122 pagesContinuity fs01iitiansrd2025No ratings yet
Common Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Common Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Uploaded by
sspsangita0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
fb22dd40-52ba-4d78-92b9-ae94fc24f0de-1706704713763-4102608560960521
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCommon Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Common Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Uploaded by
sspsangitaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
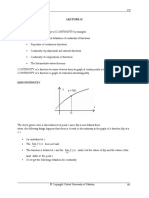
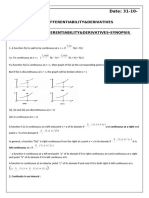
Differentiability
Common Derivatives Chain Rule and Other Examples
Continuity and Differentiability
DERIVATIVE DEFINITION
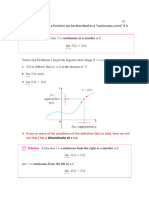
Continuity of function, f(x) at
a point a
BASIC PROPERTIES
(cf(x))’ = c(f’(x))
f(x) ± g(x))’ = f’(x) ± g’(x)
Continuity of function, f(x) in MEAN VALUE THEOREM
an interval [a, b] If f is differentiable on the interval (a, b) and
continuous at the end points there exists a c in
(a, b) such that
PRODUCT RULE
(f(x) g(x))’ = f(x)’ g(x) + f(x) g(x)’
QUOTIENT RULE
Algebra of continuous
functions
If f and g are two continuous
functions at a point c, then POWER RULE
1. f ± g is continuous at c
2. f.g is continuous at c
CHAIN RULE
4. gof is continuous at c
You might also like
- Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument56 pagesContinuity and DifferentiabilityAvirup Ray100% (1)
- 2024 3 (Updated)Document20 pages2024 3 (Updated)a.emera22No ratings yet
- Continuity: Lim LimDocument8 pagesContinuity: Lim LimKainat Komal KhanNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument21 pagesContinuityParthav MashruNo ratings yet
- Continuity SheetDocument20 pagesContinuity SheetHJNo ratings yet
- Continuity 413Document69 pagesContinuity 413ChuyiyaNo ratings yet
- Maths Project FileDocument13 pagesMaths Project FileArt GalleryNo ratings yet
- Continuity Exe SheetDocument31 pagesContinuity Exe SheetSarthak MishraNo ratings yet
- 3 ContinuityDocument16 pages3 ContinuitySupawit FuntipNo ratings yet
- m100 Chapter1 Part3Document26 pagesm100 Chapter1 Part3Vongola SunNo ratings yet
- Exempler Chapter 5Document31 pagesExempler Chapter 5King of DonsNo ratings yet
- Definition of Continuous at A Point:) (X ) (Lim ) (Lim ) (LimDocument3 pagesDefinition of Continuous at A Point:) (X ) (Lim ) (Lim ) (LimtemkimleangNo ratings yet
- C&D SynopsisDocument7 pagesC&D SynopsisprekshithreddygattlaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and It's ApplicationDocument7 pagesDifferentiation and It's ApplicationKirti Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument29 pagesContinuity and Differentiabilitynitish21012006No ratings yet
- Laws of Continuous FunctionsDocument1 pageLaws of Continuous FunctionsRafi MohammadNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 (Continuity and Differentiability)Document31 pagesUnit 5 (Continuity and Differentiability)Siddharth DubeyNo ratings yet
- Continuity and DifferentiabilityDocument31 pagesContinuity and DifferentiabilityKavyaNo ratings yet
- 1703589281Document28 pages1703589281Vince 0pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Applications of DifferentiationDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Applications of Differentiation祈翠No ratings yet
- Mathematics Mathematics: Continuity ContinuityDocument170 pagesMathematics Mathematics: Continuity ContinuitySatyajeet Mohanty100% (1)
- Lecture-6, Continuous Functions, Cal-1 IBADocument15 pagesLecture-6, Continuous Functions, Cal-1 IBAOrochi ScorpionNo ratings yet
- Calculus2014 Lecturenote 10 23Document9 pagesCalculus2014 Lecturenote 10 23盧思宇No ratings yet
- Calculus: Mrs. Dougherty's ClassDocument66 pagesCalculus: Mrs. Dougherty's ClassAbdullah SoomroNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Analysis - ApostoleDocument22 pagesMathematical Analysis - ApostoleVelliyangiriNo ratings yet
- Math 2400 Lecture Notes: Differentiation: Pete L. ClarkDocument33 pagesMath 2400 Lecture Notes: Differentiation: Pete L. ClarkEGE ERTENNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.3 Finding The Derivative of An Inverse Function-1Document5 pagesLesson 3.3 Finding The Derivative of An Inverse Function-1Hazen D'AuroraNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - ContinuityDocument16 pagesSheet - 01 - ContinuityNoob Game PlayNo ratings yet
- AppsDiff3c RemovedDocument9 pagesAppsDiff3c RemovedMuskan ParveenNo ratings yet
- Leep 205Document31 pagesLeep 205Ujjwal Singh sainiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Continuity & DifferentiationDocument31 pagesNCERT Continuity & Differentiationmastermohit1No ratings yet
- Continuity and Differentiability - Crash CourseDocument104 pagesContinuity and Differentiability - Crash CourseSarvjeet Singh Kalsi100% (1)
- 2.3. Sự liên tục hàm sốDocument31 pages2.3. Sự liên tục hàm sốDo Phuong NamNo ratings yet
- 8 - Applications of Derivatives PDFDocument15 pages8 - Applications of Derivatives PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- TheoremsDocument6 pagesTheoremsMickey BoyNo ratings yet
- MA10001 (Advanced Calculus) : C NahakDocument19 pagesMA10001 (Advanced Calculus) : C NahakSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 05 MonotonicFunctionshhDocument1 page05 MonotonicFunctionshhRaja KushwahNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - Continuity NJ - 247Document16 pagesSheet - 01 - Continuity NJ - 2471qerfdNo ratings yet
- Integral Inequalities 2014Document6 pagesIntegral Inequalities 2014Taniya SahaNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis LectureDocument21 pagesReal Analysis Lectureruchi21july25% (4)
- Continuous FunctionDocument9 pagesContinuous FunctionNur AmaninaNo ratings yet
- IOSR JournalsDocument2 pagesIOSR JournalsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- F.Y.B.Sc.C.S - Semester-Ii Paper-5: Calculus Unit - 1: Derivatives and Its Applications DefinitionsDocument8 pagesF.Y.B.Sc.C.S - Semester-Ii Paper-5: Calculus Unit - 1: Derivatives and Its Applications Definitionspreksha dixitNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Notes9Document3 pagesReal Analysis Notes9MathsisCoolV1No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Continuity of A FunctionDocument4 pagesLesson 5 - Continuity of A FunctionLewis PharmaceuticalsNo ratings yet
- 1371 EmvtDocument6 pages1371 EmvtAhmed SudanNo ratings yet
- Ch.6 Applications of Differentiation (6.1-6.2)Document16 pagesCh.6 Applications of Differentiation (6.1-6.2)hinchosyNo ratings yet
- Continuity: 1. Definition 3. The Intermediate Value TheoremDocument11 pagesContinuity: 1. Definition 3. The Intermediate Value TheoremShivam SoniNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 6. Application of DerivativesDocument14 pagesMathematics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 6. Application of DerivativesDeepak kumar KanojiyaNo ratings yet
- Rolle's, Langrage's and Cauchy's Theorem Numeric NotationDocument5 pagesRolle's, Langrage's and Cauchy's Theorem Numeric Notationchauhangoli2425No ratings yet
- Continuty and DifferentibilyDocument7 pagesContinuty and DifferentibilythinkiitNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mean Value TheoremDocument5 pages3.2 Mean Value TheoremHimal BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- CH 3. Continuity Differentiability - Differentiation (Math +2)Document68 pagesCH 3. Continuity Differentiability - Differentiation (Math +2)Sajag GargNo ratings yet
- Lecature Real16Document3 pagesLecature Real16عبدالرحمن هشامNo ratings yet
- MTH165 Unit 3Document154 pagesMTH165 Unit 3RahulNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesPart 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionmercyNo ratings yet
- Continuity fs01Document122 pagesContinuity fs01iitiansrd2025No ratings yet