Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Maps 04 - Market Systems
Mind Maps 04 - Market Systems
Uploaded by
Nivneth PeirisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 961 Beer Case PDFDocument22 pages961 Beer Case PDFayunda utariNo ratings yet
- Price and Value Communication: Strategies To Influence Willingness-To-Pay Session 4 Elkana EzekielDocument31 pagesPrice and Value Communication: Strategies To Influence Willingness-To-Pay Session 4 Elkana EzekielSakshi ShahNo ratings yet
- Eco Znotes4Document12 pagesEco Znotes4Sujay raju 13No ratings yet
- CH 10 ExternalitiesDocument39 pagesCH 10 ExternalitiesSakibNo ratings yet
- Rule-Based Investing According To Good Investing PrinciplesDocument26 pagesRule-Based Investing According To Good Investing Principlesrchawdhry123No ratings yet
- Nfo Presentation DSP Quant FundDocument26 pagesNfo Presentation DSP Quant FundPrajit NairNo ratings yet
- CHP 06-07 Household, Consumer, FirmsDocument41 pagesCHP 06-07 Household, Consumer, Firmsİkrar KoncaNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Level Economics 9708 Theory v1Document23 pagesCaie A2 Level Economics 9708 Theory v1ammarahmed8855No ratings yet
- Eapp PrintDocument7 pagesEapp PrintAnshul GoelNo ratings yet
- Caie As Economics 9708 TheoryDocument15 pagesCaie As Economics 9708 TheoryMasimba MafukidzeNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document17 pagesChap 002Alrifai Ziad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Market FailuresDocument37 pagesLecture 10 Market FailuresNguyễn TâmNo ratings yet
- CIE As Economics Notes FinalDocument15 pagesCIE As Economics Notes Finalbeditanisha6No ratings yet
- Econ Long Test ReviewerDocument7 pagesEcon Long Test ReviewerscarNo ratings yet
- What We Discuss Today: Marketing ManagementDocument10 pagesWhat We Discuss Today: Marketing ManagementaniNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Agri BusinessDocument28 pagesInnovations in Agri Businessalbum runNo ratings yet
- Focusing Marketing Strategy With Segmentation Targeting and Positioning. Chapter 08Document37 pagesFocusing Marketing Strategy With Segmentation Targeting and Positioning. Chapter 08priyapawdeNo ratings yet
- OS Preparatory 16-18 BacthDocument14 pagesOS Preparatory 16-18 BacthRajeev MehtaNo ratings yet
- T9 - Market Failure - Information Failures - Externalities and Public GoodsDocument24 pagesT9 - Market Failure - Information Failures - Externalities and Public GoodsAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Market FailuresDocument48 pagesLecture 10 Market FailuresNguyễn TâmNo ratings yet
- Week 5. Sustainable Marketing and Ethics in The Digital Age and Unit Conclusion (1) - TaggedDocument24 pagesWeek 5. Sustainable Marketing and Ethics in The Digital Age and Unit Conclusion (1) - Taggedshiyikang5100% (1)
- Public FinanceDocument19 pagesPublic Financepremgames4steveNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Frame Work: Risk Analysis-Method Risk-External Risk-ExampleDocument4 pagesRisk Management Frame Work: Risk Analysis-Method Risk-External Risk-ExampleBharathNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Business Model Innovation - Class 4 & 5Document28 pages2017 - Business Model Innovation - Class 4 & 5Jassal KarmanNo ratings yet
- Myppt (Economics Utility Wealth&Comforts)Document5 pagesMyppt (Economics Utility Wealth&Comforts)naga sNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Pricing StrategyDocument47 pagesModule 2 Pricing StrategyAmit YereshimiNo ratings yet
- Hour 12,13, Aug 16,18 Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocument36 pagesHour 12,13, Aug 16,18 Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningKushal WadheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economic ImportanceDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Economic ImportanceRajKumarNo ratings yet
- ITC Rural Marketing in India Case StudyDocument15 pagesITC Rural Marketing in India Case StudyPraveen Trivedi100% (4)
- Unit - 1 Introduction To Marketing ManagementDocument80 pagesUnit - 1 Introduction To Marketing ManagementSaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument27 pagesEconomicsnour mohammedNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research 123Document7 pagesMarketing Research 123Jayson MeperaqueNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Lecture 5Document24 pagesMarketing Management Lecture 5Mandeep Kumar HassaniNo ratings yet
- Financial Management in Intangible-Intensive Companies: Presented By, Niveditha.RDocument13 pagesFinancial Management in Intangible-Intensive Companies: Presented By, Niveditha.RPathrika NivedithaNo ratings yet
- Collective MarketingDocument13 pagesCollective MarketingMart RuralNo ratings yet
- 6 Forces - Markets, Industry Rivalry, Buyers and Sellers 2023Document8 pages6 Forces - Markets, Industry Rivalry, Buyers and Sellers 2023michaelsstrongNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 - Marketing BLANKEDDocument2 pagesPaper 1 - Marketing BLANKEDJulian MorganNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument5 pagesIntroSheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MeDocument30 pagesIntroduction To MeAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Pricing-Strategy Introduction 2Document32 pagesPricing-Strategy Introduction 2Sheam Zuzette AgustinNo ratings yet
- BSCH5C8 Business Studies Notes Igcse by Abhilash SirDocument4 pagesBSCH5C8 Business Studies Notes Igcse by Abhilash SirAbhilashPandaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rokiah AlaviDocument10 pagesDr. Rokiah Alaviasma munifatussaidahNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Lecture 4Document27 pagesMarketing Management Lecture 4Mandeep Kumar HassaniNo ratings yet
- SMK Session 1Document28 pagesSMK Session 1Manogna SNo ratings yet
- COMPETING THROUGH NEW MARKETING MIX and InnovationDocument24 pagesCOMPETING THROUGH NEW MARKETING MIX and Innovationnihayatun najahiyah0% (2)
- Economic SystemsDocument1 pageEconomic SystemsNhi YếnNo ratings yet
- Five Forces Industry Analysis: Supplier Power Buying Power Intensity of RivalryDocument11 pagesFive Forces Industry Analysis: Supplier Power Buying Power Intensity of RivalryRizki RidwanNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces: Barriers To EntryDocument2 pagesPorter's Five Forces: Barriers To EntryNimish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Market Segmentation Targeting and PositioningDocument27 pagesMarket Segmentation Targeting and PositioningmuhilvannanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy SlideDocument63 pagesMarketing Strategy SlideChan Soo Boon100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Price Decisions: Internal Factors External FactorsDocument17 pagesFactors Affecting Price Decisions: Internal Factors External FactorsDivya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial StrategiesDocument6 pagesFinancial StrategiesdeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 018Document13 pagesChapter 018Marwa HassanNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document11 pagesGroup 1Monica MinaNo ratings yet
- How To Grow Rich V1.0Document11 pagesHow To Grow Rich V1.0Hemant KhoslaNo ratings yet
- 2a - How To Grow RichV1.0Document11 pages2a - How To Grow RichV1.0Hemant KhoslaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportDinhkhanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Apple Global Supply Chain S2 Teknik IndustriDocument23 pagesApple Global Supply Chain S2 Teknik IndustriRuth Dame Pricilia0% (1)
- The Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsFrom EverandThe Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Power of Public Investment Management: Transforming Resources Into Assets for GrowthFrom EverandThe Power of Public Investment Management: Transforming Resources Into Assets for GrowthNo ratings yet
- Nov 2020 - Econ Tute2Document9 pagesNov 2020 - Econ Tute2Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- BA3 M KIT Chapter 10Document4 pagesBA3 M KIT Chapter 10Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Flash CardsDocument16 pagesFlash CardsNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Tute 04 - Market System 1Document11 pagesTute 04 - Market System 1Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- BA1 - Micro Economics - Mind Map 2Document4 pagesBA1 - Micro Economics - Mind Map 2Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Problem QuestionDocument1 pageProblem QuestionNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Econ Tute 1Document11 pagesEcon Tute 1Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- 50 Question Bank With AnswersDocument10 pages50 Question Bank With AnswersNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Answers For BA1 Revision QuestionsDocument8 pagesAnswers For BA1 Revision QuestionsNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Negative ExternalitiesDocument5 pagesNegative ExternalitiesNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Law Test July 7thDocument2 pagesLaw Test July 7thNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- June 2017 Paper 1 - QPDocument20 pagesJune 2017 Paper 1 - QPNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Law Reform Model AnswersDocument2 pagesLaw Reform Model AnswersNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Misrepresentation Sample QuestionDocument1 pageMisrepresentation Sample QuestionNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Law Test June 9thDocument2 pagesLaw Test June 9thNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- International Business: by Charles W.L. HillDocument37 pagesInternational Business: by Charles W.L. Hilllongtran1191No ratings yet
- The Analysis of IpodDocument19 pagesThe Analysis of IpodRachel WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- A Commentary On The KulbhushanDocument53 pagesA Commentary On The KulbhushanVinayak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Operations Handbook Block II Spaceraft Vol 1 Part 2Document475 pagesApollo Operations Handbook Block II Spaceraft Vol 1 Part 2Bob Andrepont100% (2)
- p2c2 ProgressmeasurementDocument19 pagesp2c2 ProgressmeasurementicetesterNo ratings yet
- Disposable HME Filter (Child) - VADI MEDICAL-800-51300Document2 pagesDisposable HME Filter (Child) - VADI MEDICAL-800-51300Spectrum IngenierosNo ratings yet
- Virginia Theological Seminary Journal, Fall 2011Document55 pagesVirginia Theological Seminary Journal, Fall 2011Susan L. ShillinglawNo ratings yet
- WWW Interfarfacing ComDocument13 pagesWWW Interfarfacing ComspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- Project-Orpheus A Research Study Into 360 Cinematic VRDocument6 pagesProject-Orpheus A Research Study Into 360 Cinematic VRjuan acuñaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Samar State University College of EducationDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Samar State University College of EducationJulius Lucas SabanyaoNo ratings yet
- Allegheny 316 PDFDocument13 pagesAllegheny 316 PDFJoshua WalkerNo ratings yet
- LacusCurtius - Strabo's Geography - Book III Chapter 3Document10 pagesLacusCurtius - Strabo's Geography - Book III Chapter 3A Miguel Simão LealNo ratings yet
- Uruguay The Owners Manual 5th EdDocument240 pagesUruguay The Owners Manual 5th EdlinkgineerNo ratings yet
- Wheter Chamber Summons Is A PleadingDocument3 pagesWheter Chamber Summons Is A Pleadingmoses machiraNo ratings yet
- Lab2 - Stereotaxic SurgeryDocument4 pagesLab2 - Stereotaxic SurgeryMichael Anthony BritoNo ratings yet
- SOP For Fenil - Bachelor's Degree in Science (Biology)Document2 pagesSOP For Fenil - Bachelor's Degree in Science (Biology)Ahmed100% (1)
- Epson R200, R210 Visão ExplodidaDocument8 pagesEpson R200, R210 Visão ExplodidaKedinaldoNo ratings yet
- Application of Consumer BehaviorDocument6 pagesApplication of Consumer BehaviorNoella Marie BaronNo ratings yet
- (New) Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Rubberized Coir Fibre SheetsDocument8 pages(New) Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Rubberized Coir Fibre SheetsPrakumarNo ratings yet
- Trimble 2 Rin ExDocument1 pageTrimble 2 Rin ExIvan.sidabutarNo ratings yet
- Artikel Ilmiah Sosialisasi English Ver KKN UNAIRDocument9 pagesArtikel Ilmiah Sosialisasi English Ver KKN UNAIRJasmine Octavia Putri BalawNo ratings yet
- sr1 Cup Infopack 2016Document8 pagessr1 Cup Infopack 2016Stef PoienaruNo ratings yet
- Resume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 5&6 - Dani Yustiardi 1906419822Document8 pagesResume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 5&6 - Dani Yustiardi 1906419822Dani Yustiardi MunarsoNo ratings yet
- Target Amplification MethodsDocument3 pagesTarget Amplification MethodsNOR-FATIMAH BARATNo ratings yet
- RPV 3Document158 pagesRPV 3Melkamu AmusheNo ratings yet
- Simulated Binar Crossover F Continuous Search Space: Comp SystemsDocument34 pagesSimulated Binar Crossover F Continuous Search Space: Comp SystemsSal Ie EmNo ratings yet
- Account Opening FormDocument11 pagesAccount Opening FormTotimeh WisdomNo ratings yet
- Capturing Deadlocks in SQL Server - Brent Ozar Unlimited® by Brent Ozar Unlimited®Document7 pagesCapturing Deadlocks in SQL Server - Brent Ozar Unlimited® by Brent Ozar Unlimited®kishore2285No ratings yet
- VIRTUAL KEYBOARD PresentationDocument18 pagesVIRTUAL KEYBOARD PresentationRä BïNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2012 Information BrochureDocument53 pagesAIEEE 2012 Information Brochuresd11123No ratings yet
Mind Maps 04 - Market Systems
Mind Maps 04 - Market Systems
Uploaded by
Nivneth PeirisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Maps 04 - Market Systems
Mind Maps 04 - Market Systems
Uploaded by
Nivneth PeirisCopyright:
Available Formats
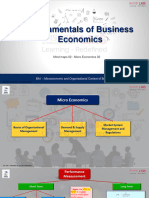
Managing Finance
in a Digital World
Mind maps 04
Market Systems
BA1 - Microeconomic and Organisational Context of Business
BA1 – Mind Maps 04 - Tharindu Ameresekere
Market Equilibrium Changes in Market Equilibrium
• Where Demand and Supply are matched Changes in either demand or supply cause changes in
• The price at which market equilibrium.
quantity demanded = quantity supplied
BA1 – Mind Maps 04 - Tharindu Ameresekere
Market Failure Public Goods
Inability of a Market to
allocate resources in a Non-Rival Non-Excludability
way that maximises
utility is called a market
failure. Consumption of
the good by one Free Rider
person does not Concept
reduce the
available for
others.
BA1 – Mind Maps 04 - Tharindu Ameresekere
Social costs or benefits that are not automatically included in the supply and demand
Externalities
curves for a product or service.
Merit Goods Merit goods are characterized by external
Positive Externality Negative Externality social benefits (i.e. positive externalities) in
consumption or by lack of knowledge of the
private benefits in consumption.
Benefit to society due
to a transaction. Cost to the society.
Government will Government will tax
provide subsidy them & control them. May be under • Ignorance of consumers of the
provided by the private benefits
market • Failure of market to reflect the
social benefits
• Excessive price, limiting access
to these services
De-merit Goods
Positive
Externalities A good or service which is
considered unhealthy,
degrading or otherwise
socially undesirable.
BA1 – Mind Maps 04 - Tharindu Ameresekere
Government Price
Controls
Minimum Price Maximum Price
** Effective Minimum ** Effective
Price should be Maximum Price
greater than should be less than
equilibrium price equilibrium price
Causes of Causes of
imposing a imposing a
Minimum Price Maximum Price
Excess Supply Misallocation of resources Shortage of supply Misallocation of resources
Wastage of Resources Arbitrary ways of allocating a product
BA1 – Mind Maps 04 - Tharindu Ameresekere
Economies of Scale Diseconomies of Scale
Reduction in unit average cost by Technical Dis-Economies of Scale
Increasing in unit average
increasing scale of production.
by increasing the scale of
Trading Dis-Economies of Scale
production in the long
run.
The existence of significant economies of scale Managerial Dis-Economies of Scale
can be expected to lead to:
i. Costs and therefore prices falling as firms
increase their scale of output To manage the cost of business better
ii. Barriers to entry for newer smaller firms; and the companies sometimes handover
Outsourcing
iii. Industries dominated by a small number of their work to outside parties. This is
large firms. called outsourcing
Transaction Costs
Cost of Searching Cost of Legal Agreements Cost of monitoring
BA1 – Mind Maps 04 - Tharindu Ameresekere
You might also like
- 961 Beer Case PDFDocument22 pages961 Beer Case PDFayunda utariNo ratings yet
- Price and Value Communication: Strategies To Influence Willingness-To-Pay Session 4 Elkana EzekielDocument31 pagesPrice and Value Communication: Strategies To Influence Willingness-To-Pay Session 4 Elkana EzekielSakshi ShahNo ratings yet
- Eco Znotes4Document12 pagesEco Znotes4Sujay raju 13No ratings yet
- CH 10 ExternalitiesDocument39 pagesCH 10 ExternalitiesSakibNo ratings yet
- Rule-Based Investing According To Good Investing PrinciplesDocument26 pagesRule-Based Investing According To Good Investing Principlesrchawdhry123No ratings yet
- Nfo Presentation DSP Quant FundDocument26 pagesNfo Presentation DSP Quant FundPrajit NairNo ratings yet
- CHP 06-07 Household, Consumer, FirmsDocument41 pagesCHP 06-07 Household, Consumer, Firmsİkrar KoncaNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Level Economics 9708 Theory v1Document23 pagesCaie A2 Level Economics 9708 Theory v1ammarahmed8855No ratings yet
- Eapp PrintDocument7 pagesEapp PrintAnshul GoelNo ratings yet
- Caie As Economics 9708 TheoryDocument15 pagesCaie As Economics 9708 TheoryMasimba MafukidzeNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document17 pagesChap 002Alrifai Ziad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Market FailuresDocument37 pagesLecture 10 Market FailuresNguyễn TâmNo ratings yet
- CIE As Economics Notes FinalDocument15 pagesCIE As Economics Notes Finalbeditanisha6No ratings yet
- Econ Long Test ReviewerDocument7 pagesEcon Long Test ReviewerscarNo ratings yet
- What We Discuss Today: Marketing ManagementDocument10 pagesWhat We Discuss Today: Marketing ManagementaniNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Agri BusinessDocument28 pagesInnovations in Agri Businessalbum runNo ratings yet
- Focusing Marketing Strategy With Segmentation Targeting and Positioning. Chapter 08Document37 pagesFocusing Marketing Strategy With Segmentation Targeting and Positioning. Chapter 08priyapawdeNo ratings yet
- OS Preparatory 16-18 BacthDocument14 pagesOS Preparatory 16-18 BacthRajeev MehtaNo ratings yet
- T9 - Market Failure - Information Failures - Externalities and Public GoodsDocument24 pagesT9 - Market Failure - Information Failures - Externalities and Public GoodsAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Market FailuresDocument48 pagesLecture 10 Market FailuresNguyễn TâmNo ratings yet
- Week 5. Sustainable Marketing and Ethics in The Digital Age and Unit Conclusion (1) - TaggedDocument24 pagesWeek 5. Sustainable Marketing and Ethics in The Digital Age and Unit Conclusion (1) - Taggedshiyikang5100% (1)
- Public FinanceDocument19 pagesPublic Financepremgames4steveNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Frame Work: Risk Analysis-Method Risk-External Risk-ExampleDocument4 pagesRisk Management Frame Work: Risk Analysis-Method Risk-External Risk-ExampleBharathNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Business Model Innovation - Class 4 & 5Document28 pages2017 - Business Model Innovation - Class 4 & 5Jassal KarmanNo ratings yet
- Myppt (Economics Utility Wealth&Comforts)Document5 pagesMyppt (Economics Utility Wealth&Comforts)naga sNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Pricing StrategyDocument47 pagesModule 2 Pricing StrategyAmit YereshimiNo ratings yet
- Hour 12,13, Aug 16,18 Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocument36 pagesHour 12,13, Aug 16,18 Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningKushal WadheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economic ImportanceDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Economic ImportanceRajKumarNo ratings yet
- ITC Rural Marketing in India Case StudyDocument15 pagesITC Rural Marketing in India Case StudyPraveen Trivedi100% (4)
- Unit - 1 Introduction To Marketing ManagementDocument80 pagesUnit - 1 Introduction To Marketing ManagementSaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument27 pagesEconomicsnour mohammedNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research 123Document7 pagesMarketing Research 123Jayson MeperaqueNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Lecture 5Document24 pagesMarketing Management Lecture 5Mandeep Kumar HassaniNo ratings yet
- Financial Management in Intangible-Intensive Companies: Presented By, Niveditha.RDocument13 pagesFinancial Management in Intangible-Intensive Companies: Presented By, Niveditha.RPathrika NivedithaNo ratings yet
- Collective MarketingDocument13 pagesCollective MarketingMart RuralNo ratings yet
- 6 Forces - Markets, Industry Rivalry, Buyers and Sellers 2023Document8 pages6 Forces - Markets, Industry Rivalry, Buyers and Sellers 2023michaelsstrongNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 - Marketing BLANKEDDocument2 pagesPaper 1 - Marketing BLANKEDJulian MorganNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument5 pagesIntroSheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MeDocument30 pagesIntroduction To MeAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Pricing-Strategy Introduction 2Document32 pagesPricing-Strategy Introduction 2Sheam Zuzette AgustinNo ratings yet
- BSCH5C8 Business Studies Notes Igcse by Abhilash SirDocument4 pagesBSCH5C8 Business Studies Notes Igcse by Abhilash SirAbhilashPandaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rokiah AlaviDocument10 pagesDr. Rokiah Alaviasma munifatussaidahNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Lecture 4Document27 pagesMarketing Management Lecture 4Mandeep Kumar HassaniNo ratings yet
- SMK Session 1Document28 pagesSMK Session 1Manogna SNo ratings yet
- COMPETING THROUGH NEW MARKETING MIX and InnovationDocument24 pagesCOMPETING THROUGH NEW MARKETING MIX and Innovationnihayatun najahiyah0% (2)
- Economic SystemsDocument1 pageEconomic SystemsNhi YếnNo ratings yet
- Five Forces Industry Analysis: Supplier Power Buying Power Intensity of RivalryDocument11 pagesFive Forces Industry Analysis: Supplier Power Buying Power Intensity of RivalryRizki RidwanNo ratings yet
- Porter's Five Forces: Barriers To EntryDocument2 pagesPorter's Five Forces: Barriers To EntryNimish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Market Segmentation Targeting and PositioningDocument27 pagesMarket Segmentation Targeting and PositioningmuhilvannanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy SlideDocument63 pagesMarketing Strategy SlideChan Soo Boon100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Price Decisions: Internal Factors External FactorsDocument17 pagesFactors Affecting Price Decisions: Internal Factors External FactorsDivya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial StrategiesDocument6 pagesFinancial StrategiesdeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 018Document13 pagesChapter 018Marwa HassanNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document11 pagesGroup 1Monica MinaNo ratings yet
- How To Grow Rich V1.0Document11 pagesHow To Grow Rich V1.0Hemant KhoslaNo ratings yet
- 2a - How To Grow RichV1.0Document11 pages2a - How To Grow RichV1.0Hemant KhoslaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportDinhkhanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Apple Global Supply Chain S2 Teknik IndustriDocument23 pagesApple Global Supply Chain S2 Teknik IndustriRuth Dame Pricilia0% (1)
- The Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsFrom EverandThe Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Power of Public Investment Management: Transforming Resources Into Assets for GrowthFrom EverandThe Power of Public Investment Management: Transforming Resources Into Assets for GrowthNo ratings yet
- Nov 2020 - Econ Tute2Document9 pagesNov 2020 - Econ Tute2Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- BA3 M KIT Chapter 10Document4 pagesBA3 M KIT Chapter 10Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Flash CardsDocument16 pagesFlash CardsNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Tute 04 - Market System 1Document11 pagesTute 04 - Market System 1Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- BA1 - Micro Economics - Mind Map 2Document4 pagesBA1 - Micro Economics - Mind Map 2Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Problem QuestionDocument1 pageProblem QuestionNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Econ Tute 1Document11 pagesEcon Tute 1Nivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- 50 Question Bank With AnswersDocument10 pages50 Question Bank With AnswersNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Answers For BA1 Revision QuestionsDocument8 pagesAnswers For BA1 Revision QuestionsNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Negative ExternalitiesDocument5 pagesNegative ExternalitiesNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Law Test July 7thDocument2 pagesLaw Test July 7thNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- June 2017 Paper 1 - QPDocument20 pagesJune 2017 Paper 1 - QPNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Law Reform Model AnswersDocument2 pagesLaw Reform Model AnswersNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Misrepresentation Sample QuestionDocument1 pageMisrepresentation Sample QuestionNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- Law Test June 9thDocument2 pagesLaw Test June 9thNivneth PeirisNo ratings yet
- International Business: by Charles W.L. HillDocument37 pagesInternational Business: by Charles W.L. Hilllongtran1191No ratings yet
- The Analysis of IpodDocument19 pagesThe Analysis of IpodRachel WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- A Commentary On The KulbhushanDocument53 pagesA Commentary On The KulbhushanVinayak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Apollo Operations Handbook Block II Spaceraft Vol 1 Part 2Document475 pagesApollo Operations Handbook Block II Spaceraft Vol 1 Part 2Bob Andrepont100% (2)
- p2c2 ProgressmeasurementDocument19 pagesp2c2 ProgressmeasurementicetesterNo ratings yet
- Disposable HME Filter (Child) - VADI MEDICAL-800-51300Document2 pagesDisposable HME Filter (Child) - VADI MEDICAL-800-51300Spectrum IngenierosNo ratings yet
- Virginia Theological Seminary Journal, Fall 2011Document55 pagesVirginia Theological Seminary Journal, Fall 2011Susan L. ShillinglawNo ratings yet
- WWW Interfarfacing ComDocument13 pagesWWW Interfarfacing ComspiraldaoNo ratings yet
- Project-Orpheus A Research Study Into 360 Cinematic VRDocument6 pagesProject-Orpheus A Research Study Into 360 Cinematic VRjuan acuñaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Samar State University College of EducationDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Samar State University College of EducationJulius Lucas SabanyaoNo ratings yet
- Allegheny 316 PDFDocument13 pagesAllegheny 316 PDFJoshua WalkerNo ratings yet
- LacusCurtius - Strabo's Geography - Book III Chapter 3Document10 pagesLacusCurtius - Strabo's Geography - Book III Chapter 3A Miguel Simão LealNo ratings yet
- Uruguay The Owners Manual 5th EdDocument240 pagesUruguay The Owners Manual 5th EdlinkgineerNo ratings yet
- Wheter Chamber Summons Is A PleadingDocument3 pagesWheter Chamber Summons Is A Pleadingmoses machiraNo ratings yet
- Lab2 - Stereotaxic SurgeryDocument4 pagesLab2 - Stereotaxic SurgeryMichael Anthony BritoNo ratings yet
- SOP For Fenil - Bachelor's Degree in Science (Biology)Document2 pagesSOP For Fenil - Bachelor's Degree in Science (Biology)Ahmed100% (1)
- Epson R200, R210 Visão ExplodidaDocument8 pagesEpson R200, R210 Visão ExplodidaKedinaldoNo ratings yet
- Application of Consumer BehaviorDocument6 pagesApplication of Consumer BehaviorNoella Marie BaronNo ratings yet
- (New) Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Rubberized Coir Fibre SheetsDocument8 pages(New) Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Rubberized Coir Fibre SheetsPrakumarNo ratings yet
- Trimble 2 Rin ExDocument1 pageTrimble 2 Rin ExIvan.sidabutarNo ratings yet
- Artikel Ilmiah Sosialisasi English Ver KKN UNAIRDocument9 pagesArtikel Ilmiah Sosialisasi English Ver KKN UNAIRJasmine Octavia Putri BalawNo ratings yet
- sr1 Cup Infopack 2016Document8 pagessr1 Cup Infopack 2016Stef PoienaruNo ratings yet
- Resume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 5&6 - Dani Yustiardi 1906419822Document8 pagesResume Frank Rothaermel - Strategic Management Chapter 5&6 - Dani Yustiardi 1906419822Dani Yustiardi MunarsoNo ratings yet
- Target Amplification MethodsDocument3 pagesTarget Amplification MethodsNOR-FATIMAH BARATNo ratings yet
- RPV 3Document158 pagesRPV 3Melkamu AmusheNo ratings yet
- Simulated Binar Crossover F Continuous Search Space: Comp SystemsDocument34 pagesSimulated Binar Crossover F Continuous Search Space: Comp SystemsSal Ie EmNo ratings yet
- Account Opening FormDocument11 pagesAccount Opening FormTotimeh WisdomNo ratings yet
- Capturing Deadlocks in SQL Server - Brent Ozar Unlimited® by Brent Ozar Unlimited®Document7 pagesCapturing Deadlocks in SQL Server - Brent Ozar Unlimited® by Brent Ozar Unlimited®kishore2285No ratings yet
- VIRTUAL KEYBOARD PresentationDocument18 pagesVIRTUAL KEYBOARD PresentationRä BïNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2012 Information BrochureDocument53 pagesAIEEE 2012 Information Brochuresd11123No ratings yet