Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PEPOccupational 2019 Final
PEPOccupational 2019 Final
Uploaded by
MaleehaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PEPOccupational 2019 Final
PEPOccupational 2019 Final
Uploaded by
MaleehaCopyright:
Available Formats
Need help?
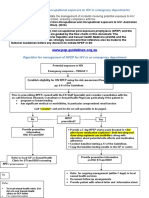
GUIDELINES FOR OCCUPATIONAL Contact the TOLL-FREE National HIV & TB Health Care Worker
Hotline at 0800 212 506 / 021 406 6782
POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS (PEP) Alternatively “whatsapp” or send an SMS or “Please Call Me”
to 071 840 1572
PEP should be initiated immediately. Don’t wait for TABLE 1: DOES THE HIV-EXPOSED NEED PEP? TABLE 3: TESTING
confirmatory results before initiating. Don’t delay initiation of Careful risk-benefit assessment needs to be done before initiating HIV PEP, as the antiretroviral drugs SOURCE HIV-EXPOSED
PEP if unsure about appropriate regimen as this can be can cause serious side-effects
PATIENT
modified after consultation with an expert HIV Status of source patient BASELINE BASELINE 2 WEEKS 6 WEEKS 3# MONTHS
Exposure Unknown or HIV Rapid test, Rapid test(s), if HIV HIV ELISA
Negative
Positive AND HIV negative confirm ELISA
Step 1: IMMEDIATE MANAGEMENT OF HEALTH CARE WORKER Intact skin to infectious or non-infectious materials no PEP no PEP ELISA with HIV ELISA
Hepatitis B Surface Surface antibody Surface
• Assess eligibility for HIV PEP (Table 1) Mucous membrane or non-intact skin exposure, including splash or no PEP 3-drug regimen antigen antigen
• Provide thorough, confidential, pre-test counselling before HIV testing contact with open wound, to blood or other infectious materials
Hepatitis C Antibody Antibody* PCR**
• Baseline HIV test in health care worker: Rapid test, if negative: initiate PEP, confirm with Percutaneous exposure (needle stick) to blood or other infectious no PEP 3-drug regimen
HIV antibody laboratory test (ELISA). materials Serum If TDF part of PEP If TDF part
If rapid positive, do confirmatory rapid. If confirmatory negative, initiate PEP and do creatinine of PEP
ELISA. If confirmatory positive, refer for initiation of ART INFECTIOUS MATERIAL FBC & diff If AZT part of PEP If AZT part
• Post-test counselling and results should be handled in strict confidence • Blood or any bloodstained fluids, tissue or other material of PEP
* Only if source patient is positive; ** Only if source antibody positive, and health care worker antibody
• If the health care worker refuses HIV testing, offer PEP but no compensation will be • Vaginal secretions or penile pre-ejaculate and semen negative #Primary Care 2018, National Department of Health recommends final HIV test at 4 months. HIV
granted if health care worker becomes HIV positive • Fluid from any body cavity such as pleural, pericardial, amniotic, peritoneal, synovial and Clinicians Society 2015 PEP Guidelines recommends 3 months
cerebrospinal fluids
Step 2: PEP • Breast milk TABLE 4: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS
Saliva, tears, vomitus, sweat and urine pose no risk of HIV, unless contaminated with infectious
• If PEP is indicated, it should ideally be initiated within one hour and not later than 72 materials e.g. blood
Vaccination status and Source patient
hours after the exposure. For higher risk exposures (injury is deep OR involves a hollow antibody response of
needle OR the source is more infectious e.g. terminal AIDS, seroconversion illness, or has healthcare worker HBsAg positive or unknown HBsAg negative
a high viral load) consider giving PEP up to 7 days after exposure TABLE 2: WHICH HIV PEP REGIMEN? • HBIG, IM, 500 units*
• Don’t wait for ELISA test results of the health care worker or source patient. If source Unvaccinated or vaccination Initiate HepB vaccination
Choose one option from each column:
incomplete • HepB vaccine (3 doses at (month 0, 1 and 6)
patient is found to be negative after ELISA test, then HIV PEP can be discontinued, unless
NRTI dual regimen PI-combination or INSTIs monthly intervals
source is showing signs of sero-conversion illness
• See Table 2 for HIV PEP regimens, and Table 4 for Hepatitis B PEP Atazanavir 300 mg PLUS ritonavir Vaccinated AND known to have
No treatment
No treatment
• Continue HIV PEP for 28 days Tenofovir 300 mg + emtricitabine 200 mg 100 mg daily HBsAb titre ≥ 10 units/mL#
• Starter packs are not recommended. Provide a full 28 day supply 1 tab daily • HBIG, IM, 500 units*
OR Vaccinated AND HBsAb ≤ 10
• HepB vaccine (3 doses at No treatment
Step 3: TESTING SOURCE PATIENT
• If possible, the source patient should be tested for Hepatitis B and C, and HIV (according
OR
Tenofovir 300 mg 1 tab daily PLUS
lamivudine 300 mg 1 tab daily
+ Aluvia® (lopinavir/ritonavir 200/50
mg) 2 tabs 12 hourly
units/mL OR unknown
monthly intervals)
*Refer to secondary level of care for HBIG, IM. HBIG should be given as soon as possible, prefera-
bly within 24-72 hours after exposure (or within 7 days); # If obtaining HBsAb titre is more than 24
to National Testing algorithm). See Table 3 OR
• If source is Hepatitis B surface antigen positive or unknown, refer to Table 4 for hepatitis hours, initiate treatment as for vaccinated with HBsAb ≤ 10 units/mL; Note: Repeat HBsAb 1-2
B post-exposure prophylaxis for the health care worker OR months after last vaccine dose to ensure adequate immune response (i.e. HBsAb > 10 units/mL)
Dolutegravir 50 mg daily
• Offer comprehensive and confidential pre-test counselling and ensure informed consent Lamivudine 150 mg + zidovudine 300 mg HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBsAb: Hepatitis B surface antibody; HBIG: Hepatitis B immunoglobulin
is given 1 tab 12 hourly OR
• If consent is refused there are 2 options: POSSIBLE SIDE-EFFECTS OF ANTIRETROVIRAL TREATMENT
HIV test can be offered anonymously; Raltegravir 400 mg 12 hourly Atazanavir/ritonavir Generally well tolerated. Jaundice with unconjugated
If there is an existing blood specimen, the HIV test can be done anonymously, after SPECIAL PRESCRIBER’S POINTS hyperbilirubinaemia occurs commonly, but is benign; hepatitis
informing the source patient. Anonymous testing means that the blood sample will not • Tenofovir is better tolerated than zidovudine Dolutegravir Usually well tolerated. Avoid during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy and in
be labelled with the source patient details, thus the result can’t be connected to the • Fixed-dose combinations preferred. (Dolutegravir + lamivudine + tenofovir now available) woman of childbearing age not on a contraceptive
source patient • Atazanavir + ritonavir is given once daily and usually better tolerated than Aluvia® Emtricitabine/ Generally well tolerated
• Stop PEP if the source patient’s HIV test is confirmed to be negative, unless patient is • Always check for drug-drug interactions. Atazanavir is contra-indicated with rifampicin and Lamivudine
showing signs of sero-converion illness. Discuss with virologist proton-pump inhibitors e.g. omeprazole, lansoprazole. Antacids should not be used with Lopinavir/ritonavir Diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, hepatitis
• If the source can’t be tested for HIV or refuses, the exposed should be treated as if the raltegravir Raltegravir Generally well tolerated. Nausea, fatigue, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
source is HIV positive • Dolutegravir should be avoided in woman of child-bearing age not on reliable Tenofovir Generally well tolerated. Nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, nephrotoxicity
contraception or during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy Zidovudine Nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, anaemia, neutropenia
• If source patients are on a third line regimen or salvage therapy or are failing second line,
Step 4: FOLLOW UP AND MONITORING other ARVs may need to be considered and consultation with an Infectious Disease
• Ongoing psychosocial support is required Specialist or the Hotline is recommended
SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS
• HIV tests should be repeated at 6 weeks and 3 or 4 months post exposure using a Note: Nevirapine and abacavir should be avoided in PEP Pregnancy: PEP is not contra-indicated in pregnancy. Avoid dolutegravir during the first 8 weeks of
laboratory antibody test (ELISA). Repeat hepatitis B surface antigen in health care NRTI: Nucleoside/tide-reverse transcriptase inhibitor; PI: Protease-inhibitor; INSTI: Integrase strand transfer inhibitor pregnancy or in woman of child-bearing age not on reliable contraception
worker at 3 months, if source was positive. See Table 3 Breastfeeding: Although some drugs are transmitted through the breastmilk, it is not considered
• Health care worker should be counselled to practice safe sex (use condoms) until a to be harmful to the breastfed child. If the health care worker is however infected with HIV, the
negative result on the HIV test at 3 or 4 months, is confirmed risk of transmitting HIV to the baby during this early stage of infection is high
• Side effects should be actively sought and managed Window period: PEP is not indicated if the source is HIV negative, unless acute
Compiled: January 2019 antiretroviral syndrome is suspected (symptoms include: fever, lymphadenopathy, sore throat,
ART: Antiretroviral treatment; PEP: Post-exposure prophylaxis; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; Based on: Standard Treatment Guidelines, Primary Level, 2018, National Department of Health, South Africa, and the
AIDS: acquired immune deficiency syndrome rash, myalgia, arthralgia, headache).
HIV Clinicians’ Society’s Guidelines on the management of occupational and non-occupational exposure to the hu-
man immunodeficiency virus and recommendations for post-exposure prophylaxis: 2015 Update.
You might also like
- Resting Membrane, Graded, Action Potentials AtfDocument4 pagesResting Membrane, Graded, Action Potentials AtfdaphneNo ratings yet
- What Would You DoDocument4 pagesWhat Would You DoNicolas GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Blood Bank Surveillance (Labs) Form 1: Epidemiology BureauDocument1 pageLaboratory and Blood Bank Surveillance (Labs) Form 1: Epidemiology BureauEvo SingsonNo ratings yet
- HIV Testing Labs FlowchartDocument1 pageHIV Testing Labs Flowcharthamody662002No ratings yet
- NPEP Procedure Flowchart TemplateDocument2 pagesNPEP Procedure Flowchart TemplatededekfridayNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Hepatitis B Blood TestsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Your Hepatitis B Blood TestsSam Sep A SixtyoneNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Hepatitis B Blood Tests Fact Sheet Updated January 2020Document2 pagesUnderstanding Your Hepatitis B Blood Tests Fact Sheet Updated January 2020taycolaramae07No ratings yet
- Protocol Needlestick InjuriesDocument1 pageProtocol Needlestick InjuriesMrLarry Dolor100% (1)
- En - Acc Exposure Blood Body Fluids - PosterDocument1 pageEn - Acc Exposure Blood Body Fluids - Posterdhira aninditaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis GeneralDocument14 pagesHepatitis GeneralMarysol UlloaNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument1 pagePDF DocumentellaNo ratings yet
- UTI Diagnostic Flowchart NICE-October 2020-FINALDocument78 pagesUTI Diagnostic Flowchart NICE-October 2020-FINALShaarikh PasandNo ratings yet
- Humanimmunodeficiency Virusinitialassessmentand Routinefollow-UpDocument16 pagesHumanimmunodeficiency Virusinitialassessmentand Routinefollow-UpBriando Stevano LinelejanNo ratings yet
- STEP 1 Could It Be HIV? STEP 2 Informed Consent and Testing STEP 3 Conveying Test ResultsDocument2 pagesSTEP 1 Could It Be HIV? STEP 2 Informed Consent and Testing STEP 3 Conveying Test ResultsahjkseflhasefNo ratings yet
- CDC LSHT STSH Brochure Pep InfographicsDocument2 pagesCDC LSHT STSH Brochure Pep Infographicskistephane5No ratings yet
- Routine HIV Screening in Health Care Settings: Background and DefinitionsDocument23 pagesRoutine HIV Screening in Health Care Settings: Background and Definitionsarya maulanaNo ratings yet
- Penny R. Thayer, FNP, BC Gastro/Hepatology NP James H. Quillen, VAMCDocument27 pagesPenny R. Thayer, FNP, BC Gastro/Hepatology NP James H. Quillen, VAMCPatresya LantanNo ratings yet
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) Recommendations - Stats - Medbullets Step 2 - 3Document5 pagesU.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) Recommendations - Stats - Medbullets Step 2 - 3mtataNo ratings yet
- Webinar Hepatitis IDI SdaDocument42 pagesWebinar Hepatitis IDI SdaUbed An'threeNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B SerologijaDocument3 pagesHepatitis B Serologijaxmen menxNo ratings yet
- Information For People We Support: How Do I Get Tested? Other Blood Borne Viruses (BBVS)Document2 pagesInformation For People We Support: How Do I Get Tested? Other Blood Borne Viruses (BBVS)Abhijeet GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- AlemayehuDocument8 pagesAlemayehuasriadiNo ratings yet
- Section 2-Session 4Document29 pagesSection 2-Session 4foleyNo ratings yet
- HIV Infection: Detection, Counseling, and ReferralDocument71 pagesHIV Infection: Detection, Counseling, and ReferralJohn Bocanegra NeriNo ratings yet
- Who Recommends Hiv Self-Testing: Reaching People With Undiagnosed HIVDocument2 pagesWho Recommends Hiv Self-Testing: Reaching People With Undiagnosed HIVtashoneNo ratings yet
- Annex 5-5Document20 pagesAnnex 5-5Dandi PremaNo ratings yet
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis For Hiv: CDC GuidelinesDocument26 pagesPost-Exposure Prophylaxis For Hiv: CDC GuidelinesnetradeepNo ratings yet
- Management 2Document16 pagesManagement 2Moin PandithNo ratings yet
- HepB Provider Tipsheet 508Document2 pagesHepB Provider Tipsheet 508Jamshaid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hiv Testing in The Era of Prep:: When The Tests Are DiscordantDocument17 pagesHiv Testing in The Era of Prep:: When The Tests Are DiscordantAldren GilanaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Vaccination PresDocument21 pagesHepatitis B Vaccination PresmaponlooNo ratings yet
- En Abbott Realtime Hiv-1: Customer Service International: Call Your Abbott RepresentativeDocument24 pagesEn Abbott Realtime Hiv-1: Customer Service International: Call Your Abbott RepresentativegdurouxNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument2 pagesHepatitismuhammad soffiudinNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding in Hiv Positive MothersDocument13 pagesBreastfeeding in Hiv Positive MothersBeverly MenendezNo ratings yet
- Anecca 10 Points Poster EnglishDocument1 pageAnecca 10 Points Poster EnglishDrake Wa YesuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Lydia Tandri, SP - PD: Treatment & Guideliness For Hepatitis B-C Virus in Practice ClinicDocument42 pagesDr. Lydia Tandri, SP - PD: Treatment & Guideliness For Hepatitis B-C Virus in Practice ClinicveraanaNo ratings yet
- Adverse Event Reporting PolicyDocument5 pagesAdverse Event Reporting Policycs nagarNo ratings yet
- LabCorpTestingProtocol6 08Document4 pagesLabCorpTestingProtocol6 08Olga CîrsteaNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS Vincent Parong Patrick TuralbaDocument10 pagesCASE ANALYSIS Vincent Parong Patrick TuralbaisaacdarylNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blood TestsDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Blood TestsAnonymous NUn6MESxNo ratings yet
- United States HIV Testing and Prophylaxis To Prevent Mother-to-Child Transmission in TheDocument10 pagesUnited States HIV Testing and Prophylaxis To Prevent Mother-to-Child Transmission in TheGerry ValdyNo ratings yet
- Blue Orange Creative Diabetes PresentationDocument8 pagesBlue Orange Creative Diabetes PresentationFernando MunaycoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guideline: HIV in PregnancyDocument18 pagesClinical Guideline: HIV in PregnancyM Iqbal EffendiNo ratings yet
- Management of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection (HIV)Document1 pageManagement of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection (HIV)zenagit123456No ratings yet
- Pre Employment Health AssessmentDocument7 pagesPre Employment Health AssessmentMP13No ratings yet
- Sharp Injury Surveillance CMEDocument47 pagesSharp Injury Surveillance CMENOR HASSIDANo ratings yet
- Understanding Blood Tests PDFDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Blood Tests PDFKishor SinghNo ratings yet
- Heatlh Care ProfessionalDocument2 pagesHeatlh Care ProfessionalawangbokNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B in PregnancyDocument12 pagesHepatitis B in PregnancyTasya Felicia MacellinNo ratings yet
- Multisystem & Genetic - BoardsDocument10 pagesMultisystem & Genetic - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Parent To Child Transmission of HIV : Dr. ShobhaDocument52 pagesPrevention of Parent To Child Transmission of HIV : Dr. ShobhajijaniNo ratings yet
- CDC Hiv Pep101Document2 pagesCDC Hiv Pep101Sangeetha HospitalNo ratings yet
- Needle: Stick Injury (NSI)Document5 pagesNeedle: Stick Injury (NSI)dr rajoreNo ratings yet
- Chronic He PB Testing FL W UpDocument2 pagesChronic He PB Testing FL W UpSumit MitraNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B PDFDocument15 pagesHepatitis B PDFAvicenna_MSCNo ratings yet
- AFAO HIV in Australia 2022Document2 pagesAFAO HIV in Australia 2022Yingying LiNo ratings yet
- DOH 2021 Interim Guidelines PrEPDocument6 pagesDOH 2021 Interim Guidelines PrEPithran khoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viral - Dr. José Gonzáles BenavidesDocument64 pagesHepatitis Viral - Dr. José Gonzáles BenavidesEfrain Brian SilvaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B (HepB Vaccine)Document6 pagesHepatitis B (HepB Vaccine)Desiree EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy C Obs 50Document17 pagesManagement of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy C Obs 50EndaleNo ratings yet
- MT 6322 - Mycology and Virology 2nd Shifting OLADocument9 pagesMT 6322 - Mycology and Virology 2nd Shifting OLAlily bluesNo ratings yet
- Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) For HIV Prevention: A Beginners Guide to PrEP for HIV Prevention.From EverandPre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) For HIV Prevention: A Beginners Guide to PrEP for HIV Prevention.No ratings yet
- ECG Notes - Eng - Doubell 2016Document57 pagesECG Notes - Eng - Doubell 2016MaleehaNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetic AgentsDocument43 pagesLocal Anaesthetic AgentsMaleehaNo ratings yet
- Andre Tans Surgery Notes Compiled-1Document117 pagesAndre Tans Surgery Notes Compiled-1MaleehaNo ratings yet
- 8.health Professional Act (See Only)Document65 pages8.health Professional Act (See Only)MaleehaNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument134 pagesRenalMaleehaNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument4 pagesRenalMaleehaNo ratings yet
- KERRIER Kit Mixing Instructions Rev 1 3Document3 pagesKERRIER Kit Mixing Instructions Rev 1 3jpsbhandalNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Research Secondary HypertensionDocument51 pagesResearch Secondary HypertensionDomeng TalksNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Angina Pectoris-2Document19 pagesTreatment of Angina Pectoris-2Habib UllahNo ratings yet
- Becozyme AmpDocument1 pageBecozyme AmpMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Poster Template - SYMPOSIUM 2023 (1) 2Document1 pagePoster Template - SYMPOSIUM 2023 (1) 2Ana PopoviciNo ratings yet
- SPC - Vpa22664-150-001Document5 pagesSPC - Vpa22664-150-001hallaqyara8No ratings yet
- Zantac (Ranitidine) - Safety Information - NDMA Found in Samples of Some Ranitidine Medicines - FDADocument2 pagesZantac (Ranitidine) - Safety Information - NDMA Found in Samples of Some Ranitidine Medicines - FDACuam CaracasNo ratings yet
- Geriatric PsychiatryDocument91 pagesGeriatric PsychiatryVipindeep SandhuNo ratings yet
- Ampi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THDocument1 pageAmpi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THAnnieNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument40 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsjawadNo ratings yet
- LT208 RIQAS EQA Programmes SEP20Document8 pagesLT208 RIQAS EQA Programmes SEP20PannaMkNo ratings yet
- Can Ethnopharmacology Contribute To The Dev of Antiviral Drug - Vlietinck1991Document13 pagesCan Ethnopharmacology Contribute To The Dev of Antiviral Drug - Vlietinck1991Tyasmeita14No ratings yet
- Review Article: DPP-4 Inhibitors As Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument11 pagesReview Article: DPP-4 Inhibitors As Treatments For Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisGREESTYNo ratings yet
- Endorsement SheetDocument2 pagesEndorsement SheetGabilou Danao BunuanNo ratings yet
- indica) as α-glucosidase inhibitor and: Endosperm of Indramayu mango (Mangifera antioxidantDocument7 pagesindica) as α-glucosidase inhibitor and: Endosperm of Indramayu mango (Mangifera antioxidantAdriani HasyimNo ratings yet
- Vinayaka College of Nursing Nadiad: Time Table 2 Year B.SC NursingDocument1 pageVinayaka College of Nursing Nadiad: Time Table 2 Year B.SC NursingSiddhiNo ratings yet
- Pone 0214727Document14 pagesPone 0214727Inanda DamantiaNo ratings yet
- KRONE Products We Manufacturer - Updated List NewDocument11 pagesKRONE Products We Manufacturer - Updated List Newneeraj kumar100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Calculations Course OutlineDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical Calculations Course OutlineAmiir KooNo ratings yet
- Toxicology: DR Frank Kakuba G MD, Mmed Path (Mak)Document24 pagesToxicology: DR Frank Kakuba G MD, Mmed Path (Mak)Mwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- AtracuriumDocument1 pageAtracuriumMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Price List - Ist Sept.2015 PDFDocument2 pagesPrice List - Ist Sept.2015 PDFMohammed shamiul ShahidNo ratings yet
- ITP Review ArticleDocument12 pagesITP Review ArticleMuhammad FauzanNo ratings yet
- BioanalyticalMethodDevelopment PDFDocument10 pagesBioanalyticalMethodDevelopment PDFvikram kushwahaNo ratings yet
- S. B. No. 2573: Second Regular SessionDocument13 pagesS. B. No. 2573: Second Regular SessionmkoguicoNo ratings yet
- Acne DissertationDocument6 pagesAcne DissertationPaySomeoneToDoMyPaperUK100% (1)
- First Aid Management of HemorrhageDocument68 pagesFirst Aid Management of HemorrhageAbdulaziz AlharbiNo ratings yet