Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Day Diet Analysis
3 Day Diet Analysis
Uploaded by
api-734755901Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Day Diet Analysis
3 Day Diet Analysis
Uploaded by
api-734755901Copyright:
Available Formats
3 Day Diet Analysis
Bri Rehborg
College of Science, Engineering, and Technology, Grand Canyon University
BIO-319: Applied Nutrition
Dr. Havenar
11/13/2022
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
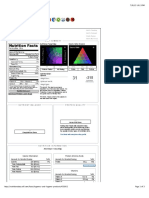
A. Energy & Macronutrient Intake
Using the Intake vs. Goals section of your PDF, compare your total calories, and grams of
protein, carbohydrates, and fats to the DRI.
Improvement
ideas if needed
DRI My intake Met/High/Low
Kilocalories 2575 2608.557 Met/ slightly high Met
High to general rec This is based
on .8g/kg body
Met/ slightly high weight. Since I
to athlete rec am an athlete, I
would but it at
1.2 which would
63(g) put me at a
recommended
Athlete rec: 95.45 g of
Protein 95.45 106.581 protein/day
289.69- Met Within range
Carbohydrates 418.44 (g) 302.476g
High Reduce fat intake
by less process
foods and
57.22- healthier ways to
Fat - Total 100.14(g) 116.774 cook with foods.
B. AMDR
Using the "Macronutrient Ranges" section of your PDF, list your percent of total calories intake
from each and compare against % AMDR.
Improvement
My % AMDR ideas if needed
Distribution Recommendations Met/High/Low
Protein 16.343% 10-35% met met
Carbohydrates 46.382% 45-65% met met
Fat - Total 40.289 20-35% high Slightly lower fat
intake. See what
made my fat
intake higher and
find better
options to replace
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
that with more
carbs and
proteins
Fiber Recommendation My Intake Met/Unmet?
151.2 25.0 g 37.82 g met
% of
DRI
If you did not meet the recommended amount of fiber, what are three foods that you would
be willing to eat regularly that contain 3 or more grams of fiber per serving?
Food Serving Size Amount of Fiber (g/serving) Reference
MET - - -
MET - - -
MET - - -
Fat Intake
Using the "fat breakdown" section of your PDF, list your percent of total calories from each fat
and compare against the American Heart Association % recommendations. Briefly list ideas for
improvement.
AHA % If out of range, what foods
My Source of Recommendations should be reduced or
Fat (% of total increased
calories) (% of total calories)
Saturated Fat 11.719% <7% Peanut butter
Monounsaturated Met
Fat 13.857% 10-15%
Polyunsaturated Met
Fat 6.445% 7-10%
Trans Fat 0.167% <1% Sugary processed foods
Essential Fatty Acid Intake Recommendations for
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
Improvement
Omega-3 17.413g Met-- 145.1 %
Omega-6 0.876g Low-- 79.66%
Add chia and help to
my oatmeal in the
morning
C. Vitamin and Mineral Intake- This section of the analysis is to be an assessment of your
dietary intake of vitamins and minerals. Be sure you have not included any vitamin or
mineral supplements that you take in your computer analysis. (Use the "Intake vs. Goals" bar
graph section of your PDF for information).
Fill in the following table to compare your average daily intake to the recommendations. Indicate
whether your average intake was less than 70% of the DRI (-), more than 200% of the DRI (+),
or close to (=) the DRI (70–200%). No hard and fast guideline for the range of acceptable
intakes exists. Instead, what is considered too high or too low varies from nutrient to nutrient.
The range of 70–200% does, however, assure intakes above minimum requirements and below
upper tolerable limits. For those nutrients below 70% of the DRI describe the deficiency
concerns. For those >200% DRI give the UL and list the toxicity concerns.
Align the order of this table to the order of nutrients in your Diet & Wellness Plus PDF
Vitamin Average %RDA --,+,= UL Deficiency or Toxicity concern
intake
(units) RDA
(units)
1. Thiamin .93mg 1.10 84.5% =
2. Riboflavin 1.10mg 1.151 164.9% =
3. Niacin 14.00mg 23.086 112.3% =
4. Vitamin 1.30mg 1.46 97.58% =
B6
5. Vitamin 2.4 mcg 2.342 45.82% - Deficiency
B12
6. Folate 400 mcg 183.318 119.5% =
7. Vitamin C 75mg 89.669 2.47% - Deficiency
8. Vitamin D 15mcg .37 16.65% - Deficiency
9. Vitamin A 2333 IU 1072.196 45.95% - Deficiency
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
10. Vitamin K 90mcg 24.357 27.06% - Deficiency
11. Vitamin E 15.00 16.685 11.2% - Deficiency
In your own words, provide a brief (1–2 sentences) explanation of each deficiency or
toxicity listed in the table. Please include your citations for where you found the
information.
Deficiency 1: Vitamin B12
o A deficiency in B12 can cause pernicious anemia which is characterized by
abnormally large RBCs. Symptoms can include Anemia (macrocytic); fatigue,
degeneration of peripheral nerves progressing to paralysis; sore tongue, loss of
appetite, constipation.
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 10
Deficiency 2: Vitamin C
o Notable signs and symptoms include pinpoint hemorrhages; joint pain; poor
wound healing, inflamed and bleeding gum.
o Scurvy is a risk of low vitamin c as well.
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 10
Deficiency 3: Vitamin D
o Deficiency in children could be rickets results in soft and weak bones while, in
adult can be osteomalacia results in soft bones; osteoporosis results in porous and
brittle bones
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 11
Deficiency 4: Vitamin A
o Symptoms of vitamin A deficiency includes night blindness, corneal drying
(xerosis), softening of the cornea (keratomalacia), and corneal degeneration and
blindness (xerophthalmia); impaired immunity (infectious diseases); plugging of
hair follicles with keratin (hyperkeratosis).
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 11
Deficiency 5: Vitamin K
o Symptoms of vitamin k deficiency is hemorrhaging and the inability to absorb fat.
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 11
Deficiency 6: Vitamin E
o Symptoms of a vitamin e deficiency are Erythrocyte hemolysis and nerve damage.
This is an antioxidant so there is not as much to balance free radicals.
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 11
Toxicity- I was not over 200% on any vitamins
List foods and beverages that you currently eat or could consume more often that are good
sources of the vitamins that fell below 70% of the RDA (do not list foods that you would not
eat). List at least 5 foods or beverages per vitamin.
Vitamin: Healthy food sources (serving size) Reputable Source
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
Vitamin B12 Eggs, fish, poultry, shellfish, milk, cheese- 8oz Textbook ch10
Vitamin C Potatoes, tomatoes, brussels sprouts, cauliflower, Textbook ch 10
broccoli, spinach- 1 cup
Vitamin D Fortified milk, liver, salmon, herring- 1 cup Textbook ch 11
Vitamin A Milk, fish, liver, broccoli, spinach - 1 cup Textbook ch11
Vitamin K Spinach, Kale, green pepper, cucumber- 1 cup, olive Textbook ch11
oil-1-2 Tbs
Vitamin E Olive oil, avocado oil- 1-2 Tbs, peanuts, sunflower Textbook ch 11
seeds, almonds- ½ cups
Align the order of this table to the order of nutrients in your Diet & Wellness Plus PDF.
Mineral Average RDA/AI % --, UL Deficiency or Toxicity
intake +,= concern
(mg) (include RDA
units)
1. Calcium 553.985 1000mg 55.39% - Deficiency
2. Iron 18.521 18mg 102.89 =
%
3. Magnesium 502.245 310mg 162.01 =
%
4. Potassium 2198.343 2600mg 84.55% =
5. Zinc 12.506 8 mg 156.32 =
6. Sodium 1559.494 1500mg 103.96 =
In your own words, provide a brief (one or two sentences) explanation of each deficiency or
toxicity concern listed in the table.
Deficiency 1: Calcium
o A deficiency in calcium can show symptoms such as stunted growth in children;
bone loss (osteoporosis) in adults.
(Whitney & Rolfes 2020) ch 12
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
List foods and beverages that you currently eat or could consume more often that are good
sources of the minerals that fell below 70% the RDA (do not list foods that you would not eat).
List at least five foods or beverages per mineral.
Mineral Healthy food sources (serving size) Reputable Source
Calcium Milk/ milk products, spinach, broccoli, kale, Textbook ch 12
cheese- 1 cup
D. Balance and Variety. Compare your intake from each group with the recommendations
found in your textbook and comment on what you might do to improve your balance or
variety. You can also use recommendation information from the choosemyplate.gov web
sites. Use the MyPlate Analysis section of your PDF.
Goal Intake Met/ Improvement ideas
High/
Low
low Increase whole grains by
Bread, Cereal, Rice, & Pasta choosing more of a whole grain
Group 9.0 oz 6.176 oz oatmeal
low Add vegetables to each meal and
Vegetable Group 3.5 cups .5 cups spinach to smoothies
Fruit Group 2.0 cups 1.8 cups met --
Meat, Poultry, Fish, Dry Beans 6.5 oz 6.083 oz met --
low More hard cheese with a snack.
Milk, Yogurt, & Cheese Group 3.0 cup .583 cups Glass of chocolate milk
high Reduce empty sugars by
replacing with substitutes like
Empty Calories 362 561.111 grains
F. Eating Behaviors: It’s not just what you eat but where, why, with whom and how that counts
too. Look over your 3-day eating behavior diary and comment on what behaviors surprised you
or what you noticed that you may try to modify now that you are more aware. Discuss at least
three things that were most revealing to you.
1. Something that was reveling to me was that I eat a lot of the same things and there is a
lot of peanut butter in my diet. I may try to modify that now and be more aware of my
intake, as it is a good source of nutrients too much will increase my fat intake.
2. I noticed that often when I would be craving something sweet sch as chocolate, my
emotion tied with that was stressed or sad or both. This is something to be aware of
because it is okay to eat some sweet but not let it be a coping mechanism for feeling
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
3. I noticed that often when I would be pretty hungry, I would be more stressed and sad.
Food effects my emotions a lot and I would like to be more aware so I can avoid of
waiting until I get to that point.
G. SMART Goals. Hopefully this assignment provided some insight into your dietary practices
and nutrient intake. List at least five different SMART goals to improve your health as it relates
to the information gleaned from this assignment (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic,
Timely). Follow with a brief explanation of why this is a good goal.
1. I will work on decreasing my fat intake in the next month by being aware of my amount of
process foods I am intaking and decreasing the amount of peanut butter I eat.
a. This is a good goal because fat intake was my only daily macro percent that was
too high
2. I will increase my omega 6 in the next 2 weeks by buying a mix of chia, hemp and flax
seeds and adding it to my oatmeal
a. This will increase my omegas as my omega 6 was too low.
3. I will increase my vitamin C intake within the next week by adding spinach to my
smoothies and including potatoes into my dinner.
a. This is a good goal because my vitamin c intake was very low, and I need to
increase it. These foods are both high in vitamin c.
4. I will increase my vitamin E intake in the next week by using olive oil to cook and eating
more nuts and seeds in my snacks.
a. This is a good goal because my vitamin E intake was low, and these foods are
high in vitamin E so its important to incorporate them in my day-to-day diet.
5. I will increase my calcium intake in the next month by adding spinach to my smoothies
and adding more dairy to my diet such as cholate milk after swimming and hard cheese as a
snack.
a. This is a good goal because my calcium intake was very low, and it is important I
raise that for bone health.
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
References
Whitney, E. & Rolfes, S.R. (2020 ) Understanding Nutrition: The Water-Soluble Vitamins: B Vitamins
and C Vitamins, Chapter 10 (16th ed.). Cengage Learning
Whitney, E. & Rolfes, S.R. (2020 ) Understanding Nutrition: The Fat-Soluble Vitamins: A, D, E, and
K, Chapter 11 (16th ed.). Cengage Learning
Whitney, E. & Rolfes, S.R. (2020 ) Understanding Nutrition: The Major Minerals, Chapter 12 (16th
ed.). Cengage Learning
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
© 2024. Grand Canyon University. All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- BMR Calc and Renaissance DietDocument10 pagesBMR Calc and Renaissance DietShali LiuNo ratings yet
- Diet Wellness PlusDocument10 pagesDiet Wellness Plusapi-283335037100% (1)
- Final CBLM On Bread and Pastry ProductionDocument67 pagesFinal CBLM On Bread and Pastry ProductionFlorinda94% (16)
- Patient Education Guide: CHI Health Immanuel Bariatric Surgery ProgramDocument84 pagesPatient Education Guide: CHI Health Immanuel Bariatric Surgery ProgramAndrea SándezNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 22 Year Old, 85 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 22 Year Old, 85 KG FemaleAgista AnnisaNo ratings yet
- BIO-319 3 Day Diet Analysis WorksheetDocument12 pagesBIO-319 3 Day Diet Analysis WorksheetArooba ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Frank HasnootDocument59 pagesFrank Hasnootgabriel torres100% (4)
- Calculate Your Macros: Carb Cycle PlanDocument11 pagesCalculate Your Macros: Carb Cycle PlanLaura Chiraş100% (2)
- Eric Helms Nutrition CalculatorDocument20 pagesEric Helms Nutrition CalculatorSmyle KatariaNo ratings yet
- Bio 319 Rs 3day Diet Analysis WK SheetDocument11 pagesBio 319 Rs 3day Diet Analysis WK Sheetreagan omondiNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 18 Year Old, 50 KG MaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 18 Year Old, 50 KG Malebabble-silvers.03No ratings yet
- Energy Balance Report Part 1Document10 pagesEnergy Balance Report Part 1jennifer_crummNo ratings yet
- NV Carob PowderDocument3 pagesNV Carob PowdertavibastiNo ratings yet
- Table 3 BPKDocument10 pagesTable 3 BPKalafiaNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 26 Year Old, 73 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 26 Year Old, 73 KG FemaleseruniallisaaslimNo ratings yet
- Baseline Low Calorie Diet Plan With CalculationsDocument8 pagesBaseline Low Calorie Diet Plan With CalculationsChilNo ratings yet
- Dieta de Um Dia CrudivoraDocument4 pagesDieta de Um Dia CrudivoraDênis CechinelNo ratings yet
- Table 3 BPKDocument10 pagesTable 3 BPKalafiaNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 19 Year Old, 59 KG FemaleDocument7 pagesCalories Needed For A 19 Year Old, 59 KG FemaleMutiarahmawati MootaluNo ratings yet
- Pulse Report 20230128080859Document1 pagePulse Report 20230128080859ANKIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- TDEEDocument3 pagesTDEEEl Mehdi AchibaneNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 21 Year Old, 65 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 21 Year Old, 65 KG FemaleLybiel Kiara RachelNo ratings yet
- Carb Cycling Calculator - Always On NutritionDocument15 pagesCarb Cycling Calculator - Always On NutritionMaria Catarina SousaNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 19 Year Old, 81 KG MaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 19 Year Old, 81 KG MaleDoaa DodeyNo ratings yet
- Ankit M: WeightDocument1 pageAnkit M: WeightANKIT AGARWALNo ratings yet
- PBT2 Nutrition PDFDocument6 pagesPBT2 Nutrition PDFgomitadelimonNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 28 Year Old, 79 KG MaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 28 Year Old, 79 KG MaleKağan KeskioğluNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance Report Part 1Document9 pagesEnergy Balance Report Part 1nishikparikhNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 17 Year Old, 70 KG MaleDocument7 pagesCalories Needed For A 17 Year Old, 70 KG Maleboom boomNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 19 Year Old, 40 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 19 Year Old, 40 KG FemaleJohn JAROENBOWORNKITNo ratings yet
- The Hat TrickDocument1 pageThe Hat Trickcceyhun010No ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 18 Year Old, 60 KG MaleDocument7 pagesCalories Needed For A 18 Year Old, 60 KG Maleboom boomNo ratings yet
- Calorie Calculator: Weight MaintenanceDocument41 pagesCalorie Calculator: Weight MaintenanceMarc David100% (3)
- Low Carb Quickstart GuideDocument21 pagesLow Carb Quickstart Guidemiles ushaw100% (1)
- Diet AnalysisDocument12 pagesDiet AnalysishusnaNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 51 Year Old, 71 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 51 Year Old, 71 KG FemaleitucandemirNo ratings yet
- DepEd Order No. 13 S. 2017Document84 pagesDepEd Order No. 13 S. 2017Jeza Lyn GibagaNo ratings yet
- Carbs in Traditional Cornish Clotted Cream - Carb ManagerDocument6 pagesCarbs in Traditional Cornish Clotted Cream - Carb ManagerDivyang BhaiNo ratings yet
- KetoDiet-Buddy CalculatorDocument12 pagesKetoDiet-Buddy CalculatorsimasNo ratings yet
- Harris Benedict Equation With Macronutrients $283 Formulas$29Document5 pagesHarris Benedict Equation With Macronutrients $283 Formulas$29neo_chemistNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol-And-Diabetes 1-Part-2Document2 pagesCholesterol-And-Diabetes 1-Part-2Deb FitzsimmonsNo ratings yet
- TDEE Calculator - ChallengeDocument7 pagesTDEE Calculator - Challenge2gasx23No ratings yet
- Leangains - Lean Bulk Calculator - Calculate Your Calories & Macros - MusclehackingDocument12 pagesLeangains - Lean Bulk Calculator - Calculate Your Calories & Macros - MusclehackingChingpheng PhounNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 29 Year Old, 52 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 29 Year Old, 52 KG FemaleIstiqomah Nurul FauziahNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 16 Year Old, 66 KG FemaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 16 Year Old, 66 KG FemaleViktoria SaerangNo ratings yet
- Emagrecimento - CICLO 1 2022Document12 pagesEmagrecimento - CICLO 1 2022Gracianny MartinsNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Facts HandoutDocument2 pagesNutrition Facts Handoutapi-595854308No ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 18 Year Old, 165 LB MaleDocument1 pageCalories Needed For A 18 Year Old, 165 LB MalevictorzhangNo ratings yet
- 1200 Calorie - Meals in Minutes Summary For Marin A: Nutritional Breakdown For Meal PlanDocument42 pages1200 Calorie - Meals in Minutes Summary For Marin A: Nutritional Breakdown For Meal PlanroxxyiNo ratings yet
- Macro CalculatorDocument1 pageMacro CalculatorrutNo ratings yet
- HighschoolDocument4 pagesHighschoolapi-349873323No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate CalculatorDocument1 pageCarbohydrate CalculatorJoul BitarNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Your Leangains Macros and MicrosaDocument15 pagesHow To Calculate Your Leangains Macros and MicrosaAlanBrettNo ratings yet
- Calories Needed For A 35 Year Old, 64 KG MaleDocument3 pagesCalories Needed For A 35 Year Old, 64 KG MaleOussama HayekNo ratings yet
- My Carbohydrate GuideDocument15 pagesMy Carbohydrate GuideFilip KesteliNo ratings yet
- Calculating TDEE and Macros For ClientsDocument8 pagesCalculating TDEE and Macros For ClientsKelo garciaNo ratings yet
- Dietetic Analysis ProjectDocument8 pagesDietetic Analysis Projectapi-613208195No ratings yet
- Diet Analysis Project Rubric PDFDocument4 pagesDiet Analysis Project Rubric PDFSkammertNo ratings yet
- Level 0: Initial Inputs: Body Weight (In LBS) : Maintenance CaloriesDocument16 pagesLevel 0: Initial Inputs: Body Weight (In LBS) : Maintenance Calorieslucas AyalaNo ratings yet
- Carb Cycling for Weight Loss: A Beginner's 3-Week Guide with Sample Curated RecipesFrom EverandCarb Cycling for Weight Loss: A Beginner's 3-Week Guide with Sample Curated RecipesNo ratings yet
- Ketogenic Diet: Types of keto Diet and Precautions While You Lose WeightFrom EverandKetogenic Diet: Types of keto Diet and Precautions While You Lose WeightNo ratings yet
- Carb Cycling for Weight Loss: A Beginner’s 3-Week Guide with Sample Curated RecipesFrom EverandCarb Cycling for Weight Loss: A Beginner’s 3-Week Guide with Sample Curated RecipesNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Research PaperDocument7 pagesExercise Physiology Research Paperapi-734755901No ratings yet
- The Effects of Resistance Training On Females With AdhdDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Resistance Training On Females With Adhdapi-734755901No ratings yet
- Benchmark - Comprehensive Program DesignDocument15 pagesBenchmark - Comprehensive Program Designapi-734755901No ratings yet
- Bri Rehborg: Grand Canyon State University, Phoenix, ArizonaDocument2 pagesBri Rehborg: Grand Canyon State University, Phoenix, Arizonaapi-734755901No ratings yet
- Tingly Cook BookDocument26 pagesTingly Cook BookNoel BurgeNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional Exercise 4 Key PDFDocument7 pagesZero Conditional Exercise 4 Key PDFeliana avila jofreNo ratings yet
- Functional Properties of StarchesDocument14 pagesFunctional Properties of StarchesHappie DilaoNo ratings yet
- How Matter Changes When Applied With Heat - FINAL07182020Document19 pagesHow Matter Changes When Applied With Heat - FINAL07182020TEAM KnightzNo ratings yet
- Food Truck DesignDocument4 pagesFood Truck DesignRaja A. AlnasrullahNo ratings yet
- 07 Seatwork 1Document2 pages07 Seatwork 1Roel John NatinggaNo ratings yet
- Maxilact Presentation - LG Versus LGi - January 2015Document12 pagesMaxilact Presentation - LG Versus LGi - January 2015Best Dairy CENZYMENo ratings yet
- Exercises: ExampleDocument2 pagesExercises: ExampleKen LeungNo ratings yet
- Elc Critic AnalysisDocument3 pagesElc Critic AnalysisAdybah Zahary100% (1)
- The Book of Donuts The Most Delicious FL - Allie Allen-2Document83 pagesThe Book of Donuts The Most Delicious FL - Allie Allen-2Johari Dagideban100% (1)
- I. Choose One Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced DifferentlyDocument27 pagesI. Choose One Word Whose Underlined Part Is Pronounced DifferentlyDiệu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Developed Thresher Cylinder On Millet CropDocument6 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Developed Thresher Cylinder On Millet CropShankar AcharNo ratings yet
- Scottish Folk MedicineDocument6 pagesScottish Folk MedicineFeNo ratings yet
- Soups: Les PotagesDocument9 pagesSoups: Les PotagesSamiranMannaNo ratings yet
- New Format Weekly Report No.29Document17 pagesNew Format Weekly Report No.29Jayson Temblor QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Food FinalDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Food FinalssalcedoNo ratings yet
- TEST 020 5đề Tuyen SinhDocument7 pagesTEST 020 5đề Tuyen SinhjasminetranNo ratings yet
- Ginger (Zingiber Officinale), Herbaceous Perennial Plant of The Family ZingiberaceaeDocument6 pagesGinger (Zingiber Officinale), Herbaceous Perennial Plant of The Family ZingiberaceaeJulia LeronNo ratings yet
- Great Sausage Recipes and Meat CuringDocument608 pagesGreat Sausage Recipes and Meat Curinglizavolkova7No ratings yet
- Skillympics Score Sheet 2018Document15 pagesSkillympics Score Sheet 2018NathanNo ratings yet
- Estimasi Tangkapan Per Unit Upaya Baku Dan ProporsDocument13 pagesEstimasi Tangkapan Per Unit Upaya Baku Dan ProporsYudiNo ratings yet
- Serna-Saldivar2004 - Foods From MaizeDocument12 pagesSerna-Saldivar2004 - Foods From MaizeKatacska18No ratings yet
- TheSeafoodCompany Product+ListDocument33 pagesTheSeafoodCompany Product+ListJamil RozaqNo ratings yet
- Physicalandchemicalchanges HWKDocument3 pagesPhysicalandchemicalchanges HWKapi-315562012No ratings yet
- Summer Detox Waters OutlinedDocument11 pagesSummer Detox Waters OutlinedAMD AndreeaNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 9 DLL Third QUARTERDocument24 pagesCOOKERY 9 DLL Third QUARTERJAYSON MALATENo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide: 2-Basket Air FryerDocument17 pagesQuick Start Guide: 2-Basket Air FryerDanielNo ratings yet