Professional Documents
Culture Documents
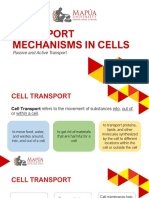
2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORT
2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORT
Uploaded by
jmd5qbmt4kCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Edited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportDocument2 pagesEdited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportTalha 1075% (4)
- Protein Structure WorksheetDocument7 pagesProtein Structure WorksheetkarendbrooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument12 pagesGen BioJohn Paul ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- Transport MembraneDocument2 pagesTransport Membranesna240839No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesCell Membrane ReviewerJohn Rey Magno SabalNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument8 pagesBiologyClare Anne Therese EsbietoNo ratings yet
- GENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument22 pagesGENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsJiro SamontañezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - Plant Physiology and Transport ProcessesDocument26 pagesMODULE 5 - Plant Physiology and Transport ProcessesNicoleBenaguaNo ratings yet
- From The Soil by The Root CellsDocument13 pagesFrom The Soil by The Root CellsChristina RañaNo ratings yet
- TISSUES BIOLOGY DOXCDocument3 pagesTISSUES BIOLOGY DOXCmaddi.ellistonNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What EntersDocument9 pagesCell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What Enterseli bermiNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Physiology TransDocument8 pagesPhysiology TranschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Membrane: Completed? Date Links Syllabus Point UnitDocument7 pagesTransportation in Membrane: Completed? Date Links Syllabus Point UnitJada DavisNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Cell TransportDocument39 pagesLec 6 Cell TransportMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument3 pagesCell StructureKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- 1.4 Membrane TransportDocument8 pages1.4 Membrane TransportmariamNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document13 pagesBio 2gapcenizalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document21 pagesChapter 7EhazNo ratings yet
- Happ Lab Mod 2Document7 pagesHapp Lab Mod 2Jerwin TullaoNo ratings yet
- BIO01 CO3.1 Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument19 pagesBIO01 CO3.1 Transport Mechanisms in CellsJustine MarillaNo ratings yet
- Simple DiffusionDocument1 pageSimple DiffusionJean Antonette Santos ManabatNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyDocument4 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism SendDocument14 pagesTransport Mechanism Sendchloe rederrickNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDocument13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- Cell Transport Recall Qs ANSDocument6 pagesCell Transport Recall Qs ANSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- L9 Cellular TransportDocument2 pagesL9 Cellular TransportStephanie SyNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Osmotic Solutions A. IsotonicDocument5 pagesThree Types of Osmotic Solutions A. IsotonicRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- 2 TransportDocument36 pages2 Transportapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Cellular Transport NotesDocument39 pagesCellular Transport NotesShen ZuNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Philip Bolko - Cell Transport ChartsDocument2 pagesKami Export - Philip Bolko - Cell Transport Chartsphilip 6969No ratings yet
- 11J Caybot Jashjovian Task13Document10 pages11J Caybot Jashjovian Task13JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- (Road Down) Cations (Reduced)Document4 pages(Road Down) Cations (Reduced)Jantzen LimNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsEugene VinaraoNo ratings yet
- Is Reviewer 2B Cell PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIs Reviewer 2B Cell Physiologyajuj jerNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Document5 pagesPhysiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Man Dejelo100% (1)
- Types of Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesTypes of Transport Across The Cell MembraneAsad ShalmaniNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Document25 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Dewi SallehNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpDocument67 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpSilver CypressNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 1 - ForeignerDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - 1 - Foreignerapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Simple Diffusion and Facilitated TransportDocument15 pagesSimple Diffusion and Facilitated TransportKristine GraceNo ratings yet
- Transport Across A MembraneDocument46 pagesTransport Across A MembraneKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- The Cell Membrane: General Biology 1 1st Grading Session 7: Transport Across MembranesDocument2 pagesThe Cell Membrane: General Biology 1 1st Grading Session 7: Transport Across MembranesBangtan SonyeondanNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes 1Document2 pagesCornell Notes 1api-333316198100% (1)
- Anaphy Chap 3Document5 pagesAnaphy Chap 3Maecel Pomida FidelinoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis and Active TransportDocument4 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis and Active TransportAshwariya BarsateeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- 8.3. Lesson Check Answer KeyDocument1 page8.3. Lesson Check Answer Keyhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDocument7 pages2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Facilitated Diffusion: + + 2+ - 3 SmallDocument2 pagesFacilitated Diffusion: + + 2+ - 3 SmallKyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document3 pagesWeek 3naomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Daniel Quiroz WORKSHOP CELL TRANSPORTDocument5 pagesDaniel Quiroz WORKSHOP CELL TRANSPORTDaniel QuirozNo ratings yet
- CMBCH 8Document2 pagesCMBCH 8Kyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet
- GenBio - 1st QuarterDocument13 pagesGenBio - 1st QuarterCc TvNo ratings yet
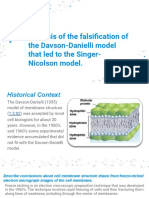
- 1.3.S3 Analysis of The Falsification of The Davson-Danielli Model That Led To The Singer-Nicolson ModelDocument13 pages1.3.S3 Analysis of The Falsification of The Davson-Danielli Model That Led To The Singer-Nicolson ModelApollo AdairNo ratings yet
- Receptor ProteinDocument7 pagesReceptor Proteinandrej.gregorcicNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project: Topic-Unit CellsDocument4 pagesInvestigatory Project: Topic-Unit CellsShifa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ebook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesEbook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDavidLeekemt100% (9)
- 2DNMRDocument37 pages2DNMRprasad0625No ratings yet
- Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument5 pagesCellular Transport MechanismsJads CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Protein Targeting: After This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument12 pagesProtein Targeting: After This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToAmeena SherinNo ratings yet
- Membrane PotentialDocument3 pagesMembrane PotentialZahra DibaNo ratings yet
- AGUSTIN - Worksheet No. 3 - Cell Membrane & Cell TransportDocument3 pagesAGUSTIN - Worksheet No. 3 - Cell Membrane & Cell Transportsam agustinNo ratings yet
- Tolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pagesTolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityZoe Alea MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Hodgkin-Huxley ModelDocument7 pagesThe Hodgkin-Huxley ModelLike Hell I'm Telling YouNo ratings yet
- Miller IndexDocument5 pagesMiller IndexKamenriderNo ratings yet
- Protein StructuresDocument6 pagesProtein StructuresKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Karp's Cell and Molecular Biology CH4 PLASMA MEMBRANEDocument54 pagesKarp's Cell and Molecular Biology CH4 PLASMA MEMBRANEPriyanka KasturiaNo ratings yet
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Neurotransmitter ReceptorsDocument5 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Neurotransmitter ReceptorsEdvard JamesNo ratings yet
- Vasp Workshop at NCHC: Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesVasp Workshop at NCHC: Lecture Notesabhinav jangirNo ratings yet
- Biochem Exam 3 Study GuideDocument17 pagesBiochem Exam 3 Study GuideGreg ZhangNo ratings yet
- Endocytosis - Exocytosis16engDocument47 pagesEndocytosis - Exocytosis16engnicole bNo ratings yet
- Imperfections in Crystalline SolidsDocument27 pagesImperfections in Crystalline SolidsMvk ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Membrane EngDocument5 pagesMembrane EngMeirbekNo ratings yet
- University of California Los Angeles .. - ,,-. - .: Approved For Release Cia-Rdp96-007B7R0004000Booic RDDocument6 pagesUniversity of California Los Angeles .. - ,,-. - .: Approved For Release Cia-Rdp96-007B7R0004000Booic RDChadNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology Digestive System Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesHonors Biology Digestive System Review WorksheetRighteousnessNo ratings yet
- Lymphocyte TraffickingDocument8 pagesLymphocyte TraffickingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 14th Edition Fox Test BankDocument50 pagesHuman Physiology 14th Edition Fox Test Bankoraliemaximusp474w3100% (33)
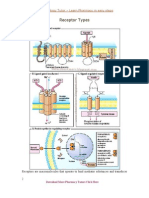
- Receptor TypesDocument3 pagesReceptor TypesPardeep SonyNo ratings yet
- Protein Deuteration Via Algal Amino Acids To Overcome Proton Back-Exchange For fast-MAS Solid-State NMR of Large ProteinsDocument4 pagesProtein Deuteration Via Algal Amino Acids To Overcome Proton Back-Exchange For fast-MAS Solid-State NMR of Large Proteinsbio.ovcharovaaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Saloni Rose)Document10 pagesAssignment 2 (Saloni Rose)saloniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Bravais LatticeDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 - Bravais Latticeريمكس REMIXNo ratings yet
2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORT
2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORT
Uploaded by
jmd5qbmt4kOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORT
2.2 Cells TYPE OF TRANSPORT
Uploaded by
jmd5qbmt4kCopyright:
Available Formats
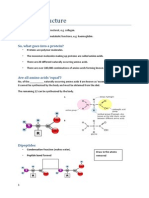
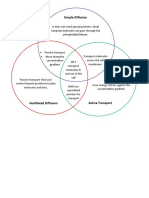
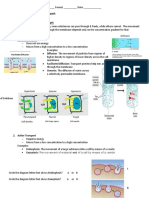
TYPE OF TRANSPORT SHORT DESCRIPTION EXAMPLES TYPES OF MATERIALS
TRANSPORTED
PASSIVE TRANSPORT Transport of molecules from a OSMOSIS Water
high to low concentration - The diffusion of Hypotonic – movement of
gradient and does not require WATER across a cell water into the cell that can
energy or ATP. membrane of cause lyse or bursting of cell if
different too much water intake
concentration
Hypertonic – movement of
water out of the cell that can
cause the cell to shrink or
shrivel which can also cause
cell death
Isotonic – water flows in and
out or in both directions with
equal amounts/concentration
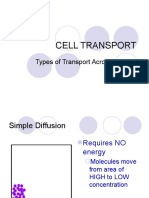
SIMPLE DIFFUSION Small molecules
- Movement of molecules from high to low Uncharged/unipolar
concentration without the use of energy molecules
- Will continue to happen if equilibrium or equal - Ex: Oxygen
concentration is reached on both sides of the cell - Ex: Carbon dioxide
membrane
FACILITATED DIFFUSION Sodium ions thru a sodium
- Movement of molecules that requires TRANSPORT specific channel protein
PROTEINS to pass thru the cell membrane without
the use of energy Sodium gated channel of
- Some require ion channels so that polar molecules nerve cell for sodium
can pass thru the cell membrane (stimulated by chemical
- Classified as passive transport because: movement of signal to open gates so the Na
material is from high to low concentration ions can get into the cell
membrane)
Large molecules like
GLUCOSE – involves both
active and passive diffusion –
glucose is too big to diffuse
easily use of carrier
proteins to move glucose
across a cell membrane
ACTIVE TRANSPORT Transport of molecules or Na-K pump Na-K pump – movement of 3
substances from a low to high Na ions out of the cell and 2 K
concentration gradient ions into the cell on high
- Because it is moving concentrated areas
against its
concentration Messages sent by neurons
gradient, it requires with the use of carrier
energy ang proteins or pumps to move
assistance from the molecules
carrier proteins to
move across the
membrane
You might also like
- Edited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportDocument2 pagesEdited - Amoeba Sisters Cell TransportTalha 1075% (4)
- Protein Structure WorksheetDocument7 pagesProtein Structure WorksheetkarendbrooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument12 pagesGen BioJohn Paul ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- Transport MembraneDocument2 pagesTransport Membranesna240839No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ReviewerDocument3 pagesCell Membrane ReviewerJohn Rey Magno SabalNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument8 pagesBiologyClare Anne Therese EsbietoNo ratings yet
- GENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument22 pagesGENBIO.1.Chapter 3 - Cellular Transport MechanismsJiro SamontañezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - Plant Physiology and Transport ProcessesDocument26 pagesMODULE 5 - Plant Physiology and Transport ProcessesNicoleBenaguaNo ratings yet
- From The Soil by The Root CellsDocument13 pagesFrom The Soil by The Root CellsChristina RañaNo ratings yet
- TISSUES BIOLOGY DOXCDocument3 pagesTISSUES BIOLOGY DOXCmaddi.ellistonNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What EntersDocument9 pagesCell Membrane Homeostasis Because It Controls What Enterseli bermiNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Physiology TransDocument8 pagesPhysiology TranschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Membrane: Completed? Date Links Syllabus Point UnitDocument7 pagesTransportation in Membrane: Completed? Date Links Syllabus Point UnitJada DavisNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Cell TransportDocument39 pagesLec 6 Cell TransportMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument3 pagesCell StructureKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- 1.4 Membrane TransportDocument8 pages1.4 Membrane TransportmariamNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document13 pagesBio 2gapcenizalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document21 pagesChapter 7EhazNo ratings yet
- Happ Lab Mod 2Document7 pagesHapp Lab Mod 2Jerwin TullaoNo ratings yet
- BIO01 CO3.1 Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument19 pagesBIO01 CO3.1 Transport Mechanisms in CellsJustine MarillaNo ratings yet
- Simple DiffusionDocument1 pageSimple DiffusionJean Antonette Santos ManabatNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyDocument4 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism SendDocument14 pagesTransport Mechanism Sendchloe rederrickNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDocument13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- Cell Transport Recall Qs ANSDocument6 pagesCell Transport Recall Qs ANSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- L9 Cellular TransportDocument2 pagesL9 Cellular TransportStephanie SyNo ratings yet
- Three Types of Osmotic Solutions A. IsotonicDocument5 pagesThree Types of Osmotic Solutions A. IsotonicRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- 2 TransportDocument36 pages2 Transportapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Cellular Transport NotesDocument39 pagesCellular Transport NotesShen ZuNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Philip Bolko - Cell Transport ChartsDocument2 pagesKami Export - Philip Bolko - Cell Transport Chartsphilip 6969No ratings yet
- 11J Caybot Jashjovian Task13Document10 pages11J Caybot Jashjovian Task13JASH JOVIAN CAYBOTNo ratings yet
- (Road Down) Cations (Reduced)Document4 pages(Road Down) Cations (Reduced)Jantzen LimNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsEugene VinaraoNo ratings yet
- Is Reviewer 2B Cell PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIs Reviewer 2B Cell Physiologyajuj jerNo ratings yet
- Physiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Document5 pagesPhysiology Chap4 (Transport of Substances Through Cell Membrane)Man Dejelo100% (1)
- Types of Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesTypes of Transport Across The Cell MembraneAsad ShalmaniNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Document25 pagesMovement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane: Compiled & Prepared by Dsalleh (2021)Dewi SallehNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpDocument67 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpSilver CypressNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 1 - ForeignerDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - 1 - Foreignerapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Simple Diffusion and Facilitated TransportDocument15 pagesSimple Diffusion and Facilitated TransportKristine GraceNo ratings yet
- Transport Across A MembraneDocument46 pagesTransport Across A MembraneKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- The Cell Membrane: General Biology 1 1st Grading Session 7: Transport Across MembranesDocument2 pagesThe Cell Membrane: General Biology 1 1st Grading Session 7: Transport Across MembranesBangtan SonyeondanNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes 1Document2 pagesCornell Notes 1api-333316198100% (1)
- Anaphy Chap 3Document5 pagesAnaphy Chap 3Maecel Pomida FidelinoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis and Active TransportDocument4 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis and Active TransportAshwariya BarsateeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- 8.3. Lesson Check Answer KeyDocument1 page8.3. Lesson Check Answer Keyhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDocument7 pages2.4 Transport Across Membrane: Passive Transport Active TransportDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Facilitated Diffusion: + + 2+ - 3 SmallDocument2 pagesFacilitated Diffusion: + + 2+ - 3 SmallKyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document3 pagesWeek 3naomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Daniel Quiroz WORKSHOP CELL TRANSPORTDocument5 pagesDaniel Quiroz WORKSHOP CELL TRANSPORTDaniel QuirozNo ratings yet
- CMBCH 8Document2 pagesCMBCH 8Kyle PeñarroyoNo ratings yet
- GenBio - 1st QuarterDocument13 pagesGenBio - 1st QuarterCc TvNo ratings yet
- 1.3.S3 Analysis of The Falsification of The Davson-Danielli Model That Led To The Singer-Nicolson ModelDocument13 pages1.3.S3 Analysis of The Falsification of The Davson-Danielli Model That Led To The Singer-Nicolson ModelApollo AdairNo ratings yet
- Receptor ProteinDocument7 pagesReceptor Proteinandrej.gregorcicNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project: Topic-Unit CellsDocument4 pagesInvestigatory Project: Topic-Unit CellsShifa SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ebook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesEbook Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7Th Edition Karp Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDavidLeekemt100% (9)
- 2DNMRDocument37 pages2DNMRprasad0625No ratings yet
- Cellular Transport MechanismsDocument5 pagesCellular Transport MechanismsJads CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Protein Targeting: After This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument12 pagesProtein Targeting: After This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToAmeena SherinNo ratings yet
- Membrane PotentialDocument3 pagesMembrane PotentialZahra DibaNo ratings yet
- AGUSTIN - Worksheet No. 3 - Cell Membrane & Cell TransportDocument3 pagesAGUSTIN - Worksheet No. 3 - Cell Membrane & Cell Transportsam agustinNo ratings yet
- Tolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pagesTolerance: Chapter 20 - Regulation of Adaptive ImmunityZoe Alea MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Hodgkin-Huxley ModelDocument7 pagesThe Hodgkin-Huxley ModelLike Hell I'm Telling YouNo ratings yet
- Miller IndexDocument5 pagesMiller IndexKamenriderNo ratings yet
- Protein StructuresDocument6 pagesProtein StructuresKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Karp's Cell and Molecular Biology CH4 PLASMA MEMBRANEDocument54 pagesKarp's Cell and Molecular Biology CH4 PLASMA MEMBRANEPriyanka KasturiaNo ratings yet
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Neurotransmitter ReceptorsDocument5 pagesMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Neurotransmitter ReceptorsEdvard JamesNo ratings yet
- Vasp Workshop at NCHC: Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesVasp Workshop at NCHC: Lecture Notesabhinav jangirNo ratings yet
- Biochem Exam 3 Study GuideDocument17 pagesBiochem Exam 3 Study GuideGreg ZhangNo ratings yet
- Endocytosis - Exocytosis16engDocument47 pagesEndocytosis - Exocytosis16engnicole bNo ratings yet
- Imperfections in Crystalline SolidsDocument27 pagesImperfections in Crystalline SolidsMvk ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Membrane EngDocument5 pagesMembrane EngMeirbekNo ratings yet
- University of California Los Angeles .. - ,,-. - .: Approved For Release Cia-Rdp96-007B7R0004000Booic RDDocument6 pagesUniversity of California Los Angeles .. - ,,-. - .: Approved For Release Cia-Rdp96-007B7R0004000Booic RDChadNo ratings yet
- Honors Biology Digestive System Review WorksheetDocument2 pagesHonors Biology Digestive System Review WorksheetRighteousnessNo ratings yet
- Lymphocyte TraffickingDocument8 pagesLymphocyte TraffickingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 14th Edition Fox Test BankDocument50 pagesHuman Physiology 14th Edition Fox Test Bankoraliemaximusp474w3100% (33)
- Receptor TypesDocument3 pagesReceptor TypesPardeep SonyNo ratings yet
- Protein Deuteration Via Algal Amino Acids To Overcome Proton Back-Exchange For fast-MAS Solid-State NMR of Large ProteinsDocument4 pagesProtein Deuteration Via Algal Amino Acids To Overcome Proton Back-Exchange For fast-MAS Solid-State NMR of Large Proteinsbio.ovcharovaaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Saloni Rose)Document10 pagesAssignment 2 (Saloni Rose)saloniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Bravais LatticeDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 - Bravais Latticeريمكس REMIXNo ratings yet