Professional Documents
Culture Documents
XM ISO 27005 - 2022 8. ISRT
XM ISO 27005 - 2022 8. ISRT
Uploaded by
DavidCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Risk Assessment 4 PipelinesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 Risk Assessment 4 PipelinesMAT-LIONNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting NotesDocument24 pagesGovernment Accounting Noteszee abadilla100% (1)
- Risk Management Process Answers: ActionsDocument1 pageRisk Management Process Answers: ActionsjohnpaulmcaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument8 pagesProject Management Frequently Asked Questionsdrsuresh26No ratings yet
- Project Risk Identification Analysis and Response TemplateDocument5 pagesProject Risk Identification Analysis and Response TemplateAshraf SeragNo ratings yet
- Risk Treatment TemplateDocument2 pagesRisk Treatment Templatepanosplh100% (1)
- Risk Definition FlashcardsDocument13 pagesRisk Definition FlashcardsHaitham El HanbolyNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Template: Cause Event ImpactDocument1 pageRisk Assessment Template: Cause Event Impactthe professionalzNo ratings yet
- PRM Lecture 6 - PLAN RISK RESPONSESDocument30 pagesPRM Lecture 6 - PLAN RISK RESPONSESYasi EemoNo ratings yet
- RiskSummary AlumnoDocument2 pagesRiskSummary AlumnoWilliams HerreraNo ratings yet
- Selection of PDRI Cycle in The Zonal Monal AreasDocument61 pagesSelection of PDRI Cycle in The Zonal Monal Areasaqib arifNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk ManagementMy HaHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Risk Decision & ActionsDocument28 pagesChapter 6-Risk Decision & ActionsErmia MogeNo ratings yet
- 1 Risk Management Principle: Tool 2EDocument6 pages1 Risk Management Principle: Tool 2EpekanselandarNo ratings yet
- STEP by STEP Guide On Project Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesSTEP by STEP Guide On Project Risk ManagementKL SimNo ratings yet
- All Projects Carry Risk: We Either Manage It or Suffer Its ConsequencesDocument12 pagesAll Projects Carry Risk: We Either Manage It or Suffer Its ConsequencesChichi AnionNo ratings yet
- Extending The Use of RiskDocument7 pagesExtending The Use of RiskRADU LAURENTIUNo ratings yet
- L06 Risk Response PlanningDocument23 pagesL06 Risk Response Planninghappiest1No ratings yet
- Pages From FW815-Seiichi Nakajima-Introduction To TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) - Productivity Press (1988)Document4 pagesPages From FW815-Seiichi Nakajima-Introduction To TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) - Productivity Press (1988)Lestari IndriNo ratings yet
- Quality Built in Into Projects: Risk Identification SessionDocument21 pagesQuality Built in Into Projects: Risk Identification SessionLokeshNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Executive Planning-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANODocument14 pagesRisk Management in Executive Planning-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANOPHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANONo ratings yet
- Project Risk Management v0.3Document50 pagesProject Risk Management v0.3rishwaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Quiz - EditedDocument9 pagesRisk Management Quiz - EditedkimberlyarileyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Individu 2 - George Juan Susanto - 2106781893Document4 pagesTugas Individu 2 - George Juan Susanto - 2106781893George Juan SusantoNo ratings yet
- Risk Documentation: ( / Resourcing The Risk Management ProcessDocument1 pageRisk Documentation: ( / Resourcing The Risk Management ProcessMichel erickson talom waboNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis Toolkit v5Document9 pagesRisk Analysis Toolkit v5Amritraj CharlesNo ratings yet
- Case Study. FD. EditedDocument10 pagesCase Study. FD. Editedogarivincent20No ratings yet
- 5 Basic Phases of Project ManagementDocument5 pages5 Basic Phases of Project ManagementRohitNo ratings yet
- Risk PlanningDocument13 pagesRisk PlanningNamitha ShajanNo ratings yet
- PMBOK 6th Ch11 567Document22 pagesPMBOK 6th Ch11 567Andi EriawanNo ratings yet
- IM Risk Management Plan v4 0.pdf-1Document13 pagesIM Risk Management Plan v4 0.pdf-1jcac2000No ratings yet
- 3 Risk ManagementDocument29 pages3 Risk ManagementAhmed EsamNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in JKR Malaysia-Utk PresentationDocument31 pagesRisk Management in JKR Malaysia-Utk PresentationKar YongNo ratings yet
- Risk Response StrategiesDocument3 pagesRisk Response StrategiesStanley Ke BadaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument10 pagesRisk Management PlanQuezon Medical Center Administrative OfficeNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis: Group Members: Reshma Ravindran Sidhiq Shamweel Vinod VipinDocument18 pagesRisk Analysis: Group Members: Reshma Ravindran Sidhiq Shamweel Vinod VipinReshma AnandNo ratings yet
- Madrid Airport Risk ManagementDocument3 pagesMadrid Airport Risk ManagementtechnicalvijayNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Strategies Risk Management Process The Risk Management CycleDocument11 pagesRisk Management Strategies Risk Management Process The Risk Management CycleKhadijaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 Ch07 - Managing RisksDocument36 pagesLec 8 Ch07 - Managing RisksPhuc LinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Risk Response PlanningDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Risk Response Planningadabotor7No ratings yet
- Risk Management: Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis-The Process of Prioritising Risks For FurtherDocument26 pagesRisk Management: Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis-The Process of Prioritising Risks For FurthershifaNo ratings yet
- Tool 36 - 38 - Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesTool 36 - 38 - Risk ManagementNick KrugerNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Environmental Risk Assessment and Management - 2011 - Green Leaves III - UKDocument9 pagesGuidelines For Environmental Risk Assessment and Management - 2011 - Green Leaves III - UKJosue RuaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Construction Project ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk Management in Construction Project ManagementShakil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Risk Response StrategyDocument34 pagesRisk Response StrategycmugaruraNo ratings yet
- Risk Template Formate Good-AliuDocument3 pagesRisk Template Formate Good-Aliuolabisi aliNo ratings yet
- Project Risk ManagementDocument16 pagesProject Risk ManagementRishabhGuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.8 Plan Risk ManagementDocument4 pages1.1.8 Plan Risk ManagementMohamed Talaat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesRisk Managementjain.aryan2004No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Risk AnalysisDocument50 pagesChapter 6 - Risk AnalysisOyungerel BattogtokhNo ratings yet
- Post-Mortem Analysis On The Analysis and Evaluatio ModifyDocument9 pagesPost-Mortem Analysis On The Analysis and Evaluatio ModifyMatthieu PotesNo ratings yet
- Risk QnA CardsDocument4 pagesRisk QnA CardsHaitham El HanbolyNo ratings yet
- 7 Risk ResponseDocument32 pages7 Risk Responses18945No ratings yet
- PMIPE 2017 1 Plan Risk Responses VFDocument32 pagesPMIPE 2017 1 Plan Risk Responses VFDavid SilvaNo ratings yet
- 11 Project Management l11Document29 pages11 Project Management l11Manal Ali GhanemNo ratings yet
- Risk Response PlanningDocument5 pagesRisk Response Planningubadjate100% (1)
- Risk Management Plan of Daycare CenterDocument15 pagesRisk Management Plan of Daycare CenterMirza MehboobNo ratings yet
- HR ExecutiveDocument16 pagesHR ExecutiveAli AbbasNo ratings yet
- PM4DEV Project Risk ManagementDocument28 pagesPM4DEV Project Risk ManagementisiphosamandlaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument5 pagesRisk Management PlanVictor EgharevbaNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis: Facilitating and Analysis Guidelines for Capital Expenditure ProjectsFrom EverandRisk Analysis: Facilitating and Analysis Guidelines for Capital Expenditure ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Sustainability For Safety ProfessionalDocument134 pagesSustainability For Safety ProfessionalDavidNo ratings yet
- Sharing 4 - Global Process Safety Regulation With Incidents and Lesson LearnedDocument51 pagesSharing 4 - Global Process Safety Regulation With Incidents and Lesson LearnedDavidNo ratings yet
- WSH 2Document243 pagesWSH 2DavidNo ratings yet
- Response Paper On Climate and Diversity - The Way Forward - 0Document65 pagesResponse Paper On Climate and Diversity - The Way Forward - 0DavidNo ratings yet
- Risk MGT Flow ChartDocument1 pageRisk MGT Flow ChartDavidNo ratings yet
- ISO 19011 - 2018 Guidelines For Auditing Management SystemsDocument1 pageISO 19011 - 2018 Guidelines For Auditing Management SystemsDavidNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction-Multimedia Data-FeaturesDocument6 pagesUnit-1 Introduction-Multimedia Data-FeaturesDavidNo ratings yet
- Energy Consumption and Load Balancing Compared With Vanet and ManetDocument10 pagesEnergy Consumption and Load Balancing Compared With Vanet and ManetDavidNo ratings yet
- An Improved Comparator Structure For 8-Bit Sar Adcs: A ReviewDocument4 pagesAn Improved Comparator Structure For 8-Bit Sar Adcs: A ReviewDavidNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Excel EssentialsDocument316 pagesModule 1 - Excel EssentialsambitiousfirkinNo ratings yet
- Bode Plot: What Do You Need To Know To Understand This Topic?Document6 pagesBode Plot: What Do You Need To Know To Understand This Topic?DavidNo ratings yet
- Aibel Sustainability Report 2022Document38 pagesAibel Sustainability Report 2022DavidNo ratings yet
- U15Ect 501 - Control SystemsDocument7 pagesU15Ect 501 - Control SystemsDavidNo ratings yet
- Multimedia and CompressionDocument2 pagesMultimedia and CompressionDavidNo ratings yet
- Price List Nails Screws BoltsDocument59 pagesPrice List Nails Screws BoltskutbiahtNo ratings yet
- MC 99 NotesDocument3 pagesMC 99 NotesVloudy Mia Serrano PangilinanNo ratings yet
- 15 12 221985Document38 pages15 12 221985zamaludin modangguNo ratings yet
- Notice of ClaimDocument4 pagesNotice of ClaimLou AragaNo ratings yet
- Banglore BPODocument2 pagesBanglore BPOwaris bhatNo ratings yet
- GPTADocument20 pagesGPTAJam AlbanoNo ratings yet
- A Global Sustainability Perspective On 3D Printing TechnologiesDocument10 pagesA Global Sustainability Perspective On 3D Printing Technologiesthanhtuan.to1993No ratings yet
- Report 20230321111742Document4 pagesReport 20230321111742Dass AniNo ratings yet
- 2021 Question PaperDocument2 pages2021 Question PaperPranjalNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod2 - The Core Principles Underlying Fairness Accountability and Transparency in Business Operation and Stewardship - Final 2Document17 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod2 - The Core Principles Underlying Fairness Accountability and Transparency in Business Operation and Stewardship - Final 2Yannah Longalong100% (1)
- الحماية القانونية للعلامات الفارقةDocument169 pagesالحماية القانونية للعلامات الفارقةEhab SwaidNo ratings yet
- For Srilanka1Document1 pageFor Srilanka1Head Department of PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Social Function of Business EthicsDocument29 pagesSocial Function of Business EthicsKevin Espinosa100% (1)
- Business Fundamentals CHK - 5740: Account Activity: All TransactionsDocument3 pagesBusiness Fundamentals CHK - 5740: Account Activity: All TransactionsAnnaly Carolina Bravo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4hassan19951996hNo ratings yet
- Limco Global Services PVT LTD - JT - 2223!1!549Document1 pageLimco Global Services PVT LTD - JT - 2223!1!549shobhaNo ratings yet
- Présentation Basique Simple en Blocs Diagonale Bleu Et BlancDocument18 pagesPrésentation Basique Simple en Blocs Diagonale Bleu Et BlancMayssa LahbibNo ratings yet
- Catherine o Reilly CVDocument5 pagesCatherine o Reilly CVapi-511833094No ratings yet
- Editorial Board - 2022 - Industrial Marketing ManagementDocument1 pageEditorial Board - 2022 - Industrial Marketing ManagementMisael Diaz HernandezNo ratings yet
- BS AU 050-3.2a-2002Document12 pagesBS AU 050-3.2a-2002amerNo ratings yet
- National IPR Policy 2016 An AnalysisDocument7 pagesNational IPR Policy 2016 An AnalysisjptripathyNo ratings yet
- Fabm Week 11 20fabm 121 Week 11 20Document3 pagesFabm Week 11 20fabm 121 Week 11 20Criscel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Johns 10e Irm ch15Document24 pagesJohns 10e Irm ch15Jacob WeiseNo ratings yet
- Unisys + C2P OPFDocument4 pagesUnisys + C2P OPFdebajyotiguhaNo ratings yet
- BS Delhi EnglishDocument20 pagesBS Delhi EnglishAshisNo ratings yet
- JAIBB - GFI - (Module-C) - CEO and Senior ManagementDocument15 pagesJAIBB - GFI - (Module-C) - CEO and Senior ManagementNaz MahoonNo ratings yet
- CIR v. Cebu Portland Cement Co. DIGESTDocument2 pagesCIR v. Cebu Portland Cement Co. DIGESTkathrynmaydeveza100% (2)
- Project ManagementDocument187 pagesProject Managementshashi puriNo ratings yet
- Film Concept Note SHEFEXILDocument2 pagesFilm Concept Note SHEFEXILBDTRNo ratings yet
XM ISO 27005 - 2022 8. ISRT
XM ISO 27005 - 2022 8. ISRT
Uploaded by
DavidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
XM ISO 27005 - 2022 8. ISRT
XM ISO 27005 - 2022 8. ISRT
Uploaded by
DavidCopyright:
Available Formats
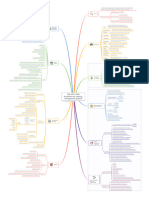
Formulate risk treatment plan.
Action
Risk Effect of uncertainty on objectives positive / negative
Risk treatment plan (RTP) Output
Process to modify risk
RTP is a plan to modify risk such that it meets the organization’s risk acceptance criteria
voiding the risk by deciding not to start or continue
A
with the activity that gives rise to the risk
a plan to implement the organization’s necessary controls 1. Project plan
Risk treatment Taking or increasing risk in order to pursue an opportunity
t he plan that not only identifies necessary controls but also describes how
2. Design plan Removing the risk source
the controls interact with their environment and each other to modify risks
RTP
can involve: Changing the likelihood
In practice, both can be used
Changing the consequences
nce the controls are in place, the project plan ceases to have any value
O
other than as a historical record, whereas the design plan is still useful. Sharing the risk with another party or parties (including contracts and risk financing)
Retaining the risk by informed decision
Priorities in relation with the level of risk and urgency of treatment
Informed decision to take a particular risk
Whether different types of controls (preventive, Terms Risk acceptance
detective, corrective) or their composition are applicable Risk acceptance can occur without risk treatment or during the process of risk treatment
rganizations should
O
Whether it is necessary to wait for a control to be settled consider the following:
Form of risk treatment involving the agreed distribution of risk with other parties
before starting to implement a new one on the same asset
.6.1 Formulation
8 Legal or regulatory requirements can limit, prohibit or mandate risk sharing
Whether there is a delay between the time the control is implemented of the RTP Risk sharing
and the moment where it is fully effective and operational e.g., insurance or other forms of contract
the rationale for selection of the treatment options, including the Risk transfer is a form of risk sharing
expected benefits to be gained
Risk retention Temporary acceptance of the potential benefit of gain, or burden of loss, from a particular risk
those who are accountable and responsible for
approving and implementing the plan Control Measure that maintains and/or modifies risk
the proposed actions Residual risk Risk remaining after risk treatment
risk avoidance
the resources required, including contingencies
or each treated
F
the performance indicators risk the plan should risk modification
include:
Options
the constraints
risk retention
the required reporting and monitoring
.6 Information
8
when actions are expected to be undertaken and completed
security RTP risk sharing
implementation status he input of the information security risk treatment is based on the risk assessment process
T
8.1 General outcomes in the form of a prioritized set of risks to be treated, based on risk criteria.
he risk treatment plan actions should be ranked by priority in
T ISO 27005:2022 he output of this process is a set of necessary information security controls that are to be
T
relation with the level of risk and urgency of treatment.
Approval of risk treatment plan(s) by risk owners Action
8. Information security deployed or enhanced in relation to one another, in accordance with the risk treatment plan (RTP)
Approved risk treatment plan(s) Output
risk treatment process eployed in this way, the effectiveness of the risk treatment plan is to modify the information
D
security risk facing the organization so that it meets the organization’s criteria for acceptance.
8.6.2 Approval by risk owners
www.patreon.com/AndreyProzorov Risk treatment can create new risks or modify existing risks
The RTP should be approved by the risk owners once it is formulated.
Action Risk treatment options should be chosen
Risk owners should also decide on the acceptance of residual information security risks.
Output A list of prioritized risks with the selected risk treatment options.
Determine whether the residual risks are acceptable. Action
.6.3 Acceptance
8
of the residual Risk avoidance, by deciding not to start or continue with the activity that gives rise to the risk
Accepted residual risks Output
information
security risks
In order to determine the residual risks, risk treatment plans should feed isk modification, by changing the likelihood of the occurrence of an
R
into the follow up assessment of residual likelihood and consequence. .2 Selecting appropriate
8 event or a consequence or changing the severity of the consequence
information security risk Options
Produce a Statement of Applicability Action
treatment options Risk retention, by informed choice
Statement of Applicability (SoA) Output isk sharing, by splitting responsibilities with other parties, either
R
internally or externally (e.g. sharing the consequences via insurance)
a) the necessary controls
isk treatment options should be selected based on the outcome of the risk assessment, the
R
b) justification for their inclusion .5 Producing a
8 expected costs for implementing these options and the expected benefits from these options
oA should
S
contain at least:
Statement of Determine all controls, from the chosen control sets as selected from an appropriate source, that are necessary for
Action
c) whether they are implemented or not Applicability treating the risks based on the risk treatment options chosen, such as to modify, retain, avoid or share the risks.
d) justification for exclusions of controls Output All necessary controls
Controls cannot be added to the SOA independent of the risk assessment ISO/IEC 27001:2022, Annex A
is it a documented control
implemented
Implementation who owns the control
partially implemented
statuses .3 Determining all controls that
8
how it is monitored
not implemented are necessary to implement the
Control description
information security risk how it can be evidenced
treatment options
ompare all necessary controls with those
C any exceptions
Action
listed in ISO/IEC 27001:2022, Annex A.
if it is not obvious then the reason why the control exists
All controls applicable to the risk treatment Output .4 Comparing the controls
8
control that is intended to prevent the occurrence of an information
a
he purpose of this is to act as a safety check to verify that no
T
determined with those in ISO/ a) preventive
security event that can lead to the occurrence of one or more consequences
necessary controls have been omitted from the risk assessment. IEC 27001:2022, Annex A
control that is intended to detect the
a
It is important to remember that this comparison of the controls is undertaken using Control classification b) detective
occurrence of an information security event
the risk assessment and is not undertaken using the Statement of Applicability.
control that is intended to limit the
a
c) corrective
consequences of an information security event
You might also like
- Chapter 6 Risk Assessment 4 PipelinesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 Risk Assessment 4 PipelinesMAT-LIONNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting NotesDocument24 pagesGovernment Accounting Noteszee abadilla100% (1)
- Risk Management Process Answers: ActionsDocument1 pageRisk Management Process Answers: ActionsjohnpaulmcaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument8 pagesProject Management Frequently Asked Questionsdrsuresh26No ratings yet
- Project Risk Identification Analysis and Response TemplateDocument5 pagesProject Risk Identification Analysis and Response TemplateAshraf SeragNo ratings yet
- Risk Treatment TemplateDocument2 pagesRisk Treatment Templatepanosplh100% (1)
- Risk Definition FlashcardsDocument13 pagesRisk Definition FlashcardsHaitham El HanbolyNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Template: Cause Event ImpactDocument1 pageRisk Assessment Template: Cause Event Impactthe professionalzNo ratings yet
- PRM Lecture 6 - PLAN RISK RESPONSESDocument30 pagesPRM Lecture 6 - PLAN RISK RESPONSESYasi EemoNo ratings yet
- RiskSummary AlumnoDocument2 pagesRiskSummary AlumnoWilliams HerreraNo ratings yet
- Selection of PDRI Cycle in The Zonal Monal AreasDocument61 pagesSelection of PDRI Cycle in The Zonal Monal Areasaqib arifNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk ManagementMy HaHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Risk Decision & ActionsDocument28 pagesChapter 6-Risk Decision & ActionsErmia MogeNo ratings yet
- 1 Risk Management Principle: Tool 2EDocument6 pages1 Risk Management Principle: Tool 2EpekanselandarNo ratings yet
- STEP by STEP Guide On Project Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesSTEP by STEP Guide On Project Risk ManagementKL SimNo ratings yet
- All Projects Carry Risk: We Either Manage It or Suffer Its ConsequencesDocument12 pagesAll Projects Carry Risk: We Either Manage It or Suffer Its ConsequencesChichi AnionNo ratings yet
- Extending The Use of RiskDocument7 pagesExtending The Use of RiskRADU LAURENTIUNo ratings yet
- L06 Risk Response PlanningDocument23 pagesL06 Risk Response Planninghappiest1No ratings yet
- Pages From FW815-Seiichi Nakajima-Introduction To TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) - Productivity Press (1988)Document4 pagesPages From FW815-Seiichi Nakajima-Introduction To TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) - Productivity Press (1988)Lestari IndriNo ratings yet
- Quality Built in Into Projects: Risk Identification SessionDocument21 pagesQuality Built in Into Projects: Risk Identification SessionLokeshNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Executive Planning-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANODocument14 pagesRisk Management in Executive Planning-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANOPHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANONo ratings yet
- Project Risk Management v0.3Document50 pagesProject Risk Management v0.3rishwaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Quiz - EditedDocument9 pagesRisk Management Quiz - EditedkimberlyarileyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Individu 2 - George Juan Susanto - 2106781893Document4 pagesTugas Individu 2 - George Juan Susanto - 2106781893George Juan SusantoNo ratings yet
- Risk Documentation: ( / Resourcing The Risk Management ProcessDocument1 pageRisk Documentation: ( / Resourcing The Risk Management ProcessMichel erickson talom waboNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis Toolkit v5Document9 pagesRisk Analysis Toolkit v5Amritraj CharlesNo ratings yet
- Case Study. FD. EditedDocument10 pagesCase Study. FD. Editedogarivincent20No ratings yet
- 5 Basic Phases of Project ManagementDocument5 pages5 Basic Phases of Project ManagementRohitNo ratings yet
- Risk PlanningDocument13 pagesRisk PlanningNamitha ShajanNo ratings yet
- PMBOK 6th Ch11 567Document22 pagesPMBOK 6th Ch11 567Andi EriawanNo ratings yet
- IM Risk Management Plan v4 0.pdf-1Document13 pagesIM Risk Management Plan v4 0.pdf-1jcac2000No ratings yet
- 3 Risk ManagementDocument29 pages3 Risk ManagementAhmed EsamNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in JKR Malaysia-Utk PresentationDocument31 pagesRisk Management in JKR Malaysia-Utk PresentationKar YongNo ratings yet
- Risk Response StrategiesDocument3 pagesRisk Response StrategiesStanley Ke BadaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument10 pagesRisk Management PlanQuezon Medical Center Administrative OfficeNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis: Group Members: Reshma Ravindran Sidhiq Shamweel Vinod VipinDocument18 pagesRisk Analysis: Group Members: Reshma Ravindran Sidhiq Shamweel Vinod VipinReshma AnandNo ratings yet
- Madrid Airport Risk ManagementDocument3 pagesMadrid Airport Risk ManagementtechnicalvijayNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Strategies Risk Management Process The Risk Management CycleDocument11 pagesRisk Management Strategies Risk Management Process The Risk Management CycleKhadijaNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 Ch07 - Managing RisksDocument36 pagesLec 8 Ch07 - Managing RisksPhuc LinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Risk Response PlanningDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Risk Response Planningadabotor7No ratings yet
- Risk Management: Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis-The Process of Prioritising Risks For FurtherDocument26 pagesRisk Management: Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis-The Process of Prioritising Risks For FurthershifaNo ratings yet
- Tool 36 - 38 - Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesTool 36 - 38 - Risk ManagementNick KrugerNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Environmental Risk Assessment and Management - 2011 - Green Leaves III - UKDocument9 pagesGuidelines For Environmental Risk Assessment and Management - 2011 - Green Leaves III - UKJosue RuaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Construction Project ManagementDocument8 pagesRisk Management in Construction Project ManagementShakil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Risk Response StrategyDocument34 pagesRisk Response StrategycmugaruraNo ratings yet
- Risk Template Formate Good-AliuDocument3 pagesRisk Template Formate Good-Aliuolabisi aliNo ratings yet
- Project Risk ManagementDocument16 pagesProject Risk ManagementRishabhGuptaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.8 Plan Risk ManagementDocument4 pages1.1.8 Plan Risk ManagementMohamed Talaat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesRisk Managementjain.aryan2004No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Risk AnalysisDocument50 pagesChapter 6 - Risk AnalysisOyungerel BattogtokhNo ratings yet
- Post-Mortem Analysis On The Analysis and Evaluatio ModifyDocument9 pagesPost-Mortem Analysis On The Analysis and Evaluatio ModifyMatthieu PotesNo ratings yet
- Risk QnA CardsDocument4 pagesRisk QnA CardsHaitham El HanbolyNo ratings yet
- 7 Risk ResponseDocument32 pages7 Risk Responses18945No ratings yet
- PMIPE 2017 1 Plan Risk Responses VFDocument32 pagesPMIPE 2017 1 Plan Risk Responses VFDavid SilvaNo ratings yet
- 11 Project Management l11Document29 pages11 Project Management l11Manal Ali GhanemNo ratings yet
- Risk Response PlanningDocument5 pagesRisk Response Planningubadjate100% (1)
- Risk Management Plan of Daycare CenterDocument15 pagesRisk Management Plan of Daycare CenterMirza MehboobNo ratings yet
- HR ExecutiveDocument16 pagesHR ExecutiveAli AbbasNo ratings yet
- PM4DEV Project Risk ManagementDocument28 pagesPM4DEV Project Risk ManagementisiphosamandlaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument5 pagesRisk Management PlanVictor EgharevbaNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis: Facilitating and Analysis Guidelines for Capital Expenditure ProjectsFrom EverandRisk Analysis: Facilitating and Analysis Guidelines for Capital Expenditure ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Sustainability For Safety ProfessionalDocument134 pagesSustainability For Safety ProfessionalDavidNo ratings yet
- Sharing 4 - Global Process Safety Regulation With Incidents and Lesson LearnedDocument51 pagesSharing 4 - Global Process Safety Regulation With Incidents and Lesson LearnedDavidNo ratings yet
- WSH 2Document243 pagesWSH 2DavidNo ratings yet
- Response Paper On Climate and Diversity - The Way Forward - 0Document65 pagesResponse Paper On Climate and Diversity - The Way Forward - 0DavidNo ratings yet
- Risk MGT Flow ChartDocument1 pageRisk MGT Flow ChartDavidNo ratings yet
- ISO 19011 - 2018 Guidelines For Auditing Management SystemsDocument1 pageISO 19011 - 2018 Guidelines For Auditing Management SystemsDavidNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction-Multimedia Data-FeaturesDocument6 pagesUnit-1 Introduction-Multimedia Data-FeaturesDavidNo ratings yet
- Energy Consumption and Load Balancing Compared With Vanet and ManetDocument10 pagesEnergy Consumption and Load Balancing Compared With Vanet and ManetDavidNo ratings yet
- An Improved Comparator Structure For 8-Bit Sar Adcs: A ReviewDocument4 pagesAn Improved Comparator Structure For 8-Bit Sar Adcs: A ReviewDavidNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Excel EssentialsDocument316 pagesModule 1 - Excel EssentialsambitiousfirkinNo ratings yet
- Bode Plot: What Do You Need To Know To Understand This Topic?Document6 pagesBode Plot: What Do You Need To Know To Understand This Topic?DavidNo ratings yet
- Aibel Sustainability Report 2022Document38 pagesAibel Sustainability Report 2022DavidNo ratings yet
- U15Ect 501 - Control SystemsDocument7 pagesU15Ect 501 - Control SystemsDavidNo ratings yet
- Multimedia and CompressionDocument2 pagesMultimedia and CompressionDavidNo ratings yet
- Price List Nails Screws BoltsDocument59 pagesPrice List Nails Screws BoltskutbiahtNo ratings yet
- MC 99 NotesDocument3 pagesMC 99 NotesVloudy Mia Serrano PangilinanNo ratings yet
- 15 12 221985Document38 pages15 12 221985zamaludin modangguNo ratings yet
- Notice of ClaimDocument4 pagesNotice of ClaimLou AragaNo ratings yet
- Banglore BPODocument2 pagesBanglore BPOwaris bhatNo ratings yet
- GPTADocument20 pagesGPTAJam AlbanoNo ratings yet
- A Global Sustainability Perspective On 3D Printing TechnologiesDocument10 pagesA Global Sustainability Perspective On 3D Printing Technologiesthanhtuan.to1993No ratings yet
- Report 20230321111742Document4 pagesReport 20230321111742Dass AniNo ratings yet
- 2021 Question PaperDocument2 pages2021 Question PaperPranjalNo ratings yet
- Bus - Ethics - q3 - Mod2 - The Core Principles Underlying Fairness Accountability and Transparency in Business Operation and Stewardship - Final 2Document17 pagesBus - Ethics - q3 - Mod2 - The Core Principles Underlying Fairness Accountability and Transparency in Business Operation and Stewardship - Final 2Yannah Longalong100% (1)
- الحماية القانونية للعلامات الفارقةDocument169 pagesالحماية القانونية للعلامات الفارقةEhab SwaidNo ratings yet
- For Srilanka1Document1 pageFor Srilanka1Head Department of PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Social Function of Business EthicsDocument29 pagesSocial Function of Business EthicsKevin Espinosa100% (1)
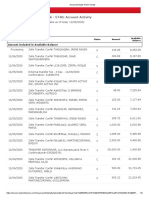
- Business Fundamentals CHK - 5740: Account Activity: All TransactionsDocument3 pagesBusiness Fundamentals CHK - 5740: Account Activity: All TransactionsAnnaly Carolina Bravo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document16 pagesUnit 4hassan19951996hNo ratings yet
- Limco Global Services PVT LTD - JT - 2223!1!549Document1 pageLimco Global Services PVT LTD - JT - 2223!1!549shobhaNo ratings yet
- Présentation Basique Simple en Blocs Diagonale Bleu Et BlancDocument18 pagesPrésentation Basique Simple en Blocs Diagonale Bleu Et BlancMayssa LahbibNo ratings yet
- Catherine o Reilly CVDocument5 pagesCatherine o Reilly CVapi-511833094No ratings yet
- Editorial Board - 2022 - Industrial Marketing ManagementDocument1 pageEditorial Board - 2022 - Industrial Marketing ManagementMisael Diaz HernandezNo ratings yet
- BS AU 050-3.2a-2002Document12 pagesBS AU 050-3.2a-2002amerNo ratings yet
- National IPR Policy 2016 An AnalysisDocument7 pagesNational IPR Policy 2016 An AnalysisjptripathyNo ratings yet
- Fabm Week 11 20fabm 121 Week 11 20Document3 pagesFabm Week 11 20fabm 121 Week 11 20Criscel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Johns 10e Irm ch15Document24 pagesJohns 10e Irm ch15Jacob WeiseNo ratings yet
- Unisys + C2P OPFDocument4 pagesUnisys + C2P OPFdebajyotiguhaNo ratings yet
- BS Delhi EnglishDocument20 pagesBS Delhi EnglishAshisNo ratings yet
- JAIBB - GFI - (Module-C) - CEO and Senior ManagementDocument15 pagesJAIBB - GFI - (Module-C) - CEO and Senior ManagementNaz MahoonNo ratings yet
- CIR v. Cebu Portland Cement Co. DIGESTDocument2 pagesCIR v. Cebu Portland Cement Co. DIGESTkathrynmaydeveza100% (2)
- Project ManagementDocument187 pagesProject Managementshashi puriNo ratings yet
- Film Concept Note SHEFEXILDocument2 pagesFilm Concept Note SHEFEXILBDTRNo ratings yet