Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resumen Ingles 2019-2020
Resumen Ingles 2019-2020
Uploaded by
Roberto AlcarazCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resumen Ingles 2019-2020
Resumen Ingles 2019-2020
Uploaded by
Roberto AlcarazCopyright:
Available Formats
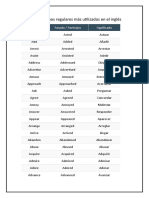
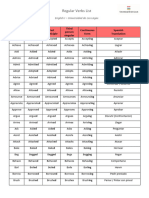
VERBOS REGULARES VERBOS REGULARES
Infinitivo Pasado Traducción Infinitivo Pasado Traducción
Act Acted Actuar Cargar /
Charge Charged
Sumar / Cobrar
Add Added
Añadir Clean Cleaned Limpiar
Aid Aidded Ayudar Climb Climbed Escalar
Arrest Arrested Arrestar Comb Combed Peinar
Assist Assisted Asistir Cover Covered Cubrir
Address Addressed Dirigirse Cry Cried Llorar
Advertise Advertised Anunciar Gatear /
Crawl Crawled
Amuse Amused Entretener Arrastrarse
Approach Approached Acercarse Dance Danced Bailar
Preguntar / Dress Dressed Vestir
Ask Asked
Pedir Soltar / Dejar
Dropp Dropped
Acompany Accompanied Acompañar caer
Accustom Accustomed Acostumbrar Die Died Morir
Estar de Declare Declared Declarar
Agree Agreed
acuerdo Delay Delayed Tardar
Annoy Annoyed Molestar Deliver Delivered Entregar
Answerd Answered Preguntar Deny Denied Negar
Appeal Applealed Atraer Dine Dined Cenar
Appear Appeared Aparecer Dry Dried Secar
Arreglar / Enjoy Enjoyed Disfrutar
Arrange Arranged
Ordenar Engage Engaged Comprometer
Arrive Arrived Llegar Envy Envied Envidiar
Board Boarded Abordar Express Expressed Expresar
Balance Balanced Equilibrado Exclaim Exclaimed Exclamar
Banish Banished Desterrar Explain Explained Explicar
Bark Barked Ladrar Fracasar /
Fail Failed
Bless Blessed Bendecir Fallar
Brush Brushed Cepillar Fasten Fastened Abrochar
Behave Behaved Comportarse Archivar /
File Filed
Belong Belonged Pertenecer Guardar
Suplicar / Fill Filled Llenar
Beg Begged
Mendigar Echar del
Boil Boiled Hervir Fire Fired trabajo /
Breathe Breathed Respirar Disparar
Complete Completed Completar Follow Followed Seguir
Consist Consisted Consistir Frighten Frightened Espantar
Count Counted Contar Fry Fried Freir
Close Closed Cerrar Finish Finished Terminar
Cook Cooked Cocinar Fish Fished Pescar
Crash Crashed Chocar Arreglar /
Fix Fixed
Call Called Llamar Solucionar
Care Cared Cuidar Gain Gained Ganar
Carry Carried Llevar Guess Guessed Adivinar
Change Changed Cambiar Help Helped Ayudar
Check Checked Comprobar Happen Happened Suceder
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 1
VERBOS REGULARES VERBOS REGULARES
Infinitivo Pasado Traducción Infinitivo Pasado Traducción
Desear / Report Reported Informar
Hope Hoped
Esperar Solicitar /
Request Requested
Hurry Hurried Apurar(se) Pedir
Imagine Imagined Imaginar Rest Rested Descansar
Iron Ironed Planchar Reach Reached Alcanzar
Judge Judged Juzgar Rehusar /
Refuse Refused
Kiss Kissed Besar Negarse
Kill Killed Matar Raise Raised Levantarse
Laugh Laughted Reir Rain Rained Llover
Leak Leaked Gotear Matricularse /
Register Registered
Like Liked Gustar Registrarse
Cerrar con Recive Recived Recibir
Lock Locked
llave Permanecer /
Look Looked Mirar Remain Remained Quedarse /
Marcar / Sobrar
Mark Marked
Señalar Remember Remembered Recordar
Miss Missed Extrañar Repair Repaired Reparar
Manage Managed Manejar Require Required Requerir
Marry Married Casar(se) Reservar /
Reserve Reserve
Massage Massaged Masajear Guardar
Measure Measured Medir Row Rowed Remar
Move Moved Mover Return Returned Volver
Observe Observed Observar Search Searched Buscar
Offer Offered Ofrecer Save Saved Salvar
Open Opened Abrir Settle Settled Establecer
Order Ordered Ordenar Sign Signed Firmar
Llamar por Smile Smiled Sonreír
Phone Phoned
teléfono Snow Snowed Nevar
Plan Planned Planear Spill Spilled Derramar
Tocar un Permanecer /
Stay Stayed
Play Played Instrumento / Quedarse
Jugar Study Studied Estudiar
Prefer Prefered Preferir Suffer Suffered Sufrir
Prepare Prepared Preparar Swallow Swalloed Tragar
Pull Pulled Tirar Slip Slipped Resbalar
Park Parked Estacionar Smoke Smoked Fumar
Pass Passed Pasar Detener /
Stop Stopped
Pick Picked Recoger Parar
Please Pleased Complacer Cambiar /
Switch Switched
Polish Polished Pulir Accionar
Practise Practised Pulir Stretch Stretched Estirar
Promise Promised Prometer Hablar /
Talk Talked
Pronounce Pronounced Pronunciar Conversar
Punish Punished Castigar Thank Thanked Agradecer
Push Pushed Empujar Touch Touched Tocar / Palpar
Repear Repeated Repetir Trap Trapped Atrapar
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 2
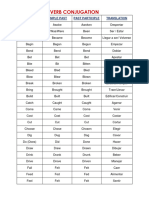
VERBOS REGULARES VERBOS IREGULARES
Infinitivo Pasado Traducción Infinitivo Pasado Participio Traducción
Cansar / Arise Arose Arisen Surgir
Tire Tired
Fatigar Awake Awoke Awoken Despertar(se)
Train Trained Entrenar Bear Bore Borne Soportar
Travel Traveled Viajar Beat Beat Beaten Golpear
Trouble Troubled Molestar Convertirse
Become Became Become
Try Tried Intentar en
Turn Turened Girar Begin Began Begun Empezar
Unpack Unpacked Desempacar Bend Bent Bent Doblar(se)
Use Used Usar Bet Bet Bet Apostar
Visit Visited Visitar Bid Bid Bid Pujar
Wait Waited Esperar Bind Bound Bound Encuadernar
Querer / Bite Bit Bitten Morder
Want Wanted
Requerir Bleed Bled Bled Sangrar
Walk Walked Caminar Blow Blew Blown Soplar
Wash Washed Lavar Break Broke Broken Romper
Observar / Breed Bred Bred Criar
Watch Watched
Mirar Bring Brought Brought Traer
Desear / Build Built Built Construir
Wish Wished
Anhelar Burn Burnt Burnt Quemar(se)
Work Worked Trabajar Burst Burst Burst Estallar
Wrap up Wrapped up Envolver Buy Bought Bought Comprar
Wreck Wrecked Naufragar Cast Cast Cast Tirar
Warm Warmed Calentar Catch Caught Caught Coger
Warn Warned Advertir Choose Chose Chosen Elegir
Water Watered Regar Cling Clung Clung Aferrarse
Weigh Weighed Pesar Come Came Come Venir
Whistle Whistled Silbar Cost Cost Cost Costar
Creep Crept Crept Arrastrar
Cut Cut Cut Cortar
Deal Dealt Dealt Tratar
Dig Dug Dug Cavar
Do Did Done Hacer
Draw Drew Drawn Dibujar
Dream Dreamt Dreamt Soñar
Drink Drank Drunk Beber
Drive Drove Driven Conducir
Eat Ate Eaten Comer
Fall Fell Fallen Caer(se)
Feed Fed Fed Alimentar
Feel Felt Felt Sentir(se)
Fight Fought Fought Pelear
Find Found Found Encontrar
Flee Fled Fled Huir
Fly Flew Flown Volar
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 3
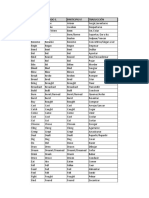
VERBOS IREGULARES VERBOS IREGULARES
Infinitivo Pasado Participio
Traducción Infinitivo Pasado Participio Traducción
Forbid Forbade Forbidden
Prohibir Run Ran Run Correr
Forget Forgot Forgotten
Olvidar(se) Saw Sawed Sawn Serrar
Forgive Forgave Forgiven
Perdonar Say Said Said Decir
Freeze Froze Frozen
Helar(se) See Saw Seen Ver
Get Got Got Conseguir Seek Sought Sought Buscar
Give Gave Given
Dar Sell Sold Sold Vender(se)
Go Went GoneIrse Send Sent Sent Enviar
Grind Ground Ground
Moler Set Set Set Poner
Grow Grew Grouwn
Crecer Sew Sewed Sewn Coser
Hang Hung HungColgar Shake Shook Shaken Agitar
Haber / Shear Sheared Shorn Esquilar
Have Had Had
Tener Shine Shone Shone Brillar
Hear Heard Heard Esuchar Shoot Shot Shot Disparar
Esconder Show Showed Shown Mostrar
Hide Hid Hidden
(se) Shrink Shrank Shrunk Encoger(se)
Hit Hit Hit Golpear Shut Shut Shut Cerrar(se)
Hold Held Held Agarrar(se) Sing Sang Sung Cantar
Hurt Hurt Hurt Hacer Daño Sink Sank Sunk Hundir(se)
Keep Kept Kept Guardar Sit Sat Sat Sentarse
Kneel Knelt Knelt Arrodillarse Sleep Slept Slept Dormir
Saber / Slide Slid Slid Resbalar
Know Knew Known
Conocer Smell Smelt Smelt Oler
Lay Laid Laid Poner Sow Sowed Sown Sembrar
Lead Led Led Llevar Speak Spoke Spoken Hablar
Lean Leant Leant Apoyarse Speed Sped Sped Acelerar
Leap Leap Leap Brincar Spell Spelt Spelt Deletrear
Learn Learnt Learnt Aprender Gastar /
Spend Spent Spent
Leave Left Left Dejar Pasar
Lend Lent Lent Prestar Spill Spilt Spilt Derramar
Let Let Let Permitir Spit Spat Spat Escupir
Lie Lay Lain Echarse Split Split Split Hender
Encender Spoil Spoilt Spoilt Estropear(se)
Light Lit Lit
(se) Spread Spread Spread Extender(se)
Lose Lost Lost Perder Stand Stood Stood Estar de pie
Make Made Made Hacer Steal Stole Stolen Robar
Mean Meant Meant Significar Stick Stuck Stuck Pegar(se)
Encontrar Stink Stank Stunk Apestar
Meet Met Met
(se) Strike Struk Struk Golpear
Overcome Overcame Overcome Vencer Strive Strove Striven Esforzarse
Pay Paid Paid Pagar Swear Swore Sworn Jurar
Put Put Put Poner Sweep Swept Swept Barrer
Read Read Read Leer Swim Swam Swum Nadar
Ride Rode Ridden Montar Take Took Taken Tomar(se)
Ring Rang Rung Sonar Teach Taught Taught Enseñar
Rise Rose Risen Levantarse Tear Tore Torn Romper(se)
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 4
VERBOS COMPUESTOS VERBOS COMPUESTOS
Break down Averiarse, estropearse Speed up Acelerar, darse prisa
Break up Romper una relación Stand for Significar
Call off Cancelar, suspender Stand out Destacar
Call out Anunciar, gritar Stand up for Defenderse
Come back Regresar, volver Start out with Empezar con
Come down on Ser duro, estricto Start up Encender, iniciar
Come up with Proponer, ocurrirse Take after Parecerse, salir a
Cut back on Recortar, reducir Take off Empezar a tener éxito
Drop out of Dejar una actividad Take on Contratar
End up Terminar Take part in Participar en
Feel like Apetecer, tener ganas de Talk back Contestar mal, replicar
Fill in Rellenar un documento Talk down to Hablar con superioridad
Find out Averiguar, descubrir Talk into Convencer de que se haga algo
Fit in Encajar, adaptarse Talk out of Convencer de que no se haga
Get along Llevarse bien Talk over Hablar sobre, discutir sobre
Get back Regresar, recuperarse Try on Probarse
Get by Arreglarselas, apañarselas Turn back Regresar, volver
Get out Bjarse de, salir Turn down Rechazar, bajar el volumen
Get together Reunirse, juntarse Turn in Entregar
Give up Darse por vencido, abandonar Turn into Convertir en
Go out with Salir con alguien Turn off Apagar, desenchufar aparato
Grow up Crecer, criarse Turn on Encender aparato
Hand out Repartir, distribuir Turn out Resultar, asistir, acudir
Hang out Pasar el tiempo Turn to Acudir a alguien
Keep at Preservar, insistir en Turn up Subir volumen
Lie down Tumbarse Watch out Tener cuidado
Live up to Estar a la altura de, cumplir Work out Funcionar
Log in Iniciar la sesión Write down Apuntar, anotar
Log out Cerrar, salir de la sesión Admit to Culpable de
Look after Cuidar a/de , Estar al cuidado a Agree on/with Estar de acuerdo en/con
Look for Buscar Aim to Tener el objetivo de
Look forward to Esperar con ansia, desear Appel to Gustar, atraer a
Look out Tener cuidado Appear in Aparecer en
Look out over Mirar desde arriba Argue with Discutir con
Look up Buscar información Arrive at Llegar a un lugar
Look up to Admirar Arrive in Llegar a una ciudad o país
Pass around Pasar de unos a otros Believe in Creer en
Pick up Coger, recoger, ir a buscar Belong to Pertenecer a
Plough into Estrellarse, chocar contra Break up with Separarse de, romper con
Point out Señalar Dream of Soñar con, imaginarse
Put off Aplazar, posponer Forget about Olvidarse de
Put on Montar, ponerse ropa Listen to Escuchar a
Run away Escaparse, marcharse Rely on Confiar en
Run out of Quedarse sin Remind of Recordar
Run over Atropellar Search for Buscar
Set up Crear, construir Succeed in Tener éxito, triunfar en
Show off Presumir Switch to Cambiar a
Show up Aparecer, llegar Talk about Hablar con
Sit down Sentarse Chance of Oportunidad de
Slow down Reducir la velocidad, frenar Way of Forma, modo de
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 5
VOCABULARIO
PROFESIONES
Accountant Contable Actor / Actress Actor / Actriz Air hostess Azafata de avión
Architect Arquitecto Archaeologist Arqueólogo Astronaut Astronauta
Baker Panadero Biologist Biologo/a Bricklayer Albañil
Butcher Carnicero Bus driver Conductor … Caretaker Portero
Carpenter Carpintero Cashier Cajero/a Cleaner Limpiador/a
Clown Payaso Cobbler Zapatero Cook Cocinero
Consultant Consultor Chef Cocinero prof. Chemist Químico, farma.
Dancer Bailarín Decorator Decorador Dentist Dentista
Designer Diseñador Doctor Médico/a Dressmaker Modista
Dustman Basurero Economist Economista Electrician Electricista
Engineer Ingeniero Farmer Granjero Fireman Bombero
Fisherman Pescador Florist Florista Fruiterer Frutero
Gardener Jardinero Hairdresser Peluquero/a Housewife Ama de casa
Hunter Cazador Jeweller Joyero/a Journalist Periodista
Judge Juez Lawyer Abogado/a Librarian Bibliotecario/a
Life guard Socorrista Lorry driver Camionero Mailman Cartero
Mechanic Mecánico Meteorologist Meterólogo Miner|Sailor Minero/a
Model Modelo Monk Monje Nanny Niñera
Nun Monja Nurse Enfermero/a Nursemaid Niñera
Painter Pintor Office worker Oficinista Pastry cook Repostero
Physicist Físico Pharmacist Farmaceútico Plumber Fontanero
Policeman Policia Photographer Fotógrafo Politician Político
Priest Cura Professor Profesor univ. Programmer Programador
Psychiatrist Psiquiatra Psychologist Psicólogo/a Receptionist Recepcionista
Salesman Vendedor Researcher Investigador Scientist Científico
Secretary Secretario Shop assistant Dependiente/a Singer Cantante
Sportsman Deportista Surgeon Cirujano Taxi driver Taxista
Teacher Profesor Truck driver Camionero Vet Veterinario
Waiter Camarero Waitress Camarera Writer Escritor
VOCABULARIO
DÍAS DE LA SEMANA
Monday Lunes Tuesday Martes Wednesday Miércoles
Thursday Jueves Friday Viernes Saturday Sábado
Sunday Domingo
VOCABULARIO
MESES DEL AÑO
January Enero February Febrero March Marzo
April Abril May Mayo June Junio
July Julio August Agosto September Septiembre
October Octubre November Noviembre December Diciembre
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 6
VOCABULARIO
MIEMBROS DE LA FAMILIA
Mother | Mom Mamá Father | Dad Papá Parents Padres
Son Hijo Daughter Hija Brother Hermano
Sister Hermana Siblings Hermanos Aunt Tía
Uncle Tío Grandfather Abuelo Grandmother Abuela
Grandparents Abuelos Cousin Primo/a Nephew Sobrino
Niece Sobrina Mother-in-law Suegra Father-in-law Suego
VOCABULARIO
ADJETIVOS
Brave Valiente Serious Serio/a Helpful Servicial
Loving Amoroso Shy Tímido/a Selfish Egoísta
Sincere Sincero/a Trustworthy Confiable Laidback Relajado
Honest Honesto Stubborn Terco/a Angry Enfadado
Asleep Dormido Awake Despierto Bad Malo
Beautiful Precioso Bright Brillante Cheap Barato
Clean Limpio Clear Claro Cold Frío
Cool Fresco Cruel Cruel Deep Profundo
Delicate Delicado Differente Diferente Dirty Sucio
Dry Seco Early Temprano Exhausted Agotado
False Falso Far Lejos Fat Gordo
Feeble Débil Flat Llano Foolish Estúpido
Free Libre Full Lleno Generous Generoso
Good Bueno Great Estupendo Handsome Atractivo
Happy Feliz Hard Duro Healthy Saludable
Heavy Pesado Hight Alto Hollow Hueco
Hot Caliente Huge Enorme Hungry Hambriento
Light Ligero Long Largo Loud Ruidoso
Lovely Bonito Mean Tacaño Messy Desordenado
Natural Natural Narrow Estrecho Near Cerca
Necessary Necesario New Nuevo Old Viejo
Open Abierto Opposite Contrario Poor Pobre
Private Privado Quick Rápido Quiet Tranquilo
Ready Preparado Rich Rico Right Correcto
Rough Áspero Sad Triste Safe Seguro
Serious Serio Sharp Afilado Short Corto
Shut Cerrado Simple Simple Smooth Delicado
Soft Suave Special Especial Spicy Picante
Steep Empinado Sticky Pegajoso Straight Recto o Directo
Strange Extraño Strong Fuerte Sudden Repentino
Sweet Dulce Thick Grueso Thin Delgado
Tight Ajustado Tired Cansado True Verdadero
Ugly Feo Violent Violento Warm Caluroso
Weak Débil Wet Húmedo Wide Ancho
Wise Sabio Wrong Erróneo Young Jóven
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 7
CONECTORES CONECTORES
CONSTRUIR UN ARGUMENTO DAR EJEMPLOS
In the first place En primer lugar For example Por ejemplo
First of all Antes que nada For instance Por ejemplo
To start with Para empezar Such as Tal como
At first sight A primera vista That is Es decir
Secondly En segundo lugar ESTABLECER UN CONTRASTE
In the second place En segundo lugar
However Sin embargo
Finally Por último Nevertheless No obstante
Lastly Por último On the contrary Por el contrario
In conclusion Para concluir Instead En cambio
Although Aunque
Whereas Mientras que
EXPRESAR REALIDADES On the hand Por una parte
On the other hand Por otra parte
Despite of A pesar de
As a matter of fact De hecho A pesar del hecho
In fact De hecho Despite the fact that
que
Actually En realidad In contrast to Por el contrario
Really En realidad
MODIFICAR LO QUE SE ESTA
EXPR. CAUSAS Y RESULTADOS DICIENDO
Because of this/that A causa de esto/eso To a certain extent Hasta cierto punto
Due to Debido a More or less Más o menos
For this/that reason Por esta/esa razón At least Al menos
Esa es la razón por Especially Especialmente
That´s way In particular En particular
la que…
Therefore Por lo tanto Above all Sobre todo
As a result Como resultado On the whole En general
Consequently En consecuencia In general En general
For this reason Por ese motivo Basically Básicamente
Essentially Esencialmente
EXPR. ALGO DE OTRO MODO EXPR. CAUSAS Y RESULTADOS
Likewise / Similar to Similar a esto…
I mean Quiero decir
No sólo / sino
In other words En otras palabras Not only / but also
también
In short En resumen
In comparison to… En comparación con
Compared to Comparado con
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 8
CONECTORES CONECTORES
ENFATIZAR LO QUE SE QUIERE OTROS
DECIR
And so on Etcétera
By the way A propósito
There is no doubt No hay duda de que
To be honest A decir verdad
that
To tell the truth A decir verdad
It´s important to Es importante
mention mencionar (qué)
It´s important to Es importante RESUMIR LO QUE SE HA DICHO
highlight señalar (qué)
In all En total
REFERIRSE A ALGO O ALGUIEN In short En resumen
In brief En resumen
In conclusion Para concluir
With regards to En relación a… To sum up Para resumir
As far as… is En cuanto a… se To summarize Para resumir
concerned refiere On the whole En general
Finalmente / Con el
Finally / Eventually
tiempo
EXPRESAR UNA OPINIÓN Last but not least Por último
PERSONAL Una vez
All things considered
considerando ésto
In my opinión En mi opinión
In my view En mi opinión INDICADORES DE TIEMPO
From my point of Desde mi punto de
view vista
Personally Personalmente First of all Primero
As far as I´m Por lo que a mí Next / Then Luego
concerned respecta After that Después
Basically Básicamente While Mientras
Especially Especialmente In the meantime Mientras tanto
In particular En particular Suddenly De repente
Above all Sobre todo Finally Finalmente
On the whole En general In the end Al final
In general En general
I think / believe that Pienso / Creo que
I agree with Estoy de acuerdo
I disagree with No estoy de acuerdo
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 9
QUESTIONS
WHO = QUIÉN
Se usa WHO cuando se refiere a personas
Who is the best football player in the world? ¿Quién es el mejor futbolista en el mundo?
Who are your best friends? ¿Quién es tu mejor amigo?
Who is that strange guy over there? ¿Quién es esa persona tan rara de ahí?
WHERE = DÓNDE
Se usa WHERE cuando nos referimos a un lugar
Where is the library? ¿Dónde está la biblioteca?
Where do you live? ¿Dónde vives?
Where are my shoes? ¿Dónde están mis zapatillas?
WHEN = CÚANDO
Se usa WHEN cuando nos referimos a tiempo
When do the shops open? ¿Cuándo abren las tiendas?
When is his birthday? ¿Cuándo es su cumpleaños?
When are we going to finish? ¿Cuándo vamos a acabar?
WHY = POR QUÉ
Se usa WHY cuando queremos una explicación
Why do we need a nanny? ¿Por qué necesitamos una niñera?
Why are they always late? ¿Por qué siempre llegan tarde?
Why does he complain all the time? ¿Por qué se queja todo el tiempo?
La respuesta a un Why empieza por Because {Porque…}
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 10
QUESTIONS
WHAT = QUÉ o CÚAL
WHAT se usa cuando queremos saber algo especifico
What is your name? ¿Cuál es tu nombre?
What is her favourite colour? ¿Cuál es su color favorito?
What time is it? ¿Qué hora es?
What do you want know? ¿Qué quieres ahora?
WHICH = CUALES
Se usa WHICH cuando hay que elegir
Which drink did you order the rum or the beer? ¿Qué bebida has pedido Ron o Cerveza?
Which day do you prefer for a meeting today or
¿Qué día prefieres quedar Hoy o mañana?
tomorrow?
Which is better this one or that one? ¿Cuál es mejor Este o Aquel?
HOW = CÓMO
Se usa HOW para conocer como se hace algo
How do you cook paella? ¿Como cocinas la paella?
How does he know the answer? ¿Como conoce la respuesta?
How can I learn English quickly? ¿Como puedo aprender inglés rápido?
HOW MUCH para cosas que no se puedan contar
How much money will I need? ¿Cuánto dinero necesitaré?
HOW MANY para cosas que se puedan contar
How many days are there in April? ¿Cuántos días tiene Abril?
How many people live in this city? ¿Cuántas personas viven en la ciudad?
HOW OFTEN significa con cuanta frecuencia haces algo
How often do you visit your grandmother? ¿Con cuanta frecuencia visitas a tu abuela?
How often are you sick? ¿Con cuanta frecuencia enfermas?
HOW FAR significa Como de lejos o A que distancia
¿A qué distancia esta tu casa de la
How far is the university from your house?
universidad?
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 11
PREPOSICIONES [AT, ON, IN]
Se utiliza la preposición IN cuando se quiere indicar: “dentro de”, “en el interior de”
In my room
In the living room In the box
Espacios cerrados In a office Dentro de objetos In the book
In a hospital
In the kitchen
In the park
In London
Lugares con límites definidos In a Street Ciudades y países
In Germany
In the garden
In 2012 In the morning
Largos periodos de tiempo In December Partes del día In the afternoon
In Spring In the evening
Se utiliza la preposición ON cuando se quiere indicar: “posición”, “encima de”
On my birthday On Monday
Días especiales Días de la semana
On Christmas Day On Sunday
On the table On the right
Sobre superficies Direcciones
On the beach On the left
On the arm Partes del Medios de On a bus
Partes del cuerpo
On the head transporte On a plane
Haciendo ref. a alguna
Fin de semana On the weekend On the page 358
página especifica
Se utiliza la preposición AT cuando se quiere indicar: “junto a”, “al lado de”
At Natural museum
At home
Lugares comunes Lugares específicos At the Cambringe
At school
University
Sitios concretos de un At the door
Direcciones y domicilios At 03008 San Gabriel
establecimiento At the window
At the party At the top / botton
Citas y acontecimientos Posiciones
At the meeting At the front / back
Horas y momentos At 4:00 am At Christmas
Periodos vacacionales
determinados del día At midnight At Easter
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 12
PRONOMBRE PERSONALES
PRONOMBRE SUJETO
PERSONA SINGULAR PLURAL
1ª persona I We
2ª persona You You
3ª persona He / She / It They
PRONOMBRE COMPLEMENTO
PERSONA SINGULAR PLURAL
1ª persona Me Us
2ª persona You You
3ª persona Him / Her / It Them
PRONOMBRE POSESIVO
PERSONA SINGULAR PLURAL
1ª persona My Our
2ª persona Your Your
3ª persona His / Her / Its Their
PRONOMBRE REFLEXIVO
PERSONA SINGULAR PLURAL
1ª persona Myself Ourselves
2ª persona Yourself Yourselves
3ª persona Himself / Herself / Itself Themselves
EJEMPLOS PRONOMBRES PERSONALES
Can you help me? ¿Puedes ayudarme?
Give it a kick Dale una patada
This is my house Esta es mi casa
Don´t burn yourself! ¡No te quemes!
The cat scratched itself El gato se rascó
He can help them El puede ayudarles
Can you see us? ¿Nos puedes ver?
These are our suitcases Estas son nuestras maletas
I saw it myself Yo mismo lo vi
These are your seats Estos son vuestros asientos
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 13
PRESENT SIMPLE
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You go I/You do not (don´t) go Do I/you go?
He/She/It goes He/She/It does not (doesn´t) go Does he/she/it go?
We/You/They go We/You/They do not (don´t) go Do we/you/they go?
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I am asking I am (I´m) not asking Am I asking?
You are asking You are not (aren´t) asking Are you asking?
He/She/It is asking He/She/It is not (isn´t) asking Is he/she/it asking?
We/You /They are asking We/You/They are not (aren´t) asking Are we/you/they asking?
PAST SIMPLE
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You worked I/You did not (didn´t) work Did I/you work?
He/She/It worked He/She/It did not (didn ´t) work Did he/she/it work?
We/You/They worked We/You/They did not (didn ´t) work Did we/you/they work?
PAST CONTINUOUS
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I was running I was (wasn´t) not running Was I running?
You were running You were not (weren´t) running Were you running?
He/She/It was running He/She/It was not (wasn ´t) running Was he/she/it running?
We/You /They were running We/You/They were not (weren´t) running Were we/you/they running?
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You have eaten I/You have not (haven´t) eaten Have I/you eaten?
He/She/It has eaten He/She/It has not (hasn´t) eaten Has he/she/it eaten?
We/You/They have eaten We/You/They have not (haven´t) eaten Have we/you/they eaten?
PAST PERFECT SIMPLE
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You had fallen I/You had not (hadn´t) fallen Had I/you fallen?
He/She/It had fallen He/She/It had not (hadn´t) fallen Had he/she/it fallen?
We/You/They had fallen We/You/They had not (hadn´t) fallen Had we/you/they fallen?
FUTURE SIMPLE
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You will win I/You will not (won´t) win Will I/you win?
He/She/It will win He/She/It will not (won´t) win Will he/she/it win?
We/You/They will win We/You/They will not (won´t) win Will we/you/they win?
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 14
BE GOING TO
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I am going to eat I am not going to eat Am I going to eat?
You are going to eat You are not (aren´t) going to eat Are you going to eat?
He/She/It is going to eat He/She/It is not (isn ´t) going to eat Is he/she/it going to eat?
We/You /They are going to eat We/You/They are not (aren´t) going to eat Are we/you/they going to eat?
FUTURE PERFECT SIMPLE
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You will have lost I/You will not (won´t) have lost Will I/you have lost?
He/She/It will have lost He/She/It will not (won´t) have lost Will he/she/it have lost?
We/You/They will have lost We/You/They will not (won´t) have lost Will we/you/they have lost?
FUTURE CONTINUOUS
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You will be swimming I/You will not (won´t) be swimming Will I/you be swimming?
He/She/It will be swimming He/She/It will not (won´t) be swimming Will he/she/it be swimming?
We/You/They will be We/You/They will not (won´t) be
Will we/you/they be swimming?
swimming swimming
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You have been sleeping I/You have not (haven´t) been sleeping Have I/you been sleeping?
He/She/It have been
He/She/It has not (hasn´t) been sleeping Has he/she/it been sleeping?
sleeping
We/You/They have been We/You/They have not (haven´t) been
Have we/you/they been sleeping?
sleeping sleeping
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You had been studying I/You had not (hadn´t) been studying Had I/you been studying?
He/She/It had been
He/She/It had not (hadn´t) been studying Had he/she/it been studying?
studying
We/You/They had been We/You/They had not (hadn´t) been
Had we/you/they been studying?
studying studying
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I/You will have been
I/You will not have been sleeping Will I/you have been sleeping?
sleeping
He/She/It will have been
He/She/It will not have been sleeping Will he/she/it have been sleeping?
sleeping
We/You/They will have Will we/you/they have been
We/You/They will not have been sleeping
been sleeping sleeping?
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 15
USOS EJEMPLOS
The Earth rotates round its axis
Hablar sobre la verdad general y acciones
It rains a lot in autumn
permanentes (hechos)
I speak English and French
Hablar sobre acciones habituales He gets up at 8 o´clock every morning
PRESENT repetidas. They never listen to their teacher
SIMPLE
Para hablar sobre una acción futura
The train leaves at 3 tomorrow
planificada (un horario)
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
Always | Usually | Generally | Regulary | Ocasionally | Frecuently | Often | Sometimes |
Rarely | Seldom | Never At 1 o´clock | At night | In the morning | on Fridays | Every week |
Once a month | How often…?
USOS EJEMPLOS
Hablar sobre acciones que están sucediendo Look! The boys are playing football. Hurry up!
ahora, al momento de hablar. The train is coming
Para hablar sobre acciones que están
We are studying very hard. We have to
sucediendo ahora, pero no exactamente en
prepare for our exams.
PRESENT el momento de hablar
CONTINUOUS What are you doing on Saturday?
Para hablar sobre lo que ya se ha acordado
I am meeting my friend at the station. She is
hacer.
arriving at 8 pm
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
Now | Right now | At the momento | This year | At present | Today | These days | This month
| This evening | Tonight | Tomorrow | Next friday | Next week | Next year | Next …
USOS EJEMPLOS
Hablar sobre acciones realizadas en el I met my friend yesterday
pasado (con expresiones terminadas) Did you go to the seaside last summer?
Hablar sobre una sucesión de acciones He opened the door, switched on the light and fed
pasadas (historias) his cat
PAST SIMPLE
Para hablar sobre una acción futura He fell asleep while the teacher was explaining
planificada (un horario) new gramar rules
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
Yesterday | Last week | Last year | Two days ago | In 2007 | In 1980s | In the 18th century |
When | Then
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 16
USOS EJEMPLOS
Hablar sobre acciones que están Look! The boys are playing football. Hurry up! The
sucediendo ahora, al momento de hablar. train is coming
Para hablar sobre acciones que están
We are studying very hard. We have to prepare for
sucediendo ahora, pero no exactamente
our exams.
PRESENT en el momento de hablar
CONTINUOUS What are you doing on Saturday?
Para hablar sobre lo que ya se ha
I am meeting my friend at the station. She is
acordado hacer.
arriving at 8 pm
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
Now | Right now | At the momento | This year | At present | Today | These days | This month
| This evening | Tonight | Tomorrow | Next friday | Next week | Next year | Next …
USOS EJEMPLOS
Siempre está conectado con el presente y
lo único que importa aquí es el resultado: I have lost my keys. I can´t open the door.
el momento en que tuvo lugar la acción
no tiene importancia:
PRESENT
Hablar sobre una acción que se ha I have seen this film and I can discuss it with you
PERFECT terminado relacionada con el presente now
SIMPLE
Cuando los períodos de tiempo no están
Have you called you mother today?
terminados en el momento de hablar
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
Never | Ever | Already | Just | Yet | Recently | Lately | How long…? | For | Since | In recent
years
USOS EJEMPLOS
Denota una acción completada antes de She has already finished her work when he came
un cierto momento en el pasado but when i wrote the letter, i posted it
PAST
I had hardly done it when they came.
PERFECT Con las conjunciones (apenas / casi) +
No sooner had they arrived than it started to
SIMPLE cuando
rain
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
Already | By the time | After | Before | Until | Never | Just
USOS EJEMPLOS
I´ll call you tomorrow
Hablar sobre acciones futuras.
Mary will get a present next month
Para predecir el futuro (con
I think it will rain tomorrow
probablemente, espero, estoy seguro, me
FUTURE I don´t think the examen Will be very difficult
pregunto, creo, tal vez)
SIMPLE
Para expresar intención en el momento Do you like these shoes?
de la decisión •Yes, I´ll buy them
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
This evening | Later | In an hour | At 4 o´clock | Tomorrow | Soon | Next month | Next year |
In a few weeks | On 8th May
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 17
USOS EJEMPLOS
She Will have finished this work by 2 o´clock
FUTURE Denota una acción completada antes de tomorrow
PERFECT un momento definido en el futuro The film Will have already started by the time
SIMPLE we come. Hurry up!
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
By this time next week | By 3 o´clock | By the end of… | By then | By August | In four months
USOS EJEMPLOS
Para hablar sobre una acción en un
momento particular en el futuro. La I´ll be playing tennis at 10 am tomorrow.
FUTURE acción comenzará antes de ese momento, This time on Sunday I´ll be bathing in the sea.
CONTINUOUS pero no habrá terminado en ese When you arrive, he Will be waiting for you.
momento:
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
At this time tomorrow | Next… | On thursday | In the next decade
USOS EJEMPLOS
Para decir cuánto tiempo han estado las I´ve been learning English for six years
PRESENT cosas hasta ahora It´s been raining all day
PERFECT Para decir cómo hemos estado ocupando Yours hands are dirty
CONTINUOUS nuestro tiempo (hasta ahora) I´ve been painting the walls
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
For a year | Since 2002 | How long…? | All night | All morning | All day | All week
USOS EJEMPLOS
Denota una acción que comenzó antes de
un momento definido en el pasado, We could not go out because it had been raining
continua hasta ese momento y aún for two hours
PAST continuaba en ese momento
PERFECT Denota una acción que ya no estaba
CONTINUOUS ocurriendo en un momento definido en el The baby´s fase was red abd wet. He had been
pasado, pero que había estado en crying
progreso no mucho antes
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
For hours | Since last April | All morning | When | Until | Before
USOS EJEMPLOS
You Will have been waiting for more tan two
Denota una acción que comenzará antes hours when her plane finaly arrives
FUTURE de un momento definido en el futuro, In the fall I Will have been studying here for 2
PERFECT continuará hasta el momento y years
CONTINUOUS continuará en ese momento. He Will be tired when he arrives. He Will have
been travelling for 24 hours
EXPRESIONES PARA RECONOCER EL TIEMPO VERBAL
For
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 18
CONDICIONALES
TIPO 0 Se utiliza cuando el tiempo al que nos referimos es ahora o siempre y la situación es real y possible
If + Present Simple Presente Simple
If it rains the grass gets wet
Si llueve la hierba se moja
If you heat ice it melts
Si calientas hielo se derrite
TIPO 1 Condición y resultado possible. Nos referimos al presente o futuro cuando la situación es real
If + Present Simple Future Simple
If you don´t hurry you will miss the train
Si no te das prisa perderás el tren
If it rains you will get wet
Si llueve te mojarás
TIPO 2 Situación no real, condición hipotética. Puede ser hora o en cualquier momento
If + Past Simple Would + be + Participio o Continuous
If it rained you would get wet
Si lloviera/lloviese te mojarías
If I spoke Italian i would be working in Italy
Si hablara Italiano estaría trabajando en Italia
ADVERBIOS [ALREADY, JUST, STILL, YET]
“Already” se refiere a algo que ha pasado antes o más pronto de lo que se esperaba y es traducido como “ya”
They have already finished their homework Ya han acabado sus deberes
Jacob has already left work Jacob ya se ha ido del trabajo
The train has already arrived El tren ya ha llegado
“Just” se utiliza para acciones que han ocurrido hace poco tiempo y se traduce como “acabar de” o “justo”
I just ate, but I’m already hungry again Acabo de comer, pero ya tengo hambre de nuevo
Where’s Jacob? He’s just left ¿Dónde está Jacob? Acaba de irse
Beth has just moved to New York Beth acaba de trasladarse a Nueva York
“Yet” es usado para algo que esperábamos que sucediera, pero todavía no ha pasado
I’m really hungry. I haven’t eaten yet Tengo mucha hambre. Todavía no he comido
Jacob hasn’t left his job at the hospital yet Jacob todavía no ha salido de trabajar del hospit.
Have they finished their homework yet? ¿Ya han terminado sus deberes?
Has the train arrived yet? ¿Ya ha llegado el tren?
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 19
MODALES
“Can” indica habilidad o posibilidad. En estos casos puede ser traducido como “poder”
I can speak five languages Puedo hablar cinco idiomas
Bill and Tom can’t help you Bill y Tom no pueden ayudarte
It can be dangerous to drive if you are tired Conducir puede ser peligroso si estás cansado
Can they work late tonight? ¿Pueden trabajar hasta tarde esta noche?
“Could” indica posibilidad o habilidad en el pasado
Joe could speak Spanish when he was young Joe podía hablar español cuando era joven
You could pass the test if you studied Podrías pasar el examen si estudiaras
I couldn’t sleep last night No pude dormir anoche
Could you pass the salt please? ¿Podrías pasarme la sal por favor?
“May o Might” indica posibilidad en el futuro
You may leave if you like Puedes salir si quieres
I would bring an umbrella, it may rain later Llevaría un paraguas, puede llover más tarde
May I have a glass of water? ¿Podría tomar un vaso de agua?
It might be better to finish this now, rather than Tal vez sea mejor terminar esto ahora, en lugar
wait until tomorrow de esperar hasta mañana
“Will o Shall” significa voluntad o determinación
We will learn English Aprenderemos inglés
Will they find a cure for cancer? ¿Encontrarán una cura para el cáncer?
Chris shall be happy to see you Chris estará feliz de verte
Shall we meet at 10pm? ¿Quedamos a las 22h?
“Should o Ought to” indica una obligación o recomendación, se traduce como “deber”
I should call my parents more often Debería llamar a mis padres más a menudo
You shouldn’t work so hard No debería trabajar tan duro
Should we leave a tip? ¿Deberíamos dejar una propina?
They ought to work less Deberían trabajar menos
“Must o Have to” indica una obligación, prohibición o necesidad
We must leave now or we will be late Tenemos que irnos ahora o llegaremos tarde
Must you always be late? ¿Siempre tienes que llegar tarde?
You have to read this book, it’s fantastic Tienes que leer este libro, es fantástico
It must be difficult to learn a new language as an Debe ser difícil aprender un idioma siendo
adult adulto
“Would” se usa para declarar una preferencia y para preguntar por algo educadamente.
She would like to go to New York someday Le gustaría ir a Nueva York algún día
I would like a beer and my wife would like a Me gustaría una cerveza y a mi mujer le gustaría
glass of wine please una copa de vino por favor
Would you help me please? ¿Me ayudas por favor?
When would you like to go to the movies? ¿Cuándo te gustaría ir al cine?
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 20
HÁBITOS
“Actually” se utiliza para hablar de hábitos en el pasado pero que ya no siguen se traduce como
SOLÍA
I actually think this a much better idea than the De hecho, creo que esta es una idea mucho mejor
mine que la mía
Was he actually avoiding conversation with his ¿Estaba realmente evitando la conversación con
father? su padre?
Her eyes actually were filled with tears. Sus ojos en realidad estaban llenos de lágrimas.
Actually, it was how my family always En realidad, así fue como mi familia siempre
celebrated Christmas. celebraba la Navidad.
They hadn't actually settled anything Ellos en realidad no habían resuelto nada
“Used to” se utiliza para hablar de hábitos en el pasado pero que ya no siguen se traduce como
SOLÍA
I used to travel a lot before I had children Solía viajar mucho antes de tener hijos
I didn't use to travel a lot before I had children No solía viajar mucho antes de tener hijos
Did you use to travel a lot before I had children? ¿Solías viajar mucho antes de tener hijos?
“be used to” nos sirve para hablar de hábitos en el presente y a situaciones que son habituales o
normales para nosotros, se traduce como SOLER o ESTAR ACOSTUMBRADO
Sharon está acostumbrada a tener plazos
Sharon is really used to having tight deadlines
ajustados
Sharon no está acostumbrada a tener plazos
Sharon isn´t really used to having tight deadlines
ajustados
¿Está Sharon realmente acostumbrada a tener
Is Sharon really used to having tight deadlines?
plazos ajustados?
“get used to” se usa para hablar de situaciones a las que nos estamos adaptando y para enfatizar un
cambio de hábitos que nos supone un esfuerzo, se traduce como ACOSTUMBRARSE
I am getting used to not smoking and I feel much Me estoy acostumbrando a no fumar y me siento
better mucho mejor
Cuando me mudé a Londres, tuve que
When I moved to London, I had to get used to
acostumbrarme a pasar mucho tiempo para ir a
spending a lot of time to go anywhere
cualquier parte.
I won’t get used to the rain No me acostumbraré a la lluvia.
Did you get used to living in a town? ¿Te acostumbraste a vivir en un pueblo?
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 21
PASIVA
PRESENT SIMPLE
Peter writes books Books are written by Peter
PAST SIMPLE
Peter wrote books Books were written by Peter
FUTURE SIMPLE
Peter will write books Books will be written by peter
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Peter is writing books Books are being written by Peter
PAST CONTINUOUS
Peter was writting books Books were being written by Peter
PRESENT PERFECT
Peter has witten books Books have being written by Peter
PAST PERFECT
Peter had written books Books had been writting by Peter
GOING TO
Peter is going to write books Books are going to be written by Peter
CONDICIONAL
Peter would write books Books would be written by Peter
ESTILO INDIRECTO
PRESENT SIMPLE
He stays at a hotel, she said She said that he stayed at a hotel
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
He is staying at a hotel, she said She said that he was staying at a hotel
PAST SIMPLE
He stayed at a hotel, she said She said that he had stayed at a hotel
PAST CONTINUOUS
He was staying at a hotel, she said She said that he had been stayed at a hotel
PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE
He has stayed at a hotel, she said She said that he had stayed at a hotel
PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS
He has been staying at a hotel, she said She said that he had been staying at a hotel
PAST PERFECT SIMPLE
He had stayed at a hotel, she said She said that he had stayed at a hotel
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS
He had been staying at a hotel, she said She said that he had been staying at a hotel
FUTURE SIMPLE
He Will stay at a hotel, she said She said that he would stay at a hotel
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 22
ESTILO INDIRECTO (Cambios en los modales)
Can Could
May Might
Must / Have to Must / Had to
Will Would
ESTILO INDIRECTO (Cambios en palabras y expresiones)
Now Then
Today That day
Tonight That night
Yesterday The previous day / The day before
Last week The previous week / The week before
A month ago The previous month / The month before
Tomorrow The following day / The day after / The next day
Next week The following week / The week after
Here There
This That
These Those
PRONOMBRES DEMOSTRATIVOS
THIS ESTE/A/O I like this car Me gusta este coche
THAT ESE/A/O AQUEL/O/A I like that car Me gusta ese coche
También lo podemos
That pizza was
THAT utilizar para referirnos a Aquella pizza estaba riquísima
delicious
algo del pasado
THESE ESTOS/AS I like these cars Me gustan estos coches
THOSE ESOS/AS AQUELLOS/AS I like those cars Me gustan aquellos coches
ARTICULO INDEFINIDO
a Se utiliza con nombre que comienzan por consonante
an Se usa con nombre que comienzan por vocal
a book Un libro an animal Un animal
a pen Un bolígrafo an ice cream Un helado
a chair Una silla an example Un ejemplo
a girl Una chica an umbrella Un paraguas
Se utiliza a antes de las palabras que comienzan por las letras “u” o “eu” cuando se pronuncian
como “yu”
Se utiliza an con palabras que comienzan por “h” solo cuando no se pronuncia.
a university Una universidad an hour Una hora
EXCEPCIONES
a euro Un euro a hospital Un hospital
Roberto Alcaraz Machado | Inglés B1,B2,C1 23
You might also like
- Signing Naturally Student Workbook Units 1 6 EbookDocument61 pagesSigning Naturally Student Workbook Units 1 6 Ebookdouglas.snyder52896% (50)
- Untangling Blackness in Greek Antiquity - Sarah F. DerbewDocument278 pagesUntangling Blackness in Greek Antiquity - Sarah F. Derbewb2vrngm7rv100% (1)
- Vine's Complete Expository Dictionary of Old and New Testament Words: With Topical IndexFrom EverandVine's Complete Expository Dictionary of Old and New Testament Words: With Topical IndexRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- EnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 3CDocument1 pageEnglishFile4e Pre-Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 3CB Mc100% (1)
- Scheme of Work For Sofia: Online One-to-One Teaching Course OutlineDocument7 pagesScheme of Work For Sofia: Online One-to-One Teaching Course OutlineViktoria Lyamina75% (4)
- Language Interrupted Signs of Non Native Acquisition in Standard Language Grammars PDFDocument332 pagesLanguage Interrupted Signs of Non Native Acquisition in Standard Language Grammars PDFjuramentatdo00No ratings yet
- Inglés 2° Medio LISTA DE VERBOSDocument7 pagesInglés 2° Medio LISTA DE VERBOSangelesNo ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares en Inglés Los 200 Más UsadosDocument10 pagesVerbos Regulares en Inglés Los 200 Más UsadosElizabeth Perez henriquezNo ratings yet
- Verbos en InglesDocument8 pagesVerbos en InglesYoscairi LunaNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares en Ingles PDFDocument5 pagesLista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares en Ingles PDFomareldelcassetteNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle MeaninngDocument6 pagesIrregular Verbs: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle MeaninngDayanaNo ratings yet
- Verbos Pasadon, Regulares, Irregulares InglesDocument11 pagesVerbos Pasadon, Regulares, Irregulares InglesAlex Diego Rivera TorresNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Regulares Más Utilizados en El InglésDocument10 pagesLista de Verbos Regulares Más Utilizados en El InglésJosue GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos InglésDocument8 pagesLista de Verbos InglésDanielaNo ratings yet
- Significado Forma Simple Pasado Participio Pdo. /ed/: Regular VerbsDocument4 pagesSignificado Forma Simple Pasado Participio Pdo. /ed/: Regular VerbsGabriela SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares e Irregulares - InglisDocument4 pagesVerbos Regulares e Irregulares - InglisValeria del Carmen Rodríguez SanchezNo ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares en InglésDocument7 pagesVerbos Regulares en InglésAlyson MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lista de VerbosDocument3 pagesLista de VerbosSebastián MoralesNo ratings yet
- Apuntes de Ingles - VerbosDocument9 pagesApuntes de Ingles - VerbosJuan Francisco ValeroNo ratings yet
- Verbs List: Construir/edificarDocument3 pagesVerbs List: Construir/edificarDayana GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos (A Colores)Document5 pagesLista de Verbos (A Colores)Angel GuillenNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Por Letra InicialDocument44 pagesLista de Verbos Por Letra InicialDiego MammatusNo ratings yet
- Participio Pasado de Los Verbos Regulares e IrregularesDocument6 pagesParticipio Pasado de Los Verbos Regulares e IrregularesGloriaSanchezNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos (A Colores)Document4 pagesLista de Verbos (A Colores)jojiphoenixjoestarNo ratings yet
- 7 - Lista de Verbos - 3er. AñoDocument2 pages7 - Lista de Verbos - 3er. AñoMaría Isabel MontoroNo ratings yet
- Verbos RegularesDocument5 pagesVerbos RegularesSalvador Canedo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Past Forma BaseDocument5 pagesInfinitive Past Forma Basejoha_lizNo ratings yet
- List of Regular Verbs 2Document2 pagesList of Regular Verbs 2ap7104554No ratings yet
- Infinitive Simple Past Past Participle TranslationDocument5 pagesInfinitive Simple Past Past Participle TranslationSalome MaribelNo ratings yet
- Regular VerbsDocument7 pagesRegular VerbsGIANCARLO SILVA SOLORZANONo ratings yet
- List of VerbsDocument6 pagesList of VerbsTatiana Vanessa Altamirano ObandoNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Past Tense Past Participle Spanish TranslateDocument5 pagesInfinitive Past Tense Past Participle Spanish TranslateRosa RosNo ratings yet
- 4 The Students of The First Year Animal ScienceDocument6 pages4 The Students of The First Year Animal ScienceAbdoul Salam DIALLONo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs List: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle SpanishDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs List: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle SpanishFrancisco Cañada LopezNo ratings yet
- Verbs For The ActivitiesDocument4 pagesVerbs For The ActivitiesMiguel Angel Rodriguez GuerraNo ratings yet
- Lista Verbos Regulares Inglés6Document7 pagesLista Verbos Regulares Inglés6fuhrercarlNo ratings yet
- Listadeverbosregulares 121124192232 Phpapp01Document5 pagesListadeverbosregulares 121124192232 Phpapp01ADRIAN ARIEL COLQUE RAMOSNo ratings yet
- VerbosDocument6 pagesVerbosAntonioRamosNo ratings yet
- Verb ListDocument5 pagesVerb Listrosavelasco584No ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesIrregular VerbsmolinahuarialbertinaNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Regulares Más UsadosDocument5 pagesLista de Verbos Regulares Más Usadosrobxamar carrasquillaNo ratings yet
- Verbs Conjugation GuideDocument4 pagesVerbs Conjugation GuideBrañas Morales Saida FabiolaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Infinitive Form Simple Past Past Participle SpanishDocument4 pagesIrregular Verbs: Infinitive Form Simple Past Past Participle SpanishJonny FloresNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument10 pagesIrregular Verbscristobal cruzNo ratings yet
- Regular Verbs ListDocument5 pagesRegular Verbs ListlakarinaestontaNo ratings yet
- Eng 01Document2 pagesEng 01Richard Alvaro Iturriaga LunaNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesIrregular VerbsNoemí BeviáNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesList of Irregular VerbsLiz Estefany Pacompia ChambillaNo ratings yet
- Infinitivo Pasado S. Participio P. TraducciónDocument6 pagesInfinitivo Pasado S. Participio P. TraducciónNELSON BELTRAN SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares - CorregidoDocument4 pagesLista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares - CorregidoMiguel Angel Luis Tarazona100% (1)
- Lista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares CorregidoDocument4 pagesLista de Verbos Regulares e Irregulares CorregidoDeysi AFNo ratings yet
- Verbos IrregularesDocument2 pagesVerbos IrregularesgraicelysNo ratings yet
- Liste Verbes Reguliers AnglaisDocument7 pagesListe Verbes Reguliers AnglaisJorge Wilstermann100% (1)
- Verbs For 2018Document9 pagesVerbs For 2018Sofia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares InglésDocument5 pagesVerbos Irregulares InglésTeckelinoNo ratings yet
- Lista Verbos 4 Letras InglesDocument8 pagesLista Verbos 4 Letras InglesJaky Diaz PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs PORTDocument3 pagesIrregular Verbs PORTAna Alexandra MendesNo ratings yet
- List of The Most Useful Regular and Irregular Verbs 2Document1 pageList of The Most Useful Regular and Irregular Verbs 2medalpqpq100% (1)
- Lista de Verbos RegularesDocument3 pagesLista de Verbos RegularesLizeth LMNo ratings yet
- Regular Verbs #1Document4 pagesRegular Verbs #1jessymariana2006No ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares: Infinitivo Pasado Simple Participio Pasado SignificadoDocument7 pagesVerbos Regulares: Infinitivo Pasado Simple Participio Pasado SignificadoLeonel L. CoaquiraNo ratings yet
- Verbs Regular - IrregularDocument2 pagesVerbs Regular - IrregularNatalia Álvarez LazcanoNo ratings yet
- Regular Verbs ListDocument2 pagesRegular Verbs ListpriscilaNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Simple Past Past Participle SpanishDocument5 pagesInfinitive Simple Past Past Participle SpanishSandra Patricia Peña VelezNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesList of Irregular VerbsLaura RamosNo ratings yet
- Helen DoronDocument4 pagesHelen DoronLUNGU IulianaNo ratings yet
- Qudsia Liaquat: ContactDocument2 pagesQudsia Liaquat: ContactAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- CULTURAL EVENTS GUIDELINES Rev. 2019Document14 pagesCULTURAL EVENTS GUIDELINES Rev. 2019C-Jay ManingasNo ratings yet
- Predictable Writing: Reading Difficulties: A Brain-Friendly Approach, Published byDocument2 pagesPredictable Writing: Reading Difficulties: A Brain-Friendly Approach, Published byMary Joyce GarciaNo ratings yet
- (Sachphotos - Com) Cambridge Practice Tests For IELTS 7Document177 pages(Sachphotos - Com) Cambridge Practice Tests For IELTS 7Hoàng Nguyễn MạnhNo ratings yet
- Unlock 1 Review Test Unit 3Document2 pagesUnlock 1 Review Test Unit 3Emirhan YılmazNo ratings yet
- Archer - Lesson Plan - Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pagesArcher - Lesson Plan - Reading Comprehensionapi-622718695No ratings yet
- Uncover L1 Custom Extension Test Unit 01Document6 pagesUncover L1 Custom Extension Test Unit 01ChrisGalarzaNo ratings yet
- Object Pronouns: Activity TypeDocument2 pagesObject Pronouns: Activity TypeRobson LeiteNo ratings yet
- Test of Past Continous TenseDocument2 pagesTest of Past Continous Tensenguyenphuongthuy10012008No ratings yet
- Killing Me Softly - Santiago Montenegro 2Document2 pagesKilling Me Softly - Santiago Montenegro 2CRISTIAN SANTIAGO MONTENEGRO BARRERONo ratings yet
- Power Or: What Gives WordsDocument24 pagesPower Or: What Gives Wordssapna sinhaNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 5 - Q3 - W6Document5 pagesDLL - English 5 - Q3 - W6Dexter MacalelongNo ratings yet
- Visual Learning GRE Words VocabularyDocument230 pagesVisual Learning GRE Words VocabularyhonchoabhiNo ratings yet
- Sworn Statement of Declaration - RepatriationDocument2 pagesSworn Statement of Declaration - RepatriationNadia LomongoNo ratings yet
- O L2022 Application 05059Document2 pagesO L2022 Application 05059Krishsn DamithNo ratings yet
- A Plea Lay Literacy Illich NotesDocument2 pagesA Plea Lay Literacy Illich NotesJose Miguel Vargas PellicerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - UlisDocument13 pagesChapter 2 - UlisNgọc AnhNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Brainstorming On EFL Reading Comprehension - Tap Chi Dai Hoc Quoc Gia Ha NoiDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Brainstorming On EFL Reading Comprehension - Tap Chi Dai Hoc Quoc Gia Ha NoiYen TranNo ratings yet
- As Soon AsDocument3 pagesAs Soon AsDang Thuy HienNo ratings yet
- Speech Acts in English Language Teaching: Written By: Ridha IlmaDocument14 pagesSpeech Acts in English Language Teaching: Written By: Ridha IlmaPhương ThanhNo ratings yet
- Hansgeorg Gadamer Hermeneutics Between History and Philosophythe Selected Writings of Hansgeorg Gadamer Volume IDocument385 pagesHansgeorg Gadamer Hermeneutics Between History and Philosophythe Selected Writings of Hansgeorg Gadamer Volume Imatlaporte100% (1)
- Simple Present Worksheet Versión 2Document2 pagesSimple Present Worksheet Versión 2daniela cardonaNo ratings yet
- English Project My Pen Pal - Example of Application FormDocument2 pagesEnglish Project My Pen Pal - Example of Application FormLucy LeonNo ratings yet
- Year 5 English SampleDocument9 pagesYear 5 English Sampletolstoy1976No ratings yet