Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New Quiz For Lab 9-29-23
New Quiz For Lab 9-29-23
Uploaded by
tcosteen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
New Quiz for Lab 9-29-23(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageNew Quiz For Lab 9-29-23
New Quiz For Lab 9-29-23
Uploaded by
tcosteenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
ELC 131 Name____________________________
Lab Quiz, 9/28/23
1. When connecting a voltmeter into a dc circuit,
(A) polarity is not important. (B) the meter is connected in series with the circuit.
(C) the voltmeter is connected in parallel. (D) the negative meter lead connects to the most
positive point in the circuit.
2. When a voltage is indicated at some point in a circuit, the actual meaning is
(A) the voltage between that point and a reference point. (B) the voltage WITHOUT reference to
any other point. (C) always the voltage between that point and the positive terminal of the source.
(D) the voltage between that point and ANY other point.
3. In a series circuit, the current is
(A) greater in the high resistance components. (B) the same in all parts of the circuit. (C) the sum
of the branch currents. (D) greater in the low resistance components.
4, In a parallel circuit, the current
(A) is greatest in the highest resistance branch. (B) in each branch is added together to determine
the total current. (C) is the same in all parts of the circuit (D) is inversely proportional to the source voltage.
5. In a SERIES circuit, the source VOLTAGE
(A) is equal to the sum of the voltages across the components. (B) is applied DIRECTLY across each
component. (C) forces a DIFFERENT amount of current through each component. (D) is ALWAYS
divided equally among all components.
6. In a PARALLEL circuit, the source VOLTAGE
(A) is equal to the SUM of the voltages across the components. (B) appears across each
branch. (C) is inversely proportional to the resistance of each branch. (D) always forces the SAME
amount of current through each branch.
7. In a series circuit, the total resistance
(A) is less than the resistance of any individual resistor. (B) is inversely proportional to the amount of
source voltage. (C) is equal to the sum of the individual resistances. (D) increases when the circuit current
increases.
8. In a parallel circuit, the total resistance
(A) is less than the resistance of any branch. (B) is equal to the sum of the branch resistances.
(C) is greater than the resistance of any branch resistor. (D) increases when the circuit current
increases.
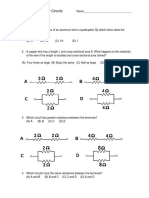
9. Referring to Figure 1 below, if the source voltage is increased from 30 volts to 60 volts,
(A) the total resistance reduces to one third its original value. (B) the voltages across R1 and R2
double. (C) the current through R1 doubles and the current through R2 is cut in half. (D) there is no
change in the circuit current.
10. In Figure 2, if R3 is INCREASED from 40 ohms to 120 ohms,
(A) the voltage across R3 decreases. (B) the current through R2 decreases. (C) the current
through R3 remains constant. (D) the current through R3 and the total current decrease.
You might also like
- BTF-ELAC Local Government Empowerment ProgramDocument10 pagesBTF-ELAC Local Government Empowerment ProgramAbdullah M. MacapasirNo ratings yet
- Business Vantage Listening Sample Paper 2 - Full TestDocument8 pagesBusiness Vantage Listening Sample Paper 2 - Full TestDaniel KottnauerNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuizDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice QuizMHLS68No ratings yet
- Task 5: Electric Circuits.: AssignmentDocument5 pagesTask 5: Electric Circuits.: AssignmentAli Al-AsadiNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choices. Choose The Best Answer. Encircle The Letter of Your ChoiceDocument3 pagesI. Multiple Choices. Choose The Best Answer. Encircle The Letter of Your ChoiceJohn Rey ComplezaNo ratings yet
- KKKKDocument4 pagesKKKKsinagNo ratings yet
- Encircle or Write Down The Letter of Correct Answer For Each Statement (1 Point Each)Document4 pagesEncircle or Write Down The Letter of Correct Answer For Each Statement (1 Point Each)Sonic HedgehogNo ratings yet
- Jaro Eric Quiz in DC CircuitsDocument6 pagesJaro Eric Quiz in DC CircuitstolisNo ratings yet
- Radian Academy:: Time: 60 Minutes. Maximum Marks: 30Document5 pagesRadian Academy:: Time: 60 Minutes. Maximum Marks: 30Eric Vidhya DharanNo ratings yet
- NA UNIT-1 BitsDocument7 pagesNA UNIT-1 BitsAnith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- BEE MCQ CH 2 Part 1Document6 pagesBEE MCQ CH 2 Part 1Ashmit RaghavNo ratings yet
- BEE MCQ CH 2 Part 1Document6 pagesBEE MCQ CH 2 Part 1Ashmit RaghavNo ratings yet
- Basic Ee 140 MCQDocument13 pagesBasic Ee 140 MCQBrandy BushNo ratings yet
- 7 Electrical Power and Lighting SystemsDocument27 pages7 Electrical Power and Lighting SystemsaguanoluNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Week 16 MC Review AnswersDocument11 pagesAP Physics 1 Week 16 MC Review AnswersAnonymous 2vwEXJNo ratings yet
- Solution - MCQ - AC FundamentalsDocument5 pagesSolution - MCQ - AC Fundamentalshod.eeNo ratings yet
- MCQ of ElectricityDocument10 pagesMCQ of ElectricityKhaled RabeaNo ratings yet
- Current and Circuits Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesCurrent and Circuits Practice ProblemsAnthony HuiNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument18 pagesElectricityrahulsenNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics - Chapter 3 Term 1Document64 pagesXii Physics - Chapter 3 Term 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Direct Current Circuit: Chelsea M. de Leon Date: JANUARY 22, 2021 Ph.D. in Science EdDocument4 pagesQuiz in Direct Current Circuit: Chelsea M. de Leon Date: JANUARY 22, 2021 Ph.D. in Science EdtolisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet # 7 Knowledge PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet # 7 Knowledge PDFSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Series DC CircuitsDocument13 pagesLecture 2 - Series DC CircuitsHassan Al MamunNo ratings yet
- AP Circuit MCQ With AnswerDocument22 pagesAP Circuit MCQ With Answeryash vijayNo ratings yet
- Electricity QPDocument13 pagesElectricity QPrishiop405No ratings yet
- PHY 108 Practice QuestionsDocument17 pagesPHY 108 Practice Questionsdavidubochi26No ratings yet
- 60 Top Most Network Theorems - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument10 pages60 Top Most Network Theorems - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersapjbalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Charge and CurrentDocument13 pagesCharge and CurrentAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- PHYS 106: Practical Physics II Second Semester: University of GhanaDocument7 pagesPHYS 106: Practical Physics II Second Semester: University of Ghanakaleab mebratuNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)Document7 pagesUnit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)aznblehtnNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 ElectDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 1 Electdavididosa40No ratings yet
- Science-10 Jayshree Periwal High School Practice Worksheet Physics Circuit Based Questions 2 MarkersDocument4 pagesScience-10 Jayshree Periwal High School Practice Worksheet Physics Circuit Based Questions 2 MarkersMihika MathurNo ratings yet
- Lab QuestionsDocument1 pageLab QuestionsKomal Singh SheemarNo ratings yet
- 11a-Circuits MC Practice ProblemsDocument37 pages11a-Circuits MC Practice Problemsminviking25No ratings yet
- 60 TOP MOST NETWORK THEOREMS - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument6 pages60 TOP MOST NETWORK THEOREMS - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answersrose maryNo ratings yet
- Class10 Electricity Module 3Document4 pagesClass10 Electricity Module 3Dr-Swarnima AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Series Circuits: Prepared By: Alexander T. Montero, Ree, RmeDocument45 pagesSeries Circuits: Prepared By: Alexander T. Montero, Ree, RmeMarc Jairro GajudoNo ratings yet
- The Equivalent ResistanceDocument9 pagesThe Equivalent ResistanceJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- CH 27-30Document69 pagesCH 27-30Richard Hammond50% (2)
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity (Book Solutions)Document22 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 - Electricity (Book Solutions)Purushottam KumarNo ratings yet
- Tta Study MaterialDocument18 pagesTta Study Materialasheokand172No ratings yet
- Assignment - 1Document2 pagesAssignment - 1Sushil NamoijamNo ratings yet
- Activity 4Document3 pagesActivity 4allen jierqsNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING MCQsDocument18 pagesBASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING MCQsVimal PalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Week16Document2 pagesWorksheet Week16iskenderbeyNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits/Network Analysis-Model QuestionsDocument32 pagesElectric Circuits/Network Analysis-Model Questionskumarreddy247No ratings yet
- Chose The Correct Answer Only: Subject: Basic Electrical Engineering Code: EE 101Document1 pageChose The Correct Answer Only: Subject: Basic Electrical Engineering Code: EE 101Bhumika Kedia XI C 9799No ratings yet
- Series CircuitsDocument9 pagesSeries CircuitsnajwaNo ratings yet
- NCERT ExamplerDocument18 pagesNCERT ExamplerGeetha.H.R 9th G.H.S.HonsigereNo ratings yet
- EEP1 Sample2 QPDocument10 pagesEEP1 Sample2 QPSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- CvvbitsDocument21 pagesCvvbitsvbharathi072No ratings yet
- Science 9-Circuit TestDocument3 pagesScience 9-Circuit TestkarlNo ratings yet
- Electric Current Circuits Practice ProblemsDocument14 pagesElectric Current Circuits Practice ProblemsSrihith MarakaNo ratings yet
- Segment 2 QB - AnswersDocument14 pagesSegment 2 QB - Answersavp sNo ratings yet
- Class-10 Electrycity MCQDocument10 pagesClass-10 Electrycity MCQNuman KhanNo ratings yet
- The Two Diode Bipolar Junction Transistor ModelDocument3 pagesThe Two Diode Bipolar Junction Transistor ModelAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical Engineering - MODULE 8 Part 2 - Series Parallel ConditionsDocument14 pagesElementary Electrical Engineering - MODULE 8 Part 2 - Series Parallel ConditionsRubdubRNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Reb 611Document76 pagesReb 611Adil KhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Discuss The System of Government of Africa Adopted by Ghana and South African IndependentDocument10 pagesAssignment Discuss The System of Government of Africa Adopted by Ghana and South African IndependentJeriel Meshack DankeNo ratings yet
- Ryanair Magazine August - September 2010Document168 pagesRyanair Magazine August - September 2010jman5000No ratings yet
- Osgi - Core 5.0.0 PFDDocument408 pagesOsgi - Core 5.0.0 PFDCarlos Salinas GancedoNo ratings yet
- Md. Hafizur Rahman Arfin: Education ExperienceDocument1 pageMd. Hafizur Rahman Arfin: Education ExperienceMohidul Islam HeeraNo ratings yet
- Infografía Jane JacobsDocument1 pageInfografía Jane JacobsKaren DíazNo ratings yet
- Online Challan Form1Document1 pageOnline Challan Form1Aashir BrothersNo ratings yet
- Intonation, Rhythm and Stress PDFDocument98 pagesIntonation, Rhythm and Stress PDFNagendra Venkat100% (4)
- BTP 1 Intro 121212024147 Phpapp01Document9 pagesBTP 1 Intro 121212024147 Phpapp01Devang ShahNo ratings yet
- Kelly: © 2019, Jo Kelly, To Be or Not To ActDocument5 pagesKelly: © 2019, Jo Kelly, To Be or Not To ActSebastián Baeza100% (1)
- Strategy & Transformation Diagrams (Volumes I & II)Document75 pagesStrategy & Transformation Diagrams (Volumes I & II)AnshulNo ratings yet
- Tullow Oil PLC 2020 Annual Report and AccountsDocument158 pagesTullow Oil PLC 2020 Annual Report and Accountsforina harissonNo ratings yet
- The Legend of Daragang Magayon: by Merito B. EspinasDocument1 pageThe Legend of Daragang Magayon: by Merito B. EspinasReu Amor AmorgandaNo ratings yet
- University of . College of .. School/Department of . Syllabus For Economics (Common Course)Document7 pagesUniversity of . College of .. School/Department of . Syllabus For Economics (Common Course)Malasa EjaraNo ratings yet
- Birla AlokyaDocument18 pagesBirla AlokyaanjaligargisbNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Skimming and ScanningDocument8 pagesMeeting 2 Skimming and ScanningDwi wanda SeptiyantiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal - Manajemen Digitalisasi - Meningkatkan Kunjungan Wisata Bah Koh Samed Island, Chumphon Province, ThailandDocument18 pagesJurnal - Manajemen Digitalisasi - Meningkatkan Kunjungan Wisata Bah Koh Samed Island, Chumphon Province, ThailandpernandusNo ratings yet
- Apollo and Daphne Whats Love Got To Do W PDFDocument1 pageApollo and Daphne Whats Love Got To Do W PDFGraceNo ratings yet
- An Outline of History of Linguistics 1Document24 pagesAn Outline of History of Linguistics 1Yára LevyNo ratings yet
- MPKDocument15 pagesMPKghaliyahalmiraNo ratings yet
- Oyster Mushroom Cultivation: Non-Sterilized Wheat StrawDocument0 pagesOyster Mushroom Cultivation: Non-Sterilized Wheat StrawEdu Ar DoNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Indian Oil Ltd.Document49 pagesFinancial Analysis of Indian Oil Ltd.manish.agrawal40% (5)
- Ford Alex3Document3 pagesFord Alex3Electroventica ElectroventicaNo ratings yet
- Rewrite These Sentences. Use The Words in Brackets Without Changing ThemDocument1 pageRewrite These Sentences. Use The Words in Brackets Without Changing Themscorbag100% (1)
- Question Bank SUBJECT: GSM (06EC844) Part-A: Unit 1 (GSM Architecture and Interfaces)Document6 pagesQuestion Bank SUBJECT: GSM (06EC844) Part-A: Unit 1 (GSM Architecture and Interfaces)Santhosh VisweswarappaNo ratings yet
- The Fargo Beat 10-21-10Document4 pagesThe Fargo Beat 10-21-10The Fargo BeatNo ratings yet
- Catalogo General PDFDocument626 pagesCatalogo General PDFKrlos A Guaillazaca GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Business Law S. Dishonour of ChequeDocument20 pagesBusiness Law S. Dishonour of ChequeJunishaNo ratings yet