Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anaesthesia
Anaesthesia
Uploaded by
Mohamed AdelCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockDocument7 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve BlockSyedMuhammadJunaidNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Important To SpeechDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves Important To SpeechMike SwiesNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic GanglionDocument33 pagesMandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic Ganglionwaniya irumNo ratings yet
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block: D. Abdullah Al NasserDocument23 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve Block: D. Abdullah Al NasserMira AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- Os 3Document11 pagesOs 3مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- Mandibular AnatomyDocument61 pagesMandibular AnatomyDeb SNo ratings yet
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockDocument4 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve BlockAnusha KurianNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Techniques of MandibleDocument10 pagesAnesthetic Techniques of MandiblealirezaNo ratings yet
- ENGanesthesiamanndibleDocument48 pagesENGanesthesiamanndibleRoxanaAnaHociungNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Mandibular NerveDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy Mandibular Nerveمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- By DR - Navindra Mentor: DR - FarisDocument63 pagesBy DR - Navindra Mentor: DR - FarisNavindra NaiduNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy - Trigeminal NerveDocument8 pagesApplied Anatomy - Trigeminal NervefrabziNo ratings yet
- BuccalDocument2 pagesBuccalFarhang Abdułła IsmahiłNo ratings yet
- LADocument93 pagesLAkaedeamira_113974100% (2)
- Inferior Alveolar TechniqueDocument8 pagesInferior Alveolar Techniquebalab2311No ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgeryDocument92 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgerySAMEENANo ratings yet
- 7 Infratemporal RegionDocument8 pages7 Infratemporal RegionNur Ain Faezah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Technique: Supraperiosteal InfiltrationsDocument11 pagesTechnique: Supraperiosteal Infiltrationsp_npsNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Nerve 2Document22 pagesMaxillary Nerve 2Sayed DrazNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument63 pagesMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument6 pagesMandibular NerveCatalina Stoicescu100% (1)
- Lecture of Temporal & InfratemporalDocument60 pagesLecture of Temporal & InfratemporalShahd YehiaNo ratings yet
- 11 PharynxDocument8 pages11 PharynxNur Ain Faezah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Injection TechniquesDocument91 pagesMandibular Injection TechniquesRobins Dhakal100% (3)
- Fracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Document67 pagesFracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Arafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- Blank Book 2Document4 pagesBlank Book 2Rawand Ra'ed D.AlshawabkehNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument2 pagesTrigeminal NerveVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- 8 Mandibular NerveDocument6 pages8 Mandibular NerveAaaNo ratings yet
- External Ear-AclandDocument1 pageExternal Ear-Aclanddale barizoNo ratings yet
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks MandibleDocument34 pagesAnatomical Landmarks Mandibleوا إسلاماهNo ratings yet
- (English) Thoracic Nerves (Intercostal + Subcostal) - Anatomy (DownSub - Com)Document10 pages(English) Thoracic Nerves (Intercostal + Subcostal) - Anatomy (DownSub - Com)shakila.soleymaniyanNo ratings yet
- Mouth, 10 Nov 2006Document2 pagesMouth, 10 Nov 2006api-19921479No ratings yet
- Local Anaesthesia & Xla Osce PrepDocument9 pagesLocal Anaesthesia & Xla Osce PrepVictoria MedfordNo ratings yet
- GRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongDocument9 pagesGRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongRainier Raul Echipare100% (1)
- Piano Hand TechniqueDocument12 pagesPiano Hand TechniquevaneriolamaNo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial NerveDocument5 pages12 Cranial NerveOwing ConejoNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Local Anesthesia 1: ReviewDocument13 pagesTechniques of Local Anesthesia 1: ReviewMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary 1Document4 pagesMaxillary 1Farhang Abdułła IsmahiłNo ratings yet
- Applied Surgical AnatomyDocument52 pagesApplied Surgical AnatomyEmad AdelNo ratings yet
- Diagram of The Ear and Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesDiagram of The Ear and Its Functionsmcheche12No ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument20 pagesMuscles of Facial ExpressionHarsha Reddy50% (2)
- Anatomy of Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal NerveNicky RomeoNo ratings yet
- The Infratemporal FossaDocument5 pagesThe Infratemporal FossaxxyumeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks MandibleDocument34 pagesAnatomical Landmarks MandibleDocshiv Dent100% (2)
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (19)
- Head Neck Anatomy Foramina of The Skull INBDEDocument3 pagesHead Neck Anatomy Foramina of The Skull INBDEHạnh TrangNo ratings yet
- 5TH NERVE STDDocument36 pages5TH NERVE STDAayusha ChipaluNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument62 pagesAnesthesiajarrie abbasNo ratings yet
- Trigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordDocument18 pagesTrigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordBharathi GudapatiNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Mastication: Seminar OnDocument54 pagesMuscles of Mastication: Seminar OnDENTALORG.COMNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDocument5 pagesParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument19 pagesMandibular Nervenadaelhamy03No ratings yet
- Auditory Phonetics Part 1.Document2 pagesAuditory Phonetics Part 1.KhlifibrahimNo ratings yet
- Handpresentation 141020140007 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument34 pagesHandpresentation 141020140007 Conversion Gate02 PDFMichael SelvarajNo ratings yet
- So Today I Will Be Talking About The Maxillary 2Document10 pagesSo Today I Will Be Talking About The Maxillary 2Daniella DukmakNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve AnatomyDocument56 pagesTrigeminal Nerve AnatomyAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
Anaesthesia
Anaesthesia
Uploaded by
Mohamed AdelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anaesthesia
Anaesthesia
Uploaded by
Mohamed AdelCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes in anesthesia
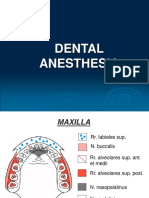
Bones in maxilla is spongy bone so can be infiltrated in any site like above the teeth ,while
mandible is formed of compact bone so it must be infiltrated in mandibular foramen and if
anesthesia is infiltrated above the teeth in mandible it wont do anything
An in nerve block technique we block the inferior alveolar nerve before it enter the
mandibular foramen and when blocking the nerve we stop sensation of all half of the lower
arch and also we block the lingual nerve as it numb the lingual tissue of teeth and floor of
the mouth and it coincide with inferior alveolar nerve block and we numb the buccal tissue
of the three molars by long buccal nerve block
Anatomical landmarks that will help me to know the location of infiltration
contralateral premolars(junction between 4 and 5) it will help to know the direction of the )1
needle
انا بحط النيدل بين الفور والفايف وهي بتساعدني نحدد المكان بتاع النيدل
occlusal plane it will help to know the height of the needle, coronoid notch in the top of )2
external oblique ridge and I know the notch when my thumb catch in it and I infiltrate the
needle in the site of middle of my thumb
pterygomandibular raphae, we must infiltrate the needle lateral to it )3
Steps
First we put needle In contralateral premolar
Then we inject the needle in coronoid notch and lateral to raphae and we inject the 2 thirds
of the needle or the last quarter of the needle remain outside the tissue and when I inject
the needle I will feel the bone contact
Then I back the needle to the half and infiltrate the lingual nerve
And we infiltrate the long buccal nerve by inject the point distal to the last buccal cusp of
the teeth
You might also like
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockDocument7 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve BlockSyedMuhammadJunaidNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Important To SpeechDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves Important To SpeechMike SwiesNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic GanglionDocument33 pagesMandibular Nerve, Chorda Tympani Nerve, Otic Ganglionwaniya irumNo ratings yet
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block: D. Abdullah Al NasserDocument23 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve Block: D. Abdullah Al NasserMira AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- Os 3Document11 pagesOs 3مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- Mandibular AnatomyDocument61 pagesMandibular AnatomyDeb SNo ratings yet
- Inferior Alveolar Nerve BlockDocument4 pagesInferior Alveolar Nerve BlockAnusha KurianNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Techniques of MandibleDocument10 pagesAnesthetic Techniques of MandiblealirezaNo ratings yet
- ENGanesthesiamanndibleDocument48 pagesENGanesthesiamanndibleRoxanaAnaHociungNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Mandibular NerveDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy Mandibular Nerveمحمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- By DR - Navindra Mentor: DR - FarisDocument63 pagesBy DR - Navindra Mentor: DR - FarisNavindra NaiduNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy - Trigeminal NerveDocument8 pagesApplied Anatomy - Trigeminal NervefrabziNo ratings yet
- BuccalDocument2 pagesBuccalFarhang Abdułła IsmahiłNo ratings yet
- LADocument93 pagesLAkaedeamira_113974100% (2)
- Inferior Alveolar TechniqueDocument8 pagesInferior Alveolar Techniquebalab2311No ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgeryDocument92 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgerySAMEENANo ratings yet
- 7 Infratemporal RegionDocument8 pages7 Infratemporal RegionNur Ain Faezah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Technique: Supraperiosteal InfiltrationsDocument11 pagesTechnique: Supraperiosteal Infiltrationsp_npsNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Nerve 2Document22 pagesMaxillary Nerve 2Sayed DrazNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument63 pagesMuscles of Facial Expressionraphaelyohana140No ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument6 pagesMandibular NerveCatalina Stoicescu100% (1)
- Lecture of Temporal & InfratemporalDocument60 pagesLecture of Temporal & InfratemporalShahd YehiaNo ratings yet
- 11 PharynxDocument8 pages11 PharynxNur Ain Faezah RoslanNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Injection TechniquesDocument91 pagesMandibular Injection TechniquesRobins Dhakal100% (3)
- Fracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Document67 pagesFracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Arafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- Blank Book 2Document4 pagesBlank Book 2Rawand Ra'ed D.AlshawabkehNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument2 pagesTrigeminal NerveVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- 8 Mandibular NerveDocument6 pages8 Mandibular NerveAaaNo ratings yet
- External Ear-AclandDocument1 pageExternal Ear-Aclanddale barizoNo ratings yet
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks MandibleDocument34 pagesAnatomical Landmarks Mandibleوا إسلاماهNo ratings yet
- (English) Thoracic Nerves (Intercostal + Subcostal) - Anatomy (DownSub - Com)Document10 pages(English) Thoracic Nerves (Intercostal + Subcostal) - Anatomy (DownSub - Com)shakila.soleymaniyanNo ratings yet
- Mouth, 10 Nov 2006Document2 pagesMouth, 10 Nov 2006api-19921479No ratings yet
- Local Anaesthesia & Xla Osce PrepDocument9 pagesLocal Anaesthesia & Xla Osce PrepVictoria MedfordNo ratings yet
- GRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongDocument9 pagesGRSANA - Lec5 Temporal Fossa, Infratemporal Fossa, and TMJ - WongRainier Raul Echipare100% (1)
- Piano Hand TechniqueDocument12 pagesPiano Hand TechniquevaneriolamaNo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial NerveDocument5 pages12 Cranial NerveOwing ConejoNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Local Anesthesia 1: ReviewDocument13 pagesTechniques of Local Anesthesia 1: ReviewMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary 1Document4 pagesMaxillary 1Farhang Abdułła IsmahiłNo ratings yet
- Applied Surgical AnatomyDocument52 pagesApplied Surgical AnatomyEmad AdelNo ratings yet
- Diagram of The Ear and Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesDiagram of The Ear and Its Functionsmcheche12No ratings yet
- Muscles of Facial ExpressionDocument20 pagesMuscles of Facial ExpressionHarsha Reddy50% (2)
- Anatomy of Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal NerveNicky RomeoNo ratings yet
- The Infratemporal FossaDocument5 pagesThe Infratemporal FossaxxyumeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks MandibleDocument34 pagesAnatomical Landmarks MandibleDocshiv Dent100% (2)
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (19)
- Head Neck Anatomy Foramina of The Skull INBDEDocument3 pagesHead Neck Anatomy Foramina of The Skull INBDEHạnh TrangNo ratings yet
- 5TH NERVE STDDocument36 pages5TH NERVE STDAayusha ChipaluNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument62 pagesAnesthesiajarrie abbasNo ratings yet
- Trigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordDocument18 pagesTrigemina Nerve Sem 2 WordBharathi GudapatiNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Mastication: Seminar OnDocument54 pagesMuscles of Mastication: Seminar OnDENTALORG.COMNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDocument5 pagesParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Mandibular NerveDocument19 pagesMandibular Nervenadaelhamy03No ratings yet
- Auditory Phonetics Part 1.Document2 pagesAuditory Phonetics Part 1.KhlifibrahimNo ratings yet
- Handpresentation 141020140007 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument34 pagesHandpresentation 141020140007 Conversion Gate02 PDFMichael SelvarajNo ratings yet
- So Today I Will Be Talking About The Maxillary 2Document10 pagesSo Today I Will Be Talking About The Maxillary 2Daniella DukmakNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve AnatomyDocument56 pagesTrigeminal Nerve AnatomyAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet