Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive
Reproductive
Uploaded by
John SmithCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Steroidogenic Pathways ChartDocument2 pagesSteroidogenic Pathways ChartAny100% (2)
- Adrenergic Receptor ChartDocument1 pageAdrenergic Receptor ChartAnkit Mehta75% (4)
- Actividad A4. Study CaseDocument2 pagesActividad A4. Study CaseDavid Padilla AcostaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet DRUGSDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet DRUGSRicky Vanguardia IIINo ratings yet
- Common Drug Stems Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCommon Drug Stems Cheat SheetRicky Vanguardia III100% (1)
- 2010 A Level H2 P3 Suggested AnswersDocument10 pages2010 A Level H2 P3 Suggested AnswersMichelle LimNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Metabolism Daniel LimDocument4 pagesFatty Acid Metabolism Daniel LimSamyuktha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- ClinicalOwl PharmSuffixandPrefixCheatSheetDocument4 pagesClinicalOwl PharmSuffixandPrefixCheatSheetSony AvioNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and The Pituitary LectureDocument51 pagesHypothalamus and The Pituitary LecturealkalicharanNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Pharmacology - Autonimic Nervous SystemDocument1 pageAdrenergic Pharmacology - Autonimic Nervous Systemprasannaipad324No ratings yet
- Enfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterDocument1 pageEnfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- HepChart 2018 10 (Nov)Document5 pagesHepChart 2018 10 (Nov)mihaela.lucaciNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 2.1 - SIKLUS MENSTRUASIDocument12 pagesKuliah 2.1 - SIKLUS MENSTRUASIErviana Dwi NurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- HORMON REPRODUKSI DAN SIKLUS HAID Prof. Dr. Dr. Nusratuddin Abdullah, SP - OG (K) MARSDocument21 pagesHORMON REPRODUKSI DAN SIKLUS HAID Prof. Dr. Dr. Nusratuddin Abdullah, SP - OG (K) MARStenri olaNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic & Pituitary SHORTDocument9 pagesHypothalamic & Pituitary SHORTa.muhsinNo ratings yet
- Metabolic BiochemistryDocument18 pagesMetabolic BiochemistryHoanNo ratings yet
- Obat Anti ParkinsonDocument1 pageObat Anti ParkinsonellenNo ratings yet
- DIPRINTDocument1 pageDIPRINTAnonymous wRiKUO07DHNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Patient With Endocrine Alterations SlidesDocument82 pagesNursing Care of The Patient With Endocrine Alterations SlidesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Infographic PosterDocument1 pageEndocrine System Infographic PosterVohn Archie EdjanNo ratings yet
- Anfis Sistem Reproduksi Pria Dan WanitaDocument62 pagesAnfis Sistem Reproduksi Pria Dan WanitaLili HamdianaNo ratings yet
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocument1 pageDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Pcol Notes 2023Document56 pagesPcol Notes 2023elleasonNo ratings yet
- Lansoprazole 2Document1 pageLansoprazole 2Ilham AchtzehnNo ratings yet
- Metabolic PathwayDocument8 pagesMetabolic PathwaysadadsadNo ratings yet
- Court 2013Document16 pagesCourt 2013Stone ColdNo ratings yet
- Steroid PathwaysDocument1 pageSteroid PathwaysCalvin ChiuNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Cycle Ovulation Menstrual AtfDocument1 pageFemale Reproductive Cycle Ovulation Menstrual AtfAkeny AranyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Summary of Porphyrin and Heme MetabolismDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Summary of Porphyrin and Heme MetabolismElaf NaifNo ratings yet
- Biochem CyclesDocument18 pagesBiochem CyclesrlmagaluedNo ratings yet
- Bagian PsikiatriDocument1 pageBagian Psikiatrirendi adi saputraNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument2 pagesAnalgesicLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Specialized Products From Amino Acids - Part 2Document16 pagesSpecialized Products From Amino Acids - Part 2Leon WarrenNo ratings yet
- Posterior PituitaryDocument1 pagePosterior PituitaryfocussedlearnerNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Anterior PituitaryDocument1 pageAnterior PituitaryVishalNo ratings yet
- Paxlovid Interaction - Update 8th June 2022Document3 pagesPaxlovid Interaction - Update 8th June 2022disbeaufortNo ratings yet
- R - TX Hewan KecilDocument8 pagesR - TX Hewan KecilNadia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Poster Edinburgh 2009Document1 pagePoster Edinburgh 2009Francisco P. ChavezNo ratings yet
- Steroid Pathways Chart Ref051021Document2 pagesSteroid Pathways Chart Ref051021JanelleNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 - Chapter 18: Endocrine Organs: Neurohypophysis Median Eminence Infundibular Stalk Pars NervosaDocument7 pagesBio 102 - Chapter 18: Endocrine Organs: Neurohypophysis Median Eminence Infundibular Stalk Pars NervosaAlly YeeNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument4 pagesAmino Acidschayiezen0301No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument15 pagesBIOCHEMKrizzia OñateNo ratings yet
- SALA Poster LasaDocument4 pagesSALA Poster LasaJhilik BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Biotransformation Reaction: Glucuronide Conjugation OxidationDocument1 pageBiotransformation Reaction: Glucuronide Conjugation OxidationJakareaNo ratings yet
- Organic Medicinal Chemistry: FunctionalizationDocument25 pagesOrganic Medicinal Chemistry: FunctionalizationPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- BSVDocument2 pagesBSVRakhee SabooNo ratings yet
- Gland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhDocument2 pagesGland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhshirleyNo ratings yet
- Yen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology (PDFDrive) - Pages-6Document18 pagesYen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology (PDFDrive) - Pages-6viramaharsaNo ratings yet
- Aula Fisiologia Hormonal BB - Aula 1 - SPDocument319 pagesAula Fisiologia Hormonal BB - Aula 1 - SPapvsbrasil.philippeNo ratings yet
- List of Antipsychotics - by Generation 260124Document12 pagesList of Antipsychotics - by Generation 260124Real IdiomNo ratings yet
- Othmani111n Easy Pharma - 220401 - 163518Document7 pagesOthmani111n Easy Pharma - 220401 - 163518Hassan HekmatNo ratings yet
- 11th STD - Class-1 - Chemical Coordination and Integration - NotesDocument7 pages11th STD - Class-1 - Chemical Coordination and Integration - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Anti Asthemic DrugDocument1 pageAnti Asthemic Drugvikramsingh046633No ratings yet
- Pharma Inicet Marathon May 2024 Annotated by DR AshaDocument100 pagesPharma Inicet Marathon May 2024 Annotated by DR AshaVickyNo ratings yet
- Illustrations Book PharmacologyDocument18 pagesIllustrations Book PharmacologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Cholenergic ToxicityDocument18 pagesCholenergic ToxicityZANo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormone Cology - GPAT - 25367565Document48 pagesGonadal Hormone Cology - GPAT - 25367565manjitplk3No ratings yet
- 41 - PDFsam - Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9eDocument20 pages41 - PDFsam - Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9eRizky Angga PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Stok Opname Tablet 2021Document3 pagesStok Opname Tablet 2021ika fatikhatun nasikhaNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument2 pagesRespiratoryJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Attestation Form - 2022Document1 pageAttestation Form - 2022John SmithNo ratings yet
- There Is Not A Form For Your Immuni-1Document1 pageThere Is Not A Form For Your Immuni-1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Renal NotesDocument4 pagesRenal NotesJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Warehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Document29 pagesWarehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Confidence and Competence, Their Relationship and Impact On Workplace PerformanceDocument87 pagesConfidence and Competence, Their Relationship and Impact On Workplace PerformanceJules Savage-MilnerNo ratings yet
- FamiliesDocument26 pagesFamiliesChaoukiNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity UitmDocument25 pagesRadioactivity UitmMoody6861No ratings yet
- Iso TS 19036 Amd 1 - 2009Document12 pagesIso TS 19036 Amd 1 - 2009oscarosorto100% (1)
- Liquid FormsDocument29 pagesLiquid Formsaman jainNo ratings yet
- N45-N67 Opm PDFDocument45 pagesN45-N67 Opm PDFAndres Sorin100% (4)
- Programme Title:: (Dd/mm/yyyy) (XXX)Document4 pagesProgramme Title:: (Dd/mm/yyyy) (XXX)ghanNo ratings yet
- Igb 0001Document15 pagesIgb 0001Дејан МркајаNo ratings yet
- Geography Mock Test PopulationDocument8 pagesGeography Mock Test PopulationMain AccountNo ratings yet
- Epojet 270Document4 pagesEpojet 270Yudi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Good News 1968 (Vol XVII No 11-12) Nov-DecDocument24 pagesGood News 1968 (Vol XVII No 11-12) Nov-DecHerbert W. ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Apr 78Document147 pagesApr 78Quality AssuranceNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 1 No: Unit QtyDocument3 pagesTechnical Specification 1 No: Unit QtySuraj KhopeNo ratings yet
- Tahun 2021Document7 pagesTahun 2021Dina Pratya NiayNo ratings yet
- Ebook Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesEbook Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFkimberly.dixon591100% (30)
- Emax 2222Document85 pagesEmax 2222camNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence ReflectionDocument5 pagesEmotional Intelligence Reflectionapi-336005635No ratings yet
- The Corporation and External StakeholdersDocument19 pagesThe Corporation and External StakeholdersNur AtierahNo ratings yet
- BacktoBasics-Fundamental Resolution Equation V2Document7 pagesBacktoBasics-Fundamental Resolution Equation V2Yeoh XWNo ratings yet
- Nepro Plastics Pvc4Document12 pagesNepro Plastics Pvc4chaouch.najehNo ratings yet
- Dettol Liquid Hand Wash SDSDocument10 pagesDettol Liquid Hand Wash SDSaskdfhaosljudgnNo ratings yet
- Effect of Plant Spacing On Yield and Fruit Characteristics of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus)Document7 pagesEffect of Plant Spacing On Yield and Fruit Characteristics of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus)Mariama BojangNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To Shifting Cultivation-248Document9 pagesAlternatives To Shifting Cultivation-248Chandrashekhar KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- AAS Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesAAS Data AnalysisGian MeniaNo ratings yet
- (NCRP Report No. 174 - ) - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure - Health Effects and Protective Guidance-National Council On Radiation (2014) PDFDocument386 pages(NCRP Report No. 174 - ) - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure - Health Effects and Protective Guidance-National Council On Radiation (2014) PDFIulia ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Ether & Phenol, Halogen Derivatives, Benzene & TolueneDocument98 pagesAlcohol Ether & Phenol, Halogen Derivatives, Benzene & TolueneMD MoonNo ratings yet
- Management Report 2012Document41 pagesManagement Report 2012Daniela AlimanNo ratings yet
Reproductive
Reproductive
Uploaded by
John SmithCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproductive
Reproductive
Uploaded by
John SmithCopyright:
Available Formats
REPRODUC TIVE REPRODUCTIVE—PHARMACOLOGY SEC TION III 655
REPRODUCTIVE—PHARMACOLOGY
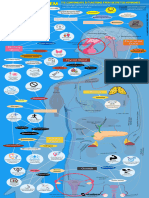
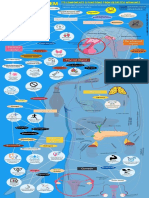
Control of reproductive hormones
Hypothalamus
via blocking negative feedback
Clomiphene + GnRH
Degarelix -
Goserelin –/+
Leuprolide
Anterior
pituitary
LH
FSH
LH LH
Ovary FSH Testis
Oral contraceptives
Danazol -
Ketoconazole
Danazol - P-450c17 - Ketoconazole
Spironolactone
Androstenedione Testosterone Testosterone
Anastrozole
5α−reductase
-
Letrozole - Aromatase Finasteride
Exemestane
Estriol Estrone Estradiol Dihydrotestosterone
Tamoxifen
Raloxifene
–/+ Androgen-receptor Flutamide
complex
- Cyproterone
Spironolactone
Gene expression Gene expression
in estrogen- in androgen-
responsive cells responsive cells
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 655 11/7/19 5:52 PM
656 SEC TION III REPRODUC TIVE REPRODUCTIVE—PHARMACOLOGY
Goserelin, leuprolide
MECHANISM GnRH analogs. When used in pulsatile Leuprolide can be used in lieu of GnRH.
fashion act as GnRH agonists. When used
in continuous fashion first transiently act as
GnRH agonists (tumor flare), but subsequently
act as GnRH antagonists (downregulate
GnRH receptor in pituitary FSH and
LH).
CLINICAL USE Uterine fibroids, endometriosis, precocious
puberty, prostate cancer, infertility.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Hypogonadism, libido, erectile dysfunction,
nausea, vomiting.
Degarelix
MECHANISM GnRH antagonist. No start-up flare.
CLINICAL USE Prostate cancer.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Hot flashes, liver toxicity.
Estrogens Ethinyl estradiol, DES, mestranol.
MECHANISM Bind estrogen receptors.
CLINICAL USE Hypogonadism or ovarian failure, menstrual abnormalities (combined OCPs), hormone
replacement therapy in postmenopausal women.
ADVERSE EFFECTS risk of endometrial cancer (when given without progesterone), bleeding in postmenopausal
women, clear cell adenocarcinoma of vagina in females exposed to DES in utero, risk of
thrombi. Contraindications—ER ⊕ breast cancer, history of DVTs, tobacco use in women > 35
years old.
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
Clomiphene Antagonist at estrogen receptors in hypothalamus. Prevents normal feedback inhibition and
release of LH and FSH from pituitary, which stimulates ovulation. Used to treat infertility due
to anovulation (eg, PCOS). May cause hot flashes, ovarian enlargement, multiple simultaneous
pregnancies, visual disturbances.
Tamoxifen Antagonist at breast; agonist at bone, uterus; risk of thromboembolic events (especially with
smoking) and endometrial cancer. Used to treat and prevent recurrence of ER/PR ⊕ breast
cancer.
Raloxifene Antagonist at breast, uterus; agonist at bone; risk of thromboembolic events (especially with
smoking) but no increased risk of endometrial cancer (vs tamoxifen); used primarily to treat
osteoporosis.
Aromatase inhibitors Anastrozole, letrozole, exemestane.
MECHANISM Inhibit peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogen.
CLINICAL USE ER ⊕ breast cancer in postmenopausal women.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 656 11/7/19 5:52 PM
REPRODUC TIVE REPRODUCTIVE—PHARMACOLOGY SEC TION III 657
Hormone replacement Used for relief or prevention of menopausal symptoms (eg, hot flashes, vaginal atrophy),
therapy osteoporosis ( estrogen, osteoclast activity).
Unopposed estrogen replacement therapy risk of endometrial cancer, progesterone/progestin is
added. Possible increased cardiovascular risk.
Progestins Levonorgestrel, medroxyprogesterone, etonogestrel, norethindrone, megestrol.
MECHANISM Bind progesterone receptors, growth and vascularization of endometrium, thicken cervical
mucus.
CLINICAL USE Contraception (forms include pill, intrauterine device, implant, depot injection), endometrial
cancer, abnormal uterine bleeding. Progestin challenge: presence of withdrawal bleeding
excludes anatomic defects (eg, Asherman syndrome) and chronic anovulation without estrogen.
Antiprogestins Mifepristone, ulipristal.
MECHANISM Competitive inhibitors of progestins at progesterone receptors.
CLINICAL USE Termination of pregnancy (mifepristone with misoprostol); emergency contraception (ulipristal).
Combined Progestins and ethinyl estradiol; forms include pill, patch, vaginal ring.
contraception Estrogen and progestins inhibit LH/FSH and thus prevent estrogen surge. No estrogen surge no
LH surge no ovulation.
Progestins cause thickening of cervical mucus, thereby limiting access of sperm to uterus.
Progestins also inhibit endometrial proliferation endometrium is less suitable to the
implantation of an embryo.
Adverse effects: breakthrough menstrual bleeding, breast tenderness, VTE, hepatic adenomas.
Contraindications: smokers > 35 years old ( risk of cardiovascular events), patients with risk of
cardiovascular disease (including history of venous thromboembolism, coronary artery disease,
stroke), migraine (especially with aura), breast cancer, liver disease.
Copper intrauterine device
MECHANISM Produces local inflammatory reaction toxic to sperm and ova, preventing fertilization and
implantation; hormone free.
CLINICAL USE Long-acting reversible contraception. Most effective emergency contraception.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Heavier or longer menses, dysmenorrhea. Risk of PID with insertion (contraindicated in active
pelvic infection).
Tocolytics Medications that relax the uterus; include terbutaline (β2-agonist action), nifedipine (Ca2+ channel
blocker), indomethacin (NSAID). Used to contraction frequency in preterm labor and allow
time for administration of steroids (to promote fetal lung maturity) or transfer to appropriate
medical center with obstetrical care.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 657 11/7/19 5:52 PM
658 SEC TION III REPRODUC TIVE REPRODUCTIVE—PHARMACOLOGY
Danazol
MECHANISM Synthetic androgen that acts as partial agonist at androgen receptors.
CLINICAL USE Endometriosis, hereditary angioedema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Weight gain, edema, acne, hirsutism, masculinization, HDL levels, hepatotoxicity, idiopathic
intracranial hypertension.
Testosterone, methyltestosterone
MECHANISM Agonists at androgen receptors.
CLINICAL USE Treat hypogonadism and promote development of 2° sex characteristics; stimulate anabolism to
promote recovery after burn or injury.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Masculinization in females; intratesticular testosterone in males by inhibiting release of LH (via
negative feedback) gonadal atrophy. Premature closure of epiphyseal plates. LDL, HDL.
Antiandrogens
Finasteride 5α-reductase inhibitor ( conversion of Testosterone 5α-reductase
DHT (more potent).
testosterone to DHT). Used for BPH and
male-pattern baldness. Adverse effects:
gynecomastia and sexual dysfunction.
Flutamide, Nonsteroidal competitive inhibitors at androgen
bicalutamide, receptors. Used for prostate carcinoma.
apalutamide,
enzalutamide
Ketoconazole Inhibits steroid synthesis (inhibits 17,20
desmolase/17α-hydroxylase). Used in PCOS to reduce androgenic symptoms.
Spironolactone Inhibits steroid binding, 17,20 desmolase/17α- Both can cause gynecomastia and amenorrhea.
hydroxylase.
Tamsulosin α1-antagonist used to treat BPH by inhibiting smooth muscle contraction. Selective for α1A/D
receptors (found on prostate) vs vascular α1B receptors.
Minoxidil
MECHANISM Direct arteriolar vasodilator.
CLINICAL USE Androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), severe refractory hypertension.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 658 11/7/19 5:52 PM
You might also like
- Steroidogenic Pathways ChartDocument2 pagesSteroidogenic Pathways ChartAny100% (2)
- Adrenergic Receptor ChartDocument1 pageAdrenergic Receptor ChartAnkit Mehta75% (4)
- Actividad A4. Study CaseDocument2 pagesActividad A4. Study CaseDavid Padilla AcostaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet DRUGSDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet DRUGSRicky Vanguardia IIINo ratings yet
- Common Drug Stems Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCommon Drug Stems Cheat SheetRicky Vanguardia III100% (1)
- 2010 A Level H2 P3 Suggested AnswersDocument10 pages2010 A Level H2 P3 Suggested AnswersMichelle LimNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Metabolism Daniel LimDocument4 pagesFatty Acid Metabolism Daniel LimSamyuktha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- ClinicalOwl PharmSuffixandPrefixCheatSheetDocument4 pagesClinicalOwl PharmSuffixandPrefixCheatSheetSony AvioNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and The Pituitary LectureDocument51 pagesHypothalamus and The Pituitary LecturealkalicharanNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Pharmacology - Autonimic Nervous SystemDocument1 pageAdrenergic Pharmacology - Autonimic Nervous Systemprasannaipad324No ratings yet
- Enfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterDocument1 pageEnfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- HepChart 2018 10 (Nov)Document5 pagesHepChart 2018 10 (Nov)mihaela.lucaciNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 2.1 - SIKLUS MENSTRUASIDocument12 pagesKuliah 2.1 - SIKLUS MENSTRUASIErviana Dwi NurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- HORMON REPRODUKSI DAN SIKLUS HAID Prof. Dr. Dr. Nusratuddin Abdullah, SP - OG (K) MARSDocument21 pagesHORMON REPRODUKSI DAN SIKLUS HAID Prof. Dr. Dr. Nusratuddin Abdullah, SP - OG (K) MARStenri olaNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic & Pituitary SHORTDocument9 pagesHypothalamic & Pituitary SHORTa.muhsinNo ratings yet
- Metabolic BiochemistryDocument18 pagesMetabolic BiochemistryHoanNo ratings yet
- Obat Anti ParkinsonDocument1 pageObat Anti ParkinsonellenNo ratings yet
- DIPRINTDocument1 pageDIPRINTAnonymous wRiKUO07DHNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Patient With Endocrine Alterations SlidesDocument82 pagesNursing Care of The Patient With Endocrine Alterations SlidesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Infographic PosterDocument1 pageEndocrine System Infographic PosterVohn Archie EdjanNo ratings yet
- Anfis Sistem Reproduksi Pria Dan WanitaDocument62 pagesAnfis Sistem Reproduksi Pria Dan WanitaLili HamdianaNo ratings yet
- Different Body Receptors PDFDocument1 pageDifferent Body Receptors PDFSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Pcol Notes 2023Document56 pagesPcol Notes 2023elleasonNo ratings yet
- Lansoprazole 2Document1 pageLansoprazole 2Ilham AchtzehnNo ratings yet
- Metabolic PathwayDocument8 pagesMetabolic PathwaysadadsadNo ratings yet
- Court 2013Document16 pagesCourt 2013Stone ColdNo ratings yet
- Steroid PathwaysDocument1 pageSteroid PathwaysCalvin ChiuNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Cycle Ovulation Menstrual AtfDocument1 pageFemale Reproductive Cycle Ovulation Menstrual AtfAkeny AranyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Summary of Porphyrin and Heme MetabolismDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Summary of Porphyrin and Heme MetabolismElaf NaifNo ratings yet
- Biochem CyclesDocument18 pagesBiochem CyclesrlmagaluedNo ratings yet
- Bagian PsikiatriDocument1 pageBagian Psikiatrirendi adi saputraNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument2 pagesAnalgesicLA BriguelaNo ratings yet
- Specialized Products From Amino Acids - Part 2Document16 pagesSpecialized Products From Amino Acids - Part 2Leon WarrenNo ratings yet
- Posterior PituitaryDocument1 pagePosterior PituitaryfocussedlearnerNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Anterior PituitaryDocument1 pageAnterior PituitaryVishalNo ratings yet
- Paxlovid Interaction - Update 8th June 2022Document3 pagesPaxlovid Interaction - Update 8th June 2022disbeaufortNo ratings yet
- R - TX Hewan KecilDocument8 pagesR - TX Hewan KecilNadia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Poster Edinburgh 2009Document1 pagePoster Edinburgh 2009Francisco P. ChavezNo ratings yet
- Steroid Pathways Chart Ref051021Document2 pagesSteroid Pathways Chart Ref051021JanelleNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 - Chapter 18: Endocrine Organs: Neurohypophysis Median Eminence Infundibular Stalk Pars NervosaDocument7 pagesBio 102 - Chapter 18: Endocrine Organs: Neurohypophysis Median Eminence Infundibular Stalk Pars NervosaAlly YeeNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument4 pagesAmino Acidschayiezen0301No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument15 pagesBIOCHEMKrizzia OñateNo ratings yet
- SALA Poster LasaDocument4 pagesSALA Poster LasaJhilik BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Biotransformation Reaction: Glucuronide Conjugation OxidationDocument1 pageBiotransformation Reaction: Glucuronide Conjugation OxidationJakareaNo ratings yet
- Organic Medicinal Chemistry: FunctionalizationDocument25 pagesOrganic Medicinal Chemistry: FunctionalizationPrincess RonsableNo ratings yet
- BSVDocument2 pagesBSVRakhee SabooNo ratings yet
- Gland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhDocument2 pagesGland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhshirleyNo ratings yet
- Yen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology (PDFDrive) - Pages-6Document18 pagesYen & Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology (PDFDrive) - Pages-6viramaharsaNo ratings yet
- Aula Fisiologia Hormonal BB - Aula 1 - SPDocument319 pagesAula Fisiologia Hormonal BB - Aula 1 - SPapvsbrasil.philippeNo ratings yet
- List of Antipsychotics - by Generation 260124Document12 pagesList of Antipsychotics - by Generation 260124Real IdiomNo ratings yet
- Othmani111n Easy Pharma - 220401 - 163518Document7 pagesOthmani111n Easy Pharma - 220401 - 163518Hassan HekmatNo ratings yet
- 11th STD - Class-1 - Chemical Coordination and Integration - NotesDocument7 pages11th STD - Class-1 - Chemical Coordination and Integration - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Anti Asthemic DrugDocument1 pageAnti Asthemic Drugvikramsingh046633No ratings yet
- Pharma Inicet Marathon May 2024 Annotated by DR AshaDocument100 pagesPharma Inicet Marathon May 2024 Annotated by DR AshaVickyNo ratings yet
- Illustrations Book PharmacologyDocument18 pagesIllustrations Book PharmacologyScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Cholenergic ToxicityDocument18 pagesCholenergic ToxicityZANo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormone Cology - GPAT - 25367565Document48 pagesGonadal Hormone Cology - GPAT - 25367565manjitplk3No ratings yet
- 41 - PDFsam - Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9eDocument20 pages41 - PDFsam - Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 9eRizky Angga PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Stok Opname Tablet 2021Document3 pagesStok Opname Tablet 2021ika fatikhatun nasikhaNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument2 pagesRespiratoryJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Attestation Form - 2022Document1 pageAttestation Form - 2022John SmithNo ratings yet
- There Is Not A Form For Your Immuni-1Document1 pageThere Is Not A Form For Your Immuni-1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Renal NotesDocument4 pagesRenal NotesJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Warehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Document29 pagesWarehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Confidence and Competence, Their Relationship and Impact On Workplace PerformanceDocument87 pagesConfidence and Competence, Their Relationship and Impact On Workplace PerformanceJules Savage-MilnerNo ratings yet
- FamiliesDocument26 pagesFamiliesChaoukiNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity UitmDocument25 pagesRadioactivity UitmMoody6861No ratings yet
- Iso TS 19036 Amd 1 - 2009Document12 pagesIso TS 19036 Amd 1 - 2009oscarosorto100% (1)
- Liquid FormsDocument29 pagesLiquid Formsaman jainNo ratings yet
- N45-N67 Opm PDFDocument45 pagesN45-N67 Opm PDFAndres Sorin100% (4)
- Programme Title:: (Dd/mm/yyyy) (XXX)Document4 pagesProgramme Title:: (Dd/mm/yyyy) (XXX)ghanNo ratings yet
- Igb 0001Document15 pagesIgb 0001Дејан МркајаNo ratings yet
- Geography Mock Test PopulationDocument8 pagesGeography Mock Test PopulationMain AccountNo ratings yet
- Epojet 270Document4 pagesEpojet 270Yudi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Good News 1968 (Vol XVII No 11-12) Nov-DecDocument24 pagesGood News 1968 (Vol XVII No 11-12) Nov-DecHerbert W. ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Apr 78Document147 pagesApr 78Quality AssuranceNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 1 No: Unit QtyDocument3 pagesTechnical Specification 1 No: Unit QtySuraj KhopeNo ratings yet
- Tahun 2021Document7 pagesTahun 2021Dina Pratya NiayNo ratings yet
- Ebook Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesEbook Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine PDF Full Chapter PDFkimberly.dixon591100% (30)
- Emax 2222Document85 pagesEmax 2222camNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence ReflectionDocument5 pagesEmotional Intelligence Reflectionapi-336005635No ratings yet
- The Corporation and External StakeholdersDocument19 pagesThe Corporation and External StakeholdersNur AtierahNo ratings yet
- BacktoBasics-Fundamental Resolution Equation V2Document7 pagesBacktoBasics-Fundamental Resolution Equation V2Yeoh XWNo ratings yet
- Nepro Plastics Pvc4Document12 pagesNepro Plastics Pvc4chaouch.najehNo ratings yet
- Dettol Liquid Hand Wash SDSDocument10 pagesDettol Liquid Hand Wash SDSaskdfhaosljudgnNo ratings yet
- Effect of Plant Spacing On Yield and Fruit Characteristics of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus)Document7 pagesEffect of Plant Spacing On Yield and Fruit Characteristics of Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus)Mariama BojangNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To Shifting Cultivation-248Document9 pagesAlternatives To Shifting Cultivation-248Chandrashekhar KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- AAS Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesAAS Data AnalysisGian MeniaNo ratings yet
- (NCRP Report No. 174 - ) - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure - Health Effects and Protective Guidance-National Council On Radiation (2014) PDFDocument386 pages(NCRP Report No. 174 - ) - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure - Health Effects and Protective Guidance-National Council On Radiation (2014) PDFIulia ChiriacNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Ether & Phenol, Halogen Derivatives, Benzene & TolueneDocument98 pagesAlcohol Ether & Phenol, Halogen Derivatives, Benzene & TolueneMD MoonNo ratings yet
- Management Report 2012Document41 pagesManagement Report 2012Daniela AlimanNo ratings yet