Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry Class Notes
Geometry Class Notes
Uploaded by
Tomasz ZiebaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geometry Class Notes
Geometry Class Notes
Uploaded by
Tomasz ZiebaCopyright:
Available Formats
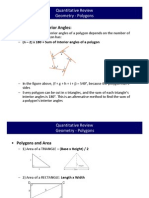
Geometry Notes: Circles and Triangles
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, and properties of figures, as
well as the space they occupy.
Key Concepts:
1. Circles:
- Radius: The distance from the center to any point on the circle.
- Diameter: Twice the radius, the longest distance across the circle.
- Circumference: The perimeter or boundary line of a circle.
2. Triangles:
- Types: Equilateral (all sides equal), Isosceles (two sides equal), Scalene (no sides equal).
- Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), where 'c' is the hypotenuse.
Example Problems:
- Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 4 cm (\(C = 2\pi r\)).
- Using the Pythagorean theorem, find the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle with sides 3
cm and 4 cm.
These notes provide a concise overview of the basic properties and calculations related to circles
and triangles.
You might also like
- GRAPHICS 01 Geometric ConstructionsDocument20 pagesGRAPHICS 01 Geometric ConstructionsRachel Faith GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law CalculatorDocument4 pagesIdeal Gas Law Calculatorapi-140032165No ratings yet
- Geometry WorksheetsDocument4 pagesGeometry Worksheetsapi-150547803No ratings yet
- This Website Uses Cookies To Ensure You Get The Best Experience On Our Website. Got It!Document8 pagesThis Website Uses Cookies To Ensure You Get The Best Experience On Our Website. Got It!Janice BulaoNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Quantitative ReviewDocument108 pagesFlashcards - Quantitative ReviewEduardo KidoNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths ShortcutsDocument108 pagesFlashcards Quantitative Aptitude Revision Maths Shortcutskvdheerajkumar100% (1)
- Chord, Arcs, Central Angels, Tangents and SecantsDocument5 pagesChord, Arcs, Central Angels, Tangents and SecantsLucille BallaresNo ratings yet
- Geometry HistoryDocument2 pagesGeometry HistoryManilyn Requejo ObalNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument7 pagesIntroductionDhanush AnimationNo ratings yet
- CAT Geometry: Obtuse Triangles - IntegersDocument15 pagesCAT Geometry: Obtuse Triangles - IntegersALOK BAJPAINo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument5 pagesTriangleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- 7th Introduction To Basic GeometryDocument13 pages7th Introduction To Basic GeometryKeily1029No ratings yet
- Introduction To GeometryDocument2 pagesIntroduction To GeometryMay ShizzyNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument5 pagesGeometrylolileeNo ratings yet
- Geometry BasicsDocument1 pageGeometry BasicssarlavmalpaniNo ratings yet
- Encyclipedia of Trignometry - Andrew BarnesDocument140 pagesEncyclipedia of Trignometry - Andrew Barnessaka1977No ratings yet
- Ussd CodeDocument37 pagesUssd CodeksmNo ratings yet
- MathDocument13 pagesMathAlibasher MacalnasNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics IntroductionDocument1 pageBasic Mathematics IntroductionTomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet
- Math2-Planegeom Anageom SolidgeomDocument18 pagesMath2-Planegeom Anageom SolidgeomMae Anne GNo ratings yet
- Definition of Geometric FiguresDocument8 pagesDefinition of Geometric FiguresScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Basic Science of MathematicsDocument7 pagesBasic Science of MathematicsDESIGN ZarNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument5 pagesGeometry FormulasAlyzza Rose Pampliega LedesmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesAaron BrennNo ratings yet
- CircolDocument12 pagesCircol202130054No ratings yet
- J S S 1 Maths 3RD TermDocument62 pagesJ S S 1 Maths 3RD Termpossyodoabuchi20No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Geometrykssuhasreddy_3743947No ratings yet
- Circle Facts - Area, Circumference, Diameter, RadiusDocument1 pageCircle Facts - Area, Circumference, Diameter, Radiussunnah12349No ratings yet
- Geometry 2021Document30 pagesGeometry 2021Dan AchimescuNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1Aditya VermaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet GeometryDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet GeometrysamuthrarajaNo ratings yet
- Math CircleDocument2 pagesMath Circleclhclh723No ratings yet
- Synergetics in The PlaneDocument27 pagesSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- Geometry ReviewDocument3 pagesGeometry ReviewJose Luis PiñaNo ratings yet
- Netcircle Problems With SolutionsDocument34 pagesNetcircle Problems With SolutionsFynn NiallNo ratings yet
- Geometry Team 10 - Bip-2Document23 pagesGeometry Team 10 - Bip-2Rosiana RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Area TrianglesDocument6 pagesArea TrianglesFatos ShuliNo ratings yet
- 3 Diocton Edward ADocument46 pages3 Diocton Edward AgdhehhhdbdbdnhwNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing 8 (Q1-Week 1)Document4 pagesTechnical Drawing 8 (Q1-Week 1)chaNo ratings yet
- Tec Milenio - Geometry Trigonometry AnglesDocument4 pagesTec Milenio - Geometry Trigonometry AnglesBryan CamargoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Pea306Document127 pagesUnit 4 Pea306Aryan Rathore100% (1)
- Unit 4 Pea306Document156 pagesUnit 4 Pea306Aryan RathoreNo ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument9 pagesSolid Geometryfachira_humairaNo ratings yet
- Course Hero 41Document5 pagesCourse Hero 41Maria Helen MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Basic GeometryDocument8 pagesBasic GeometrymorrenbonnieNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document34 pagesModule 7Laika EnriquezNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument52 pagesQuadrilateralsbrazcell domNo ratings yet
- Circles and Its Related TermsDocument3 pagesCircles and Its Related Termsapi-174391216No ratings yet
- Triangles in Geometry (Definition, Shape, Types, Properties & Examples)Document13 pagesTriangles in Geometry (Definition, Shape, Types, Properties & Examples)Thanuja RaniNo ratings yet
- Gr8 Math Notes (ch25)Document5 pagesGr8 Math Notes (ch25)Akshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics in GeometryDocument1 pageAdvanced Topics in GeometryTomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet
- Lavanya Akka OriginalDocument38 pagesLavanya Akka OriginalKALAM WORKSNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument101 pagesTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 TrianglesDocument9 pagesLesson 2.3 TrianglesAllan Gabriel LariosaNo ratings yet
- A Treatise on Spherical Trigonometry, and Its Application to Geodesy and Astronomy, with Numerous ExamplesFrom EverandA Treatise on Spherical Trigonometry, and Its Application to Geodesy and Astronomy, with Numerous ExamplesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Chemistry Notes 4Document10 pagesDetailed Chemistry Notes 4Tomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Chemistry Notes 1Document10 pagesDetailed Chemistry Notes 1Tomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and StatisticsDocument1 pageIntroduction To Probability and StatisticsTomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Teaching MaterialDocument13 pages1 - Teaching MaterialTomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry IntroductionDocument2 pagesBasic Chemistry IntroductionTomasz ZiebaNo ratings yet