Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Another Procedure For Writing Lewis Structures: Qtmrttrka
Another Procedure For Writing Lewis Structures: Qtmrttrka
Uploaded by
Marvel AcademyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Another Procedure For Writing Lewis Structures: Qtmrttrka
Another Procedure For Writing Lewis Structures: Qtmrttrka
Uploaded by
Marvel AcademyCopyright:
Available Formats
Another Procedure for Writing Lewis Structures
T h o m a s J. Clark
Humboldt State University, Arcata, CA 95521
Many students have difficulty in learning to write Lewis I ) Place the hydrogen atomson the formula in a way whichmini-
structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. Several proce- mizes the number of atoms carrying formal charge and mini-
dures for writing them are presented in general chemistry mizes the magnitude of formal charges. Characteristics of atoms
having zero formal charge when the octet rule is obeyed are given
texts. I recently devised a scheme which has two uncommon
in the table.
features: (1) whether multiple bond& or expanded valence Group IV V VI VII
shells are present is first determined using the method de- Number of Shared Pairs 4 3 2 1
scribed by Lever'; (2) the dots representing electrons are en- Number of Unshared Pairs 0 1 2 3
tered before any hydrogen atoms are placed on the structure. The formal charge is mare positive by one for each additional
. . . -
T h e verv simnle orocedure for writine a correct. or a t least
reasonable, Lewis structure for a molecule or ion containing
shared pair and more negative by one for each additional un-
shared paw.
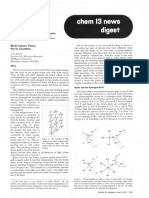
onlv s-block and D-block elements can be summarized in a Development of the Lewis structure of formic acid illus-
series of steps. trates the procedure. Using step (2) one finds that the formula
1) Identifv anv monatomic cations. The rules far writine Lewis CHzOz requires 18 dots to be shown. Steps (3) and (4) lead to
qtmrttrka
.~~ ~ ~~ ~ ~~~ ~ ~~ ~ ~
. . . to
which follow are not needed for and do nat&lv the conclusion t h a t one double bond is present. Carbon, a
rnonarmnlc cxiun*. Croup I and Gnmp I1 elrrnrntsarr almoqf Group IV element, is central, and placing the dots on the
nlusy~present ascations. Exceptions arc He in moct nmp,unds formula as directed in step ( 6 ) gives the partial structbre
and the other elements of these two groups in organometallic shown on the left below. A glance shows that the 0 on the right
compounds. having twoshared and twiunshared pairsalready has formal
2) Determine the number of dots to be shown in the structure of charee of zero. T h e other 0 and the C can have formal charce
a molecule or polyatomic ion. There is one for each s and p
electron in the valence shell of each constituent atom; there is of zero if each shares a pair with H, and entering the H S
one more for each neeative charee on an anion and one less for completes the structure.
"
each positive charge on a cation.
3) Evaluate 6y + 2 where y is the number of atoms other than
hydrogen in the molecule or ion.
4) Compare the number of dots to be shown with 6y + 2.
a) If the two are equal, all atoms in the aggregate obey the octet
rule, and there are no multiple bonds. T h e procedure is not flawless, of course. T h e simple rules
Examnles: P O P . CIHR.CCla. Br?. NHnC. C10s- would have t o be modified to account for n i c k structures, to
b) If the number of d o c tobe shiwnk lessthan 6; + 2, either allow correct placement of the single H of formate ion, and to
of the following holds. deal with odd-electron structures. T h e rules do not lead t o a
i) There are multiple hands in the structure, a deficiency decision atomis central in thiosulfate ion, and
Of two indicating a bond and a four they do lead to a n incorrect structure for phosphorous acid.
indicating either a triple bond or two double bonds.
ii) An atom a Group I, 11, or 111element has less than an
T h e most serious flaw is t h a t a n incorrect choice of central
octet of electrons. atom (e.g., 0 in CzH40)can occasionally cause the student to
Examnles: CHIO. GHa, NI, COz, CO, BeH2, LiCHz spend time developing a structure which cannot be properly
C) If the number of dog to be shown is greater than 6y + 2, the completed.
central atom has an exoanded valence shell. Examoles: SF&. These defects do not seriouslv imoair the usefulness of this
SeC4, XeFz, SbFs- procedure. One should make s i r e i h a t a t the start students
5) Arrange the non-hydrogens in a likely fashion using the fol- encounter only examples which are dealt with correctly by the
lowing principles asguides. Atoms of elements in GroupsK 111, simple rules. Students quickly become aware of the features
IV, and likelyto be central atoms. If just One atom of some possessed by correct Lewis structures, and one can then make
element and several atoms of some other element are present,
the unique atom is likely to he central. modifications of the rules t o extend the range of applicability
6) Enter the dots making use of the decision made in step (4). Start the procedure.
with the dots far any multiple bond, placing them between the
central atom and one of its neighboring atoms. Then complete
the octets for the atoms attached to the central atom. Finally
enter dots for any pairs on the central atom. Lever, A.B.P., J. CHEM.EDUC.,49,819 (1972).
100 Journal of Chemical Education
You might also like
- EXU enDocument122 pagesEXU enMahmoud Elpop ElsalhNo ratings yet
- Designing Urea ReactorDocument21 pagesDesigning Urea ReactorAdawiyah Al-jufri100% (4)
- Teaching A Model For Writing Lewis Structures: Qullez PardoDocument3 pagesTeaching A Model For Writing Lewis Structures: Qullez PardoMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- Richard S. Moog - Chemistry - A Guided Inquiry, 7th Edition-Wiley (2017) - 85Document45 pagesRichard S. Moog - Chemistry - A Guided Inquiry, 7th Edition-Wiley (2017) - 85Siti SupriyantiNo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures, Formal Charge, and OxidationDocument3 pagesLewis Structures, Formal Charge, and OxidationjosueNo ratings yet
- 51a Chapter 1 2014 Copy 2Document37 pages51a Chapter 1 2014 Copy 2Efrain AnayaNo ratings yet
- 04E ExercisesDocument9 pages04E ExercisesBlack VelvetNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Weeks 1-10 PDFDocument22 pagesTutorial Questions Weeks 1-10 PDFCharlotteNo ratings yet
- 03 Lewis StructuresDocument22 pages03 Lewis Structuresadeshinasamuel017No ratings yet
- 4.0 ChemicalbondingDocument219 pages4.0 ChemicalbondingTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Examples of Chemical BondsDocument11 pagesExamples of Chemical BondsRondel ForjesNo ratings yet
- Psfsiee ReviewDocument10 pagesPsfsiee Reviewlimichael000No ratings yet
- Drawing Lewis Structures Using Formal ChargeDocument6 pagesDrawing Lewis Structures Using Formal Chargemeg megNo ratings yet
- Symmetry 3820Document7 pagesSymmetry 3820KnspeisNo ratings yet
- Bonding Student Study GuideDocument15 pagesBonding Student Study GuideJohn Philip NapalNo ratings yet
- Mol ShapesDocument22 pagesMol ShapesTshiamo MotaungNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Workshop Handout - Topic 6 & 7 - SolutionsDocument9 pagesWeek 7 Workshop Handout - Topic 6 & 7 - SolutionsSandesh BNo ratings yet
- Lec1 PDFDocument3 pagesLec1 PDFSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document18 pagesModule 3tamaraolayanievasNo ratings yet
- Covelent BondingDocument4 pagesCovelent BondingMBOTAKE LawsonNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry IiDocument23 pagesIntroductory Chemistry IiAnonymous lcT0sipb5No ratings yet
- CHEM1 Q2 M2-Lewis-StructuresDocument32 pagesCHEM1 Q2 M2-Lewis-StructuresMark TerradoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Modeling and Lewis StructuresDocument14 pagesMolecular Modeling and Lewis StructuresJack DavisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument147 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryOrianna SanoNo ratings yet
- (BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFDocument8 pages(BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFChris Andrew Mendoza100% (1)
- Geometry BkgdroundDocument7 pagesGeometry Bkgdroundtanique.nembhard1022No ratings yet
- Molecular Modeling by Roxie AllenDocument5 pagesMolecular Modeling by Roxie AllenPaul SchumannNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 8 NotesmrbookoNo ratings yet
- Eastern Visayas State UniversityDocument6 pagesEastern Visayas State UniversityShaun Patrick AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - COVALENT COMPOUNDDocument19 pagesGroup 3 - COVALENT COMPOUNDWendy BorjaNo ratings yet
- Review of Fundamental Concepts F12Document7 pagesReview of Fundamental Concepts F12DerrickGMcCoyNo ratings yet
- (Mohan) Assignment 1-Covalent BondDocument7 pages(Mohan) Assignment 1-Covalent BondMohan GoelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument20 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureWoodlem Park Calicut LRCNo ratings yet
- Science 112 STUDY GUIDE 2Document15 pagesScience 112 STUDY GUIDE 2Dominador RomuloNo ratings yet
- Lewis StructureDocument38 pagesLewis StructureNicole Joyce Catabay FloresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4maittt.22ba13211No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding (Con't) : (4 + 6) 10 Valence ElectronsDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical Bonding (Con't) : (4 + 6) 10 Valence ElectronsPineraserNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Interactive General Chemistry 1st Edition Macmillan LearningDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Interactive General Chemistry 1st Edition Macmillan LearningChristopherWigginsnbme100% (34)
- Organic Chemistry 1Document324 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1Bellony Sanders100% (7)
- ChemQuest 29Document4 pagesChemQuest 29Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondsDocument29 pagesCovalent Bondsbasaallen566No ratings yet
- 8 BondingDocument25 pages8 BondingBharat NimeshNo ratings yet
- Group Worksheet Week 11 Blank-1Document3 pagesGroup Worksheet Week 11 Blank-1Krumpus H.No ratings yet
- Soil 2Document83 pagesSoil 2Jason StoneNo ratings yet
- 16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I - Tutorial 5Document6 pagesGeneral Chemistry I - Tutorial 5Duc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lewis StructureDocument7 pagesLewis StructureKed LukkedNo ratings yet
- 4 Chemical BondingDocument63 pages4 Chemical BondingArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Lewis TutorialDocument13 pagesLewis TutorialJc Borlaza QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical BondingShashank BgNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (ADV)Document84 pagesChemical Bonding (ADV)DreamwastakenNo ratings yet
- Vsepr GeometryDocument42 pagesVsepr Geometrykylamalonzo2No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Chemical BondsDocument41 pagesChapter 6 - Chemical BondsDn ZackNo ratings yet
- CHEM225 Organic Chemistry 1 Module Week 1-4Document17 pagesCHEM225 Organic Chemistry 1 Module Week 1-4Kezia CaratorNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument53 pagesIonic and Covalent BondingdomaincontrollerNo ratings yet
- Use The Following Information To Answer The Next QuestionDocument6 pagesUse The Following Information To Answer The Next QuestionMashun PutraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document30 pagesLecture 5Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document35 pagesPart 1Ola100% (1)
- Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleDocument89 pagesChapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleAnn BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Bond NoteDocument9 pagesChemical-Bond NoteDixit GautamNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Teaching A Model For Writing Lewis Structures: Qullez PardoDocument3 pagesTeaching A Model For Writing Lewis Structures: Qullez PardoMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- Friesen,: EditorDocument2 pagesFriesen,: EditorMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Bonding and Heat of Solution: FriedmanDocument1 pageHydrogen Bonding and Heat of Solution: FriedmanMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- Chemicd Principle1 Revi I Ted: The Rule" For Writing Lewis Octet StructuresDocument4 pagesChemicd Principle1 Revi I Ted: The Rule" For Writing Lewis Octet StructuresMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Assumption English School AnswerDocument8 pages2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Assumption English School AnswerMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Chua Chu Kang Secondary AnswerDocument7 pages2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Chua Chu Kang Secondary AnswerMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Assumption English SchoolDocument43 pages2019 Sec 4 Pure Chemistry SA2 Assumption English SchoolMarvel AcademyNo ratings yet
- MSA Sample PresentationDocument9 pagesMSA Sample PresentationTom@GGCNo ratings yet
- Production of Liquid, Cream, Ointment: Chapter FourDocument8 pagesProduction of Liquid, Cream, Ointment: Chapter FourArifur Rahman TanzilNo ratings yet
- Service & Operating Manual: 1/2" Elima-Matic Bolted MetalDocument14 pagesService & Operating Manual: 1/2" Elima-Matic Bolted MetalCalNo ratings yet
- 7-7-2019 19 55 42 ErrorLogDocument4 pages7-7-2019 19 55 42 ErrorLogMarvin CustodioNo ratings yet
- HPCL SYLLABUS 2022 Chemical PediaDocument6 pagesHPCL SYLLABUS 2022 Chemical PediaRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- EstimationDocument146 pagesEstimationHaymanAHMEDNo ratings yet
- DBR MediniNagar JharkhandDocument7 pagesDBR MediniNagar JharkhandinfohydNo ratings yet
- Vo2 Max Lab Report DoneDocument6 pagesVo2 Max Lab Report Doneapi-547193352No ratings yet
- SDL 700 DataDocument1 pageSDL 700 DataPetinggi TElektroNo ratings yet
- Revalidated - MATH - GR8 - QTR1-MODULE-2 - (28 Pages)Document28 pagesRevalidated - MATH - GR8 - QTR1-MODULE-2 - (28 Pages)Andrei MemanNo ratings yet
- Asmiv T I Dwgs For 3keDocument14 pagesAsmiv T I Dwgs For 3kePSI Guillermo Francisco RuizNo ratings yet
- FMEA Nu CorkDocument19 pagesFMEA Nu CorkAjit SamalNo ratings yet
- Mobile Harbour Crane PDFDocument7 pagesMobile Harbour Crane PDFJatin KumarNo ratings yet
- LED FLOOD LIGHT 100 - SMD NewDocument1 pageLED FLOOD LIGHT 100 - SMD NewAlvin RejisNo ratings yet
- 9702 w22 Ms 42 PDFDocument16 pages9702 w22 Ms 42 PDFsangdeepNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Experimental Archaeology - Outram PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Experimental Archaeology - Outram PDFDasRakeshKumarDasNo ratings yet
- Sample Preparation For EBSDDocument6 pagesSample Preparation For EBSDTNNo ratings yet
- Criotom Server Manual PDFDocument282 pagesCriotom Server Manual PDFAlex RaileanNo ratings yet
- Fibers: Porosity Prediction of Plain Weft Knitted FabricsDocument11 pagesFibers: Porosity Prediction of Plain Weft Knitted FabricsAnonymous Pt7NHkat9No ratings yet
- 1.7 Combining Like Terms & Distrib PropDocument2 pages1.7 Combining Like Terms & Distrib PropJackNo ratings yet
- Acker Rig Specs PDFDocument2 pagesAcker Rig Specs PDFAsif KhanzadaNo ratings yet
- Coaching Actuaries Exam IFM Suggested Study Schedule: Phase 1: LearnDocument7 pagesCoaching Actuaries Exam IFM Suggested Study Schedule: Phase 1: LearnKamilahNo ratings yet
- 2013 / 1 6 Power System Analysis and Stability Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument32 pages2013 / 1 6 Power System Analysis and Stability Representation of Power System ComponentsPooja AshishNo ratings yet
- Polymer Membranes in Biomedical FieldDocument35 pagesPolymer Membranes in Biomedical FieldAbufathima CheruvadiNo ratings yet
- Argus Input Modules Connection DiagramDocument2 pagesArgus Input Modules Connection DiagramMd. Biplob HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document55 pagesChapter 6Amanu WorkuNo ratings yet
- Rake ReceiverDocument48 pagesRake ReceiverIk Ram100% (1)
- How To Achieve Speed in Maths Calculations PDFDocument6 pagesHow To Achieve Speed in Maths Calculations PDFAnonymous 9Yv6n5qvSNo ratings yet