Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 2
Lab 2
Uploaded by
Syed Muhammad Hasan DanishCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Expt 5.1Document6 pagesExpt 5.1Joel Catapang0% (1)
- Lab1 Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pagesLab1 Circuit AnalysisSyed Muhammad Hasan DanishNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Document6 pagesDC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Ratul kumarNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document5 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2Document6 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2THE LEARNER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- DC-Lab Report 02Document10 pagesDC-Lab Report 02Shahriar Ahsan JohaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document8 pagesLab 3TOP 5 GHOSTNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Series DC CircuitsDocument4 pagesExp 2 Series DC Circuitsmaskrasheed777No ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreDocument20 pagesCircuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreNicoNo ratings yet
- DC Exp 2 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDC Exp 2 Student ManualAsifur R. HimelNo ratings yet
- Activity3 Group1Document16 pagesActivity3 Group1NicoNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Kirchoff Law Sea19029, Sea19004, Sea19027Document14 pagesLab 4 Kirchoff Law Sea19029, Sea19004, Sea19027Muhammad NaguibNo ratings yet
- UNIT2L2SDocument20 pagesUNIT2L2SJack CardiagNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2Document7 pagesExp - 2Shakil Rahman AfidNo ratings yet
- Nec2102 Villamor Experiment No5Document16 pagesNec2102 Villamor Experiment No5Lynndon VillamorNo ratings yet
- Date: Experiment: 1 AIM: To Study Various Symbols Used in Electrical Engineering. Sr. No. Particular SymbolDocument33 pagesDate: Experiment: 1 AIM: To Study Various Symbols Used in Electrical Engineering. Sr. No. Particular SymbolAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Thesis CorrectedDocument63 pagesThesis CorrectedChidume NonsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Analysis AllDocument32 pagesChapter 2 DC Analysis Allyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- To Investigate The Characteristics of A Parallel DC Circuit and To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Document4 pagesTo Investigate The Characteristics of A Parallel DC Circuit and To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Apu Sarkar0% (2)
- Circuit Analysis Laboratory ManualDocument50 pagesCircuit Analysis Laboratory ManualYAMINI D SDECT013No ratings yet
- Network Analysis and Simulation LaboratoryDocument33 pagesNetwork Analysis and Simulation Laboratoryswis29No ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24mahinc021No ratings yet
- EEE - 122 - Exp1 (8 Files Merged)Document5 pagesEEE - 122 - Exp1 (8 Files Merged)SHAJEDA AKTHER 2102154No ratings yet
- 1 Circuit Theory - MZMDocument47 pages1 Circuit Theory - MZMSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)Document5 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)NickNo ratings yet
- Iec Exp 8Document9 pagesIec Exp 8mursalinleon2295No ratings yet
- PHY547 - LAb Manual-2019Document26 pagesPHY547 - LAb Manual-2019zulhaimirasheedNo ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24rakibulislamakash40No ratings yet
- Unit 1: DC Circuits: Summary and Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesUnit 1: DC Circuits: Summary and Learning OutcomesKevin CheeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2atefm7959No ratings yet
- Pee Lab ManualDocument77 pagesPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)
- EEE207Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 2Document21 pagesEEE207Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 2tyoudalpenaNo ratings yet
- IEC - EXP - 8 - Analysis of RC, RL, RLC Series Circuits and Verification of KVL in RLC Series Circuit Related To AC CircuitDocument8 pagesIEC - EXP - 8 - Analysis of RC, RL, RLC Series Circuits and Verification of KVL in RLC Series Circuit Related To AC Circuitsajid_hossain_6No ratings yet
- Circuit Transformations: 2.1 Series CircuitsDocument15 pagesCircuit Transformations: 2.1 Series CircuitsljjbNo ratings yet
- Ec2155 Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEc2155 Lab ManualSuresh Ponnusamy50% (2)
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Document4 pagesDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsDocument39 pagesLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarNo ratings yet
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- Frederick Terry's Lab Report Electrical SystemsDocument9 pagesFrederick Terry's Lab Report Electrical SystemsFreddie TerryNo ratings yet
- Impedance of RL Circuits: Series RL Circuits: Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesImpedance of RL Circuits: Series RL Circuits: Experiment No. 2NicoNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 6 ModifiedDocument4 pagesLab Handout 6 ModifiedAmeer JaanNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetDocument3 pagesEEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Alexander CH 02 Final R 1Document16 pagesAlexander CH 02 Final R 1kifle203No ratings yet
- Final Review PDFDocument19 pagesFinal Review PDFurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- Ecx3231 Lab01 2015-2016Document6 pagesEcx3231 Lab01 2015-2016Lackith Chandimal HettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- كهرباء من الميش الى السوبر بوزشنDocument33 pagesكهرباء من الميش الى السوبر بوزشنljjb100% (1)
- EXP. 2 Series DC CircuitDocument4 pagesEXP. 2 Series DC CircuitghlafhlyNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal AnalysisDocument9 pagesLab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal Analysismatteo rossiNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument19 pagesGeneral Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyIzaNo ratings yet
- BEEI Lab Manual CompressedDocument85 pagesBEEI Lab Manual CompressedkavithaNo ratings yet
- Exp3 (Ac Series)Document2 pagesExp3 (Ac Series)Deepankar Synthesizer Playist DspNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDocument11 pagesChapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab Manual CSVTUDocument44 pagesBEEE Lab Manual CSVTUMulty TalantedNo ratings yet
- GRP 07 Exp 08 IeclabDocument19 pagesGRP 07 Exp 08 IeclabesumshunNo ratings yet
- Engr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesEngr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveJonathan MischNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab Manual StudentDocument59 pagesElectrical Machines Lab Manual StudentJunaid SheikhNo ratings yet
- Circuit LabDocument7 pagesCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Basic Writing Skill TxtbookDocument16 pagesBasic Writing Skill Txtbookyacob sozoNo ratings yet
- Gravity Lab - Advanced VersionDocument7 pagesGravity Lab - Advanced VersionTeachLABScINo ratings yet
- Wind Diesel Systems by Krishna Raghavan, Arrakis AssociateDocument7 pagesWind Diesel Systems by Krishna Raghavan, Arrakis Associateanhhung80No ratings yet
- NPSH CalculationDocument14 pagesNPSH Calculationgrabetty100% (1)
- Ian Stewart: The Missing Link...Document7 pagesIan Stewart: The Missing Link...mjf2222No ratings yet
- Point Shield BrochureDocument6 pagesPoint Shield BrochureIsrael ExporterNo ratings yet
- Cahier Technique: Protection of MV/LV Substation TransformersDocument37 pagesCahier Technique: Protection of MV/LV Substation TransformersDheeraj Yadav100% (1)
- Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting: 4008-30 Industrial EngineDocument42 pagesSystems Operation Testing and Adjusting: 4008-30 Industrial EngineMARCO100% (1)
- 2011 MX5 Service ManualDocument3,841 pages2011 MX5 Service ManualSandocars MotorNo ratings yet
- Eaton Dilet 70Document2 pagesEaton Dilet 70chamberlanesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Description: See Page 05-5 See Page 05-5Document8 pagesCircuit Description: See Page 05-5 See Page 05-5Jonn Sim-One100% (1)
- Boiler BriefDocument9 pagesBoiler BrieffelramNo ratings yet
- Final Report,,,ChevronDocument21 pagesFinal Report,,,ChevronemonenjoyNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemDocument11 pagesElectro ChemAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Details - Ecology UnitsDocument4 pagesTechnical Details - Ecology Unitsprashant.jadhavNo ratings yet
- Civil Works Guidelines MHP NepalDocument5 pagesCivil Works Guidelines MHP Nepalsaurav_mobileNo ratings yet
- SR No. Vendors Scope of Supply Address Proprietary Vendor'S ListDocument10 pagesSR No. Vendors Scope of Supply Address Proprietary Vendor'S ListCOLONEL ZIKRIANo ratings yet
- AC Rectifier Bulk Capacitor Selection With Analysis+SPICE (Walker) PDFDocument5 pagesAC Rectifier Bulk Capacitor Selection With Analysis+SPICE (Walker) PDFjazbo8No ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument6 pagesReaction PaperKirby IngcoNo ratings yet
- Space Vector Modulation of Multi-Level and Multi-Module Converters For High Power ApplicationsDocument176 pagesSpace Vector Modulation of Multi-Level and Multi-Module Converters For High Power ApplicationsharkoneneNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalacion Detector de MetalesDocument28 pagesManual de Instalacion Detector de MetalesMirla Marisel Chavez NajeraNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument21 pagesSimple Harmonic MotionHabimana HassanNo ratings yet
- Censter 6200 Main BoardDocument8 pagesCenster 6200 Main Boardibula emmanuelNo ratings yet
- 1 DirtyDozenWeb TraducidoDocument77 pages1 DirtyDozenWeb TraducidoKevin Arteaga100% (1)
- Investigate The Use of Solar Energy Into Small Houses For Sustainable LivingDocument27 pagesInvestigate The Use of Solar Energy Into Small Houses For Sustainable LivingChristianLouisNoquisNo ratings yet
- Infrared Theory PDFDocument9 pagesInfrared Theory PDFATNo ratings yet
- SANS 10313:2010 & IEC 62305 Part 2 & 3 Explained: Session TwoDocument12 pagesSANS 10313:2010 & IEC 62305 Part 2 & 3 Explained: Session Twojosethompson100% (2)
- AaaaaaDocument80 pagesAaaaaaRishab100% (2)
- Year 11 Jacaranda PhysicsDocument336 pagesYear 11 Jacaranda PhysicsJonathan Skelton50% (2)
- Usa ST 036 072 PK Motor OnlyDocument4 pagesUsa ST 036 072 PK Motor Onlyjmpateiro1985No ratings yet
- University of New Mexico Divestment ComplaintDocument63 pagesUniversity of New Mexico Divestment ComplaintAlbuquerque JournalNo ratings yet
Lab 2
Lab 2
Uploaded by
Syed Muhammad Hasan DanishOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 2
Lab 2
Uploaded by
Syed Muhammad Hasan DanishCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab # 02: Dc analysis of parallel resistive circuit.
SSUET/QR/114
Lab # 02
Follows DC analysis of parallel resistive circuits.
Description/Theory:
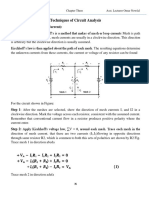
Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows
through all of the components. A circuit composed solely of components connected in series is
known as a series circuit. In a series circuit, the current through each of the components is the
same, and the voltage across the components is the sum of the voltages across each component in
accordance with Kirchhoff’s voltage law.
CIRCUIT NO 1(C1):
Build the following given Series circuits:
Figure 2.1
CIRCUIT NO 2(C2):
Figure 2.2
EE-122L: Circuit Analysis 3
Lab # 02: Dc analysis of parallel resistive circuit. SSUET/QR/114
Description/Theory:
Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows
through all of the components. A circuit composed solely of components connected in series is
known as a series circuit. In a series circuit, the current through each of the components is the
same, and the voltage across the components is the sum of the voltages across each component in
accordance with Kirchhoff’s voltage law.
CIRCUIT NO 1(C1):
Build the following given Series circuits:
Figure 2.1
CIRCUIT NO 2(C2):
Figure 2.2
TASK 1:
Determine what will be the value of voltage across each branch. Also find the value of total
current.
EE-122L: Circuit Analysis 4
Lab # 02: Dc analysis of parallel resistive circuit. SSUET/QR/114
TASK 2:
Prove Kirchhoff’s Voltage law that total voltage is equal to the sum of the voltage drop across
each resistor.
TASK 3:
If R2=2(R1) and R3=2(R2),now take five different values of R1 and observe that what happens
with the voltage across each resistor in a particular if the resistance of the branch increases or
decreases.
TASK 4:
Calculate the power of each resistor and prove the law of conservation of energy.(Apply for all
cases of task 3).
OBSERVATION TABLE:
S. APPLIED CURRENT RESISTORS VOLTAGE TOTAL POWER POWER
N VOLTAGE FLOWING ACROSS POWER ACROSS EACH SUPPLED
O EACH SUPPLIED RESISTOR Pr1+Pr2+Pr3
BRANCH
Vs Is R R R VR VR VR Pt=Vs Is PR PR PR
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Table 2.2: For task no 3 and task no 4
TASK 5:
Calculate the total input resistance (RT) as seen by the source using Digital Multimeter(DMM).
EE-122L: Circuit Analysis 5
Lab # 02: Dc analysis of parallel resistive circuit. SSUET/QR/114
EE-122L: Circuit Analysis 6
You might also like
- Expt 5.1Document6 pagesExpt 5.1Joel Catapang0% (1)
- Lab1 Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pagesLab1 Circuit AnalysisSyed Muhammad Hasan DanishNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Document6 pagesDC Lab Exp 2 Student Manual (Fall 22-23)Ratul kumarNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Document5 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2 - Student - Manual (Spring 22-23)Bahesty Monfared AkashNo ratings yet
- DC Lab - Exp - 2Document6 pagesDC Lab - Exp - 2THE LEARNER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- DC-Lab Report 02Document10 pagesDC-Lab Report 02Shahriar Ahsan JohaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document8 pagesLab 3TOP 5 GHOSTNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Series DC CircuitsDocument4 pagesExp 2 Series DC Circuitsmaskrasheed777No ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- Circuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreDocument20 pagesCircuits 2 Laboratory L31A: ScoreNicoNo ratings yet
- DC Exp 2 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDC Exp 2 Student ManualAsifur R. HimelNo ratings yet
- Activity3 Group1Document16 pagesActivity3 Group1NicoNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Kirchoff Law Sea19029, Sea19004, Sea19027Document14 pagesLab 4 Kirchoff Law Sea19029, Sea19004, Sea19027Muhammad NaguibNo ratings yet
- UNIT2L2SDocument20 pagesUNIT2L2SJack CardiagNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2Document7 pagesExp - 2Shakil Rahman AfidNo ratings yet
- Nec2102 Villamor Experiment No5Document16 pagesNec2102 Villamor Experiment No5Lynndon VillamorNo ratings yet
- Date: Experiment: 1 AIM: To Study Various Symbols Used in Electrical Engineering. Sr. No. Particular SymbolDocument33 pagesDate: Experiment: 1 AIM: To Study Various Symbols Used in Electrical Engineering. Sr. No. Particular SymbolAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Thesis CorrectedDocument63 pagesThesis CorrectedChidume NonsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Analysis AllDocument32 pagesChapter 2 DC Analysis Allyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- To Investigate The Characteristics of A Parallel DC Circuit and To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Document4 pagesTo Investigate The Characteristics of A Parallel DC Circuit and To Verify Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Apu Sarkar0% (2)
- Circuit Analysis Laboratory ManualDocument50 pagesCircuit Analysis Laboratory ManualYAMINI D SDECT013No ratings yet
- Network Analysis and Simulation LaboratoryDocument33 pagesNetwork Analysis and Simulation Laboratoryswis29No ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24mahinc021No ratings yet
- EEE - 122 - Exp1 (8 Files Merged)Document5 pagesEEE - 122 - Exp1 (8 Files Merged)SHAJEDA AKTHER 2102154No ratings yet
- 1 Circuit Theory - MZMDocument47 pages1 Circuit Theory - MZMSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)Document5 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering (EEE)NickNo ratings yet
- Iec Exp 8Document9 pagesIec Exp 8mursalinleon2295No ratings yet
- PHY547 - LAb Manual-2019Document26 pagesPHY547 - LAb Manual-2019zulhaimirasheedNo ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24rakibulislamakash40No ratings yet
- Unit 1: DC Circuits: Summary and Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesUnit 1: DC Circuits: Summary and Learning OutcomesKevin CheeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2atefm7959No ratings yet
- Pee Lab ManualDocument77 pagesPee Lab ManualRajendraTuraka100% (1)
- EEE207Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 2Document21 pagesEEE207Electrics and Electronics-Chapter 2tyoudalpenaNo ratings yet
- IEC - EXP - 8 - Analysis of RC, RL, RLC Series Circuits and Verification of KVL in RLC Series Circuit Related To AC CircuitDocument8 pagesIEC - EXP - 8 - Analysis of RC, RL, RLC Series Circuits and Verification of KVL in RLC Series Circuit Related To AC Circuitsajid_hossain_6No ratings yet
- Circuit Transformations: 2.1 Series CircuitsDocument15 pagesCircuit Transformations: 2.1 Series CircuitsljjbNo ratings yet
- Ec2155 Lab ManualDocument32 pagesEc2155 Lab ManualSuresh Ponnusamy50% (2)
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Document4 pagesDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsDocument39 pagesLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarNo ratings yet
- ET Lab ManualDocument52 pagesET Lab Manualcholleti sriram100% (1)
- Frederick Terry's Lab Report Electrical SystemsDocument9 pagesFrederick Terry's Lab Report Electrical SystemsFreddie TerryNo ratings yet
- Impedance of RL Circuits: Series RL Circuits: Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesImpedance of RL Circuits: Series RL Circuits: Experiment No. 2NicoNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 6 ModifiedDocument4 pagesLab Handout 6 ModifiedAmeer JaanNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetDocument3 pagesEEE 202 Lab Experiment SheetAlamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Alexander CH 02 Final R 1Document16 pagesAlexander CH 02 Final R 1kifle203No ratings yet
- Final Review PDFDocument19 pagesFinal Review PDFurfriend_jjn05No ratings yet
- Ecx3231 Lab01 2015-2016Document6 pagesEcx3231 Lab01 2015-2016Lackith Chandimal HettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- كهرباء من الميش الى السوبر بوزشنDocument33 pagesكهرباء من الميش الى السوبر بوزشنljjb100% (1)
- EXP. 2 Series DC CircuitDocument4 pagesEXP. 2 Series DC CircuitghlafhlyNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal AnalysisDocument9 pagesLab 04 - KVL, KCL, Nodal Analysismatteo rossiNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument19 pagesGeneral Physics Lab Report: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyIzaNo ratings yet
- BEEI Lab Manual CompressedDocument85 pagesBEEI Lab Manual CompressedkavithaNo ratings yet
- Exp3 (Ac Series)Document2 pagesExp3 (Ac Series)Deepankar Synthesizer Playist DspNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDocument11 pagesChapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- BEEE Lab Manual CSVTUDocument44 pagesBEEE Lab Manual CSVTUMulty TalantedNo ratings yet
- GRP 07 Exp 08 IeclabDocument19 pagesGRP 07 Exp 08 IeclabesumshunNo ratings yet
- Engr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesEngr 2001-Circuits I Lab Laboratory Experiment 2 Voltage and Current Division Reference: ObjectiveJonathan MischNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab Manual StudentDocument59 pagesElectrical Machines Lab Manual StudentJunaid SheikhNo ratings yet
- Circuit LabDocument7 pagesCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNo ratings yet
- Basic Writing Skill TxtbookDocument16 pagesBasic Writing Skill Txtbookyacob sozoNo ratings yet
- Gravity Lab - Advanced VersionDocument7 pagesGravity Lab - Advanced VersionTeachLABScINo ratings yet
- Wind Diesel Systems by Krishna Raghavan, Arrakis AssociateDocument7 pagesWind Diesel Systems by Krishna Raghavan, Arrakis Associateanhhung80No ratings yet
- NPSH CalculationDocument14 pagesNPSH Calculationgrabetty100% (1)
- Ian Stewart: The Missing Link...Document7 pagesIan Stewart: The Missing Link...mjf2222No ratings yet
- Point Shield BrochureDocument6 pagesPoint Shield BrochureIsrael ExporterNo ratings yet
- Cahier Technique: Protection of MV/LV Substation TransformersDocument37 pagesCahier Technique: Protection of MV/LV Substation TransformersDheeraj Yadav100% (1)
- Systems Operation Testing and Adjusting: 4008-30 Industrial EngineDocument42 pagesSystems Operation Testing and Adjusting: 4008-30 Industrial EngineMARCO100% (1)
- 2011 MX5 Service ManualDocument3,841 pages2011 MX5 Service ManualSandocars MotorNo ratings yet
- Eaton Dilet 70Document2 pagesEaton Dilet 70chamberlanesNo ratings yet
- Circuit Description: See Page 05-5 See Page 05-5Document8 pagesCircuit Description: See Page 05-5 See Page 05-5Jonn Sim-One100% (1)
- Boiler BriefDocument9 pagesBoiler BrieffelramNo ratings yet
- Final Report,,,ChevronDocument21 pagesFinal Report,,,ChevronemonenjoyNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemDocument11 pagesElectro ChemAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Details - Ecology UnitsDocument4 pagesTechnical Details - Ecology Unitsprashant.jadhavNo ratings yet
- Civil Works Guidelines MHP NepalDocument5 pagesCivil Works Guidelines MHP Nepalsaurav_mobileNo ratings yet
- SR No. Vendors Scope of Supply Address Proprietary Vendor'S ListDocument10 pagesSR No. Vendors Scope of Supply Address Proprietary Vendor'S ListCOLONEL ZIKRIANo ratings yet
- AC Rectifier Bulk Capacitor Selection With Analysis+SPICE (Walker) PDFDocument5 pagesAC Rectifier Bulk Capacitor Selection With Analysis+SPICE (Walker) PDFjazbo8No ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument6 pagesReaction PaperKirby IngcoNo ratings yet
- Space Vector Modulation of Multi-Level and Multi-Module Converters For High Power ApplicationsDocument176 pagesSpace Vector Modulation of Multi-Level and Multi-Module Converters For High Power ApplicationsharkoneneNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalacion Detector de MetalesDocument28 pagesManual de Instalacion Detector de MetalesMirla Marisel Chavez NajeraNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument21 pagesSimple Harmonic MotionHabimana HassanNo ratings yet
- Censter 6200 Main BoardDocument8 pagesCenster 6200 Main Boardibula emmanuelNo ratings yet
- 1 DirtyDozenWeb TraducidoDocument77 pages1 DirtyDozenWeb TraducidoKevin Arteaga100% (1)
- Investigate The Use of Solar Energy Into Small Houses For Sustainable LivingDocument27 pagesInvestigate The Use of Solar Energy Into Small Houses For Sustainable LivingChristianLouisNoquisNo ratings yet
- Infrared Theory PDFDocument9 pagesInfrared Theory PDFATNo ratings yet
- SANS 10313:2010 & IEC 62305 Part 2 & 3 Explained: Session TwoDocument12 pagesSANS 10313:2010 & IEC 62305 Part 2 & 3 Explained: Session Twojosethompson100% (2)
- AaaaaaDocument80 pagesAaaaaaRishab100% (2)
- Year 11 Jacaranda PhysicsDocument336 pagesYear 11 Jacaranda PhysicsJonathan Skelton50% (2)
- Usa ST 036 072 PK Motor OnlyDocument4 pagesUsa ST 036 072 PK Motor Onlyjmpateiro1985No ratings yet
- University of New Mexico Divestment ComplaintDocument63 pagesUniversity of New Mexico Divestment ComplaintAlbuquerque JournalNo ratings yet