Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pma4 1500 00 CV1
Pma4 1500 00 CV1
Uploaded by
aswinCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math Stem Lesson Ecs 585Document10 pagesMath Stem Lesson Ecs 585Jacqueline MedinaNo ratings yet
- "What Time Is It?" Lesson PlanDocument4 pages"What Time Is It?" Lesson PlanTaylor DunlapNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson - Telling TimeDocument6 pagesMath Lesson - Telling TimeOctaviAnaNo ratings yet
- The Chernobyl Zone Survival GuideDocument685 pagesThe Chernobyl Zone Survival GuideDavidNo ratings yet
- Time 2017 PlannerDocument3 pagesTime 2017 Plannerapi-374359720No ratings yet
- Math Measurment Time 1Document13 pagesMath Measurment Time 1api-640764419No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Reading A Digital Clock Lesson 4: Reading A Digital ClockDocument2 pagesLesson 4: Reading A Digital Clock Lesson 4: Reading A Digital ClockFinapapNo ratings yet
- Telling The Time To The Half Hour Analogue Clock Starter Sheet - 21411Document2 pagesTelling The Time To The Half Hour Analogue Clock Starter Sheet - 21411FinapapNo ratings yet
- 5.11B Elapsed TimeDocument5 pages5.11B Elapsed Timemark anthony fontanos100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan 3api-352613082No ratings yet
- Tpack Template Iwb sp18 PJ DavisDocument2 pagesTpack Template Iwb sp18 PJ Davisapi-404220188No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-352613082No ratings yet
- Teach Live Micro LessonDocument5 pagesTeach Live Micro Lessonapi-372343626No ratings yet
- G Is For Googol PDFDocument8 pagesG Is For Googol PDFMichelle SpiteriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Learning Program - Year 8 MeasurementDocument8 pagesMathematics Learning Program - Year 8 MeasurementJames HarrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 6Document3 pagesLesson Plan 6api-352613082No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: TopicDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: TopicRobert FlynnNo ratings yet
- 13-3 Telling and Writing Time To The Half HourDocument3 pages13-3 Telling and Writing Time To The Half Hourapi-411104780No ratings yet
- Final Lesson Plan Assignment 2 DesigningDocument17 pagesFinal Lesson Plan Assignment 2 Designingapi-485798829No ratings yet
- IV Day1Document4 pagesIV Day1Robin LayugNo ratings yet
- Elapsed Time Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesElapsed Time Lesson PlanGina Caroddo100% (4)
- Maths Time Lesson LiasonDocument2 pagesMaths Time Lesson Liasonapi-492582965No ratings yet
- Maths Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMaths Lesson Planapi-481483709No ratings yet
- Copy of Blank Lesson Plan Template 2022 4Document3 pagesCopy of Blank Lesson Plan Template 2022 4api-616369916No ratings yet
- Common Core Lesson PlannerDocument3 pagesCommon Core Lesson Plannerapi-419135285No ratings yet
- Year 2-Methodology and Practice of ELT-Lesson Plan DraftDocument6 pagesYear 2-Methodology and Practice of ELT-Lesson Plan Draftemmanouelavagia96No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlantarbeecatNo ratings yet
- DemotellingtimepreviewpdfDocument10 pagesDemotellingtimepreviewpdfJamila NoorNo ratings yet
- Standards Based Lesson Plan Elements: Ccss - Math.Content.2.G.A.2Document4 pagesStandards Based Lesson Plan Elements: Ccss - Math.Content.2.G.A.2api-610136255No ratings yet
- Time and Elapsed Time Work Sample: Teacher Work Sample 4th Grade - Central Noble Elementary School Kenzie TeelDocument7 pagesTime and Elapsed Time Work Sample: Teacher Work Sample 4th Grade - Central Noble Elementary School Kenzie Teelapi-488011782No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 8Document3 pagesLesson Plan 8api-352613082No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5Document3 pagesLesson Plan 5api-352613082No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document4 pagesLesson 2api-428818739No ratings yet
- Time Week3 MondayDocument2 pagesTime Week3 Mondayapi-320437238No ratings yet
- DR - Isaac Li Physics 50minutes Grade 10Document3 pagesDR - Isaac Li Physics 50minutes Grade 10api-350728128No ratings yet
- Elapsed TimeDocument41 pagesElapsed TimeMarcelo FloresNo ratings yet
- Multiple Means of ExpressionDocument6 pagesMultiple Means of Expressionapi-456276800No ratings yet
- Sage Blackmore Viva LessonsDocument5 pagesSage Blackmore Viva Lessonsapi-465825072No ratings yet
- Maths Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMaths Lesson Planapi-481484384No ratings yet
- 3 MathDocument4 pages3 Mathapi-640764419No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan 1api-352613082No ratings yet
- Physics S4 TGDocument256 pagesPhysics S4 TGAurelius Jean de DieuNo ratings yet
- Tpa 3 - Unit PlanDocument8 pagesTpa 3 - Unit Planapi-479504572No ratings yet
- Midp Micro TeachingDocument2 pagesMidp Micro Teachingapi-548305578No ratings yet
- DLP 3rd MathDocument3 pagesDLP 3rd MathAyen AguilaNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Math 205e 20lesson 20planning 20 - 20brianne 20mitchem-1Document3 pagesAnnotated-Math 205e 20lesson 20planning 20 - 20brianne 20mitchem-1api-675700192No ratings yet
- Chemistry 30 - Unit 4 Equilibrium - Graphical Analysis Le Chateliers PrincipleDocument4 pagesChemistry 30 - Unit 4 Equilibrium - Graphical Analysis Le Chateliers Principleapi-717601244No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson Planapi-631885966No ratings yet
- Tpack Template Iwb Summer2022 - Julianne WernerDocument1 pageTpack Template Iwb Summer2022 - Julianne Wernerapi-624108237No ratings yet
- Telling Time Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesTelling Time Lesson Planapi-582257412No ratings yet
- Tat1 Task 2 8Document1 pageTat1 Task 2 8api-404465268No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2aDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 2aapi-332424736No ratings yet
- Roomsburg Domain3lessonDocument2 pagesRoomsburg Domain3lessonapi-328303850No ratings yet
- Telling Time Unit PlanDocument9 pagesTelling Time Unit Planapi-296947885No ratings yet
- Sequence of 3 Time - Analogue and Digital ClocksDocument3 pagesSequence of 3 Time - Analogue and Digital Clocksapi-356375283No ratings yet
- Future Time: Chapter SummaryDocument8 pagesFuture Time: Chapter Summarymatthew wongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Maths Yr7b - Wed 27 Nov - Periods 1 and 2 Rev 0Document12 pagesLesson Plan - Maths Yr7b - Wed 27 Nov - Periods 1 and 2 Rev 0api-532162660No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4Document3 pagesLesson Plan 4api-352613082No ratings yet
- 3 Grade 2 Term SmilesDocument27 pages3 Grade 2 Term SmilesjanNo ratings yet
- Designing Teaching and Learning Assignment 2 The Lesson Plan AnalysisDocument18 pagesDesigning Teaching and Learning Assignment 2 The Lesson Plan Analysisapi-408529428No ratings yet
- Elementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsFrom EverandElementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsNo ratings yet
- SwipeDocument9 pagesSwipeaswinNo ratings yet
- Pma4 1500 00 SW1Document2 pagesPma4 1500 00 SW1aswinNo ratings yet
- 4 Linear Inequalities Notes COMPLETED - StudentDocument17 pages4 Linear Inequalities Notes COMPLETED - StudentaswinNo ratings yet
- 2 Variations (Power Modelling) Notes - StudentDocument4 pages2 Variations (Power Modelling) Notes - StudentaswinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Y3 Ma CT2 v1 (MS)Document3 pages2021 Y3 Ma CT2 v1 (MS)aswinNo ratings yet
- A Math C2 AnswersDocument5 pagesA Math C2 AnswersaswinNo ratings yet
- Paket 6 AkpolDocument8 pagesPaket 6 AkpolaswinNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 03-26-2024 17.37Document9 pagesCamScanner 03-26-2024 17.37aswinNo ratings yet
- 2019-07-07Document1,479 pages2019-07-07Hass0% (1)
- Leadership Across CulturesDocument36 pagesLeadership Across CulturesRommel LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument57 pagesChapter 1. Introductionsisay gemNo ratings yet
- 6-OTC107601 OptiX NG WDM Network Design ISSUE1.14Document80 pages6-OTC107601 OptiX NG WDM Network Design ISSUE1.14HachidSofianeNo ratings yet
- Axial Deformation On FramesDocument31 pagesAxial Deformation On FramesAndy OretaNo ratings yet
- Strap or Cantilever Footings ExampleDocument11 pagesStrap or Cantilever Footings ExamplehNo ratings yet
- TROLL Care and Maintenance GuideDocument6 pagesTROLL Care and Maintenance GuideFrancisco GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Referência de BlephariceridaeDocument1 pageReferência de BlephariceridaeCaio DiasNo ratings yet
- Compendex 2013 Source List 4 Aptil 2013Document333 pagesCompendex 2013 Source List 4 Aptil 2013Zelalem MengistuNo ratings yet
- Test Format: Allegato A Decreto MinisterialeDocument5 pagesTest Format: Allegato A Decreto Ministerialenilanjan1969No ratings yet
- Practiceproblemsfor Studentuse: Chapter 5: NonelectrolytesDocument2 pagesPracticeproblemsfor Studentuse: Chapter 5: NonelectrolytesBenjamin DanielNo ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFevelyn.trudnowski238100% (18)
- Stats and Probablity 3Document8 pagesStats and Probablity 3lgupili accountingNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution EssayDocument8 pagesWater Pollution Essayb725c62j100% (2)
- Control Air DryerDocument23 pagesControl Air DryerGeorgiNo ratings yet
- What Is RespectDocument3 pagesWhat Is RespectsaniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank FictionDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank Fictionvkm_ctrNo ratings yet
- Accessories Specifications: For Use With Chaparral Physics Infrasound SensorsDocument5 pagesAccessories Specifications: For Use With Chaparral Physics Infrasound SensorsAbdurrahman WafiNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Application Form and Endorsement of Immediate SupervisorDocument2 pagesResearch Proposal Application Form and Endorsement of Immediate SupervisorRommel YabisNo ratings yet
- Shenna Mea O. Alama Beed 2B: Content Areas Topics To Be TaughtDocument2 pagesShenna Mea O. Alama Beed 2B: Content Areas Topics To Be TaughtShenna Mea O. AlamaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bottle Filling System Using PLC: Shweta Suryawanshi, Dhananjay Shelke, Akshay Patil, Mangesh TandaleDocument4 pagesAutomatic Bottle Filling System Using PLC: Shweta Suryawanshi, Dhananjay Shelke, Akshay Patil, Mangesh TandaleJamil JelkiNo ratings yet
- Zybio Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit Insert - CompressedDocument2 pagesZybio Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit Insert - CompressedMiloud Bengharbi0% (1)
- Learner Guide - US 115230Document88 pagesLearner Guide - US 115230Sithole SabeloNo ratings yet
- Main-Idea (KHÔNG KEYS)Document20 pagesMain-Idea (KHÔNG KEYS)Tien TrandinhNo ratings yet
- Computers and Electrical Engineering: Uche A. NnolimDocument12 pagesComputers and Electrical Engineering: Uche A. NnolimibmplaceNo ratings yet
- A 12.5-ENOB 10-kS/s Redundant SAR ADC in 65nm CMOS: Dai Zhang, Member, IEEE, and Atila Alvandpour, Senior Member, IEEEDocument5 pagesA 12.5-ENOB 10-kS/s Redundant SAR ADC in 65nm CMOS: Dai Zhang, Member, IEEE, and Atila Alvandpour, Senior Member, IEEESilpa VelagaletiNo ratings yet
- Design of Trade Off III Precast ConcreteDocument9 pagesDesign of Trade Off III Precast ConcretemateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- Cati Solidworks Training GuideDocument5 pagesCati Solidworks Training GuideMohamad Haziq Mohamad ZinNo ratings yet
- Use of Solid-State Fermentation On Selected Agricultural Wastes For Mass Production of Beauveria BassianaDocument113 pagesUse of Solid-State Fermentation On Selected Agricultural Wastes For Mass Production of Beauveria BassianayasinNo ratings yet
Pma4 1500 00 CV1
Pma4 1500 00 CV1
Uploaded by
aswinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pma4 1500 00 CV1
Pma4 1500 00 CV1
Uploaded by
aswinCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER
15 Time
Chapter Overview
Maths Background
Pupils have learnt to read time from an analog clock to the hour and half hour in Primary 1. In Primary 2, they have
learnt about the minute hand and the fact that time after the hour can be read in skips of 5 minutes. In Primary 3,
pupils have learnt about reading and telling time to the minute using past (Example: 20 minutes past 4) and to
(Example: 15 minutes to noon). They have also learnt to find the duration of time spent on an activity.
In this chapter, pupils will learn to read time to the second. They will learn that 60 seconds = 1 minute, just as
60 minutes = 1 hour. They will also learn how to read and write time using the 24-hour clock. Pupils will also learn to
convert time from the 12-hour clock to the 24-hour clock, and vice versa. Building on what pupils have learnt about
drawing time lines to solve word problems involving time in Primary 3, pupils will learn to apply the skills to problems
involving the 24-hour clock. It is important to remind pupils that a common error made when using addition and
subtraction algorithms is to regroup 1 hour as 100 minutes.
Cross-curricular Connections • make a diary of their daily schedules using the
24-hour clock
Reading / Language Arts • talk about activities that will take less than 1 minute
Have pupils find instances of time written using the
(or 60 seconds)
24-hour clock in newspapers and other print materials.
• draw and label time lines for some of the word
Then, have pupils display them around the classroom to
problems in the chapter
show how the 24-hour clock is used in our daily lives.
• read the problems and summarise using their own
words
Science • discuss the Chapter Summary, encouraging them to
Pupils learn about temperature changes in the lower use the chapter vocabulary
block of the primary science syllabus. Temperature
changes can be very fast. For instance, have pupils
For Struggling Learners
measure the temperature of water at room temperature
Select activities that go back to the appropriate stage of
and then add hot water to it. Have pupils measure the
the Concrete-Pictorial-Abstract spectrum, such as having
change in temperature after 10 seconds. Alternatively,
pupils
they can also measure the temperature drop within
• use real or play analog and digital (both 12-hour
10 seconds.
and 24-hour) clocks to show and identify times and
elapsed times
Additional Support • work backwards to find or check an answer related to
For English Language Learners elapsed time
Select activities that reinforce the chapter vocabulary and • draw time lines in different ways to solve the same
the connections among these words, such as having problem
pupils If necessary, review:
• add terms and examples to the Word Wall • Primary 3 Chapter 13 (Time)
• create flashcards with time in 12-hour format on one
side and the corresponding time in 24-hour format on
the other side
Chapter 15 Overview 1
(M)MPaHTPG4B_15.indd 1 4/1/16 3:54 pm
Vocabulary
Chapter Preparation • second
Pre-Test
Administer the Pre-Test in the to check
that pupils have acquired the prerequisite knowledge In this chapter, you will need:
needed to understand this chapter. If pupils are unable
to answer all the questions correctly, go through Let’s • 1 demonstration clock with movable hands
Recall and Let’s Check with them. for the teacher
• 1 large analog clock with a second hand for
Let’s Recall (pages 5 and 6) the teacher
In earlier levels, pupils have learnt to convert hour and • 1 large digital clock with seconds for the
minutes to minutes, and vice versa, as well as solve word teacher
problems involving elapsed time, starting and finishing
• 1 stopwatch per pair of pupils
times. Use these pages to review the prerequisite
concepts. • 1 copy of Activity Table (TR12) per pair of
pupils
Converting units of time
Help pupils recall that 1 h = 60 min. Then, use the
examples to recall how they can convert hours and minutes to minutes, and vice versa.
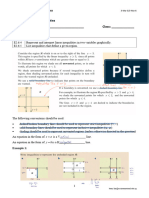
Using time lines to solve problems involving time
Demonstrate the steps involved in drawing time lines to solve word problems to find the duration given the starting
time and the finishing time, the finishing time given the starting time and the duration, and the starting time given
the finishing time and the duration. Highlight to pupils that there are multiple ways of drawing the time lines. In the
second word problem, for example, pupils can also add 1 h to the starting time first, followed by 10 min, instead of
finding the next nearest hour first. Remind pupils to indicate a.m. and p.m. on their time lines to avoid ambiguity.
(page 7)
Use this section as a diagnostic tool to assess pupils’ level of prerequisite knowledge before they progress to this
chapter.
1 assesses pupils’ ability to convert time from hours and minutes to minutes.
2 assesses pupils’ ability to convert time from minutes to hours and minutes.
3 assess pupils’ ability to find the duration in hours and minutes given the starting time and the finishing time.
4 assess pupils’ ability to find the finishing time given the starting time and the duration.
5 assess pupils’ ability to find the starting time given the finishing time and the duration.
Dif ferentiation Options in the
Based on the Pre-Test results, the
will assign:
• Extra Support Lesson Package to struggling learners
• On-level Lesson Package to on-level learners
• Advanced Lesson Package to advanced learners
4 Chapter 15 Preparation
(M)MPaHTPG4B_15.indd 4 7/1/16 3:57 pm
Chapter Introduction
Big Idea (Pupil’s Book 4B page 163)
Expressing time in different units of measurement is the main focus of this chapter.
• Pupils measure time in seconds.
• Pupils read and write time using the 24-hour clock.
• Pupils use time lines to solve word problems involving the 24-hour clock.
Chapter Opener (Pupil’s Book 4B page 163)
The picture illustrates a scene in a gym. The opening Digital Element
hours of the gym are displayed using the 24-hour clock
and the physical activities accomplished are measured Launch Chapter Opener from the .
in seconds. In this chapter, pupils gain an understanding
Discuss the big ideas with pupils using the questions
of time in the scale of seconds and to read time using the
24-hour clock. provided.
• Have pupils look at the picture. Ask: Where is this
place? (A gymnasium or a gym)
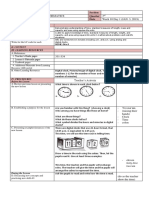
• Draw pupils’ attention to the pair of girls doing sit-ups. Say: The girl did 6 sit-ups in 10 seconds.
• Then, have a pair of pupil volunteers count the number of sit-ups they can complete in 10 seconds. Have them do
it for a minute to have a sense of the difference between 10 seconds and 1 minute (or 60 seconds).
• Next, draw pupils’ attention to the boy doing push-ups. Have pupils find out if they take about 1 second to do
1 push-up.
• Finally, draw pupils’ attention to the board indicating the opening hours of the gym. Have pupils attempt to interpret
what those times refer to. For example, say: The gym is open from 06 00 to 23 00 on Fridays. Ask: What time is
06 00? (6 a.m.) What time is 23 00? (11 p.m.)
• Have pupils discuss with their partners and share their thoughts.
• Explain that they will learn to express time in different units of measurement and clock systems.
8 Chapter 15 Introduction
(M)MPaHTPG4B_15.indd 8 4/1/16 3:54 pm
Pupil’s Book 4B p. 163
15
CHAPTER
Time
You did 6 sit-ups
in 10 seconds!
I can do 1 push-up
every second.
dea
Big I
Time can be expressed
ns
Lesso
1 Seconds in different units of
2 24-Hour Clock measurement.
(M)MPaHTB4B_15.indd 163 8/20/15 10:45 AM
Chapter 15 Introduction 9
(M)MPaHTPG4B_15.indd 9 4/1/16 3:54 pm
72
(M)MPaHTPG4B_15.indd 72
Teacher Resource
Activity 1s More than 1 s Less than 1 s
Say “thirty-four”
Blink once
Raise your hand
Nod twice
Say your full name
Use with Pupil’s Book as necessary.
Activity Table (TR12)
© 2016 Marshall Cavendish Education Pte Ltd. Copying is permitted.
4/1/16 3:54 pm
You might also like
- Math Stem Lesson Ecs 585Document10 pagesMath Stem Lesson Ecs 585Jacqueline MedinaNo ratings yet
- "What Time Is It?" Lesson PlanDocument4 pages"What Time Is It?" Lesson PlanTaylor DunlapNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson - Telling TimeDocument6 pagesMath Lesson - Telling TimeOctaviAnaNo ratings yet
- The Chernobyl Zone Survival GuideDocument685 pagesThe Chernobyl Zone Survival GuideDavidNo ratings yet
- Time 2017 PlannerDocument3 pagesTime 2017 Plannerapi-374359720No ratings yet
- Math Measurment Time 1Document13 pagesMath Measurment Time 1api-640764419No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Reading A Digital Clock Lesson 4: Reading A Digital ClockDocument2 pagesLesson 4: Reading A Digital Clock Lesson 4: Reading A Digital ClockFinapapNo ratings yet
- Telling The Time To The Half Hour Analogue Clock Starter Sheet - 21411Document2 pagesTelling The Time To The Half Hour Analogue Clock Starter Sheet - 21411FinapapNo ratings yet
- 5.11B Elapsed TimeDocument5 pages5.11B Elapsed Timemark anthony fontanos100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan 3api-352613082No ratings yet
- Tpack Template Iwb sp18 PJ DavisDocument2 pagesTpack Template Iwb sp18 PJ Davisapi-404220188No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-352613082No ratings yet
- Teach Live Micro LessonDocument5 pagesTeach Live Micro Lessonapi-372343626No ratings yet
- G Is For Googol PDFDocument8 pagesG Is For Googol PDFMichelle SpiteriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Learning Program - Year 8 MeasurementDocument8 pagesMathematics Learning Program - Year 8 MeasurementJames HarrisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 6Document3 pagesLesson Plan 6api-352613082No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: TopicDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: TopicRobert FlynnNo ratings yet
- 13-3 Telling and Writing Time To The Half HourDocument3 pages13-3 Telling and Writing Time To The Half Hourapi-411104780No ratings yet
- Final Lesson Plan Assignment 2 DesigningDocument17 pagesFinal Lesson Plan Assignment 2 Designingapi-485798829No ratings yet
- IV Day1Document4 pagesIV Day1Robin LayugNo ratings yet
- Elapsed Time Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesElapsed Time Lesson PlanGina Caroddo100% (4)
- Maths Time Lesson LiasonDocument2 pagesMaths Time Lesson Liasonapi-492582965No ratings yet
- Maths Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMaths Lesson Planapi-481483709No ratings yet
- Copy of Blank Lesson Plan Template 2022 4Document3 pagesCopy of Blank Lesson Plan Template 2022 4api-616369916No ratings yet
- Common Core Lesson PlannerDocument3 pagesCommon Core Lesson Plannerapi-419135285No ratings yet
- Year 2-Methodology and Practice of ELT-Lesson Plan DraftDocument6 pagesYear 2-Methodology and Practice of ELT-Lesson Plan Draftemmanouelavagia96No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlantarbeecatNo ratings yet
- DemotellingtimepreviewpdfDocument10 pagesDemotellingtimepreviewpdfJamila NoorNo ratings yet
- Standards Based Lesson Plan Elements: Ccss - Math.Content.2.G.A.2Document4 pagesStandards Based Lesson Plan Elements: Ccss - Math.Content.2.G.A.2api-610136255No ratings yet
- Time and Elapsed Time Work Sample: Teacher Work Sample 4th Grade - Central Noble Elementary School Kenzie TeelDocument7 pagesTime and Elapsed Time Work Sample: Teacher Work Sample 4th Grade - Central Noble Elementary School Kenzie Teelapi-488011782No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 8Document3 pagesLesson Plan 8api-352613082No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5Document3 pagesLesson Plan 5api-352613082No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document4 pagesLesson 2api-428818739No ratings yet
- Time Week3 MondayDocument2 pagesTime Week3 Mondayapi-320437238No ratings yet
- DR - Isaac Li Physics 50minutes Grade 10Document3 pagesDR - Isaac Li Physics 50minutes Grade 10api-350728128No ratings yet
- Elapsed TimeDocument41 pagesElapsed TimeMarcelo FloresNo ratings yet
- Multiple Means of ExpressionDocument6 pagesMultiple Means of Expressionapi-456276800No ratings yet
- Sage Blackmore Viva LessonsDocument5 pagesSage Blackmore Viva Lessonsapi-465825072No ratings yet
- Maths Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMaths Lesson Planapi-481484384No ratings yet
- 3 MathDocument4 pages3 Mathapi-640764419No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan 1api-352613082No ratings yet
- Physics S4 TGDocument256 pagesPhysics S4 TGAurelius Jean de DieuNo ratings yet
- Tpa 3 - Unit PlanDocument8 pagesTpa 3 - Unit Planapi-479504572No ratings yet
- Midp Micro TeachingDocument2 pagesMidp Micro Teachingapi-548305578No ratings yet
- DLP 3rd MathDocument3 pagesDLP 3rd MathAyen AguilaNo ratings yet
- Annotated-Math 205e 20lesson 20planning 20 - 20brianne 20mitchem-1Document3 pagesAnnotated-Math 205e 20lesson 20planning 20 - 20brianne 20mitchem-1api-675700192No ratings yet
- Chemistry 30 - Unit 4 Equilibrium - Graphical Analysis Le Chateliers PrincipleDocument4 pagesChemistry 30 - Unit 4 Equilibrium - Graphical Analysis Le Chateliers Principleapi-717601244No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson Planapi-631885966No ratings yet
- Tpack Template Iwb Summer2022 - Julianne WernerDocument1 pageTpack Template Iwb Summer2022 - Julianne Wernerapi-624108237No ratings yet
- Telling Time Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesTelling Time Lesson Planapi-582257412No ratings yet
- Tat1 Task 2 8Document1 pageTat1 Task 2 8api-404465268No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2aDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 2aapi-332424736No ratings yet
- Roomsburg Domain3lessonDocument2 pagesRoomsburg Domain3lessonapi-328303850No ratings yet
- Telling Time Unit PlanDocument9 pagesTelling Time Unit Planapi-296947885No ratings yet
- Sequence of 3 Time - Analogue and Digital ClocksDocument3 pagesSequence of 3 Time - Analogue and Digital Clocksapi-356375283No ratings yet
- Future Time: Chapter SummaryDocument8 pagesFuture Time: Chapter Summarymatthew wongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Maths Yr7b - Wed 27 Nov - Periods 1 and 2 Rev 0Document12 pagesLesson Plan - Maths Yr7b - Wed 27 Nov - Periods 1 and 2 Rev 0api-532162660No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4Document3 pagesLesson Plan 4api-352613082No ratings yet
- 3 Grade 2 Term SmilesDocument27 pages3 Grade 2 Term SmilesjanNo ratings yet
- Designing Teaching and Learning Assignment 2 The Lesson Plan AnalysisDocument18 pagesDesigning Teaching and Learning Assignment 2 The Lesson Plan Analysisapi-408529428No ratings yet
- Elementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsFrom EverandElementary Science Experiments: Analyzing Data to Make PredictionsNo ratings yet
- SwipeDocument9 pagesSwipeaswinNo ratings yet
- Pma4 1500 00 SW1Document2 pagesPma4 1500 00 SW1aswinNo ratings yet
- 4 Linear Inequalities Notes COMPLETED - StudentDocument17 pages4 Linear Inequalities Notes COMPLETED - StudentaswinNo ratings yet
- 2 Variations (Power Modelling) Notes - StudentDocument4 pages2 Variations (Power Modelling) Notes - StudentaswinNo ratings yet
- 2021 Y3 Ma CT2 v1 (MS)Document3 pages2021 Y3 Ma CT2 v1 (MS)aswinNo ratings yet
- A Math C2 AnswersDocument5 pagesA Math C2 AnswersaswinNo ratings yet
- Paket 6 AkpolDocument8 pagesPaket 6 AkpolaswinNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 03-26-2024 17.37Document9 pagesCamScanner 03-26-2024 17.37aswinNo ratings yet
- 2019-07-07Document1,479 pages2019-07-07Hass0% (1)
- Leadership Across CulturesDocument36 pagesLeadership Across CulturesRommel LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. IntroductionDocument57 pagesChapter 1. Introductionsisay gemNo ratings yet
- 6-OTC107601 OptiX NG WDM Network Design ISSUE1.14Document80 pages6-OTC107601 OptiX NG WDM Network Design ISSUE1.14HachidSofianeNo ratings yet
- Axial Deformation On FramesDocument31 pagesAxial Deformation On FramesAndy OretaNo ratings yet
- Strap or Cantilever Footings ExampleDocument11 pagesStrap or Cantilever Footings ExamplehNo ratings yet
- TROLL Care and Maintenance GuideDocument6 pagesTROLL Care and Maintenance GuideFrancisco GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Referência de BlephariceridaeDocument1 pageReferência de BlephariceridaeCaio DiasNo ratings yet
- Compendex 2013 Source List 4 Aptil 2013Document333 pagesCompendex 2013 Source List 4 Aptil 2013Zelalem MengistuNo ratings yet
- Test Format: Allegato A Decreto MinisterialeDocument5 pagesTest Format: Allegato A Decreto Ministerialenilanjan1969No ratings yet
- Practiceproblemsfor Studentuse: Chapter 5: NonelectrolytesDocument2 pagesPracticeproblemsfor Studentuse: Chapter 5: NonelectrolytesBenjamin DanielNo ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFevelyn.trudnowski238100% (18)
- Stats and Probablity 3Document8 pagesStats and Probablity 3lgupili accountingNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution EssayDocument8 pagesWater Pollution Essayb725c62j100% (2)
- Control Air DryerDocument23 pagesControl Air DryerGeorgiNo ratings yet
- What Is RespectDocument3 pagesWhat Is RespectsaniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank FictionDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank Fictionvkm_ctrNo ratings yet
- Accessories Specifications: For Use With Chaparral Physics Infrasound SensorsDocument5 pagesAccessories Specifications: For Use With Chaparral Physics Infrasound SensorsAbdurrahman WafiNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Application Form and Endorsement of Immediate SupervisorDocument2 pagesResearch Proposal Application Form and Endorsement of Immediate SupervisorRommel YabisNo ratings yet
- Shenna Mea O. Alama Beed 2B: Content Areas Topics To Be TaughtDocument2 pagesShenna Mea O. Alama Beed 2B: Content Areas Topics To Be TaughtShenna Mea O. AlamaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bottle Filling System Using PLC: Shweta Suryawanshi, Dhananjay Shelke, Akshay Patil, Mangesh TandaleDocument4 pagesAutomatic Bottle Filling System Using PLC: Shweta Suryawanshi, Dhananjay Shelke, Akshay Patil, Mangesh TandaleJamil JelkiNo ratings yet
- Zybio Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit Insert - CompressedDocument2 pagesZybio Viral Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit Insert - CompressedMiloud Bengharbi0% (1)
- Learner Guide - US 115230Document88 pagesLearner Guide - US 115230Sithole SabeloNo ratings yet
- Main-Idea (KHÔNG KEYS)Document20 pagesMain-Idea (KHÔNG KEYS)Tien TrandinhNo ratings yet
- Computers and Electrical Engineering: Uche A. NnolimDocument12 pagesComputers and Electrical Engineering: Uche A. NnolimibmplaceNo ratings yet
- A 12.5-ENOB 10-kS/s Redundant SAR ADC in 65nm CMOS: Dai Zhang, Member, IEEE, and Atila Alvandpour, Senior Member, IEEEDocument5 pagesA 12.5-ENOB 10-kS/s Redundant SAR ADC in 65nm CMOS: Dai Zhang, Member, IEEE, and Atila Alvandpour, Senior Member, IEEESilpa VelagaletiNo ratings yet
- Design of Trade Off III Precast ConcreteDocument9 pagesDesign of Trade Off III Precast ConcretemateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- Cati Solidworks Training GuideDocument5 pagesCati Solidworks Training GuideMohamad Haziq Mohamad ZinNo ratings yet
- Use of Solid-State Fermentation On Selected Agricultural Wastes For Mass Production of Beauveria BassianaDocument113 pagesUse of Solid-State Fermentation On Selected Agricultural Wastes For Mass Production of Beauveria BassianayasinNo ratings yet