Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Theory Timeline
Atomic Theory Timeline
Uploaded by
hibasiddiquii20240 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesAtomic Theory Timeline
Atomic Theory Timeline
Uploaded by
hibasiddiquii2024Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
wgdfy9sfs7 12/22/2023
Atomic Theory Timeline
Origin Of Atomic Theory (2500 Years Ago)
The theory that atoms are the minuscule, indivisible
particles that comprise all matter was first
proposed by the Greek philosophers Leucippus and
Democritus. They claimed that different substances
were made up of specific forms of particles.
The Electron (Late 1800s)
Using discharge tubes, physicist J.J. Thompson
discovered that negatively charged electrons exist. He
concluded that the mass of an electron is approximately
1000 times smaller than that of a hydrogen atom, which
put the theory of atomic structure to a test.
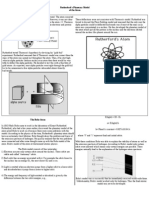
The Plum Pudding Model (Late 1800s)
The Plum Pudding Model, brought out by J.J. Thompson,
claimed that electrons were dispersed at random within
a positively charged structure. This concept aimed to
explain why atoms are often neutrally charged.
The Nucleus (1909)
Through experiments with alpha particles on
gold foil, physicist Ernest Rutherford developed
the model. He concluded that the majority of an
atom is made up of empty space, and that atoms
have a concentrated positively charged nucleus.
Since most of the alpha particles went through the foil, he
further concluded that atoms are mostly comprised of empty
space.
The Proton (Early 20th Century)
Through the alpha particle experiments,
Rutherford discovered protons, establishing them
as fundamental particles with a positive charge.
His discoveries made a substantial contribution
to our knowledge of atomic structure.
The Planetary Model (1911)
Led by Rutherford, Neils Bohr theorized the Planetary
Model, demonstrating electrons circling a central nucleus.
This concept proposed particular electron orbits.
The resulting model is called the Planetary Model. It represents
the electrons in orbit around a central nucleus.
The Quantum Model (1927)
Precise electron position and momentum at the same
time were questioned by Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty
principle. The result was the creation of the Quantum
Model, which claimed that electrons possess properties of
both particles and waves. Orbitals are introduced, and
electron locations are expressed in terms of probability. Heisenberg mathematically determined that it is impossible to
know with certainty both the momentum of an electron and its
exact position.
You might also like
- How The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedDocument50 pagesHow The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedChosen ExeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document9 pagesLesson 2Mary Ann Elacion AballaNo ratings yet
- A History of The AtomDocument4 pagesA History of The AtomKeith Kevin ChuaNo ratings yet
- Not Indivisible (The Structure of Atom)Document15 pagesNot Indivisible (The Structure of Atom)Sheena DalguntasNo ratings yet
- Models of Atoms: The Thomson ModelDocument6 pagesModels of Atoms: The Thomson ModelIacob Ventum LeonardusNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4Document4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4Alona Cello ParagesNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesHistorical Development of Atomic TheoryDivyeshNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesHistorical Development of Atomic TheoryDivyeshNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-11-28 at 4.34.42 PMDocument4 pagesScreenshot 2022-11-28 at 4.34.42 PMBaneen HassanNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of The Lesson, I CAN: - Discover The Scientists Behind The Development of The Atomic StructureDocument30 pagesObjectives: at The End of The Lesson, I CAN: - Discover The Scientists Behind The Development of The Atomic StructureMary Grace SalvadorNo ratings yet
- History of Atomic Theory NotesDocument22 pagesHistory of Atomic Theory Notesapi-281924829No ratings yet
- Atomic Theory ExpierimentsDocument8 pagesAtomic Theory Expierimentsapi-323082319No ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageAtomic TheoryAnnaoj SalesNo ratings yet
- The History of Atoms: What Led Up To The Building BlocksDocument1 pageThe History of Atoms: What Led Up To The Building BlockspabrgpbawprigNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument35 pagesAtomic Modelsrinlacer100% (1)
- Structure of AtomDocument26 pagesStructure of AtomsyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument8 pagesNuclear PhysicsPrithviraj DuttaNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic Theorybinaroth03No ratings yet
- History of The Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageHistory of The Atomic TheoryjosewuNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesAtomic TheoryasharaqueenNo ratings yet
- Rutherford FactsDocument1 pageRutherford Factssomethingisverysuperstrange9No ratings yet
- Prince Harold Silvania 12-Eleazar: Dalton's TheoryDocument4 pagesPrince Harold Silvania 12-Eleazar: Dalton's TheoryAllen AcojidoNo ratings yet
- Document 240419 083512 240419 100344Document70 pagesDocument 240419 083512 240419 100344SARA EMELIN FARISHA MUHAMAD FARIDNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Fa 4 On ModelsDocument16 pagesChemistry Project Fa 4 On ModelsVARIGALA SAI CHARAN GUPTANo ratings yet
- Development of Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Atomic TheoryRohit SahuNo ratings yet
- LB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesLB1D3 20220824 Inorganic ChemistryPhoebe BironNo ratings yet
- Not IndivisibleDocument5 pagesNot IndivisibleColette Muncal JoseNo ratings yet
- The Historical Development of Atomic ModelsDocument18 pagesThe Historical Development of Atomic ModelsIvenks EeNo ratings yet
- Atoms: Atom N. A Unit of Matter, The Smallest Unit of An Element, Consisting of A DenseDocument17 pagesAtoms: Atom N. A Unit of Matter, The Smallest Unit of An Element, Consisting of A DenseschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Rutherford Atomic ModelDocument5 pagesRutherford Atomic ModelDevank RajvanshiNo ratings yet
- Kunci Struktur Atom Perkembangan Model STUDENT WORKSHEET-1Document9 pagesKunci Struktur Atom Perkembangan Model STUDENT WORKSHEET-1sanihgholiyahNo ratings yet
- History of The Atom TimelineDocument6 pagesHistory of The Atom Timelineur momNo ratings yet
- History of An AtomDocument1 pageHistory of An AtomZineb KandoussiNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument17 pagesAtomic StructureVandana Khator100% (1)
- The Historical Development of Atom2Document1 pageThe Historical Development of Atom2Nor anisa BaguindaNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument13 pagesAtomic Modelsmax mishraNo ratings yet
- Development of Atomic TheoryDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Atomic TheoryPedro NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Atom Precy LicupDocument12 pagesHistorical Development of The Atom Precy LicupAdrian John Manaloto100% (1)
- Activity 2 ESL History of Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesActivity 2 ESL History of Atomic StructureAshmi KNo ratings yet
- Science ProjectDocument20 pagesScience ProjectRalph Justin MandalNo ratings yet
- The History of The AtomDocument5 pagesThe History of The AtomHussain AliNo ratings yet
- 1 Atomic IntroDocument34 pages1 Atomic Introapi-273966469No ratings yet
- Atoms 3rd TopicDocument36 pagesAtoms 3rd TopicReynalie BotonNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physic By: Susi Susanti: HistoryDocument8 pagesNuclear Physic By: Susi Susanti: HistoryAldi CakepsNo ratings yet
- History of Atomic TheoryDocument38 pagesHistory of Atomic TheorylovelyshaneibrahimNo ratings yet
- SCI Q2 ReviewerDocument14 pagesSCI Q2 ReviewerJonash Miguel LorzanoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument91 pagesAtomic StructureUmmu juraijNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY NO. 6: The Discovery of The Structure of The Atom and Its Subatomic Particles Name: Date: Year & Section: Score: Concept NotesDocument2 pagesACTIVITY NO. 6: The Discovery of The Structure of The Atom and Its Subatomic Particles Name: Date: Year & Section: Score: Concept NotesDexter DizonNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Atomic ModelsDocument52 pagesEvolution of Atomic ModelsJayson OlipasNo ratings yet
- Nr. Phys Chapter OneDocument23 pagesNr. Phys Chapter Oneabdii100% (1)
- Atomic Theory and ModelsDocument42 pagesAtomic Theory and ModelsJesiah PascualNo ratings yet
- People Who Contributed To The Atomic TheoryDocument1 pagePeople Who Contributed To The Atomic Theoryjayvee hullanaNo ratings yet
- 1 HistoryDocument31 pages1 Historyapi-259864095No ratings yet
- Chemistry TimelineDocument5 pagesChemistry TimelineLyncell Martin VillarNo ratings yet
- Discovery Theory of Atoms 400bc-21st CenturyDocument2 pagesDiscovery Theory of Atoms 400bc-21st CenturyMikaella JungcoNo ratings yet
- Chem HistoryDocument21 pagesChem HistoryMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nuclear PhysicsDocument105 pagesAdvanced Nuclear PhysicsAyesh aldiri100% (6)
- Advanced Nuclear PhysicsDocument105 pagesAdvanced Nuclear Physicssimonliu_68No ratings yet
- A Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisFrom EverandA Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chemistry For Engineers Final Module 2Document26 pagesChapter 2 Chemistry For Engineers Final Module 2Alex Jr. Rosadiño C.No ratings yet
- JR Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions Part 1Document21 pagesJR Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions Part 1ntofficial18No ratings yet
- 01 03Document32 pages01 03humayunbashaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry DPPDocument16 pagesChemistry DPPAyan KhanNo ratings yet
- Illumination and Rendering MethodDocument22 pagesIllumination and Rendering MethodranjuNo ratings yet
- Analisis SPM 2021Document2 pagesAnalisis SPM 2021Pavina baskyNo ratings yet
- A Grand Tour of Physics: Quantum MechanicsDocument27 pagesA Grand Tour of Physics: Quantum MechanicsrickyjamesNo ratings yet
- Double Slit Interference Write-UpDocument2 pagesDouble Slit Interference Write-UpAnonymous BH74KR8No ratings yet
- Techniques: All Photographers Should MasterDocument69 pagesTechniques: All Photographers Should MastertazzorroNo ratings yet
- Spectrometer SolidDocument2 pagesSpectrometer Solidansh rajNo ratings yet
- Electron Microscopy: by Dr. Kaustab GhoshDocument9 pagesElectron Microscopy: by Dr. Kaustab GhoshNehal Aswani 19BEC1125No ratings yet
- What Is A Pinhole CameraDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Pinhole CameraSuniil PachisiaNo ratings yet
- Index of Refraction Lab Lesson Plan E-Portfolio VersionDocument8 pagesIndex of Refraction Lab Lesson Plan E-Portfolio Versionapi-668691050No ratings yet
- 5.2 Refraction of Light 2018Document47 pages5.2 Refraction of Light 2018nur aqilahNo ratings yet
- Theories of Light: FeaturesDocument4 pagesTheories of Light: FeaturesNoor JabetyNo ratings yet
- Binoculars A Guide by NikonDocument4 pagesBinoculars A Guide by Nikonjose cabelloNo ratings yet
- XDR1Document83 pagesXDR1zeyadwaeli500No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Practice Questions: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding - Practice Questions: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionasti dNo ratings yet
- Fourier OpticsDocument15 pagesFourier OpticsWhalsy nNo ratings yet
- SEM and STMDocument25 pagesSEM and STMZhanarNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 - 4 Are Worth Two Points Each. Questions 5 - 28 Are Worth Four Points EachDocument5 pagesQuestions 1 - 4 Are Worth Two Points Each. Questions 5 - 28 Are Worth Four Points EachLouis ParrNo ratings yet
- X-Ray FluorescenceDocument16 pagesX-Ray Fluorescencevasilik0787No ratings yet
- Raman Effect Fingerprinting of UniverseDocument7 pagesRaman Effect Fingerprinting of UniverseAnurag TripathiNo ratings yet
- Polarization Independent, Tunable Waveguide Bragg Gratings in Lithium Niobate by Femtosecond Laser MicromachiningDocument2 pagesPolarization Independent, Tunable Waveguide Bragg Gratings in Lithium Niobate by Femtosecond Laser MicromachiningjohnNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations Practice-17Document3 pagesElectron Configurations Practice-17api-368121935No ratings yet
- REP HandBook PDFDocument6 pagesREP HandBook PDFeduardo heviaNo ratings yet
- FUJINON Binoculars Catalog enDocument10 pagesFUJINON Binoculars Catalog enJosé Carlos MartinsNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Solutions Class 9 Chapter 7 Reflection of LightDocument30 pagesSelina Concise Physics Solutions Class 9 Chapter 7 Reflection of LightElite BrickmanNo ratings yet
- CHM 1102 Worksheet 2 2021Document2 pagesCHM 1102 Worksheet 2 2021kevin persaudNo ratings yet
- 27 Aug 2011 Test Along With AnswersDocument4 pages27 Aug 2011 Test Along With AnswersdnagwaliorNo ratings yet