Professional Documents
Culture Documents
19.2 Ultrasound CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlocked
19.2 Ultrasound CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlocked
Uploaded by
maze.putumaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
19.2 Ultrasound CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlocked
19.2 Ultrasound CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlocked
Uploaded by
maze.putumaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasound
Mark Scheme 2
Level International A Level
Subject Physics
Exam Board CIE
Topic Waves
Sub Topic Ultrasound
Paper Type Theory
Booklet Mark Scheme 2
Time Allowed: 51 minutes
Score: /42
Percentage: /100
A* A B C D E U
>85% 777.5% 70% 62.5% 57.5% 45% <45%
Dr. Asher Rana www.chemistryonlinetuition.com asherrana@chemistryonlinetuition.com
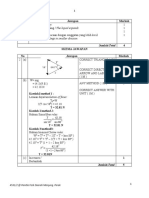
1 (a) product of density (of medium) and speed of sound (in the medium) B1 [1]
(b) α would be nearly equal to 1 M1
either reflected intensity would be nearly equal to incident intensity
or coefficient for transmitted intensity = (1 – α) M1
transmitted intensity would be small A1 [3]
(c)
c) ( α = (1.7 – 1.3)2 / (1.7 + 1.3)2 C1
= 0.018 A1 [2]
(ii) attenuation in fat = exp(–48 × 2x × 10–2) C1
0.012 = 0.018 exp(–48 × 2x × 10–2) C1
x = 0.42 cm A1 [3]
2 (a) (i) density × speed of wave (in the medium) B1 [1]
(ii) ρ = (7.0 × 106) / 4100
= 1700 kg m–3 A1 [1]
(b) (i) I = IT + IR B1 [1]
(ii) 1. α = (0.1 × 106)2 / (3.1 × 106)2 C1
= 0.001 A1 [2]
2. α ≈ 1 A1 [1]
(c) either very little transmission at an air-skin boundary M1
(almost) complete transmission at a gel-skin boundary M1
when wave travels in or out of the body A1 [3]
or no gel, majority reflection (M1)
with gel, little reflection (M1)
when wave travels in or out of the body (A1)
3 either quartz or piezo-electric crystal B1
opposite faces /two sides coated (with silver) to act as electrodes B1
either molecular structure indicated
or centres of (+) and (–) charge not coincident B1
potential difference across crystal causes crystal to change shape B1
alternating voltage (in US frequency range) applied across crystal B1
causes crystal to oscillate / vibrate B1
(crystal cut) so that it vibrates at resonant frequency B1 [6]
(max 6)
Dr. Asher Rana www.chemistryonlinetuition.com asherrana@chemistryonlinetuition.com
4 (a) pulse of ultrasound (1)
reflected at boundaries / boundary (1)
received / detected (at surface) by transducer (1)
signal processed and displayed (1)
time between transmission and receipt of pulse gives
(information about) depth of boundary (1)
reflected intensity gives information as to nature of boundary (1)
(any four points, 1 each, max 4) B4 [4]
(b) (i) coefficient = (Z2 – Z1)2 / (Z2 + Z1)2
= (6.3 – 1.7)2 / (6.3 + 1.7)2 C1
= 0.33 (unit quoted, then –1) A1 [2]
(ii) fraction = exp(–µx) C1
= exp(–23 × 4.1 × 10–2)
= 0.39 A1 [2]
(iii) intensity = 0.33 × 0.392 × I C1
= 0.050 I A1 [2]
(do not allow e.c.f. from (i) and (ii) if these answers are greater than 1)
5 (a) product of density (of medium) and speed of sound (in medium) ............................... B1 [1]
(b) difference in acoustic impedance ................................................................................ M1
determines fraction of incident intensity
that is reflected/amount of reflection ............................................................................ A1 [2]
(c) pulse of ultrasound (directed into body) ...................................................................... B1
reflected at boundary (between tissues) ...................................................................... B1
(reflected pulse is) detected and processed ................................................................ B1
time for return of echo gives (information on) depth .................................................... B1
amount of reflection gives information on tissue structures ......................................... B1 [5]
Dr. Asher Rana www.chemistryonlinetuition.com asherrana@chemistryonlinetuition.com
You might also like
- 18.3 Wave Basics CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument6 pages18.3 Wave Basics CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 20.1 Stationary Waves CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages20.1 Stationary Waves CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 9702 s10 Ms 23Document4 pages9702 s10 Ms 23Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- As Prelim P2 2020-2021 (MS Final Draft)Document4 pagesAs Prelim P2 2020-2021 (MS Final Draft)Nathaniel BasukiNo ratings yet
- 13.1 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages13.1 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages13.2 Deformation of Solids CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Motion Graphs CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument6 pages4.3 Motion Graphs CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Physical Qualtities CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument6 pages1.2 Physical Qualtities CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Waves MSDocument4 pages2.3 Waves MSBenedict YamvwaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeDocument6 pages2016 Specimen Paper 4 Mark SchemeRafay SaifNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 2 MSDocument3 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 2 MSasbab bdNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 3 MSDocument3 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 3 MSAli SiddiqNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Motion Graphs CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument3 pages4.4 Motion Graphs CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Refraction & Superposition AnswerDocument6 pagesRefraction & Superposition Answergrace_ng_45No ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 1 MSDocument4 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 1 MSherawatiNo ratings yet
- Answer Marks Guidance 1 (A) AllowDocument5 pagesAnswer Marks Guidance 1 (A) AllowYfdNo ratings yet
- Sound 4 MSDocument5 pagesSound 4 MSRhea AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Final Mark Scheme 2821 Forces and MotionDocument6 pagesFinal Mark Scheme 2821 Forces and MotionHome Of Math OfficialNo ratings yet
- Code-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456Document15 pagesCode-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456rhevaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NDocument3 pages1.1 Atomic Structure Test Mark Scheme: Allow No. of Nucleons / Amount of P & NalexisNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 26Document26 pagesPage 1 of 26albinjensNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1Document14 pagesSkema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1lilysuhanyNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties IGCSE Physics MSDocument2 pagesGeneral Wave Properties IGCSE Physics MSeren parkNo ratings yet
- Light 9 MSDocument4 pagesLight 9 MSRhea AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 9702 s07 Ms 4Document5 pages9702 s07 Ms 4api-3765617No ratings yet
- PHY2016Document3 pagesPHY2016Advita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter 5 MSDocument4 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter 5 MSDana A.No ratings yet
- Specimen (IAL) MSDocument6 pagesSpecimen (IAL) MSKarim OwnNo ratings yet
- AQA Newtons - Laws - MSDocument9 pagesAQA Newtons - Laws - MSkailistaceyNo ratings yet
- CHM1 Structure & Bonding ADocument55 pagesCHM1 Structure & Bonding AHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Physics June 2007 Paper 3Document11 pagesPhysics June 2007 Paper 3wb4qv7yzvzNo ratings yet
- Light 3 MSDocument3 pagesLight 3 MSRhea AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument4 pages9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 Seriesthanhlam266xNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Provisional Key AnswerDocument36 pagesNEET 2024 Provisional Key Answerjaspindervirdi7No ratings yet
- Statics & Resolving Forces 2 MSDocument8 pagesStatics & Resolving Forces 2 MSelsieNo ratings yet
- NEET 2024 Provisional Key Answer HAYATH'S IIT & NEET ACADEMYDocument36 pagesNEET 2024 Provisional Key Answer HAYATH'S IIT & NEET ACADEMYMohammed Obaid MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Length & Time 1 MSDocument3 pagesLength & Time 1 MSShoaib aliNo ratings yet
- Physics I Phys 1001 - 2022Document6 pagesPhysics I Phys 1001 - 2022xilag49210No ratings yet
- Esophageal DiseaseDocument36 pagesEsophageal DiseaseSaurabh RokadeNo ratings yet
- 89 StructDocument5 pages89 StructgazmanNo ratings yet
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersrafeeah nawrinNo ratings yet
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument4 pages9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teacherseminkoganyan.yNo ratings yet
- 9702/42/FM/24Document14 pages9702/42/FM/24RatchetNo ratings yet
- M1. (I) Weight Greater Than Air Resistance: Max 5 QWC 2Document5 pagesM1. (I) Weight Greater Than Air Resistance: Max 5 QWC 2Ritik YadavNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationsHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Newton - S Laws of Motion CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages5.1 Newton - S Laws of Motion CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Resolving & Moments MSDocument6 pagesResolving & Moments MSleesha.sahaNo ratings yet
- 9702 s10 Ms 41Document5 pages9702 s10 Ms 41Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- AS Mock - MSDocument4 pagesAS Mock - MSHizbullah AnsariNo ratings yet
- Able To Give Readings in Smaller Division.: No Jawapan MarkahDocument10 pagesAble To Give Readings in Smaller Division.: No Jawapan MarkahNORAINI BINTI KHALID MoeNo ratings yet
- Wave AnswersDocument10 pagesWave AnswerselezabethNo ratings yet
- TWSS 2018 5076 SciPhy 4E5N Prelims MS v2 (Edited)Document5 pagesTWSS 2018 5076 SciPhy 4E5N Prelims MS v2 (Edited)leetaishenNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument5 pagesSolutionAnadi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Light 7 MSDocument3 pagesLight 7 MSRhea AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cse It Me Ce Ph101 Physics - I 18Document4 pagesCse It Me Ce Ph101 Physics - I 18dsreNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2manoj jaiswalNo ratings yet
- 9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9702 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersxiaokiaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme 6 Summer 2006Document5 pagesMark Scheme 6 Summer 2006Jing Wang100% (1)
- On the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)From EverandOn the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)No ratings yet
- 20.2 Stationary Waves-Cie Ial Physics-Qp Theory-UnlockedDocument10 pages20.2 Stationary Waves-Cie Ial Physics-Qp Theory-Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 10.6 Work Energy - Power CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument5 pages10.6 Work Energy - Power CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 18.2 Wave Basics-Cie Ial Physics-Qp Theory-UnlockedDocument13 pages18.2 Wave Basics-Cie Ial Physics-Qp Theory-Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Newton - S Laws of Motion CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument4 pages5.1 Newton - S Laws of Motion CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Measurement Techniques CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlocked 3Document6 pages2.2 Measurement Techniques CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlocked 3maze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Measurement Techniques CIE IAL Physics MS Theory UnlockedDocument6 pages2.1 Measurement Techniques CIE IAL Physics MS Theory Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Physical Qualtities-Cie Ial Physics-Theory Qp-UnlockedDocument15 pages1.3 Physical Qualtities-Cie Ial Physics-Theory Qp-Unlockedmaze.putumaNo ratings yet
- Dead Poet SocietyDocument3 pagesDead Poet Societyreniddh sri rahayuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Thorndike'S Connectionism: ThinkDocument3 pagesLesson 2: Thorndike'S Connectionism: ThinkKervien UlgasanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan English2 q4 Wk1-2Document3 pagesWeekly Learning Plan English2 q4 Wk1-2Evelyn Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- FINAL CERTIFICATE OF RECOGNITION Grade 11 For Finals 2nd SemDocument3 pagesFINAL CERTIFICATE OF RECOGNITION Grade 11 For Finals 2nd Semjefferson cristobalNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation FormDocument1 pageClassroom Observation FormDondee PalmaNo ratings yet
- QP Set1Document6 pagesQP Set1parthsinghdpsgmNo ratings yet
- TORRESDocument61 pagesTORRESChristine TorresNo ratings yet
- Đề 70 Đề 71 Năm 2024Document10 pagesĐề 70 Đề 71 Năm 2024dangkirito123No ratings yet
- Dissertation Le Japon Et La MerDocument6 pagesDissertation Le Japon Et La MerWebsiteThatWillWriteAPaperForYouUK100% (1)
- English - PEAC Streamlining The K 12 CurriculumDocument122 pagesEnglish - PEAC Streamlining The K 12 CurriculumPaulus Villanueva100% (1)
- 329 Modals Advanced Level Test Quiz Online Exercise With Answers 3Document5 pages329 Modals Advanced Level Test Quiz Online Exercise With Answers 3oussamaNo ratings yet
- January 2013 MS - Paper 2B Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument9 pagesJanuary 2013 MS - Paper 2B Edexcel Biology IGCSEvishmitha malingaNo ratings yet
- 2nd GRADE - SPELLING - CUADERNILLO DE APOYODocument36 pages2nd GRADE - SPELLING - CUADERNILLO DE APOYOJuan Pablo CatañoNo ratings yet
- 3 NSTP Manual AY 2021 2022 Self Awareness and Values Development 1Document5 pages3 NSTP Manual AY 2021 2022 Self Awareness and Values Development 1asdfqwertyNo ratings yet
- TEACHER I III AnnotationTemplateDocument6 pagesTEACHER I III AnnotationTemplateDENVER MOSCOSONo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan For Math 4Document6 pagesCot Lesson Plan For Math 4Marites AcasioNo ratings yet
- Sambung Master Coursework Atau ResearchDocument6 pagesSambung Master Coursework Atau Researchbcrqs9hr100% (2)
- Railway Recruitment Cell - East Central Railway KAILAS MDocument2 pagesRailway Recruitment Cell - East Central Railway KAILAS Mgitesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 4 - Q1 - W3Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 4 - Q1 - W3daniel AguilarNo ratings yet
- History of Umiray, DingalanDocument3 pagesHistory of Umiray, DingalanSarah Lombres Antigua MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Visit of Iit Gandhinagar On 28 Jan 2023Document4 pagesVisit of Iit Gandhinagar On 28 Jan 2023singhbishtkuulNo ratings yet
- (@DTUAlertBot) File0857Document3 pages(@DTUAlertBot) File0857Rishab DNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Course Syllabus of The College of Engineering and ArchitectureDocument7 pagesOutcome Based Course Syllabus of The College of Engineering and ArchitectureDaille Wroble GrayNo ratings yet
- CL 2nd 2Document6 pagesCL 2nd 2Teacher MikkaNo ratings yet
- Acr Project MichelleDocument10 pagesAcr Project Michelleiam.sumaoangNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub Self Directed Learning A Guide For Learners and Teachers 0695811169Document140 pagesDokumen - Pub Self Directed Learning A Guide For Learners and Teachers 0695811169K Chuong DangNo ratings yet
- Fort San Pedro National High SchoolDocument2 pagesFort San Pedro National High SchoolRoldan MateoNo ratings yet
- DNB Post MBBS Allotments - R2 2020 - Course WiseDocument152 pagesDNB Post MBBS Allotments - R2 2020 - Course WiseSuresh YadavNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson 53 Determining The Missing TermsDocument19 pagesMath Lesson 53 Determining The Missing Termsmariane.delacruzNo ratings yet
- The History of Education As The HistoryDocument16 pagesThe History of Education As The Historythaislane_No ratings yet