Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Science Fidp
Physical Science Fidp
Uploaded by
Misha WilliamsCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-General MathDocument2 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan-General MathHerra Luna Bautista93% (14)
- Media and Information Literacy FIDPDocument9 pagesMedia and Information Literacy FIDPJomark Rebolledo100% (2)
- Discipline and Ideas in The Social Science - FIDP (De Guia) Hum2Document8 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in The Social Science - FIDP (De Guia) Hum2patrixia73% (11)
- FIDP Oral Com 1Document5 pagesFIDP Oral Com 1Jomark Rebolledo100% (1)
- Fidp Personal DevelopmentDocument10 pagesFidp Personal DevelopmentJayvee Jarina100% (9)
- Creative Writing FIDPDocument8 pagesCreative Writing FIDPLeah Jean VillegasNo ratings yet
- FIDP - 21st CenturyDocument9 pagesFIDP - 21st CenturyLeah Jean VillegasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Free Fall - FIDPDocument4 pagesMechanics and Free Fall - FIDPAustin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateAisa Edza100% (5)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Edward Barber100% (3)
- Bio 101 Sample Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBio 101 Sample Lab ReportRavinderenPichan67% (3)
- Fidp PhysciDocument13 pagesFidp PhysciDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) Grade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionDocument1 pageFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) Grade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionJoy TamalaNo ratings yet
- Fidp Diss IbabaoDocument10 pagesFidp Diss IbabaoNikki Anne BerlanasNo ratings yet
- Fidp UcspDocument22 pagesFidp Ucspkaren bacquialNo ratings yet
- FIDP StatandProbDocument9 pagesFIDP StatandProbGian NotorNo ratings yet
- Relativity - FIDPDocument2 pagesRelativity - FIDPAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)Document7 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)John paul siaNo ratings yet
- FIDP-Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument7 pagesFIDP-Sampling and Sampling DistributionHoney Mae VillaverNo ratings yet
- Fidp DissDocument9 pagesFidp DissFranklin II Isla100% (2)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Fidp Genbio2Document8 pagesFidp Genbio2Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery PlanDocument4 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery PlanImie Omamalin GuisehanNo ratings yet
- Models of The Universe - FidpDocument9 pagesModels of The Universe - FidpAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- FIDP Creative WritingDocument12 pagesFIDP Creative WritingVan Jasper AranetaNo ratings yet
- Fidp Basic CalculusDocument10 pagesFidp Basic CalculusKaye CabangonNo ratings yet
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion - FIDPDocument2 pagesKepler's Laws of Planetary Motion - FIDPAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fidp ResearchDocument3 pagesFidp ResearchIn SanityNo ratings yet
- MIL - For CheckingDocument18 pagesMIL - For CheckingPaul Jeremiah UrsosNo ratings yet
- Fidp ElsDocument6 pagesFidp ElsDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Fidp Gen. Math2Document8 pagesFidp Gen. Math2Mark Anthony AnchetaNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Fidp 2022-2023Document10 pagesPR1 - Fidp 2022-2023ardrian malangenNo ratings yet
- What To Teach? Why Teach?Document2 pagesWhat To Teach? Why Teach?John Mickel NaelgaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science FidpDocument9 pagesEarth Science FidpJohn Keven VallespinNo ratings yet
- Household and Personal Care Products - FIDPDocument5 pagesHousehold and Personal Care Products - FIDPAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fidp EsDocument6 pagesFidp EsDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- The Development of Listening and Speaking Skills and Strategies For Effective Communication in Various SituationsDocument3 pagesThe Development of Listening and Speaking Skills and Strategies For Effective Communication in Various SituationsBea TanglaoNo ratings yet
- FIDP - Creative WritingDocument13 pagesFIDP - Creative WritingGen TalladNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp) School Year 2021-2022Document11 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp) School Year 2021-2022Paul Jeremiah UrsosNo ratings yet
- Fidp DissDocument12 pagesFidp DissRexijay PagatpatNo ratings yet
- FIDP Oral CommDocument8 pagesFIDP Oral CommGenelyn TabladaNo ratings yet
- Fidp Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument3 pagesFidp Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonHeather MarcoNo ratings yet
- FIDP Emp - Tech 11Document12 pagesFIDP Emp - Tech 11Jan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Fidp Darwin UrbanoDocument32 pagesEarth and Life Science Fidp Darwin UrbanoMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- GEN PHYSICS 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Document8 pagesGEN PHYSICS 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Crisanta Ganado67% (3)
- JAVA-OOP - Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template (FIDP)Document27 pagesJAVA-OOP - Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template (FIDP)Filifish KnowNo ratings yet
- FIDP Template R4 DRAFTDocument4 pagesFIDP Template R4 DRAFTClaire Joy GeonzonNo ratings yet
- FIDPDocument3 pagesFIDPLloyd GarilloNo ratings yet
- Sample FIDPDocument5 pagesSample FIDPDan Vincent Mapalo100% (1)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)Melissa Ann BuhianNo ratings yet
- San Antonio, Alicia, Isabela 2022-2023: With Digital Tools: Without Digital ToolsDocument6 pagesSan Antonio, Alicia, Isabela 2022-2023: With Digital Tools: Without Digital ToolsMicheal CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 2ND Sem FidpDocument14 pagesGenphysics 2ND Sem FidpCris Simon100% (3)
- FIDP BasCalDocument11 pagesFIDP BasCalGian NotorNo ratings yet
- 1 - FIDP - Diaz, Roger M.Document2 pages1 - FIDP - Diaz, Roger M.Chekahay ni 'Cher Ojie ug 'Cher Alven DiazNo ratings yet
- Fidp - Tamala, Sharmaine JoyDocument2 pagesFidp - Tamala, Sharmaine JoyJoy TamalaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Filled - FIDP - Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanDocument5 pagesPre-Filled - FIDP - Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanGen TalladNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document4 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Annie Rose Ansale JamandreNo ratings yet
- Fidp Personal DevelopmentDocument1 pageFidp Personal DevelopmentEloisa Micah GuabesNo ratings yet
- FIDP GenMath11 SY2021 2022 GCNEsguerraDocument12 pagesFIDP GenMath11 SY2021 2022 GCNEsguerraGian NotorNo ratings yet
- Fidp Diss Fidp For Disciplines and IdeasDocument14 pagesFidp Diss Fidp For Disciplines and IdeasJunedelMirallesPerezNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Asraf Bansuan (DAR)Document2 pagesAsraf Bansuan (DAR)Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Misha ProfileDocument2 pagesMisha ProfileMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Document25 pagesScience 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Misha Semi-LpDocument4 pagesMisha Semi-LpMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document5 pagesExercise 5Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocument27 pagesScience 10 Lesson PlanMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction of VirusesDocument6 pagesAn Introduction of VirusesMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologypptDocument32 pagesMicrobiologypptMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument23 pagesKingdom FungiMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Asraf FileDocument7 pagesAsraf FileMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- BANSUAN'Document2 pagesBANSUAN'Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Diass q1 Module 1 1st Quarter 1st SemDocument17 pagesDiass q1 Module 1 1st Quarter 1st SemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesModule 1 INTRODUCTIONMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument23 pagesModule 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- High Performance Lining Selection Chart For 90C Immersion - Belzona GuidesDocument2 pagesHigh Performance Lining Selection Chart For 90C Immersion - Belzona GuidesBobby SatheesanNo ratings yet
- CN5050 IntroductionDocument19 pagesCN5050 Introductionhenri_deterdingNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Thermal ExpansionDocument12 pagesTemperature and Thermal ExpansionAsa KaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual On Water and Waste Water Analysis by Santosh Kumar KharoleDocument58 pagesLab Manual On Water and Waste Water Analysis by Santosh Kumar KharoleSantosh Kumar75% (4)
- THE PHASE DIAGRAM OF THE SYSTEM Bi2O3-Fe2O3Document2 pagesTHE PHASE DIAGRAM OF THE SYSTEM Bi2O3-Fe2O3netxanderNo ratings yet
- NEDALDocument1 pageNEDALkhan4luvNo ratings yet
- McatDocument11 pagesMcatE12H12100% (1)
- LNG SummaryDocument10 pagesLNG SummaryDILIP MATALNo ratings yet
- UOP 603 Trace CO and CO2 in Hydrogen and Light Gases Hydrocarbon by GCDocument6 pagesUOP 603 Trace CO and CO2 in Hydrogen and Light Gases Hydrocarbon by GCMorteza SepehranNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis: Gravi - Metric (Weighing - Measure)Document23 pagesGravimetric Analysis: Gravi - Metric (Weighing - Measure)Ulfa WulandariNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium (Advanced) : (A) Solution of A Polyprotic Weak Acid: Der1: Let Us Take A Weak Diprotic Acid (HDocument20 pagesIonic Equilibrium (Advanced) : (A) Solution of A Polyprotic Weak Acid: Der1: Let Us Take A Weak Diprotic Acid (HJatin BhasinNo ratings yet
- Applications of Photoswitches in The Storage of Solar EnergyDocument16 pagesApplications of Photoswitches in The Storage of Solar Energymarina liñanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study Guide: Answer The Following Questions On A Separate Piece of PaperDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Study Guide: Answer The Following Questions On A Separate Piece of Paperapi-483662721No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Electrical Engineering MaterialsDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Electrical Engineering MaterialsKiran NNo ratings yet
- Condensation Exam Q - 4Document4 pagesCondensation Exam Q - 4sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)Document4 pagesPlug Flow Reactor (PFR)Elaine PuiNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument16 pagesCHEMUmer AnwarNo ratings yet
- Test de RadiadorDocument10 pagesTest de RadiadorOmar Reinoso TigreNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table NeetDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table NeetYash ChopadeNo ratings yet
- LechatDocument8 pagesLechataniseclassNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 4 - Makox MCQsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 4 - Makox MCQsنونه الحنونةNo ratings yet
- The Thermal ConductivityDocument6 pagesThe Thermal ConductivityLuc LeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FIITJEE Hints To QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemistry FIITJEE Hints To QuestionsAnjana JoshiNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Document8 pagesEnergy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Mri Basic PrincipleDocument38 pagesMri Basic PrincipleGokul LeeNo ratings yet
- ETİBOR-48: Sodium Tetraborate Pentahydrate (Na B O .5H O)Document7 pagesETİBOR-48: Sodium Tetraborate Pentahydrate (Na B O .5H O)Üstün Onur BaktırNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Solid StateDocument77 pagesChapter 16 Solid StateChicken ChickenNo ratings yet
- 23-07-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2020 (P-I) - Wat-12 - QP - Key, SolDocument15 pages23-07-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2020 (P-I) - Wat-12 - QP - Key, SolAnonymous A6Jnef04No ratings yet
- THU-002-Michel Ravers, Kaneka Belgium NVDocument19 pagesTHU-002-Michel Ravers, Kaneka Belgium NVŞafakNo ratings yet
Physical Science Fidp
Physical Science Fidp
Uploaded by
Misha WilliamsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Science Fidp
Physical Science Fidp
Uploaded by
Misha WilliamsCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical-Science-FIDP
Bsed-Biology (Caraga State University)
Scan to open on Studocu
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
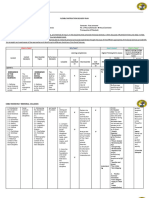
Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP)
Grade: 11/12 Semester: Second Semester
No. of Hours/Semester: 80 hours
Core Subject Title: Physical Science Prerequisites (if needed): None
Vision
Timber City Academy, a non-sectarian, Filipino Chinese Institution, envisions to be a valued-oriented, nationalistic, relevant, liberating, and performing schools that
delivers excellent basic education needed for a much-improved quality.
Mission
We Deliver technology
We equip students in the field of Business & Sciences
We conserve nature
Core Values
Trustworthiness- We maintain the trust of our family, friends and colleagues
Competence- We manifest competence in all our endeavors
Excellence- We perform one task with excellence
Accountability- We are accountable for what we do
Nationalistic- We love our origins.
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
Core Subject Description:
Evolution of our understanding of matter, motion, electricity, magnetism, light, and the universe from ancient times to the present; applications of physics and chemistry
concepts in contexts such as atmospheric phenomena, cosmology, astronomy, vision, medical instrumentation, space technology, drugs, sources of energy, pollution and
recycling, fitness and health, and cosmetics.
Culminating Performance Standard: Create a PubMat showing the day to day application of the principles of chemistry and physics and reflects on the social, political,
economic, cultural, environmental, and health dimensions that these may represent.
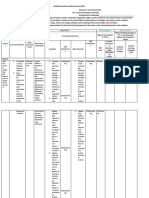
What to Teach? Why Teach? How to Assess? How to Teach?
Highest Enabling Strategy to
Highest Thinking Skill to Use in developing the
Learning Competencies
Assess Highest Thinking Skill to
Assess
Most Flexible
Content Performance
Content Essential Assessmen
Standards Standards Flexible
Topics KUD KUD t Activities Enabling
Most Learning
Complete Classificatio Classificatio RBT Level General Strategies
Essential (FAA)
n n Strategy
Performanc (FLS)
e Checks
THIRD QUARTER
How the The learners The Origin of The learners: The learners: U Give U Analyzing Think pair Communicatio Make a multi-
elements demonstrate an the Elements evidence for share n media
found in the understanding (Understandin and describe (Understandin activity presentation
g) g)
universe of: 1. Make a 1. Give the that explain
“Will the
were formed 1. The Light creative evidence for how the
formation of universe
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
1. The formation Elements representatio and explain heavier
of the elements n of the the formation elements
during the Big historical of the light during star
Bang and during 2. The Heavy development elements in
stellar evolution; of the atom the Big Bang formation
Elements and
or the theory;
chemical evolution.
2. The element in a 2. Give
3. Formation
distribution of the timeline. evidence for
of Elements
chemical Heavier than and describe
elements and Iron the formation continue to
of heavier U
the isotopes in expand as
the universe; elements (Understandin Applying light and Connection
during star g) heavy universe was
4. Chemical formation elements created
Elements and are also
and Isotopes evolution; continuously
in the and formed?
Universe
3. Write the
nuclear
fusion
reactions that
take place in K Understandin Representativ
stars, which (Knowing) g e
lead to the
formation of
new
elements.
How the 3. How the Understandin The learners: 4. Describe Quiz about Create a
idea of the concept of the g the how U nuclear graphic
atom, along atom evolved Elements elements reactions of Communicatio organizer
(Understandin Analyzing
with the from Ancient and the Make a heavier than trans- n that connects
iron are g)
idea of the Greek to the Atoms creative uranium the historical
elements present; representatio formed; elements development
evolved n of the 5. Describe of atom or
historical the ideas of U chemical
1. The Communicatio
4. How the Atomic development the Ancient (Understandin Analyzing element in a
n
concept of the Theory: From of the atom Greeks on g) timeline
element evolved the Ancient or the the atom;
from Ancient Greeks Up to chemical 6. Describe U Analyzing Communicatio
Greek to the the Present element in a
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
present; timeline the ideas of
the Ancient (Understandin
2. The n
Greeks on g)
Structure of the elements;
the Atom
7. Describe
the
contributions U
3. The Communicatio
of the (Understandin Analyzing
Synthetic n
alchemists to g)
Elements the science
of chemistry;
8. Point out
the main
ideas in the
discovery of U
Communicatio
the structure (Understandin Analyzing
n
of the atom g)
and its
subatomic
particles;
9. Cite the
contributions
of J.J.
Thomson,
Ernest
Rutherford, U
Henry Reasoning
(Understandin Evaluating
Moseley, and and Proof
Niels Bohr to g)
the
understandin
g of the
structure of
the atom;
10. Describe K Understandin Representativ
the nuclear (Knowing) g e
model of the
atom and the
location of its
major
components
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
(protons,
neutrons,
and
electrons);
11. Explain Explain how
how the the concept
concept of of atomic
atomic number
number led U U
to the led to the Communicatio
(Understandin (Understandin Analyzing
synthesis of synthesis of n
g) new g)
new
elements in elements in
the the
laboratory; laboratory.
12. Write the
nuclear
reactions
K Understandin Representativ
involved in
(Knowing) g e
the synthesis
of new
elements;
13. Cite the
contribution
of John
Dalton
toward the
K Understandin Representativ
understandin
(Knowing) g e
g of the
concept of
the chemical
elements;
and
14. Explain
how Dalton’s
theory U
Communicatio
contributed to (Understandin Analyzing
n
the discovery g)
of other
elements.
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
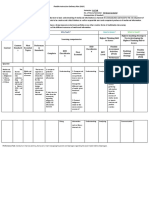
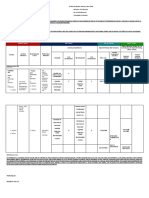
How the The learners Bonding and The learners: The learners: Determine if Long quiz Home
properties demonstrate an Physical a molecule is about the experiment
of matter understanding Properties of polar or properties of vlog about
relate to of: Matter U nonpolar U matter
Make a 1. Determine the
Reasoning
their creative if a molecule (Understandin (Understandin Evaluating properties of
given its and Proof
chemical representatio is polar or g) structure. g) liquid
structure 1. how the uses 1. Ionic, n of the non-polar
of different Covalent, historical given its
development structure;
materials are and Metallic
related to their Bonds of the atom 2. Relate the Relate the
properties and or the polarity of a U polarity of a U
structures; and chemical molecule to molecule to Communicatio
(Understandin (Understandin Analyzing
element in a its properties; its n
2. Bond g) g)
Energies timeline
Properties.
2. the
3. Describe Describe the
relationship
the general general types
between the 3. Properties K K Understandin Representativ
types of of intermole-
function and of Ionic and (Knowing) (Knowing) g e
intermole- cular forces.
structure of Covalent cular forces;
biological Compounds
macromolecules 4. Give the
type of
intermolecula K Understandin Representativ
r forces in the (Knowing) g e
properties of
substances
5. Explain Explain the
the effect of effect of
intermolecula U intermolecula U
Communicatio
r forces on (Understandin r forces on (Understandin Analyzing
n
the g) the g)
properties of properties of
substances substances.
6. Explain U Analyzing Communicatio
how the uses n
of the (Understandin
g)
following
materials
depend on
their
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
properties:
a. medical
implants,
prosthesis
b. sports
equipment
c. electronic
devices
d.
construction
supplies for
buildings and
furniture
e. household
gadgets;
7. Explain
how the
properties of
the above U
Communicatio
materials are (Understandin Analyzing
n
determined g)
by their
structure;
and
8. Explain U Explain how U Analyzing Communicatio
how the the structures n
structures of (Understandin of biological (Understandin
g) g)
biological
macromolecu macromolecu
les such as les such as
carbohydrate carbohydrate
s, lipids, s,
nucleic acid, lipids, nucleic
and proteins acid, and
determine proteins
their determine
properties
and their
functions. properties
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
and
functions.
How The learners Bonding and The learners: The learners: Use simple Long quiz
chemical demonstrate an Electro- collision about
changes understanding negativity theory to bonding of
take place of: Make either a 1. Use simple explain the electronegat
poster, a collision effects of ivity
1. Nonpolar flyer, or a theory to concentration
U U
1. The following Molecules brochure on explain the , Communicatio
effects of (Understandin (Understandin Analyzing
aspects of a product temperature, n
concentration g) g) Students will
chemical (such as and
, create a
changes: 2. Polar fuels,
temperature, particle size brochure of
Molecules household, or
a. how fast a and particle on the rate of any available
personal care reaction.
reaction takes size on the product
products) rate of
place inside their
indicating its reaction;
3. Bond home and
b. how much uses,
Character 2. Define Define identify its
reactants are properties,
catalyst and catalyst and uses,
needed and how mode of K K Understandin Representativ
describe how describe how properties
much products action, and (Knowing) (Knowing) g e
4. it affects it affects mode of
are formed in a precautions.
Intermolecula reaction rate; action and
reaction reaction rate.
r Forces precautions.
c. how much 3. Calculate
the amount
energy is
of U
involved in a
substances
reaction: and (Understandin Applying Connection
used or
produced in a g)
chemical
2. How energy is reaction;
harnessed.
4. Calculate U
percent yield Applying Connection
of a reaction; (Understandin
g)
5. Determine U Determine U Applying Connection
the limiting the limiting
reactant in a (Understandin reactant in a (Understandin
g) g)
reaction and
reaction and
calculate the
calculate the
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
amount of amount of
product
formed; product
formed.
6. Recognize
that energy is
released or
K Understandin Representativ
absorbed
(Knowing) g e
during a
chemical
reaction; and
7. Describe Describe how
how energy energy is
is harnessed harnessed
from different from different
sources: sources:
a. fossil fuels a. fossil fuels
b. biogas U b. biogas U
Communicatio
(Understandin (Understandin Analyzing
c. geothermal c. geothermal n
g) g)
d. d.
hydrothermal hydrothermal
e. batteries e. batteries
f. solar cells f. solar cells
g. biomass. g. biomass.
How The learners Properties of The learners: The learners: K Understandin Students will Representativ Divide the
chemistry demonstrate an Matter and (Knowing) g carry with e class in
contributes understanding their Uses in them any groups of 3-4
to the of: Certain Make either a 1. Give home members
understand- Materials poster, a common product that and have
ding of flyer, or a examples of available them explore
household The properties brochure on cleaning with them homemade
and and mode of 1. Medical a product materials for and identify alternative
personal (such as the house its product products for
action of the Implants
care and for label and their personal
following fuels,
products personal uses hygiene and
consumer household, or
care;
personal care their
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
products: 2. Sports products) household
Equipment indicating its cleaning use.
a. cleaning
uses, Have them
materials
properties, research to
b. cosmetics 3. mode of create/replica
Construction action, and te the
Supplies and precautions. alternative
the product.
Properties of Each group
Substance will have to
demonstrate
the process
4. Household to the
Products: class,
Cleaning describe the
Agents creation, use,
mode of
action and
5. Personal disposal of
Care the
Products homemade
product.
The
demonstratio
n can span 5-
6 minutes,
including a
short
question and
answer
portion.
2. From K From product K Understandin Representativ
product (Knowing) labels, (Knowing) g e
labels, identify the
identify the active
active
ingredient(s) ingredient(s)
of cleaning
of cleaning
products
products
used at
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
used at home.
home;
3. Give the Give the use
use of the of the other
other K ingredients in K Understandin Representativ
ingredients in (Knowing) (Knowing) g e
cleaning cleaning
agents; agents.
4. Give
common
examples of
personal care
products K Understandin Representativ
used to (Knowing) g e
enhance the
appearance
of the human
body;
5. Identify the
major
ingredients of
cosmetics
such as body
K Understandin Representativ
lotion, skin
(Knowing) g e
whitener,
deodorants,
shaving
cream, and
perfume; and
6. Explain the
precautionary
measures U
indicated in Communicatio
(Understandin Analyzing
various n
cleaning g)
products and
cosmetics.
FOURTH QUARTER
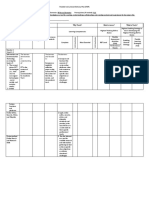
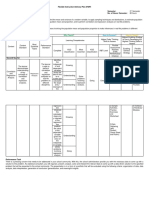
How we The learners The Earth . The learners: U Analyzing Give a Communicatio Create a
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
come to demonstrate an and the
realize that understanding Universe
1. Explain matching
the Earth is of:
what the type quiz
not the
Greeks (Understandin that
center of 1. Ancient considered to n
g) connects
the 1. Greek views Astronomy be the three philosophers
Universe of matter, types of with their
motion, and the terrestrial
philosophica
universe; 2. Modern motion;
l
Astronomy 2. Explain contribution.
what is
2. Competing meant by Another
models of the diurnal U option is to
universe by motion, fill out a Communicatio
(Understandin Analyzing
Eudoxus, annual diagram with n diagram that
motion, g) domains
Aristotle, compare and
Aristarchus, precession of with contrast the
Ptolemy, the correspondi models of the
Copernicus, equinoxes; ng elements universe
Brahe, and 3. Explain Explain how and motions
Kepler; and how the U the Greeks U found
Greeks knew knew that the Communicatio
(Understandin (Understandin Analyzing in these
that the Earth n
g) Earth is g) domains.
is spherical;
3. Evidence that spherical.
the Earth is not Ask the
4. Explain learners to
the center of the
how Plato’s provide
problem of naked-eye
“Saving the U
observations Communicatio
Appearances (Understandin Analyzing
showing that n
” constrained g) the Earth is
Greek
round.
models of the
Universe;
5. Compare U Evaluating Reasoning
and contrast and Proof
the (Understandin
g)
models/descr
iptions of the
universe by
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
Eudoxus,
Aristotle,
Aristarchus,
Ptolemy, and
Copernicus;
6. Cite Cite
examples of examples of
astronomical astronomical
phenomena phenomena
known to
astronomers K known to K Understandin Representativ
(Knowing) astronomers (Knowing) g e
before the
advent of before the
telescopes; advent
of
telescopes.
7. Compare
and contrast
explanations
and models
of U
Reasoning
astronomical (Understandin Evaluating
and Proof
phenomena g)
(Copernican,
Ptolemaic,
and
Tychonic);
8. Explain U Analyzing Communicatio
how Galileo’s n
astronomical (Understandin
g)
discoveries
and
observations
(lunar
craters,
phases of
Venus,
moons of
Jupiter, sun
spots,
supernovas,
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
the
apparently
identical size
of stars as
seen through
the naked
eye, and
telescope
observations)
helped
weaken the
support for
the Ptolemaic
model;
9. Explain Explain how
how Brahe’s Brahe’s
innovations innovations
and and
extensive extensive
collection of collection of
data in data in
observational U U
astronomy observational Communicatio
(Understandin astronomy (Understandin Analyzing
paved the n
way for g) paved the g)
Kepler’s way
discovery of for Kepler’s
his laws of discovery of
planetary his laws of
motion; and
planetary
motion.
10. Apply
Kepler’s 3rd
law of U
planetary (Understandin Applying Connection
motion to g)
objects in the
solar system.
Why we The learners The . The learners: U Compare and U Evaluating Illustration of Communicatio Book review
believe that demonstrate an Universal contrast the Reasoning n with a
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
the laws of understanding Laws of 1. Compare Aristotelian and Proof
physics are of: Physics and contrast and Galilean situational
universal the conceptions occurrences
Aristotelian of vertical through
and Galilean motion, pictures
1. Aristotelian vs. 1. Aristotle’s teacher’s
conceptions where each
Galilean views of View of (Understandin horizontal (Understandin supplement
of vertical law are
motion; Motion g) motion, and g) through video
motion, applied with
horizontal projectile a follow up presentation
motion, and motion. explanations
2. how Galileo 2. Galileo;s projectile
used his Views of motion;
group
discoveries in Motion
upload)
mechanics (and
astronomy) to 2. Explain explain how Situational
address 3. Newton’s how Galileo Galileo analysis
scientific Laws of inferred that inferred that (students
objections to the Motion object in object are tasked
Copernican vacuum fall to drop two
with uniform in vacuum
model; fall with different
acceleration, objects with
4. Newton’s and that uniform Situational
Law of acceleration, different
force is not analysis
3. Newton’s Universal objects with
necessary to and that
Laws of Motion; Gravitation different
sustain force is not
horizontal masses at
necessary to
motion; the same
sustain
4. Newton’s Law height and
of Universal horizontal time)
motion.
Gravitation; and
3. Explain U Analyzing Communicatio
5. Mass, how the n
momentum, and position vs. (Understandin
energy g)
time, and
conservation. velocity vs.
time graphs
of constant
velocity
motion are
different from
those of
constant
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
acceleration
motion;
4. Recognize
that the
everyday
usage and
the physics
usage of the
term
“acceleration” U
differ: In Reasoning
(Understandin Evaluating
physics an and Proof
object that is g)
slowing
down,
speeding up,
or changing
direction is
said to be
accelerating;
5. Explain
each of U
Communicatio
Newton’s (Understandin Analyzing
n
three laws of g)
motion;
6. Explain the U Analyzing Communicatio
subtle n
distinction (Understandin
g)
between
Newton’s 1st
Law of
Motion (or
Law of
Inertia) and
Galileo’s
assertion that
force is not
necessary to
sustain
horizontal
motion;
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
7. Use
algebra,
Newton’s 2nd
Law of
Motion, and
Newton’s
Law of
Universal
Gravitation to
show that, in U
the absence (Understandin Applying Connection
of air g)
resistance,
objects close
to the surface
of the Earth
fall with
identical
accelerations
independent
of their mass;
8. Explain the
statement
“Newton's
laws of
motion are U
Communicatio
axioms while (Understandin Analyzing
n
Kepler's laws g)
of planetary
motion are
empirical
laws.”.
9. Explain the U Analyzing Communicatio
contributions n
of scientists (Understandin
g)
to our
understandin
g of mass,
momentum,
and energy
conservation;
and
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
10. Use the
law of
conservation
of U
momentum (Understandin Applying Connection
to solve one- g)
dimensional
collision
problems.
How light Light The learners: Venn Home
acts as a diagram experiment of
wave and a about how lights
particle 1. Classical 1. Describe comparison travel though
and Modern what of reflection different
happens K Understandin and Representativ mediums that
Theories of
when light is (Knowing) g refraction e describe the
Light
reflected, characteristic
refracted, s and
transmitted, theories of
2. Reflection, and
Refraction, light waves.
absorbed;
Transmission
, and 2. Explain
how Newton
Absorption of
and
Light
Descartes
described the U
Communicatio
emergence (Understandin Analyzing
n
3. of light in g)
Understandin various
g the colors
different light through
phenomena prisms;
3. Cite K Understandin Representativ
examples of (Knowing) g e
4. Light: An waves (e.g.,
electromagne water,
tic wave stadium,
sound, string,
and light
waves);
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
4. Describe Describe how
how the the
propagation propagation
of light, of light,
reflection, reflection,
and and
K K Understandin Representativ
refraction are refraction are
(Knowing) (Knowing) g e
explained by explained by
the wave the wave
model and model and
the particle the particle
model of model of
light; light.
5. Explain
how the
photon U
Communicatio
theory of light (Understandin Analyzing
n
accounts for g)
atomic
spectra;
6. Explain U Explain how U Analyzing Communicatio
how the the photon n
photon (Understandin concept and (Understandin
g) g)
concept and the fact that
the fact that the energy of
the energy of a photon is
a photon is directly
directly proportional
proportional to its
to its frequency
frequency can be used
can be used to explain
to explain why red light
why red light is used in
is used in photographic
photographic dark rooms,
dark rooms, why we get
why we get easily
easily sunburned in
sunburned in ultraviolet
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
ultraviolet light but not
light but not in visible
in visible light, and
light, and how we see
how we see colors.
colors;
7. Apply the
wavelength- U
speed- (Understandin Applying Connection
frequency g)
relation;
8. Describe
how Galileo
and Roemer
contributed to
the eventual K Understandin Representativ
acceptance (Knowing) g e
of the view
that the
speed of light
is finite;
9. Cite Cite
experimental experimental
evidence evidence
K K Understandin Representativ
showing that showing that
(Knowing) (Knowing) g e
electrons can electrons can
behave like behave like
waves; and waves.
10. Differen- Differentiate
tiate dispersion,
dispersion, U scattering, U
Reasoning
scattering, (Understandin interference, (Understandin Evaluating
and Proof
interference, g) and g)
and diffraction.
diffraction.
How The learners Understandin The learners: U Explain how U Analyzing Make a Communicatio Create a
physics demonstrate an g the special research n model of
(Understandin relativity (Understandin
helps us understanding Cosmos abut 2020
g) g)
understand of: Through 1. Explain resolved the exoplanet of habitable
Physics how special conflict your choice. exoplanets in
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
the Cosmos relativity between From the any form of
resolved the Newtonian facts that art materials
1. Relativity and 1. Einstein’s conflict mechanics you will available in
the Big Bang Theory of between and gather about your home
Relativity Newtonian Maxwell’s
2. Planets in and the
mechanics electromagne exoplanet,
beyond the Solar
and tic theory. explain
System
2. Doppler Maxwell’s
through
Effect and electromagne
essay
the Cosmic tic theory;
whether it
Distance 2. Explain the Explain the can be
Ladder consequence consequence considerable
s of the s of the habitable or
postulates of postulates of not. Justify
3. Planet In Special Special
your answer.
Relativity Relativity
and Beyond
(e.g., U (e.g., U
the Solar
relativity of relativity of Communicatio
System (Understandin (Understandin Analyzing
simultaneity, simultaneity, n
time dilation, g) time dilation, g)
length length
contraction, contraction,
mass-energy mass-energy
equivalence, equivalence,
and cosmic and cosmic
speed limit); speed limit).
3. Explain the U Explain the U Analyzing Communicatio
consequence consequence n
s of the (Understandin s of the (Understandin
g) g)
postulates of postulates of
General General
Relativity Relativity
(e.g., correct (e.g., correct
predictions of predictions of
shifts in the shifts in the
orbit of orbit of
Mercury, Mercury,
gravitational gravitational
bending of bending of
light, and light, and
black holes); black holes).
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
4. Explain Explain how
how the the speeds
speeds and and
distances of distances of
far-off objects U far-off objects U
Communicatio
are estimated (Understandin are estimated (Understandin Analyzing
n
(e.g., Doppler g) (e.g., Doppler g)
effect and effect and
cosmic cosmic
distance distance
ladder); ladder);
5. Explain Explain how
how we know we know that
that we live in we live in an
an expanding expanding
universe, U universe, U
Communicatio
which used (Understandin which used (Understandin Analyzing
n
to be hot and g) to be hot and g)
is is
approximatel approximatel
y 14billion y 14billion
years old; years old.
6. Explain
how Doppler
shifts and U
transits can Communicatio
(Understandin Analyzing
be used to n
detect extra g)
solar planets;
and
7. Explain
why Pluto
was once U
thought to be Communicatio
(Understandin Analyzing
a planet but n
is no longer g)
considered
one.
Performance Task:
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
As a concerned citizen, you are to submit a pubmat to the concerned office (e.g. homeowners association, barangay, etc.) it must showcase captured photos of an identifies
socio-scientific issue (SSI) that relates to the day-to-day applications of the principles of Chemistry and physics. The photo essay must include the following:
a. Appropriate physics and chemistry concepts and principles:
b. Proposed solution and call for action. The PubMat will released to the netizens
c. Reflections or insights on the social, political, economic, cultural, environmental, and health aspects of the captured images
d. Reflections or insights on the social, political, economic, cultural, environmental and health aspects of the captured images
The content should be accurate, comprehensive, reader-friendly and relevant. The proposed solution must be sustainable, equitable, feasible and viable.
The reflection/insight should be meaningful.
Prepared by: Noted by: Checked by:
JAYVEE M. JARINA,LPT KIM CHRISTIAN T. MATILDO, MAEd AIDA C. ABAD, Ph.D.
Science Teacher SHS Coordinator School Principal
Downloaded by Mishaira Macalnas (macalnasmishaira50@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-General MathDocument2 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan-General MathHerra Luna Bautista93% (14)
- Media and Information Literacy FIDPDocument9 pagesMedia and Information Literacy FIDPJomark Rebolledo100% (2)
- Discipline and Ideas in The Social Science - FIDP (De Guia) Hum2Document8 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in The Social Science - FIDP (De Guia) Hum2patrixia73% (11)
- FIDP Oral Com 1Document5 pagesFIDP Oral Com 1Jomark Rebolledo100% (1)
- Fidp Personal DevelopmentDocument10 pagesFidp Personal DevelopmentJayvee Jarina100% (9)
- Creative Writing FIDPDocument8 pagesCreative Writing FIDPLeah Jean VillegasNo ratings yet
- FIDP - 21st CenturyDocument9 pagesFIDP - 21st CenturyLeah Jean VillegasNo ratings yet
- Mechanics and Free Fall - FIDPDocument4 pagesMechanics and Free Fall - FIDPAustin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateAisa Edza100% (5)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template CONTENT 5Edward Barber100% (3)
- Bio 101 Sample Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBio 101 Sample Lab ReportRavinderenPichan67% (3)
- Fidp PhysciDocument13 pagesFidp PhysciDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) Grade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionDocument1 pageFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) Grade: Semester: Core Subject Title: No. of Hours/ Semester: Core Subject DescriptionJoy TamalaNo ratings yet
- Fidp Diss IbabaoDocument10 pagesFidp Diss IbabaoNikki Anne BerlanasNo ratings yet
- Fidp UcspDocument22 pagesFidp Ucspkaren bacquialNo ratings yet
- FIDP StatandProbDocument9 pagesFIDP StatandProbGian NotorNo ratings yet
- Relativity - FIDPDocument2 pagesRelativity - FIDPAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)Document7 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)John paul siaNo ratings yet
- FIDP-Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument7 pagesFIDP-Sampling and Sampling DistributionHoney Mae VillaverNo ratings yet
- Fidp DissDocument9 pagesFidp DissFranklin II Isla100% (2)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan TemplateMonica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Fidp Genbio2Document8 pagesFidp Genbio2Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery PlanDocument4 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery PlanImie Omamalin GuisehanNo ratings yet
- Models of The Universe - FidpDocument9 pagesModels of The Universe - FidpAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- FIDP Creative WritingDocument12 pagesFIDP Creative WritingVan Jasper AranetaNo ratings yet
- Fidp Basic CalculusDocument10 pagesFidp Basic CalculusKaye CabangonNo ratings yet
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion - FIDPDocument2 pagesKepler's Laws of Planetary Motion - FIDPAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fidp ResearchDocument3 pagesFidp ResearchIn SanityNo ratings yet
- MIL - For CheckingDocument18 pagesMIL - For CheckingPaul Jeremiah UrsosNo ratings yet
- Fidp ElsDocument6 pagesFidp ElsDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Fidp Gen. Math2Document8 pagesFidp Gen. Math2Mark Anthony AnchetaNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Fidp 2022-2023Document10 pagesPR1 - Fidp 2022-2023ardrian malangenNo ratings yet
- What To Teach? Why Teach?Document2 pagesWhat To Teach? Why Teach?John Mickel NaelgaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science FidpDocument9 pagesEarth Science FidpJohn Keven VallespinNo ratings yet
- Household and Personal Care Products - FIDPDocument5 pagesHousehold and Personal Care Products - FIDPAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Fidp EsDocument6 pagesFidp EsDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- The Development of Listening and Speaking Skills and Strategies For Effective Communication in Various SituationsDocument3 pagesThe Development of Listening and Speaking Skills and Strategies For Effective Communication in Various SituationsBea TanglaoNo ratings yet
- FIDP - Creative WritingDocument13 pagesFIDP - Creative WritingGen TalladNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp) School Year 2021-2022Document11 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp) School Year 2021-2022Paul Jeremiah UrsosNo ratings yet
- Fidp DissDocument12 pagesFidp DissRexijay PagatpatNo ratings yet
- FIDP Oral CommDocument8 pagesFIDP Oral CommGenelyn TabladaNo ratings yet
- Fidp Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument3 pagesFidp Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonHeather MarcoNo ratings yet
- FIDP Emp - Tech 11Document12 pagesFIDP Emp - Tech 11Jan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Fidp Darwin UrbanoDocument32 pagesEarth and Life Science Fidp Darwin UrbanoMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- GEN PHYSICS 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Document8 pagesGEN PHYSICS 1 FIDP (Q1 and Q2)Crisanta Ganado67% (3)
- JAVA-OOP - Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template (FIDP)Document27 pagesJAVA-OOP - Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan Template (FIDP)Filifish KnowNo ratings yet
- FIDP Template R4 DRAFTDocument4 pagesFIDP Template R4 DRAFTClaire Joy GeonzonNo ratings yet
- FIDPDocument3 pagesFIDPLloyd GarilloNo ratings yet
- Sample FIDPDocument5 pagesSample FIDPDan Vincent Mapalo100% (1)
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)Document2 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (Fidp)Melissa Ann BuhianNo ratings yet
- San Antonio, Alicia, Isabela 2022-2023: With Digital Tools: Without Digital ToolsDocument6 pagesSan Antonio, Alicia, Isabela 2022-2023: With Digital Tools: Without Digital ToolsMicheal CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 2ND Sem FidpDocument14 pagesGenphysics 2ND Sem FidpCris Simon100% (3)
- FIDP BasCalDocument11 pagesFIDP BasCalGian NotorNo ratings yet
- 1 - FIDP - Diaz, Roger M.Document2 pages1 - FIDP - Diaz, Roger M.Chekahay ni 'Cher Ojie ug 'Cher Alven DiazNo ratings yet
- Fidp - Tamala, Sharmaine JoyDocument2 pagesFidp - Tamala, Sharmaine JoyJoy TamalaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Filled - FIDP - Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanDocument5 pagesPre-Filled - FIDP - Flexible Instruction Delivery PlanGen TalladNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Document4 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan (FIDP) : What To Teach?Annie Rose Ansale JamandreNo ratings yet
- Fidp Personal DevelopmentDocument1 pageFidp Personal DevelopmentEloisa Micah GuabesNo ratings yet
- FIDP GenMath11 SY2021 2022 GCNEsguerraDocument12 pagesFIDP GenMath11 SY2021 2022 GCNEsguerraGian NotorNo ratings yet
- Fidp Diss Fidp For Disciplines and IdeasDocument14 pagesFidp Diss Fidp For Disciplines and IdeasJunedelMirallesPerezNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Asraf Bansuan (DAR)Document2 pagesAsraf Bansuan (DAR)Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Misha ProfileDocument2 pagesMisha ProfileMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Document25 pagesScience 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Misha Semi-LpDocument4 pagesMisha Semi-LpMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document5 pagesExercise 5Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocument27 pagesScience 10 Lesson PlanMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction of VirusesDocument6 pagesAn Introduction of VirusesMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologypptDocument32 pagesMicrobiologypptMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument23 pagesKingdom FungiMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Asraf FileDocument7 pagesAsraf FileMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- BANSUAN'Document2 pagesBANSUAN'Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Diass q1 Module 1 1st Quarter 1st SemDocument17 pagesDiass q1 Module 1 1st Quarter 1st SemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesModule 1 INTRODUCTIONMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMDocument23 pagesModule 4 SKELETAL SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- High Performance Lining Selection Chart For 90C Immersion - Belzona GuidesDocument2 pagesHigh Performance Lining Selection Chart For 90C Immersion - Belzona GuidesBobby SatheesanNo ratings yet
- CN5050 IntroductionDocument19 pagesCN5050 Introductionhenri_deterdingNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Thermal ExpansionDocument12 pagesTemperature and Thermal ExpansionAsa KaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual On Water and Waste Water Analysis by Santosh Kumar KharoleDocument58 pagesLab Manual On Water and Waste Water Analysis by Santosh Kumar KharoleSantosh Kumar75% (4)
- THE PHASE DIAGRAM OF THE SYSTEM Bi2O3-Fe2O3Document2 pagesTHE PHASE DIAGRAM OF THE SYSTEM Bi2O3-Fe2O3netxanderNo ratings yet
- NEDALDocument1 pageNEDALkhan4luvNo ratings yet
- McatDocument11 pagesMcatE12H12100% (1)
- LNG SummaryDocument10 pagesLNG SummaryDILIP MATALNo ratings yet
- UOP 603 Trace CO and CO2 in Hydrogen and Light Gases Hydrocarbon by GCDocument6 pagesUOP 603 Trace CO and CO2 in Hydrogen and Light Gases Hydrocarbon by GCMorteza SepehranNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis: Gravi - Metric (Weighing - Measure)Document23 pagesGravimetric Analysis: Gravi - Metric (Weighing - Measure)Ulfa WulandariNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium (Advanced) : (A) Solution of A Polyprotic Weak Acid: Der1: Let Us Take A Weak Diprotic Acid (HDocument20 pagesIonic Equilibrium (Advanced) : (A) Solution of A Polyprotic Weak Acid: Der1: Let Us Take A Weak Diprotic Acid (HJatin BhasinNo ratings yet
- Applications of Photoswitches in The Storage of Solar EnergyDocument16 pagesApplications of Photoswitches in The Storage of Solar Energymarina liñanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study Guide: Answer The Following Questions On A Separate Piece of PaperDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Study Guide: Answer The Following Questions On A Separate Piece of Paperapi-483662721No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Electrical Engineering MaterialsDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Electrical Engineering MaterialsKiran NNo ratings yet
- Condensation Exam Q - 4Document4 pagesCondensation Exam Q - 4sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)Document4 pagesPlug Flow Reactor (PFR)Elaine PuiNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument16 pagesCHEMUmer AnwarNo ratings yet
- Test de RadiadorDocument10 pagesTest de RadiadorOmar Reinoso TigreNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table NeetDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table NeetYash ChopadeNo ratings yet
- LechatDocument8 pagesLechataniseclassNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 4 - Makox MCQsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 4 - Makox MCQsنونه الحنونةNo ratings yet
- The Thermal ConductivityDocument6 pagesThe Thermal ConductivityLuc LeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FIITJEE Hints To QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemistry FIITJEE Hints To QuestionsAnjana JoshiNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Document8 pagesEnergy Changes in Reactions: For Advanced Chemistry Special Science High School in Grade 10 Quarter 3/ Week 5Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Mri Basic PrincipleDocument38 pagesMri Basic PrincipleGokul LeeNo ratings yet
- ETİBOR-48: Sodium Tetraborate Pentahydrate (Na B O .5H O)Document7 pagesETİBOR-48: Sodium Tetraborate Pentahydrate (Na B O .5H O)Üstün Onur BaktırNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Solid StateDocument77 pagesChapter 16 Solid StateChicken ChickenNo ratings yet
- 23-07-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2020 (P-I) - Wat-12 - QP - Key, SolDocument15 pages23-07-23 - JR - Iit - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) - Jee Adv - 2020 (P-I) - Wat-12 - QP - Key, SolAnonymous A6Jnef04No ratings yet
- THU-002-Michel Ravers, Kaneka Belgium NVDocument19 pagesTHU-002-Michel Ravers, Kaneka Belgium NVŞafakNo ratings yet