Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
arjunsatviCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
arjunsatviCopyright:
Available Formats
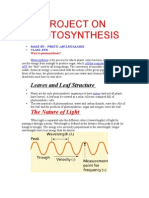
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a biological process used by plants, algae, and certain bacteria to convert
light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. It occurs mainly within the chloroplasts
of plant cells. This process is fundamental for life on Earth as it provides the primary energy
source for nearly all ecosystems and supplies oxygen to the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis can be split into two main stages: light-dependent reactions and the Calvin
cycle (light-independent reactions). In the light-dependent reactions, which take place in the
thylakoid membranes, sunlight energizes electrons that are then used to convert water
molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons and to generate ATP and NADPH. In the
Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma, ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon
dioxide from the air into organic molecules like glucose. The overall chemical equation for
photosynthesis is generally represented as:
6��2+6�2�+���ℎ�→�6�12�6+6�26CO2+6H2O+light→C6H12
O6+6O2
You might also like
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisdanielNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisjeankayzelrodelasNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio ReportDocument23 pagesGen Bio ReportRhean Reyle VelardeNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisSai SubuNo ratings yet
- Report Group 11Document5 pagesReport Group 11Boyd benson kayomboNo ratings yet
- Integrated ScienceDocument12 pagesIntegrated ScienceMalinda GreeneNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- 15 PhotosynthesisDocument10 pages15 PhotosynthesisEarl Adam LambacoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureMatthew BetinolNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cell Biology FileDocument16 pagesPhotosynthesis Cell Biology FileRei KaplanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cell Biology FileDocument16 pagesPhotosynthesis Cell Biology FileRei KaplanNo ratings yet
- The Erudite'sDocument4 pagesThe Erudite'sfestusatere192No ratings yet
- Photosenthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosenthesis and Cellular RespirationMonkey D. AilaNo ratings yet
- Plants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The BiosphereDocument12 pagesPlants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The Biosphereюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Topic PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesTopic PhotosynthesisJacob AssoulineNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisErwin Grey Pereña Peji100% (1)
- Chapter 10 OutlineDocument13 pagesChapter 10 OutlineJosephinemwNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesGroup 4 PhotosynthesisJv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A in Agri 501-BiochemistryDocument14 pagesA in Agri 501-BiochemistryIvan Jhon AnamNo ratings yet
- Hotosynthesis: Big PictureDocument3 pagesHotosynthesis: Big Picturehomamunfat100% (1)
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument2 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISVivien LancinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- What Is Light and Dark ReactionDocument1 pageWhat Is Light and Dark ReactionSheharyar The PRONo ratings yet
- Biochemical Processes at Cellular Level Pres1.Document14 pagesBiochemical Processes at Cellular Level Pres1.immanuel ndawedapoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Vs RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Vs Respirationapi-231516879No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Respiration Report FinalDocument53 pagesPhotosynthesis Respiration Report FinalIvan Jhon AnamNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesism.benchaitaNo ratings yet
- PhotosyntesisDocument1 pagePhotosyntesisSteven AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Bio HWDocument9 pagesBio HWedgar batotoNo ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotesDocument14 pagesBiology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotessarayoshicaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Gen Bio Light Dark Reaction Phase PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesLecture Gen Bio Light Dark Reaction Phase PhotosynthesisAshley BinasNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesistanaythegreat999No ratings yet
- The PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesThe Photosynthesisamity nocedaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReadingDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis ReadingLogan ParkisonNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisNimesh BariyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Photosynthesis-1Document7 pagesUnit 4 Photosynthesis-1Abraham BanjoNo ratings yet
- The Wonders of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Wonders of Photosynthesisarvinraghubar9No ratings yet
- ZumdahlDocument17 pagesZumdahlmohammedraafat1977No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Week 7 PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesWeek 7 PhotosynthesisCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast Photosynthesis-FileDocument17 pagesChloroplast Photosynthesis-Filesiguro hwahahahNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Reviewer) - JMDPDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis (Reviewer) - JMDPJhianne Mylz ParañalNo ratings yet
- My Photosynthesis NotesDocument1 pageMy Photosynthesis NoteswkwickaNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Terang Dan Gelap: Dua Tahapan Fotosintesis Tanaman Sekar Arum Wulandari (1302619067)Document7 pagesReaksi Terang Dan Gelap: Dua Tahapan Fotosintesis Tanaman Sekar Arum Wulandari (1302619067)Adila KurniatiNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument4 pagesEnergy TransformationAsh Nico BanquilloNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Nakodar (G)Document4 pagesPhotosynthesis Nakodar (G)api-3703711No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesisMason PeinNo ratings yet
- Midterm NotesDocument2 pagesMidterm Noteshernys NietoNo ratings yet
- Process of BBK JalandharDocument14 pagesProcess of BBK Jalandharapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Dark Reaction and Calvin Cycle Class 9 NotesDocument130 pagesPhotosynthesis - Dark Reaction and Calvin Cycle Class 9 Notesbrajeshitc.raiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Handouts)Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis (Handouts)Jelea MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Metabolic ProcessesDocument23 pagesMetabolic ProcessesJerson Lloyd OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis, Process by Which Green Plants and Certain Other OrganismsDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis, Process by Which Green Plants and Certain Other OrganismsAbhinavNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 PointersDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Pointersrobertbernales2007No ratings yet
- NeuroplasticityDocument2 pagesNeuroplasticityarjunsatviNo ratings yet
- CrisprDocument1 pageCrisprarjunsatviNo ratings yet
- Quantum ComputingDocument1 pageQuantum ComputingarjunsatviNo ratings yet
- ThoeryrelativDocument1 pageThoeryrelativarjunsatviNo ratings yet