Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lect 06 Kernel
Lect 06 Kernel
Uploaded by
usereddit69420 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views16 pagesOriginal Title
Lect_06_Kernel
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views16 pagesLect 06 Kernel
Lect 06 Kernel
Uploaded by
usereddit6942Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 16
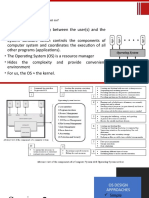
OPERATING SYSTEMS CS F372
BIJU K RAVEENDRAN & TEAM
LECT #06: KERNEL
UNIX
• UNIX – limited by hardware functionality, the original
UNIX operating system had limited structuring. The
UNIX OS consists of two separable parts
– Systems programs
– The kernel
• Consists of everything below the system-call
interface and above the physical hardware
• Provides the file system, CPU scheduling, memory
management, and other operating-system
functions; a large number of functions for one
level
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 2
UNIX System Structure
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 3
UNIX Kernel Space
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 4
Linux System Structure
Monolithic
with Modular
Design
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 5
Microkernel System Structure
• Moves as much from the kernel into “user” space
• Communication takes place between user modules using message
passing
• Kernel consist of only essential components
• The kernel will be very small
• Main function of the Micro kernel is to provide communication
facility (using Message passing)
• Benefits:
– Easier to extend a microkernel
– Easier to port the operating system to new architectures
– More reliable (less code is running in kernel mode)
– More secure
• Detriments:
– Performance overhead of user space to kernel space communication
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 6
Microkernel System Structure
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 7
Monolithic Vs Micro Kernel
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 8
Modules
• Most modern operating systems implement
kernel modules
– Uses object-oriented approach
– Each core component is separate
– Each talks to the others over known
interfaces
– Each is loadable as needed within the kernel
• Overall, similar to layers but with more flexible
– Linux, Solaris
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 9
Solaris Modular Approach
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 10
Hybrid Systems
• Most modern OSs are actually not one pure model
– Hybrid combines multiple approaches to address
performance, security, usability needs
– Linux and Solaris kernels in kernel address space
are monolithic and are modular for dynamic
loading of functionality
– Windows mostly monolithic, plus microkernel
for different subsystem personalities
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 11
Why Applications are OS Specific?
• Apps compiled on one system usually not executable on other OS
• Each OS provides its own unique system calls, file formats etc..
• Apps can be multi-operating system
– Written in interpreted language like Python, Ruby, and
interpreter available on multiple OSs
– App written in language that includes a VM containing the
running app (like Java)
– Use standard language (like C), compile separately on each OS
to run on each
• Application Binary Interface (ABI) is architecture equivalent of API,
defines how different components of binary code can interface for
a given operating system on a given architecture, CPU, etc .
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 12
System Design
• System Design Goals
– User goals – operating system should be convenient
to use, easy to learn, reliable, safe, and fast.
– System goals – operating system should be easy to
design, implement, and maintain, as well as flexible,
reliable, error-free, and efficient
• Mechanisms and Policies
– Mechanisms determine how to do something,
policies decide what will be done.
– The separation of policy from mechanism is a very
important principle, it allows maximum flexibility if
policy decisions are to be changed later.
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 13
System Implementation
• Traditionally written in assembly language,
operating systems can now be written in higher-
level languages.
• Code written in a high-level language:
– can be written faster.
– is more compact.
– is easier to understand and debug.
• An operating system is far easier to port (move
to some other hardware) if it is written in a
high-level language.
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 14
General System Architecture
• Why we need protection?
– In single task / programming environment
• To protect OS from incorrect program
– In multiprogramming / multitasking environment
• To protect OS and other programs from incorrect
program
• Given the I/O instructions are privileged, how does
the user program perform I/O?
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 15
Use of a System call to perform I/O
January 22, 2024 Biju K Raveendran @ BITS Pilani Goa 16
You might also like
- NetacadDocument15 pagesNetacadGuteNo ratings yet
- Lect 05 DualModeOperationDocument14 pagesLect 05 DualModeOperationusereddit6942No ratings yet
- Perating Ystems: CS C372 & IS C362Document7 pagesPerating Ystems: CS C372 & IS C362shoaib_mohammed_28No ratings yet
- Questions AnsweredDocument20 pagesQuestions AnsweredAvinash AllaNo ratings yet
- Session 2: Os Design ApproachesDocument18 pagesSession 2: Os Design ApproachesSai susheel gupta sanagapalliNo ratings yet
- Operating System For Advanced Processors: DR - Kanthi.MDocument22 pagesOperating System For Advanced Processors: DR - Kanthi.MVinit PkNo ratings yet
- LinuxDocument17 pagesLinuxkabita maharjanNo ratings yet
- Lubi - SO - Pertemuan 4Document27 pagesLubi - SO - Pertemuan 4lubeiNo ratings yet
- LGLinux 1 PDFDocument149 pagesLGLinux 1 PDFAkshay PmNo ratings yet
- Os MD 1Document137 pagesOs MD 1sivakrishna_munagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Introduction To Operating SystemDocument23 pagesChapter - 1 - Introduction To Operating SystemHardikNo ratings yet
- AT Unit1 Distributed - SystemsDocument30 pagesAT Unit1 Distributed - Systemsroger.bastida01No ratings yet
- OS-CO1-Session 05 System CallsDocument59 pagesOS-CO1-Session 05 System CallsElangovan GuruvaReddyNo ratings yet
- Open Source QBDocument37 pagesOpen Source QBUmme SanaNo ratings yet
- Midori Cloud Base OsDocument24 pagesMidori Cloud Base OsTulshinarayan Giri0% (1)
- Unit 4 22MD5PCESDDocument145 pagesUnit 4 22MD5PCESDlakshmi.ml21No ratings yet
- CH One IntroductionDocument35 pagesCH One Introductionlemi bkNo ratings yet
- Lect 07 SystemCallDocument19 pagesLect 07 SystemCallusereddit6942No ratings yet
- Oracle Linux 001Document17 pagesOracle Linux 001Yellanki100% (1)
- Moving To DesignDocument40 pagesMoving To DesignErsa AlfathonaNo ratings yet
- Lect 03 IntroductionDocument5 pagesLect 03 Introductionusereddit6942No ratings yet
- OS-CO1-Session 03 Resource ManagementDocument18 pagesOS-CO1-Session 03 Resource ManagementElangovan GuruvaReddyNo ratings yet
- Lec2 OS StructureDocument31 pagesLec2 OS StructureSavani NaotunnaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Research's: MidoriDocument17 pagesMicrosoft Research's: Midorisanthosh859No ratings yet
- q2 Module1 g12 Css Ncii Luciano Millan NhsDocument12 pagesq2 Module1 g12 Css Ncii Luciano Millan NhsALBERT ALGONESNo ratings yet
- Module IIDocument74 pagesModule IISwethaNo ratings yet
- OS CO1 Session 01 IntroductionDocument18 pagesOS CO1 Session 01 IntroductionElangovan GuruvaReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Week 3 - Platform Technologies PDFDocument17 pagesModule 2 - Week 3 - Platform Technologies PDFRonald Bautista RiveraNo ratings yet
- OS Ast#1... Muhammad UmairDocument10 pagesOS Ast#1... Muhammad UmairMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Advanced Distributed Systems: Chapter - 1Document38 pagesAdvanced Distributed Systems: Chapter - 1Ng MeriedNo ratings yet
- 19pwbcs0681-Zeeshan Haider-Os (T) - A1Document8 pages19pwbcs0681-Zeeshan Haider-Os (T) - A1Nasir AbbasNo ratings yet
- Week1ConceptsofOperatingsystemsandnetworking E2a8b93e 5cf9 49ba 9039 16d155353c53 93472Document33 pagesWeek1ConceptsofOperatingsystemsandnetworking E2a8b93e 5cf9 49ba 9039 16d155353c53 93472bdipdarshan27No ratings yet
- w2 1 Characterization of Distributed SystemsDocument53 pagesw2 1 Characterization of Distributed SystemsjayanthikrishnanNo ratings yet
- OS 01 CustomizedDocument79 pagesOS 01 Customizedalekhyamanda6No ratings yet
- Lect 02 IntroductionDocument5 pagesLect 02 Introductionusereddit6942No ratings yet
- G1 Midori PPTDocument17 pagesG1 Midori PPTShah DishankNo ratings yet
- KODUL.25704 3. Distributed Systems 2014 Part 1Document62 pagesKODUL.25704 3. Distributed Systems 2014 Part 1Myat Su SanNo ratings yet
- OS 02 ArchitectureDocument63 pagesOS 02 ArchitectureSUSHANTA SORENNo ratings yet
- Unit I LINUX: The Operating SystemDocument103 pagesUnit I LINUX: The Operating SystemYogesh Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- CH20 COA11eDocument40 pagesCH20 COA11eninosensei1999No ratings yet
- Software ArchitectureDocument63 pagesSoftware ArchitectureSeung woo's collarbone cut my veinsNo ratings yet
- Dfc2063 Chapter 1Document43 pagesDfc2063 Chapter 1Ashifa0% (1)
- UNIT-I Operating System - Compatibility ModeDocument56 pagesUNIT-I Operating System - Compatibility ModeRudraksh sahNo ratings yet
- Operating System IIDocument21 pagesOperating System IIOmar AustinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Operating SystemsDocument68 pagesChapter 5 Operating SystemsOJOBILE HABIBUNo ratings yet
- Session - 2 - Lecture Notes - Operating-System Design Approaches PDFDocument15 pagesSession - 2 - Lecture Notes - Operating-System Design Approaches PDFAvinash AllaNo ratings yet
- Li Why Your Os Still Matters Ebook enDocument15 pagesLi Why Your Os Still Matters Ebook enEduard SamachisNo ratings yet
- Operating System: Lecture #3Document36 pagesOperating System: Lecture #3srinivas yanamandraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 Os Functions and Components Oct22Document28 pagesTopic 1.2 Os Functions and Components Oct22AISYAH FARHANANo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Operating System Design by FQDocument21 pagesLecture 8 Operating System Design by FQaina syafNo ratings yet
- 1.1 OS Struture, Operations and TypesDocument47 pages1.1 OS Struture, Operations and TypesVIJAYA PRABA PNo ratings yet
- Module 05Document51 pagesModule 05santoshpatilrao33No ratings yet
- U3 - C8 - T2 - Peer-To-Peer MiddlewareDocument9 pagesU3 - C8 - T2 - Peer-To-Peer MiddlewareAshutosh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CSCI 4717/5717 Computer Architecture: Topic: Introduction Reading: Chapter 1Document22 pagesCSCI 4717/5717 Computer Architecture: Topic: Introduction Reading: Chapter 1Narender KumarNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument20 pagesOperating SystemMohit TanejaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 For StudentsDocument59 pagesUnit 2 For Studentsshaanmd7651No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1parmarkrish531No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part BDocument30 pagesLecture 1 Part BUvanesNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Concepts to Save Money, Time, and FrustrationFrom EverandOperating Systems: Concepts to Save Money, Time, and FrustrationNo ratings yet
- FHCDocument6 pagesFHCyunying21No ratings yet
- UML Sequence Diagrams: CSE 403: Software Engineering, Spring 2015Document36 pagesUML Sequence Diagrams: CSE 403: Software Engineering, Spring 2015Syed Hamza KazmiNo ratings yet
- Oasismontaj TutorialnewDocument297 pagesOasismontaj TutorialnewArmando Cesar Landa FerrelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan No. 22Document3 pagesLesson Plan No. 22Mico Quioco SalitaNo ratings yet
- Module 07a SEHDocument21 pagesModule 07a SEHoscar tebarNo ratings yet
- Labsheet AutoCADDocument13 pagesLabsheet AutoCADMuhamad Ameenurrashid IsmailNo ratings yet
- Attribute Changer 9: User GuideDocument25 pagesAttribute Changer 9: User GuideLaurentiu ScrabaNo ratings yet
- PSpice InstructionsDocument3 pagesPSpice InstructionsGerhard BetNo ratings yet
- PC Das English Grammar PDFDocument3 pagesPC Das English Grammar PDFKingshuk Saha Palas0% (2)
- Ch8 XII SolutionsDocument7 pagesCh8 XII SolutionsMedha RoyNo ratings yet
- CA7 33 MessagesDocument634 pagesCA7 33 MessagesHellion1982No ratings yet
- Microkernel - WikipediaDocument69 pagesMicrokernel - WikipediaziaullahNo ratings yet
- YUMI ReadmeDocument4 pagesYUMI ReadmeAlber PuyorNo ratings yet
- ANURAG Engineering College: Answer The Following 3 X 5M 15 MarksDocument1 pageANURAG Engineering College: Answer The Following 3 X 5M 15 MarksK. VIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- JRFX - Cookie Policy - v1.0Document3 pagesJRFX - Cookie Policy - v1.0hino hinxNo ratings yet
- QTMS TechDocument34 pagesQTMS TechMarcos XavierNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument13 pagesMini ProjectChalla RohitNo ratings yet
- HTML5 PathDocument45 pagesHTML5 PathJuan López VillegasNo ratings yet
- Manual Onyx - Boox NovaDocument136 pagesManual Onyx - Boox NovapiramidonNo ratings yet
- JSPDocument96 pagesJSPA SAI KIRANNo ratings yet
- Exchange Recipient Types: Table 1 Recipient Type DescriptionDocument2 pagesExchange Recipient Types: Table 1 Recipient Type DescriptionSudheesh PuthusseryNo ratings yet
- A Study On Evaluation of Customer Centricity at Value Format Reliance Fresh Stores DelhiDocument39 pagesA Study On Evaluation of Customer Centricity at Value Format Reliance Fresh Stores DelhiBirjesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Testing MCQs SampleDocument18 pagesSoftware Testing MCQs SamplethejashwiniNo ratings yet
- DeployedgeDocument1,784 pagesDeployedgeMGNo ratings yet
- Cardware V 6.00 Fuer Pcu 50 Mit Windows NT 4.0 Auf Cd-Rom Einfache Lizenz 6FC5264-6BX10-0AG0Document5 pagesCardware V 6.00 Fuer Pcu 50 Mit Windows NT 4.0 Auf Cd-Rom Einfache Lizenz 6FC5264-6BX10-0AG0BALDEV SINGHNo ratings yet
- How To Import Multiple VCard Files in MS OutlookDocument2 pagesHow To Import Multiple VCard Files in MS OutlookSanja Lugonjic-IlicNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction To Database: Project PresentationDocument88 pagesUnit-1: Introduction To Database: Project PresentationKarmashree Dhiren PatelNo ratings yet
- Name: Abhijit Biswas: Profile SummaryDocument3 pagesName: Abhijit Biswas: Profile SummaryQa TutorNo ratings yet
- Finance Demo Script - Audit WorkbenchDocument14 pagesFinance Demo Script - Audit WorkbenchhnoamanNo ratings yet
- Marc-Andre Giroux - Production Ready GraphQL (2020) PDFDocument186 pagesMarc-Andre Giroux - Production Ready GraphQL (2020) PDFNahid HossainNo ratings yet