Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardio Drugs
Cardio Drugs
Uploaded by
emranalshaibaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardio Drugs
Cardio Drugs
Uploaded by
emranalshaibaniCopyright:
Available Formats
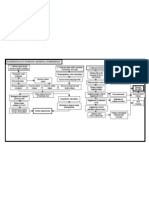
vasoactive Trigger of release action of of vasoactive inhibitor drugs
Amines
angiotensin II Renin release stimulate AGll ● potent pressor beta-blockers.
release: ● stimulates autonomic ganglia. ● block renin
● Decreased stretch ● increases the release of secretion
(hypotension) catecholamine aliskiren
● Decreased distal delivery of ● direct inotropic action on the heart. ● Renin
sodium ● aldosterone biosynthesis. inhibitors
● SNS stimulates renin ● Stimulates drinking. captopril
release ● Increases the secretion of ● ACE inhibitor
vasopressin. losartan
● renal vasoconstriction. ● AT-1 receptor
● Increases sodium reabsorption. antagonists
● Inhibits the secretion of renin.
● development of cardiovascular
hypertrophy.
Aldosterone ● Decrease BP ● Acts on late distal tubule and spironolactone
collecting duct.
● Causes salt and water retention.
● Increases K+ and H+ excretion
Bradykinin ● Plasma kininases ● vasodilatation
● rapid and very brief decrease in
blood pressure.when given IV
● natriuresis
○ inhibiting sodium
reabsorption
ADH ● rising plasma tonicity increase water reabsorption. Conivaptan
● falling blood pressure. ● long term treat (hyponatremia)
vasoconstrictor ● V1a and V2
● Vasoconstriction antagonist
Tolvaptan
treat (hyponatremia)
● V2 antagonists
vasoactive Trigger of release action of of vasoactive inhibitor drugs
Amines
ANP ● atrial stretch. ● Increases sodium excretion and
● sympathetic stimulation, urine flow
● endothelins and ● increase in glomerular filtration
vasopressin. rate.
● decrease in proximal tubular
sodium reabsorption.
● Inhibits the release of renin,
aldosterone and vasopressin
● increase sodium and water
excretion.
● vasodilation
● decreases arterial blood pressure.
Endothelins ● vasoconstriction in vascular beds Bosentan
● exert direct positive inotropic and ● ETA-ETB
chronotropic actions. receptor
● potent coronary vasoconstrictors. antagonist
● Decrease GFR and sodium and ● pulmonary
water excretion. arterial
● ETA receptors:vasoconstriction hypertension.
● ETB receptors: PGI2 and nitric Ambrisentan
oxide. ● ETA
antagonist.
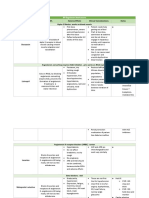
Positive inotropic agents
Drug Action Effect Used Adverse effect
Digoxin inhibit the cardiac increase Force of Heart failure. ▪Narrow margin of safety.
Na+/K+ pump cardiac contraction. Atrial flutter ▪Altered color perception
Atrial fibrillation. ▪Nausea, vomiting and
Increase [Na+]i increase Stroke Paroxysmal atrial abdominal pain.
concentration volume atrioventricular nodal ▪Arrhythmias (most
tachycardia. frequent and most
Increase [Ca++]i . Increase Cardiac serious).
output. ▪Headache, fatigue, and
sleeplessness
Increase vagal activity ▪Gynecomastia
Reduce conduction
through AV Toxicity
▪Hypokalemia.
▪Hypercalcemia.
▪Hypomagnesmia.
▪Renal failure.
Dopamine Activation of Beta 1 increase contractility Severe Heart failure
force
Dobutamine selective β-1 agonist increase cardiac short-term treatment increased blood
contractility of congestive heart pressure and
Increase cardiac failure. heart rate, ventricular
output. ectopic activity.
Milrinone Inhibits increase cAMP acute heart failure
phosphodiesterase increase cardiac Used for an
enzyme contractility and exacerbation of chronic
vasodilatation. heart failure.
Increases cardiac
output and reduce
peripheral
vascular resistance.
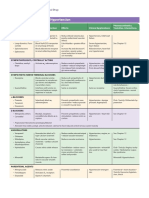
Diuretics
Thiazide furosemide Potassium sparing diuretics
Site Distal convoluted tubule Thick ascending limb Late distal tubule and collecting duct
Action Inhibition of Na\Cl channel Block Na/K/Cl spironolactone
Reduce reabsorption of Na ● Direct antagonism of
mineralocorticoid receptors
amiloride
● Inhibition of Na+ influx through
ion channels in the luminal
membrane (
Side effect Metabolic alkalosis. Metabolic alkalosis hyperkalemia
Hypokalemia. Hypokalemia.
Hyponatremia. Hypomagnesemia.
Hyperglycemia. Ototoxicity.
Hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia.
Hyperlipidemia Allergic reactions.
● Reduce salt and water retention
● reduce ventricular preload.
● reduction in venous pressure
○ Reduction of edema
○ Reduction of cardiac size
type Drug effect
Vasodilators Hydralazine Afterload reduction
Vasodilators Nitrates mainly Preload reduction
ACEI Enalapril Reduce salt and water retention by
Lisinopril reducing aldosterone secretion
● reduce preload.
Reduce peripheral resistance
● reduce afterload.
Reduce sympathetic activity.
Reduce long-term remodeling
Beta-adrenoceptors blockers Carvedilol (non selective) reduce Heart rate.
Metoprolol reduce Renin angiotensin system.
Bisoprolol (beta 1 selective reduce Atrial and ventricular
arrhythmias
Anti-ischemic effects.
Reduce remodeling.
Angiotensin receptor Valsartan and sacubitril inhibiting neprilysin
neprilysin inhibitor ● degradation of NPs and other
peptides slowed.
High circulating (ANP) and BNP
● enhancing diuresis, natriuresis
and anti-remodelling.
ANP and BNP inhibit renin and
aldosterone secretion.
Selective AT1-receptor blockade reduce:
● vasoconstriction,
● sodium and water retention
● myocardial hypertrophy.
cardiac pacemaker inhibitor Ivabradine Slow HR
You might also like
- Practical (3+4+5)Document19 pagesPractical (3+4+5)Asma Alenezy50% (2)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (47)
- Clinical Pharmacy - Simple Notes PDFDocument186 pagesClinical Pharmacy - Simple Notes PDFsmart hussain86% (79)
- Drug Dosages 3 IGDocument122 pagesDrug Dosages 3 IGDonna LLerandi100% (2)
- Quantum Techniques Client ManualDocument42 pagesQuantum Techniques Client ManualVeres Beatrix100% (4)
- Pathophysilogy of Primary HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysilogy of Primary Hypertensionromeo rivera75% (4)
- CML Research EssayDocument7 pagesCML Research Essayapi-358692407No ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- Ace InhibitorsDocument26 pagesAce InhibitorsDeipa KunwarNo ratings yet
- Renal & Heme PharmacologyDocument15 pagesRenal & Heme Pharmacologyradhikabpatel12No ratings yet
- Generalao, Unit Task #1 Aug 17, 2021Document13 pagesGeneralao, Unit Task #1 Aug 17, 2021Frietzyl Mae GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsDocument29 pagesLect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsRaneem ShiferNo ratings yet
- Medsurg 8 Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument10 pagesMedsurg 8 Cardiovascular MedicationsAlaa OmarNo ratings yet
- Drugs SummaryDocument23 pagesDrugs Summaryapi-3832811100% (1)
- Drugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticDocument3 pagesDrugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument97 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- RAASDocument1 pageRAAShydrocodoonieNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneNewteNo ratings yet
- BP Regulation Medications ChartDocument5 pagesBP Regulation Medications ChartLovely CervantesNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- 201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pages201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemEidelen Lovani Sembiring100% (1)
- Anti-Hypertensive Agents: Aznan Lelo Tri WidyawatiDocument49 pagesAnti-Hypertensive Agents: Aznan Lelo Tri WidyawatiNiel Riri DawroexNo ratings yet
- Medicatia Antihipertensiva - AmgDocument54 pagesMedicatia Antihipertensiva - AmgCarciugNo ratings yet
- Terapi Farmakologi Gagal Jantung - Sept - 2020Document58 pagesTerapi Farmakologi Gagal Jantung - Sept - 2020FAUZAN ILHAM PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Pharmacology OF Anti-Hypertensive: Siti SyarifahDocument38 pagesPharmacology OF Anti-Hypertensive: Siti SyarifahAnnurul Badry IINo ratings yet
- SUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionDocument11 pagesSUMMARY Drugs Used in HypertensionPAULINE ANGELI DIEGONo ratings yet
- BP Regulation Medications ChartDocument6 pagesBP Regulation Medications ChartsydNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedDocument24 pagesAnti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedputryaNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of HypertensionDocument36 pagesDrug Treatment of HypertensionAngetile KasangaNo ratings yet
- CPT Drugs TableDocument28 pagesCPT Drugs TablePranav SankarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Finals ReviewerDocument8 pagesPharmacology Finals ReviewerCherry Lou GuanzingNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drug NameDocument3 pagesHypertension Drug NameWahaj MujahidNo ratings yet
- Note Oct 23, 2022 at 5 - 30 - 47 PMDocument3 pagesNote Oct 23, 2022 at 5 - 30 - 47 PMMARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- ShockDocument19 pagesShockNitesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Pharma 7 To 13Document212 pagesPharma 7 To 13Loai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure 2Document18 pagesHeart Failure 2Anita DeviNo ratings yet
- Vasoactive PeptidesDocument6 pagesVasoactive PeptidesMehwish HammadNo ratings yet
- Angio Tens in Ren in Al DostDocument18 pagesAngio Tens in Ren in Al Dostatik mayasariNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Angiotensin: Verapamil, Diltiazem, Dipine, Felodipine, Isradipine, Nicardipine, NifedipineDocument4 pagesInhibitors of Angiotensin: Verapamil, Diltiazem, Dipine, Felodipine, Isradipine, Nicardipine, Nifedipinerpascua123No ratings yet
- PHARMACILOGY SUMMryDocument16 pagesPHARMACILOGY SUMMryKathy Real VillsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 - 306Document15 pagesLecture 05 - 306ShAkil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte - Water BalanceDocument5 pagesElectrolyte - Water BalancechrisibinuNo ratings yet
- MODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsDocument2 pagesMODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Cardiac Output X Peripheral ResistanceDocument52 pagesBlood Pressure Cardiac Output X Peripheral Resistancelourdes kusumadiNo ratings yet
- Anti HTNDocument59 pagesAnti HTNzaha shamseerNo ratings yet
- C. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Document10 pagesC. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Nabeel AsifNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Review PDFDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Review PDFMacy Grace Yuzon GuingabNo ratings yet
- Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) : Hyponatremia or Increased Sympathetic ToneDocument2 pagesRenin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) : Hyponatremia or Increased Sympathetic ToneDrbee10No ratings yet
- How To Deal Acute Pulmonary OedemDocument23 pagesHow To Deal Acute Pulmonary Oedemdhika2496No ratings yet
- Medication ReviewDocument2 pagesMedication ReviewJn CaducoyNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Renin-Angiotensin SystemDocument36 pagesDrugs Affecting Renin-Angiotensin SystempradeephdNo ratings yet
- Class 6 - Cardiac DrugsDocument83 pagesClass 6 - Cardiac DrugsKeron Chang100% (1)
- RAAS & RAAS AntagonistsDocument7 pagesRAAS & RAAS AntagonistsMahmoud AboudNo ratings yet
- Treatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesDocument2 pagesTreatment of CHF: Therapeutic UsesAsma AlfaouriNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument3 pagesHeart FailureDr. Jennie Kim100% (3)
- Entresto in Insuficienta CardiacaDocument2 pagesEntresto in Insuficienta CardiacaRadu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Brachial PlexusDocument2 pagesBrachial PlexusemranalshaibaniNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument10 pagesStudyemranalshaibaniNo ratings yet
- Important Concepts DocDocument40 pagesImportant Concepts DocemranalshaibaniNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument1 pageOsmosisemranalshaibaniNo ratings yet
- Wurzel 2016Document8 pagesWurzel 2016prolanis pkmmulyoharjoNo ratings yet
- Researchpaper Anesthesia Drugs in The Medieval Muslim EraDocument9 pagesResearchpaper Anesthesia Drugs in The Medieval Muslim EraLily HbpNo ratings yet
- Breakthrough Discovery - Need For T3 Could Be Genetic DR Gary PepperDocument4 pagesBreakthrough Discovery - Need For T3 Could Be Genetic DR Gary PepperAna SmithNo ratings yet
- Body Language Iii: Dr.V. Veera Balaji KumarDocument29 pagesBody Language Iii: Dr.V. Veera Balaji KumarveerabalajiNo ratings yet
- Brain, Drugs, Its Neurobiological MechanismsDocument19 pagesBrain, Drugs, Its Neurobiological MechanismsIvan Palafox MarderoNo ratings yet
- Preventive Therapy of Migraine: Pembimbing: Dr. Anyeliria Sutanto, SP.SDocument39 pagesPreventive Therapy of Migraine: Pembimbing: Dr. Anyeliria Sutanto, SP.SClaudia TariNo ratings yet
- The American Journal of Public HealthDocument3 pagesThe American Journal of Public HealthgautamkurtNo ratings yet
- ASA Physical Status Classification: GuidelineDocument3 pagesASA Physical Status Classification: GuidelineLUISNo ratings yet
- Pharma 12Document16 pagesPharma 12Mary Roan RonatoNo ratings yet
- ProvengeDocument7 pagesProvengeapi-675909478No ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube NGT 1215082454278959 8Document107 pagesNasogastric Tube NGT 1215082454278959 8Raquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Colds FluDocument4 pagesColds FlucameliadronNo ratings yet
- Hardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyDocument7 pagesHardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyCynthia CarolineNo ratings yet
- Lee ResumeDocument1 pageLee Resumeapi-284977620No ratings yet
- CORATEX Si e MSDSDocument5 pagesCORATEX Si e MSDSabhinavdoitNo ratings yet
- A Crtitical Appraisal of Viral Taxnomomy - Matthews 2018 PDFDocument263 pagesA Crtitical Appraisal of Viral Taxnomomy - Matthews 2018 PDFJansen SantosNo ratings yet
- School Form 8 (SF 8)Document1 pageSchool Form 8 (SF 8)Aquino ButsNo ratings yet
- Death Obituary Bbjme PDFDocument3 pagesDeath Obituary Bbjme PDFWatkinsGraves9No ratings yet
- Good Documentation Practice in Clinical ResearchDocument9 pagesGood Documentation Practice in Clinical Researchsreeraj.guruvayoor100% (1)
- Org Med LMDocument52 pagesOrg Med LMVirginia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Instrumentation Project Report: Submitted byDocument7 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation Project Report: Submitted bymahsa sherbafiNo ratings yet
- DCYF Data Book 2019Document27 pagesDCYF Data Book 2019JasonNo ratings yet
- Scene WDocument180 pagesScene Wasdeqa2010No ratings yet
- Efco Stark 44Document72 pagesEfco Stark 44Makito HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Proximal Femoral Focal Deficiency 3Document26 pagesProximal Femoral Focal Deficiency 3chinmayghaisasNo ratings yet