Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH 9 Activity Sheet 2 Q3 Week 1
MATH 9 Activity Sheet 2 Q3 Week 1
Uploaded by
Reng Carlo CadornaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MATH 9 Activity Sheet 2 Q3 Week 1
MATH 9 Activity Sheet 2 Q3 Week 1
Uploaded by
Reng Carlo CadornaCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)
Division of Leyte
GREGORIO C. CATENZA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Tunga, Leyte
ACTIVITY SHEET 2.1
Mathematics 9, Quarter 3, Week 1 (Solving for Angles of Parallelograms)
Content Objective: Uses properties to find measures of angles, sides and other quantities involving parallelograms.
General Reminders: Use this activity sheet with care. Do not put unnecessary mark/s on any part of the activity sheet.
Read the direction carefully before doing each task. Please use the answer sheet provided. Use a separate sheet for your
answers if needed. Do not forget to submit your answer sheets on time. Submit the answer sheets ONLY. Keep this activity
sheet and compile in a long folder for future reference.
Solutions:
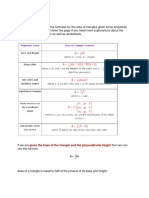
Explore a. ∠C + ∠A = 180° ∠C and ∠A are supplementary angles
Identify which quadrilateral is being described.
2x+4 + 60 = 180 Substitute the values of ∠C and ∠A
_________1. A parallelogram with four congruent sides and four
congruent angles. 2x + 64 = 180 Simplify and combine like terms
_________ 2. A quadrilateral with only one pair of opposite sides are 2x = 180-64 Subtract 64 from each side of the equation
parallel. 2x = 116 Divide each side of the equation by 2
_________ 3. A parallelogram with four congruent sides. x = 58
_________ 4. A quadrilateral in which two pairs of opposite sides b. ∠E ≅ ∠A ∠E and ∠A are congruent therefore they are equal
are parallel. 3y + 9 = 60 Substitute the value of ∠E and ∠A.
_________ 5. A parallelogram with four congruent angles 3y = 60-9 Subtract 9 from each side of the equation.
3y = 51 Divide each side of the equation by 3.
Learn y = 17
In the previous lesson, the conditions that make a c. ∠R + ∠A = 180° ∠R and ∠A are supplementary angles.
quadrilateral a parallelogram and its properties were ∠R + 60° = 180° Substitute the value of ∠A.
discussed thoroughly. ∠R = 180°-60° Subtract 60° from each side of the equation
Now we are ready to use the properties to find the ∠R = 120°
measures of the angles involving parallelograms. d. ∠E ≅ ∠A
Given: CARE is a parallelogram. If m∠A = 60°, then m∠E = 60°
e. ∠C ≅ ∠R
1. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠R If m∠R = 120°, then m∠C = 120°
∠𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐸
Using the property of parallelogram in which any two
opposite angles are congruent. Engage
2. ∠𝐶 + ∠𝐴 =180° Using the property of parallelogram A. □WISH is a parallelogram and m∠𝐻𝑆𝐼 = 110°,
∠𝑅 + ∠𝐴 = 180° in which any two consecutive angles m∠𝑆𝐼𝑋 = 50°, m ∠𝑆𝑋𝐼 = 60°, find the following angles:
∠𝑅 + ∠E = 180° are supplementary. 1. m ∠𝑊𝐻𝑆
∠𝐶 + ∠E = 180° 2. m ∠WI𝑋
3. ∆𝐶𝐴𝐸 ≅ ∆𝑅𝐴𝐸 3. m ∠W𝑋I
Using the property in which a diagonal of a parallelogram 4. m ∠WSH
divides the parallelogram in two congruent triangles. 5. m ∠HWS
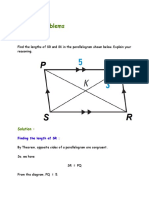
Example 1: □CALM is a parallelogram. B. In parallelogram HOPE, find the following;
If m ∠𝐶𝐿𝑀= 18° and m ∠𝐿𝐶𝑀= 27°, find: 1. x
a. m ∠𝐶𝑀𝐿 2. m ∠𝑂𝐻𝐸
C A
b. m ∠𝐶𝐴𝐿 3. m ∠𝑂𝑃𝐸
27°
c. m ∠𝐴𝐶𝐿 4. m ∠𝐻𝑂𝑃
18°
d. m ∠𝐴𝐿𝐶 M L 5. m ∠𝐻𝐸𝑃
Solutions:
a. In ∆𝐶𝑀𝐿, m∠𝐶𝐿𝑀 + m∠𝐿𝐶𝑀 + m∠𝐶𝑀𝐿 = 180° Apply
(Angle Addition Postulate) Direction: Find the measure of the missing angles of the
18° + 27° + m ∠𝐶𝑀𝐿 = 180° (By substitution) given parallelogram. Show your solution.
m ∠𝐶𝑀𝐿 = 135° L U
b. In □CALM, ∠𝐶𝑀𝐿 ≅∠𝐶𝐴𝐿 42° □ LUCK is a parallelogram with
(Opposite angles are congruent)
∠𝐶 = 68° and ∠𝐿𝑈𝐾 = 42° find:
If m∠𝐶𝑀𝐿 = 135° then m ∠𝐶𝐴𝐿 = 135° 1. m∠𝐶𝑈𝐾
c. Since CA is parallel to ML and CM is parallel to AL, 2. m∠𝐾
then alternate interior angles are congruent.
∠𝐶𝐿𝑀 ≅∠𝐴𝐶𝐿
If m ∠𝐶𝐿𝑀= 18°, then m∠𝐴𝐶𝐿 = 18°
d. Similarly, ∠𝐿𝐶𝑀 ≅ ∠𝐴𝐿𝐶 K 68° C
If m ∠𝐿𝐶𝑀= 27°, then m∠𝐴𝐿𝐶 = 27°
Example 2. Given □CARE is a parallelogram, find: □ FATE is a parallelogram with
a. x ∠𝐸 = (8x+11)° and ∠𝑇 = (3x+4)°
b. y find:
c. ∠𝑅 1. x
d. ∠𝐸 2. m∠𝐴
e. ∠𝐶 3. m∠𝐹
1|Page
You might also like
- Chapter 7 LeadershipDocument38 pagesChapter 7 LeadershipvanivyasNo ratings yet
- Briggs, Leslie J. - Instructional Design - Principles and Applications-Educational Technology Publ. (1992) PDFDocument189 pagesBriggs, Leslie J. - Instructional Design - Principles and Applications-Educational Technology Publ. (1992) PDFIbtissem Had100% (1)
- Mathematics - Quarter 4Document6 pagesMathematics - Quarter 4Vittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 3Document9 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding Quadrilaterals Exercise 3 3nandisunilkumar3No ratings yet
- Uses Properties To Find Measures of Angles, Sides and Other Quantities Involving Parallelograms.Document8 pagesUses Properties To Find Measures of Angles, Sides and Other Quantities Involving Parallelograms.Josefina Nesperos Soriano100% (2)
- Math 9 Q3 M2Document13 pagesMath 9 Q3 M2Eve0% (1)
- Mathematics: Self-Learning Module 2Document13 pagesMathematics: Self-Learning Module 2Julie Ann GernaNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Lesson4Document6 pagesLESSON PLAN Lesson4Ezrine UmaniNo ratings yet
- Las Math9 Q4 W5Document12 pagesLas Math9 Q4 W5Maxene Angelie RabanalNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Q3 - M1 7 MergedDocument48 pagesGrade 9 - Q3 - M1 7 Mergedno one75% (4)
- Parallelogram Properties and Conditions 1Document28 pagesParallelogram Properties and Conditions 1Dana Mae GeslaniNo ratings yet
- Parallelograms and Their PropertiesDocument14 pagesParallelograms and Their PropertiesTJNo ratings yet
- Trigo Q.4 L5 - 1 1Document9 pagesTrigo Q.4 L5 - 1 1Angel AquinoNo ratings yet
- Observation 2 2020 2Document3 pagesObservation 2 2020 2Ellen Mae Roldan GicoleNo ratings yet
- Angle Pair Relationships: You Should LearnDocument7 pagesAngle Pair Relationships: You Should LearnLavan NimsNo ratings yet
- SOLMEN 113 Module 2 Quadrilaterals and PolygonsDocument9 pagesSOLMEN 113 Module 2 Quadrilaterals and PolygonsChoy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q3 M1Document4 pagesMath 9 Q3 M1jese.vesereNo ratings yet
- Rhombus SquareDocument17 pagesRhombus SquareAltheus Miguel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Review Module 1Document5 pagesReview Module 1aljohnbondad121521No ratings yet
- Polygons TasksDocument16 pagesPolygons TasksнуркызNo ratings yet
- Learners Math Handouts Part IDocument13 pagesLearners Math Handouts Part IDark ShadowNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 Mod4 ProvingTheoremsOnTheDifferentKindsOfParallelogram v3-EDITEDDocument11 pagesMath9 Q3 Mod4 ProvingTheoremsOnTheDifferentKindsOfParallelogram v3-EDITEDMavis VermillionNo ratings yet
- Math - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesDocument9 pagesMath - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesFree TemplatesNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Grade 7 - Week 2Document38 pagesQuarter 3 - Grade 7 - Week 2Carmina CunananNo ratings yet
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 3rd Quarter Module 1Document37 pagesMathematics 9 3rd Quarter Module 1OneDuhhNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q4 SLM WK2Document7 pagesMath8 Q4 SLM WK2Juvelyn Teves MunalemNo ratings yet
- Mathematics9 Quarter4 Week6 Module6Document6 pagesMathematics9 Quarter4 Week6 Module6Wilson OrtizNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21Document7 pagesLesson 21Jeany Pearl EltagondeNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Parallel Lines and Transversals LessonDocument9 pages3.2 Parallel Lines and Transversals LessonXxShadowGamingNo ratings yet
- Finals ModuleDocument22 pagesFinals ModuleTin MhudzNo ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 3 TeacherDocument12 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 3 TeacherKyra LewisNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 4Document12 pagesMath 9 Quarter 4Maria Sadaran100% (1)
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Trigonometrymarjorie antonioNo ratings yet
- Geometry ConceptsDocument7 pagesGeometry ConceptsLendonee OperianoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4: Week 6 (W8-W9) Learning Activity SheetDocument8 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4: Week 6 (W8-W9) Learning Activity SheetMagilyn DonatoNo ratings yet
- Math 9 q3 Week 1B With SummativeDocument8 pagesMath 9 q3 Week 1B With SummativeKarell AnnNo ratings yet
- Q4 W4 Solving Right TrianglesDocument41 pagesQ4 W4 Solving Right TrianglesAkysha sheenNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 3 Module 2Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Quarter 3 Module 2Maria Resureccion MaanNo ratings yet
- Properties TrianglesDocument13 pagesProperties TrianglesCaletha BurtonNo ratings yet
- Deductive Geometry: This Chapter at A GlanceDocument46 pagesDeductive Geometry: This Chapter at A Glancesquishyapply100% (1)
- Area of TrianglesDocument7 pagesArea of TrianglesAngelica MontezonNo ratings yet
- Vidar g9 q3 Lp1 KiteDocument4 pagesVidar g9 q3 Lp1 KiteMary Jane De YroNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q4 W8Document6 pagesMath9 Q4 W8Maria Eleonor BanaresNo ratings yet
- Topic 6-Introduction To TrigonometryDocument26 pagesTopic 6-Introduction To Trigonometryshaunjali21No ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 1Document8 pagesQuarter 4 Week 1Josiah hernandezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Q3 MathematicsDocument23 pages1 - Q3 Mathematicsmaximo meridaNo ratings yet
- Cot 1Document14 pagesCot 1Mark Johnson VillaronNo ratings yet
- Lecture and Assessment On Solving A Right TriangleDocument6 pagesLecture and Assessment On Solving A Right TriangleCynthia Ocampo BoneteNo ratings yet
- Math Grade9 Quarter3 Week1 Module1Document4 pagesMath Grade9 Quarter3 Week1 Module1ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Non-Perpendicular Resultant CalculationsDocument9 pagesNon-Perpendicular Resultant Calculationsangelinayin322No ratings yet
- Parallel Lines and Transversals Parallel Lines and TransversalsDocument2 pagesParallel Lines and Transversals Parallel Lines and TransversalsOliviaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - W2part1Theorems On Different Kinds of ParallelogramsDocument27 pagesQ3 - W2part1Theorems On Different Kinds of ParallelogramsRicci Angel Masadao100% (1)
- Mathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 7 - 2021Document6 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 7 - 2021martinajoan1No ratings yet
- Math 9-Q3-Module-1Document11 pagesMath 9-Q3-Module-1Jeanette Agumbay AgunosNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Activity Sheet 1 Q3 Week 1Document2 pagesMATH 9 Activity Sheet 1 Q3 Week 1Reng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- P5Maths Week 35Document4 pagesP5Maths Week 35အင္တာေနရွင္နယ္ေက်ာင္းမ်ား၏ ေမးခြန္လႊာဘာသာစံုျဖန္႕ခ်ီေရးNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14From EverandMathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14No ratings yet
- Mathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesFrom EverandMathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sample Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSample Lesson PlanReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument2 pagesSample QuestionsReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- School AssignmentDocument9 pagesSchool AssignmentReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Activity Sheet 1 Q3 Week 1Document2 pagesMATH 9 Activity Sheet 1 Q3 Week 1Reng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Resident Users ManualDocument2 pagesResident Users ManualReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Violation ReportDocument1 pageViolation ReportReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Admin Users ManualDocument6 pagesAdmin Users ManualReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Decision of The Second-Year IT Students To Shop Online. (AutoRecovered)Document19 pagesFactors Affecting The Decision of The Second-Year IT Students To Shop Online. (AutoRecovered)Reng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Test DesignDocument3 pagesAcceptance Test DesignReng Carlo CadornaNo ratings yet
- Essay Hist106Document6 pagesEssay Hist106api-358162850No ratings yet
- Advice For ExamsDocument3 pagesAdvice For ExamsPahola Peña FlorezNo ratings yet
- Anand Hulli: Industrial ExperienceDocument2 pagesAnand Hulli: Industrial ExperiencecaddNo ratings yet
- Interview 1Document3 pagesInterview 1Teacher VeronicaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument13 pagesCurriculum VitaeBaby Jane MilloNo ratings yet
- K DLP Week 22 Day 3 CarinaDocument6 pagesK DLP Week 22 Day 3 Carinacarina pelaezNo ratings yet
- FS2 Learning Episode11Document10 pagesFS2 Learning Episode11Maryrose Añana RedubladoNo ratings yet
- Coninuation of The Job Final Jss2Document2 pagesConinuation of The Job Final Jss2sunliasNo ratings yet
- Delta State Ministry of Technical EducationDocument2 pagesDelta State Ministry of Technical EducationEmmanuel OkaforNo ratings yet
- Drdo - Gov.in Drdo Ceptam FAQsDocument20 pagesDrdo - Gov.in Drdo Ceptam FAQskumarnani333No ratings yet
- Home Visit FormDocument1 pageHome Visit FormEDMIE BANCASNo ratings yet
- III. School Current Situation and School Profile Geography of The SchoolDocument4 pagesIII. School Current Situation and School Profile Geography of The SchoolMelina Buer LopezNo ratings yet
- PMP Certification - Know It AllDocument10 pagesPMP Certification - Know It AlleimisjaneisiNo ratings yet
- Swayam All Courses Details 22.02.2021 - CompressedDocument157 pagesSwayam All Courses Details 22.02.2021 - Compressedraji rajiNo ratings yet
- THE CLUP.2016 2026. ApprovedDocument46 pagesTHE CLUP.2016 2026. ApprovedBRYLLE KYLLE OIDEMNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Machine DesignDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Machine DesignLnd MsziNo ratings yet
- Newsletter 169Document3 pagesNewsletter 169St Bede's Catholic CollegeNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School SocietyDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School SocietyRakesh MaherNo ratings yet
- Math3 Q2 Mod1 v3Document15 pagesMath3 Q2 Mod1 v3Serena Almond100% (1)
- Prosp e Cuts 2023 Versio in 1Document339 pagesProsp e Cuts 2023 Versio in 1ahsanshahjee34No ratings yet
- Post Practicum ReportDocument8 pagesPost Practicum ReportNaqiuddin HashimNo ratings yet
- DLLE Project Report FinaleDocument38 pagesDLLE Project Report FinaleRajvi Dedhia0% (1)
- Assam Down Town University: "Disseminate Scientific Findings: Ensure Quality Practice"Document2 pagesAssam Down Town University: "Disseminate Scientific Findings: Ensure Quality Practice"Amy LalringhluaniNo ratings yet
- Educators' Society: Confidence Through PassarellaDocument3 pagesEducators' Society: Confidence Through Passarellajohncyrus dela cruzNo ratings yet
- 01 Soal LatihanDocument1 page01 Soal LatihanMuhammad Khairuna SyahPutraNo ratings yet
- Factors of Learning in Filipino and Students' Performance of Secondary Education in Eastern Visayas PhilippinesDocument16 pagesFactors of Learning in Filipino and Students' Performance of Secondary Education in Eastern Visayas PhilippinesSEAN KENZO SULITNo ratings yet
- Adventures in Phenomenology - Ga - Eileen Rizo-PatronDocument340 pagesAdventures in Phenomenology - Ga - Eileen Rizo-PatronGeorgy Plekhanov100% (3)
- Personal Philosphy Olivia Durbin-3Document3 pagesPersonal Philosphy Olivia Durbin-3api-582819687No ratings yet