Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Strategic Planning and Management Harris
Strategic Planning and Management Harris
Uploaded by
warren.a.harris1Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Strategic Planning and Management Harris
Strategic Planning and Management Harris
Uploaded by
warren.a.harris1Copyright:
Available Formats
Warren Harris – 50904805 Engineering Management 4023/5023
April 10, 2023
Assignment 3: What is Strategic Planning and Management with an introduction to industrial material
handling.
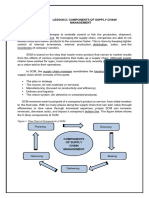
Strategic planning is the process to establish, implement, correct and continuously improve a corporate
strategic plan. Strategic management is the tools and techniques utilized to implement strategy and the
efforts needed to quickly respond to special events that occur before the formal planning process
recycles. (EMBOK)
It follows that strategic planning uses high level planning tools such as Strengths, Weaknesses, Threats
and Opportunities (SWOT) analysis, the 5 Forces, and Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customer
(SIPOC) analysis to help set a mission and vision for the company. The EM must thoroughly understand
the customer requirements, and analyze the market needs and potential opportunities and threats. The
supply chain must be extensively analyzed, with long range contracts planned to ensure firm supply.
When implementing the plan, the Engineering Manager (EM) uses strategic management tools. The EM
must first communicate the vision and mission to all shareholders, and especially staff members to
ensure buy in of the plan. One could argue that gaining acceptance and buy in of the mission and vision
is one of the most important strategic management goals, as the enterprise will surely fail if there is
dissension and disagreement on the goals of the company. Using strategic change management tools
will help ensure buy in by using leadership, holding open and frank discussions, allowing others to be
heard and valuing their opinions, and constantly reinforcing the goals, mission and vision.
The EM must help design and build the processes and procedures to create the product. Consideration
must be carefully given to industrial material handling, especially if the end product is heavy or difficult
to move. Thought must be given to raw material deliveries, inventory storage, and moving material and
inventory to assembly points. Trucks or trains will need to deliver material and take finished product
offsite. Forklifts, conveyors or cranes will be required to move materials between areas. Consideration
must be given to ensure the materials flow smoothly from one area to the other, with raw materials
going through further processes and assemblies to become the end product. The end product may then
need to be stored properly until shipping to the customer can occur. Shipping bays for receipt of
material and outgoing shipments are required, ensuring the two can occur smoothly with little
interference. Lighting, heating and cooling, power, possibly steam or various gases, and air supplies
must all be in the areas where it is required, and in the correct amounts. All of these issues must be
carefully planned before construction, as it will be costly and difficult to change once production starts.
The EM must also establish measurement systems to ensure quality assurance and control and make
adjustments to the process to continuously improve and drive out waste while reducing cost. Checklists
and scorecards can help monitor performance of the enterprise and guide managers in making changes
to the process. If careful planning and thorough consideration is given to all the above, the enterprise
may have a chance of success. Failure to take these issues in hand while planning will make the chances
of success much lower.
References:
Shah, H; Nowocin, W. A guide to the Engineering Management Body of Knowledge, 5th ed, 2019
You might also like
- SMRP Guide To The Maintenance and Reliability Body of KnowledgeDocument20 pagesSMRP Guide To The Maintenance and Reliability Body of KnowledgeMikeGrabill86% (7)
- Como Tool and Die - WK 2-1Document3 pagesComo Tool and Die - WK 2-1danielaNo ratings yet
- Ms-05-Management of Machines and MaterialsDocument19 pagesMs-05-Management of Machines and Materialszordotcom100% (2)
- Very IMP & Latest Interview Ques - Master FileDocument138 pagesVery IMP & Latest Interview Ques - Master FilesammusalluNo ratings yet
- Product Operation Management PPT (Unit 1&2)Document110 pagesProduct Operation Management PPT (Unit 1&2)Sudhir Singh100% (2)
- Case Study Inventory ManagementDocument8 pagesCase Study Inventory ManagementMohammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Strategic Facilities PlanningDocument23 pagesStrategic Facilities PlanningOwais GharaibehNo ratings yet
- OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT SadssDocument6 pagesOPERATIONS MANAGEMENT SadssAlibabaNo ratings yet
- Module 15Document11 pagesModule 15ZarishaNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument16 pagesOperations ManagementVarsha BeedassyNo ratings yet
- Research Intro OpManDocument8 pagesResearch Intro OpManReiner TayabanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Module 2Document6 pagesAssignment Module 2Akash Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Strategic Issues in Operation Management - Session 19 - 14C-0729 - Alva JerralynDocument14 pagesStrategic Issues in Operation Management - Session 19 - 14C-0729 - Alva JerralynJERRALYN ALVANo ratings yet
- Related TopicsDocument4 pagesRelated TopicsjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management A ToolDocument4 pagesOperations Management A ToolVivekananda PalNo ratings yet
- Production ManagmentDocument39 pagesProduction ManagmentKamran Khan KhalilNo ratings yet
- Production ManagementDocument20 pagesProduction ManagementJen Aquino ZetaNo ratings yet
- Task3 MONTERDE TM3ADocument4 pagesTask3 MONTERDE TM3AEstella Mariz MonterdeNo ratings yet
- Scope Managmenet PlanDocument9 pagesScope Managmenet Planwriter topNo ratings yet
- Assignments: Mba - 2Nd Sem Subject Code - MB0044 (Book ID: B1133)Document40 pagesAssignments: Mba - 2Nd Sem Subject Code - MB0044 (Book ID: B1133)Indranand SinghNo ratings yet
- Management Sw2Document3 pagesManagement Sw2Jess Rebb CostinNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Thesis TitleDocument8 pagesOperations Management Thesis Titleannemarieolathe100% (1)
- Production and Operation Management: REG. NO.: BIMS/HP/02/2007/1311Document25 pagesProduction and Operation Management: REG. NO.: BIMS/HP/02/2007/1311anjypetNo ratings yet
- MB0044 Set IDocument16 pagesMB0044 Set IArunkumar GuravNo ratings yet
- 5 Tips For Feed SuccessDocument3 pages5 Tips For Feed SuccessStephen EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Handout 03 04Document71 pagesHandout 03 04Tommba TommyNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument8 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementMahfooz AlamNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations ManagementDocument9 pagesProduction and Operations Managementaryanboxer786No ratings yet
- Networking PlanDocument23 pagesNetworking Planapi-639172668No ratings yet
- Explain Quality Circles and Its Importance? Explain How CAD and CIM Aid in Reducing The Concept To Market TimeDocument7 pagesExplain Quality Circles and Its Importance? Explain How CAD and CIM Aid in Reducing The Concept To Market TimeRohit KpNo ratings yet
- Facility Layout Narrative ReportDocument21 pagesFacility Layout Narrative Reportshaina mae arnezNo ratings yet
- Job OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesJob OpportunitiesdasfagagNo ratings yet
- Lean Start-Up Management Mgt1022: Digital Assignment - 2Document24 pagesLean Start-Up Management Mgt1022: Digital Assignment - 2PHK. DEEKSHITHNo ratings yet
- Assignment - MB0044-Production & Operations Management-AnsDocument20 pagesAssignment - MB0044-Production & Operations Management-AnsMehdi HasanNo ratings yet
- Ems 113 Production ManagementDocument38 pagesEms 113 Production ManagementLiberatus MpetaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Wide Integration Systems (4pg)Document8 pagesEnterprise Wide Integration Systems (4pg)Kevin KibugiNo ratings yet
- Operations Important TopicsDocument8 pagesOperations Important TopicsRuchi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Building MaintenanceDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Building Maintenancefvfee39d100% (1)
- Concurrent EngineeringDocument37 pagesConcurrent EngineeringPramod GowdaNo ratings yet
- Installing An Erp System With A Methodology Based On The Principles of Goal Directed Project ManagementDocument38 pagesInstalling An Erp System With A Methodology Based On The Principles of Goal Directed Project Managementtrangcun2206No ratings yet
- Production & Operations Management: Unit - 1Document148 pagesProduction & Operations Management: Unit - 1Sumatthi Devi Chigurupati100% (1)
- IGNOU MBA MS-05 Free Solved Assignment 2012Document33 pagesIGNOU MBA MS-05 Free Solved Assignment 2012ahesan aliNo ratings yet
- Written Report 3Document15 pagesWritten Report 3John BenedickNo ratings yet
- Using Value Methodology Tools To Enhance Competitive Bid Proposals: A Secret WeaponDocument12 pagesUsing Value Methodology Tools To Enhance Competitive Bid Proposals: A Secret WeaponGeeta RamsinghNo ratings yet
- Operations Management.Document9 pagesOperations Management.Hrithik GollarNo ratings yet
- Operation MNGMNT Group1Document6 pagesOperation MNGMNT Group1Lilian FredelucesNo ratings yet
- Quality Circles and Its Importance and Aid of CAD and CIM in Reducing To Market TimeDocument18 pagesQuality Circles and Its Importance and Aid of CAD and CIM in Reducing To Market TimeHina KhanNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management: at Manipal UniversityDocument44 pagesProduction and Operations Management: at Manipal UniversityVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- Placement Preparation - Strategic Decision - OperationsDocument10 pagesPlacement Preparation - Strategic Decision - OperationsTopsy KreateNo ratings yet
- Production ManagementDocument435 pagesProduction ManagementKota Mani Kanta100% (1)
- Management Processes CatDocument6 pagesManagement Processes CatSteve OgolaNo ratings yet
- ENGG 406 - Module 3 - Planning or Coordinating Technical ActivitiesDocument40 pagesENGG 406 - Module 3 - Planning or Coordinating Technical ActivitiesMonique UnicoNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1Document7 pagesModule 2.1ParalogityNo ratings yet
- Activity 01 Operations and Operations StrategyDocument2 pagesActivity 01 Operations and Operations StrategyIce IsidroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Producing Materials and ServicesDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - Producing Materials and ServicesArmanNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Product, Process, and Schedule DesignDocument20 pagesModule 3: Product, Process, and Schedule DesignMichael Jim C. MalasaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument9 pagesUntitled Document768 Rakshit KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Project Feasibility StudyDocument20 pages3.2 Project Feasibility Studydawit tibebuNo ratings yet
- Opm549 Individual Assignment 2 - Muhd Adib Bin Daman Huri 2021239468Document14 pagesOpm549 Individual Assignment 2 - Muhd Adib Bin Daman Huri 2021239468muhd adibNo ratings yet
- IT GOVERNANCE APPROACHES FOR AGILE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INVESTMENTSFrom EverandIT GOVERNANCE APPROACHES FOR AGILE SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT INVESTMENTSRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Basic of PVC Resin ProcessDocument56 pagesBasic of PVC Resin Processnguyensontuan100% (1)
- Abrasive Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesAbrasive Technical Data SheetZaid Raslan AyoubNo ratings yet
- Articles of Dissolution (Manitoba)Document2 pagesArticles of Dissolution (Manitoba)Ernest WooNo ratings yet
- Analysis & Design of Combined Footing: Condition:1Document3 pagesAnalysis & Design of Combined Footing: Condition:1Nikhil PoriyaNo ratings yet
- Fuld & Company - JD Business and Strategic ResearchDocument2 pagesFuld & Company - JD Business and Strategic ResearchShivangi Gupta Student, Jaipuria LucknowNo ratings yet
- Feliciano V VillasinDocument22 pagesFeliciano V VillasinTriccie Coleen MangueraNo ratings yet
- PaySlip-34 (LANKALAPALLI DURGA PRASAD) - JUN - 2022Document2 pagesPaySlip-34 (LANKALAPALLI DURGA PRASAD) - JUN - 2022Durga PrasadNo ratings yet
- O Level Commerce 1Document393 pagesO Level Commerce 1TapiwanasheNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health Protection On The JobDocument1 pageSafety and Health Protection On The JobCPSSTNo ratings yet
- Asam MCD-2 MCDocument1 pageAsam MCD-2 MCAyşenur KoseNo ratings yet
- My Drive - Google DriveDocument65 pagesMy Drive - Google DriveDraven WebbNo ratings yet
- Generative AI in EU LawDocument35 pagesGenerative AI in EU Lawpatricio silvaNo ratings yet
- Building Materials PortfolioDocument75 pagesBuilding Materials PortfolioMikaela Marie GilleraNo ratings yet
- Final Pts-21wc329Document349 pagesFinal Pts-21wc329Eyad Abu AlRoubNo ratings yet
- Manual TransmissionDocument60 pagesManual Transmissionʞǝǝs Uǝ ƎpıɥNo ratings yet
- Sss Requirements and ProcessDocument3 pagesSss Requirements and ProcessRheu ReyesNo ratings yet
- Java Programming ExercisesDocument50 pagesJava Programming ExerciseskeitoumaNo ratings yet
- Subject: ICAO & FAA Airfield Rescue and Fire Fighting Categories For Airbus AircraftDocument2 pagesSubject: ICAO & FAA Airfield Rescue and Fire Fighting Categories For Airbus AircraftAon ThummachaiNo ratings yet
- Chinhoyi University of Technology: Question OneDocument2 pagesChinhoyi University of Technology: Question OnefanwellsibandaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Latihan - Matematik Tingkatan 1Document6 pagesSoalan Latihan - Matematik Tingkatan 1TamilselviMohanNo ratings yet
- Status of Value Addition and Export of Moringa Produce in Tamil Nadu A Case StudyDocument14 pagesStatus of Value Addition and Export of Moringa Produce in Tamil Nadu A Case StudyvarunbeNo ratings yet
- On W.D Ross and His Ethics of DutyDocument2 pagesOn W.D Ross and His Ethics of DutyAbegail Ada QuiselNo ratings yet
- Ticket 11 DecDocument2 pagesTicket 11 DecShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- Tugas Case Red Bull - WidyanasariDocument4 pagesTugas Case Red Bull - WidyanasariwdyNo ratings yet
- 2020-12-30 Sro ADocument4 pages2020-12-30 Sro AAbdullahAbroNo ratings yet
- CarSim Math ModelsDocument4 pagesCarSim Math Modelsmikael bezerra cotias dos santosNo ratings yet
- Combofix 1Document10 pagesCombofix 1Nur Faizah AzizanNo ratings yet
- Brief in Opposition To RemandDocument11 pagesBrief in Opposition To RemandGregory MontelaroNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kelompok 6 SANKRIDocument13 pagesJurnal Kelompok 6 SANKRITinka Vedyra JothaNo ratings yet