Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buad 803 Assignment 1
Buad 803 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
jeff4real2007Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Buad 803 Assignment 1
Buad 803 Assignment 1
Uploaded by
jeff4real2007Copyright:
Available Formats
BUAD 803 ASSIGNMENT 1
Difference between the following:
-Current and non-current assets
-Tangible and Intangible assets
-Subsidiary books and Source Documents
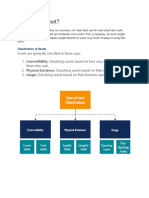
1. Current and Non-current Assets:
Current Assets: These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year
or the normal operating cycle of a business. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and
short-term investments.
Non-current Assets: Also known as long-term assets, these are assets held for a longer period, typically
more than a year. They are not expected to be converted into cash or consumed within the normal
operating cycle. Non-current assets include property, plant, equipment, long-term investments, and
intangible assets.
2. Tangible and Intangible Assets:
Tangible Assets: These are physical assets with a definite physical substance that can be touched, seen,
and quantified. Examples include land, buildings, machinery, equipment, and vehicles.
Intangible Assets: These are non-physical assets lacking a physical presence but hold significant value to
a business. They include intellectual property like patents, copyrights, trademarks, goodwill, brand
recognition, and software.
3. Subsidiary Books and Source Documents:
Source Documents: These are original documents providing evidence of a transaction, such as invoices,
receipts, purchase orders, sales contracts, bank statements, and vouchers. They are the initial records
that serve as proof of a business transaction.
Subsidiary Books: These are books or registers used to record transactions systematically based on their
nature. Subsidiary books include journals like the sales journal, purchases journal, cash book, and ledger.
They help in classifying and summarizing transactions before posting them to the general ledger.
In summary, the distinctions lie in the nature, timing, and purpose of these assets and record-keeping
methods within accounting and business operations.
You might also like
- Real Estate Agent: The Keys To Start Your Career and Beyond as a Real Estate AgentFrom EverandReal Estate Agent: The Keys To Start Your Career and Beyond as a Real Estate AgentNo ratings yet
- Examples of AssetsDocument3 pagesExamples of AssetsLuise MauieNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Audit of Fixed AssetsDocument10 pagesUnit 5 Audit of Fixed Assetssolomon adamuNo ratings yet
- M09-Preparing Financial ReportsDocument39 pagesM09-Preparing Financial Reportsmahammedabrahim693No ratings yet
- 1 Asset AccountsDocument3 pages1 Asset Accountsapi-299265916No ratings yet
- Classification of AssetsDocument3 pagesClassification of Assetssuvansh majmudarNo ratings yet
- Assets and LiabilityDocument2 pagesAssets and LiabilityDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Accounting of Fixed AssetsDocument6 pagesAccounting of Fixed Assetsnallarahul86No ratings yet
- What Is An AssetDocument6 pagesWhat Is An AssetrimpyNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset in AccountingDocument7 pagesFixed Asset in Accountingnallarahul86No ratings yet
- Peter Goa - English Exercise Unit 4Document14 pagesPeter Goa - English Exercise Unit 4Ronaldo Stevent SitohangNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Audit of Fixed AssetsDocument4 pagesUnit 5: Audit of Fixed AssetsTilahun S. KuraNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet: The Accounting Is One of The Major Financial Statements Used by Accountants and Business OwnersDocument4 pagesBalance Sheet: The Accounting Is One of The Major Financial Statements Used by Accountants and Business OwnersChristy BascoNo ratings yet
- AssetsDocument9 pagesAssetsRakshitAgarwalNo ratings yet
- A Quick Glance On Balance SheetDocument2 pagesA Quick Glance On Balance SheetAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Statement of Financial Position: I. AssetsDocument1 pageLesson 1: Statement of Financial Position: I. AssetsKristineNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Main ArticleDocument2 pagesAccounting: Main ArticleAnn StylesNo ratings yet
- Assets - Meaning and ClassificationDocument6 pagesAssets - Meaning and ClassificationJann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Classification of Assets and LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesClassification of Assets and Liabilitieschand1234567893No ratings yet
- Unit 1 IPRDocument3 pagesUnit 1 IPRMukul KumarNo ratings yet
- Noncurrent AssetsDocument6 pagesNoncurrent AssetsJohn Matthew CallantaNo ratings yet
- What Is An Intangible Asset?: Goodwill Intellectual Property Trademarks Exist in Opposition To Tangible AssetsDocument4 pagesWhat Is An Intangible Asset?: Goodwill Intellectual Property Trademarks Exist in Opposition To Tangible AssetsSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2 Week 2 DQ 1Document2 pagesIntermediate Accounting 2 Week 2 DQ 1Donald112No ratings yet
- Plant Assets and Intangible AssetsDocument14 pagesPlant Assets and Intangible AssetsSamuel DebebeNo ratings yet
- 1.fundamentals of ABM 2Document27 pages1.fundamentals of ABM 2MaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Accounting ElementsDocument2 pagesLecture 2 Accounting ElementsSAROL, Gwen Alessandra V.No ratings yet
- Fixed Assets - SAP Q&ADocument11 pagesFixed Assets - SAP Q&Adhamu199670atNo ratings yet
- Asset: Formal DefinitionDocument5 pagesAsset: Formal DefinitionAngelo AristizabalNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset Vs Current AssetDocument3 pagesFixed Asset Vs Current AssetSheila Mae LiraNo ratings yet
- AssetsDocument3 pagesAssetsTrixiaNo ratings yet
- AssetsDocument4 pagesAssetsCLLN FILESNo ratings yet
- Classification of AssetsDocument4 pagesClassification of Assetssuvansh majmudarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 (Group 1 Bascug, Basilio, Espineda)Document2 pagesAssignment 3 (Group 1 Bascug, Basilio, Espineda)jbbascugNo ratings yet
- What Is A Tangible Asset Comparison To Non-Tangible AssetsDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Tangible Asset Comparison To Non-Tangible AssetshieutlbkreportNo ratings yet
- Article About Assets What Are Assets? Understanding Assets Are All Economic Resources or Assets Owned by An Entity That Are Expected ToDocument2 pagesArticle About Assets What Are Assets? Understanding Assets Are All Economic Resources or Assets Owned by An Entity That Are Expected ToGhifary Yusuf AdrianNo ratings yet
- General Valuation Concepts and Principles: International Valuation Standards CommitteeDocument20 pagesGeneral Valuation Concepts and Principles: International Valuation Standards CommitteeRaju RanjanNo ratings yet
- English Active PasiveDocument15 pagesEnglish Active PasiveAna DanaNo ratings yet
- MCom - Accounts ch-8 Topic5Document16 pagesMCom - Accounts ch-8 Topic5Sameer GoyalNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Terms l1 Accountancy Class 11 Cbse by Ushank SirDocument11 pagesBasic Accounting Terms l1 Accountancy Class 11 Cbse by Ushank Sirrajput442007No ratings yet
- ABM ReviewerDocument2 pagesABM Reviewermary christy mantalabaNo ratings yet
- Types of AssetsDocument19 pagesTypes of AssetsMylene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document13 pagesCH 12Hanif MusyaffaNo ratings yet
- In Business and AccountingDocument6 pagesIn Business and AccountingHarish AroraNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminologies of Accounting: 1. AssetsDocument10 pagesBasic Terminologies of Accounting: 1. AssetsSophiya PrabinNo ratings yet
- 007 - Fixed AssetDocument1 page007 - Fixed AssetThelma DancelNo ratings yet
- Real Estate ManagementDocument118 pagesReal Estate Managementfinlifecon63100% (1)
- Individual Assignment - Definitionofassets - BasedOnPP71 THN 2010Document3 pagesIndividual Assignment - Definitionofassets - BasedOnPP71 THN 2010Adilla DillaNo ratings yet
- Report Junaid Group 8Document7 pagesReport Junaid Group 8Junaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Financial Assets VsDocument4 pagesFinancial Assets Vsm.g.sh0011No ratings yet
- Cash Flow and Funds FlowDocument17 pagesCash Flow and Funds FlowNitinNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers. 1pdfDocument168 pagesAccounting For Managers. 1pdfAkash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Pink GurlzDocument423 pagesPink Gurlzmygurlz1991No ratings yet
- Mission RBI 2018 - Financial SystemDocument6 pagesMission RBI 2018 - Financial SystemsaidheerendrapalkNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Statement of Financial PositionDocument17 pagesBalance Sheet Statement of Financial PositionAhmed FawzyNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint - Statement of Financial Position IDocument8 pagesPowerpoint - Statement of Financial Position IHood FerrelNo ratings yet
- Types of AssetsDocument8 pagesTypes of AssetsSanthosh Kumar T MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsDocument46 pagesChapter 6: Accounting For Plant Assets and Depreciation. ContentsSimon MollaNo ratings yet
- Notes Fa - 1Document5 pagesNotes Fa - 1Ali HassanNo ratings yet
- Record KeepingDocument5 pagesRecord KeepingBhasker KharelNo ratings yet
- BUAD 802 Examination 2023 Weekend GroupDocument2 pagesBUAD 802 Examination 2023 Weekend Groupjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- BUAD 803 Examination 2023 Weekend GroupDocument2 pagesBUAD 803 Examination 2023 Weekend Groupjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- BUAD 806 AssignmentDocument3 pagesBUAD 806 Assignmentjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- Buad 803 Assignment 2Document3 pagesBuad 803 Assignment 2jeff4real2007No ratings yet
- BUAD 804 Examination 2023 Weekday GroupDocument1 pageBUAD 804 Examination 2023 Weekday Groupjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- BUAD 801 Examination 2023 Weekend GroupDocument1 pageBUAD 801 Examination 2023 Weekend Groupjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- Buad 803 Gradeable ForumDocument1 pageBuad 803 Gradeable Forumjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- Buad 801 AssignmentDocument2 pagesBuad 801 Assignmentjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- BUAD 805 AssignmentDocument2 pagesBUAD 805 Assignmentjeff4real2007No ratings yet
- Buad 801 Gradeable ForumDocument3 pagesBuad 801 Gradeable Forumjeff4real2007No ratings yet