Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Concepts Qs
Basic Concepts Qs
Uploaded by
g4fp.cmCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Concepts Qs
Basic Concepts Qs
Uploaded by
g4fp.cmCopyright:
Available Formats
11 Basic concepts of organic
OCR Chemistry A chemistry
Exam-style questions
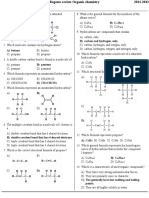
1 The following compounds, A–H, include hydrocarbons and compounds
containing oxygen.
a Define the term hydrocarbon.
(1 mark)
b Which of the compounds A–H are unsaturated?
(1 mark)
c Which of the compounds A–H can be described as branched and aliphatic?
(1 mark)
d i Name compound C.
(1 mark)
d ii Give the empirical formula of compound C.
(1 mark)
e i Compounds F and G contain the same functional group. In which
homologous series do both of these molecules belong?
(1 mark)
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 1
11 Basic concepts of organic
OCR Chemistry A chemistry
Exam-style questions
e ii Deduce the general formula for compounds F and G.
(1 mark)
f Give the molecular formula of compound H.
(1 mark)
g Are compounds A and B structural isomers? Explain your answer.
(1 mark)
2 There are three types of organic mechanism: addition, substitution, and
elimination.
a Which type of organic mechanism will always have an atom economy of
100%? Explain your answer.
(1 mark)
b Classify each of the following reactions as addition, substitution, or
elimination:
i CH3CHBrCH3 NaOH → CH3CH(OH)CH3 NaBr
(1 mark)
ii CH3CHBrCH3 NaOH → CH2CHCH3 NaBr H2O
(1 mark)
c i Name the homologous series that the organic product from the reaction in
b ii belongs to.
(1 mark)
ii Draw the skeletal formula of the structural isomer of the organic product
in b ii and name it.
(2 marks)
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 2
11 Basic concepts of organic
OCR Chemistry A chemistry
Exam-style questions
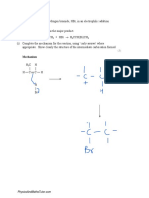
3 Depending on the conditions used, the C–Br bond in the compound below can
break either homolytically or heterolytically.
a i When UV radiation is used, the C–Br bond fission is homolytic.
Describe what happens to the bonding electrons when the C–Br bond
undergoes homolytic fission.
(1 mark)
ii When the C–Br bond breaks homolytically, what name is given to the
type of particle produced?
(1 mark)
b i Name the type of particle produced when the C–Br bond breaks
heterolytically.
(1 mark)
ii Use curly arrows and partial charges to show the breaking of the C–Br
bond via heterolytic fission on the molecule drawn below.
(2 marks)
iii What does a curly arrow represent?
(1 mark)
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 3
11 Basic concepts of organic
OCR Chemistry A chemistry
Exam-style questions
4 An organic compound, known to be an alcohol, was analysed and found to
contain 64.87% carbon, 13.51% hydrogen and 21.62% oxygen by mass. Its
molecular mass was determined to be 74.
a Calculate the empirical formula.
(2 marks)
b Determine the molecular formula.
(1 mark)
c Draw and name all possible structures of this compound.
(8 marks)
© Oxford University Press 2015 www.oxfordsecondary.co.uk/acknowledgements
This resource sheet may have been changed from the original 4
You might also like
- Alkenes HWDocument6 pagesAlkenes HWestherNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts About Matter: Test BankDocument12 pagesBasic Concepts About Matter: Test BankRalph Aubrey CulhiNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- IB Bonding MCQs PDFDocument24 pagesIB Bonding MCQs PDFtaimoor2No ratings yet
- The Berkeley Review - The Berkeley Review MCAT Organic Chemistry Part 1 (2011)Document332 pagesThe Berkeley Review - The Berkeley Review MCAT Organic Chemistry Part 1 (2011)Lord M.100% (3)
- Exam - Styled QuestionsDocument6 pagesExam - Styled QuestionsestherNo ratings yet
- Topic 15: Organic Chemistry: Carbonyls, Carboxylic Acids and ChiralityDocument3 pagesTopic 15: Organic Chemistry: Carbonyls, Carboxylic Acids and Chiralitysalma100% (1)
- OCR A AS Chemistry 11 Practice Question AnswersDocument6 pagesOCR A AS Chemistry 11 Practice Question AnswersFiaz RahmanNo ratings yet
- Principles of General Chemistry 3rd Edition Silberberg Test BankDocument17 pagesPrinciples of General Chemistry 3rd Edition Silberberg Test Banksiennaadelaideatknmp100% (28)
- Principles of General Chemistry 3Rd Edition Silberberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesPrinciples of General Chemistry 3Rd Edition Silberberg Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBrettClinewdjc100% (13)
- IsomerismDocument62 pagesIsomerismsubesinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - IUPAC PDFDocument28 pagesLecture Notes - IUPAC PDFmercury dragonNo ratings yet
- Bschcemc502-09 03 21Document3 pagesBschcemc502-09 03 21Subhsdfg majihggdgNo ratings yet
- CH12 - GOC - Shobhit NirwanDocument61 pagesCH12 - GOC - Shobhit NirwanRao GootleyNo ratings yet
- J.Avis@manchester - Ac.uk Jan 2013Document12 pagesJ.Avis@manchester - Ac.uk Jan 2013Estefanía ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Organic Practice TestDocument5 pagesOrganic Practice Testapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic Chemistry QP PDFDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Organic Chemistry QP PDFПолина ЩукаNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 2015 Exam Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesAlkanes 2015 Exam Style QuestionsellachloedeeksNo ratings yet
- Organic SL With AnswersDocument38 pagesOrganic SL With Answerswakoaisha2No ratings yet
- ZigZag: AS Chemistry Depth Paper CDocument7 pagesZigZag: AS Chemistry Depth Paper CnickychestNo ratings yet
- Bonding Key To In-Class Group Activity 1Document1 pageBonding Key To In-Class Group Activity 1Seema ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry - 1Document40 pagesBasic Principles of Organic Chemistry - 1nimesh Kashyap100% (1)
- 8 Class Test Paper 10-11-2023Document2 pages8 Class Test Paper 10-11-2023ranjit02051997No ratings yet
- Regents Review Organic Chemistry KeyDocument6 pagesRegents Review Organic Chemistry KeyRALPH MATHEW DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Questionssafwaanraqeeb786786No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds, Carboxylic Acids, Esters & Polyesters 1 QPDocument16 pagesCarbonyl Compounds, Carboxylic Acids, Esters & Polyesters 1 QPNeen NaazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemistry Exam QuestionsHarry WangNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument3 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Alkenes AssessmentDocument6 pagesAlkenes AssessmentTharany SureshkumarNo ratings yet
- Halo AssessmentDocument5 pagesHalo AssessmentTharany SureshkumarNo ratings yet
- HL Bonding Revision QuestionsDocument9 pagesHL Bonding Revision QuestionsMrunal JadhavNo ratings yet
- Prep Final-EX CHAP-7Document15 pagesPrep Final-EX CHAP-7dunghd.ba12-056No ratings yet
- Alkenes QuestionsDocument54 pagesAlkenes QuestionsBObNo ratings yet
- 2021 Intro To Organic - Lecture Notes - AnnotatedDocument29 pages2021 Intro To Organic - Lecture Notes - AnnotatedPROgamer GTNo ratings yet
- Cbse 12 Chemistry SP1Document6 pagesCbse 12 Chemistry SP1Girish SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Revision Organic Tutorial 2 - MSDocument5 pagesRevision Organic Tutorial 2 - MSDanish HamizanNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 2 QP AnsDocument11 pagesAlkenes 2 QP AnshhheeeNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Basic Organic Chemistry NJ - 247Document3 pagesDPP - 01 - Basic Organic Chemistry NJ - 247sumit.1024iitNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Basic Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesDPP - 01 - Basic Organic ChemistryHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Org Nic ChemistryDocument76 pagesLecture Notes: Org Nic ChemistryRaviNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry QuestionsDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Questionsmatseawangagift3dNo ratings yet
- Section A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 6 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 ScienceDocument8 pagesSection A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 6 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 ScienceVVS. G.S1074No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds, Carboxylic Acids, Esters & Polyesters 1 QPDocument16 pagesCarbonyl Compounds, Carboxylic Acids, Esters & Polyesters 1 QP5w8bh4jxw2No ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Chemistry Model Paper 10thDocument9 pagesMarking Scheme Chemistry Model Paper 10thChemistry ConceptNo ratings yet
- CH110 Tutorial SHEET 8 - Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesCH110 Tutorial SHEET 8 - Organic ChemistryJames MukopaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 12thDocument13 pagesSample Paper 2 12thShreya DubeyNo ratings yet
- CH102 Principles and Reactions in Organic Chemistry: Fste School of Biological and Chemical SciencesDocument13 pagesCH102 Principles and Reactions in Organic Chemistry: Fste School of Biological and Chemical SciencesTetzNo ratings yet
- 4.1.1 Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry QPDocument9 pages4.1.1 Basic Concepts of Organic Chemistry QPHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2020 Set 3Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2020 Set 3Rajendra SolankiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 11 - Practice - Test - CHEMICAL REACTIONDocument6 pagesChapter - 11 - Practice - Test - CHEMICAL REACTIONLourdesCorpusMendoza100% (1)
- CAPE Chemistry U2P1 2007 - 2022Document201 pagesCAPE Chemistry U2P1 2007 - 2022Cowboy XxNo ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry Set 1Document4 pagesXi Chemistry Set 1aashirwad2076No ratings yet
- Task 5 and 6 PracticeDocument11 pagesTask 5 and 6 PracticeJannat JeetNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2326 Chemistry Assignment PaperDocument9 pagesALPS 2326 Chemistry Assignment PaperAryan GoelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument14 pagesChemistry Notesgv07gamingNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry IArjayle Airobail LlevadoNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 IDocument6 pagesModel Test Paper Chemistry CBSE Class XII 2023 IAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- Complete Organic by Aman DhattarwalDocument6 pagesComplete Organic by Aman DhattarwalGhoruNo ratings yet
- OrganicDocument6 pagesOrganicTrent SwordsNo ratings yet
- 749861.EC2013 Book of Abstracts PDFDocument432 pages749861.EC2013 Book of Abstracts PDFAnonymous 7HfeABhNo ratings yet
- IChO-2013 Teoretical Problem With SolutionsDocument38 pagesIChO-2013 Teoretical Problem With SolutionsNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Basf-Ucrete Ud 200 - TdsDocument3 pagesBasf-Ucrete Ud 200 - TdsAbdul ZailaniNo ratings yet
- Biobased Epoxy Synthesized From A Vanillin Derivative and Its Reinforcement Using Lignin-Containing Cellulose NanofibrilsDocument10 pagesBiobased Epoxy Synthesized From A Vanillin Derivative and Its Reinforcement Using Lignin-Containing Cellulose NanofibrilsMaria FilipNo ratings yet
- Radl Week 1Document36 pagesRadl Week 1Zeian Jacob BaylaNo ratings yet
- Research ProjectDocument38 pagesResearch ProjectKarena NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 5 12thDocument13 pagesSample Paper 5 12thShreya DubeyNo ratings yet
- Effects of PH, Temperature and Concentration On Enzyme PepsinDocument4 pagesEffects of PH, Temperature and Concentration On Enzyme PepsinDebrah DebbieNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles AnswerDocument11 pagesPhysical Principles AnswerPepy PeachNo ratings yet
- Volatile OilsDocument36 pagesVolatile OilsGeillan Kim ManolidNo ratings yet
- 3.projekt PrEN 15014Document33 pages3.projekt PrEN 15014Karolina SoleckaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Prelims Set B.Document6 pagesBiochem Prelims Set B.Lymberth BenallaNo ratings yet
- VCO Standard Flyer - VCO Standard APCCDocument2 pagesVCO Standard Flyer - VCO Standard APCCRiza Muhammad100% (1)
- Chemistry QP in English Set 2Document4 pagesChemistry QP in English Set 2Annesha MondalNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7Document61 pagesAlkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination: Organic Chemistry, 7ravenclaw2426No ratings yet
- The Effect of Particle Size On The LeachingDocument11 pagesThe Effect of Particle Size On The LeachingW ZuoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Water and Oil PaintsDocument16 pagesComparison of Water and Oil PaintsMg H100% (1)
- OAVS PGT SyllabusDocument15 pagesOAVS PGT Syllabuspriyabrata biswalNo ratings yet
- StereoisomerismDocument32 pagesStereoisomerismbruno de jesus fontesNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Vinyl Acetate Monomer From Syntesis Gas TustinDocument11 pagesSynthesis of Vinyl Acetate Monomer From Syntesis Gas Tustindesigat4122No ratings yet
- WK 14 Myp 5 Chem HW ExemplarDocument3 pagesWK 14 Myp 5 Chem HW ExemplarJustteenNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Exam 20100503Document3 pagesInorganic Chemistry Exam 20100503曾鈞浩No ratings yet
- Hospital Waste Water TreatmentDocument5 pagesHospital Waste Water TreatmentNP100% (1)
- Nomenclature AnsDocument8 pagesNomenclature Ansdlc352-sc1No ratings yet
- Expt 8B Quali PDFDocument20 pagesExpt 8B Quali PDFNazrene LeysaNo ratings yet
- Production of Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty AcidDocument14 pagesProduction of Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acidkanbur.191No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Introductory BiochemistryDocument15 pagesLecture 2 - Introductory BiochemistryJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biochemistry Module 2Document8 pagesAdvanced Biochemistry Module 2Kenny Jim GambongNo ratings yet
- Biodegradation Using Microbes: Dr.T.V.Poonguzhali Department of Botany Queen Mary's College, Chennai-4Document20 pagesBiodegradation Using Microbes: Dr.T.V.Poonguzhali Department of Botany Queen Mary's College, Chennai-4Preethi GopalanNo ratings yet
- Homocysteine Supreme Doc RTDocument4 pagesHomocysteine Supreme Doc RTdianeculikNo ratings yet