Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsThermodynamics 14 Weeks of Hell
Thermodynamics 14 Weeks of Hell
Uploaded by
seirphenyoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Viscous Fluid Flow Frank M White Third Edition - Compress PDFDocument4 pagesViscous Fluid Flow Frank M White Third Edition - Compress PDFDenielNo ratings yet
- Astm E473-03 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm E473-03 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTA100% (1)
- DP 1 Unit Planner 3Document10 pagesDP 1 Unit Planner 3Mona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bits f111 Thermodynamics Ho 2019Document3 pagesBits f111 Thermodynamics Ho 2019avriolopes1308No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)Document2 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)Shubhash JoshiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument8 pagesThermodynamics SyllabusCarlo BensurtoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan CHE433 150914 3Document8 pagesLesson Plan CHE433 150914 3Mohd Hafiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic-Thermodynamics KLS PDFDocument6 pagesBasic-Thermodynamics KLS PDFAnonymous 5HYsyrddpNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Science 10 B PhysicsDocument4 pagesCourse Syllabus Science 10 B PhysicsNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Defense Engineering College Department of Motor Vehicle TechnologyDocument5 pagesDefense Engineering College Department of Motor Vehicle TechnologyGODNo ratings yet
- CHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedDocument24 pagesCHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedJULLIE MAE SAULON100% (1)
- Grade 10 Physics - Term 3Document8 pagesGrade 10 Physics - Term 3Trevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusTMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Course Code: 3350505Document5 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Course Code: 3350505Arpit vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Unit Standards, Learning Goals, Competencies and Targets: 8 HeatDocument4 pagesUnit Standards, Learning Goals, Competencies and Targets: 8 HeatRevilyn WonNo ratings yet
- PhyCompulsory & Elective Part-Revised Curriculum-20151211 PDFDocument29 pagesPhyCompulsory & Elective Part-Revised Curriculum-20151211 PDFonlineyykNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument6 pagesCourse OutlineanleyedemeNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusTMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument4 pagesBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusKrish RobertsNo ratings yet
- Physics XIIDocument255 pagesPhysics XIIQulb e AbbasNo ratings yet
- BITS F111 1004 UpdatedDocument6 pagesBITS F111 1004 UpdatedSUGEET SOODNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesSyllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsGautam GunjanNo ratings yet
- 2015.462984.mechanical Engineering TextDocument545 pages2015.462984.mechanical Engineering Textcaserisimo hechoconamorNo ratings yet
- Thermal Science 2ndDocument2 pagesThermal Science 2ndSyh TfkNo ratings yet
- Department Dept. Code Course Title Course Code Pre-Requisite(s) Credit Hours Course Objective No. Assigned Program Learning Outcome (PLO) Level ToolDocument4 pagesDepartment Dept. Code Course Title Course Code Pre-Requisite(s) Credit Hours Course Objective No. Assigned Program Learning Outcome (PLO) Level ToolShahzad AsifNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 10 - Q4Document32 pagesDLL - Science 10 - Q4Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Definitions, and PrinciplesDocument65 pagesChapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Definitions, and PrinciplesPrincess Oria-ArebunNo ratings yet
- Astm e 473 Rev A 2006 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm e 473 Rev A 2006 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- MEF 217 Applied ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesMEF 217 Applied ThermodynamicsAmbarish ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Atd Course HandoutDocument5 pagesAtd Course Handoutmaaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document17 pagesUnit 1wartha10000No ratings yet
- Course Outline SKF1013Document4 pagesCourse Outline SKF1013Munir EffendyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Combustion: Fundamental Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics and Combustion: Fundamental Concepts of ThermodynamicsVineeth SivarajNo ratings yet
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesFirst Law of ThermodynamicsewannnkobaNo ratings yet
- Me201 - Applied Thermodynamics: National University of Computer & Emerging Sciences, Fast-NuDocument2 pagesMe201 - Applied Thermodynamics: National University of Computer & Emerging Sciences, Fast-NuHamzaNo ratings yet
- ME201 - Rubrics v.00.00.01 2017-8-27Document2 pagesME201 - Rubrics v.00.00.01 2017-8-27Shahzad AsifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Document36 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Ng Kee NainNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Pilani Campus AUGS/AGSR DivisionDocument6 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Pilani Campus AUGS/AGSR DivisionAmanNo ratings yet
- Course Guide in Thermodynamics 1Document2 pagesCourse Guide in Thermodynamics 1mansang.mc62No ratings yet
- Bits F111 1004 20230811181755Document6 pagesBits F111 1004 20230811181755Sourabh KumarNo ratings yet
- C FakepathBasics Chemical Thermodinamics SyllabusDocument4 pagesC FakepathBasics Chemical Thermodinamics Syllabusxz4wvhpks6No ratings yet
- Thermalphysics (3403)Document7 pagesThermalphysics (3403)Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- 9202 International Gcse Chemistry Scheme of WorkDocument84 pages9202 International Gcse Chemistry Scheme of WorklxyshjphoebeNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Chemical EngineeringDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University Chemical EngineeringNeel ShelatNo ratings yet
- Bits F111-Course HandoutDocument3 pagesBits F111-Course HandoutPPNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument1 pageFlow ChartJP SaunarNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: by The End of Chapter 1, Students Should Be Able ToDocument10 pagesObjectives:: by The End of Chapter 1, Students Should Be Able ToAbdulrahman DesoukyNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Scheme of Work: Dtopic SubtopicDocument6 pagesTeacher'S Scheme of Work: Dtopic SubtopicAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Syllabus On CHE ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSyllabus On CHE ThermodynamicsJannineNo ratings yet
- TABIANAN Major Requirement - 2 Curriculum Plan - PDF - PDFDocument6 pagesTABIANAN Major Requirement - 2 Curriculum Plan - PDF - PDFJeramy BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Week 30 RPH Physics F4Document2 pagesWeek 30 RPH Physics F4Mohamad Shahir Ismail100% (1)
- Che 205Document7 pagesChe 205Moyin OlaoyeNo ratings yet
- FE - 16 ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesFE - 16 ThermodynamicsRizki FebrianNo ratings yet
- XE SampleDocument31 pagesXE SampleJerome HarinaNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 TermoDocument23 pagesBab 1 TermoChella YuanharNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS - Course OutlineDocument2 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS - Course OutlineNduati JohnNo ratings yet
- Mass & Energy Balances by DR Hilmi Mukhtar, FichemeDocument12 pagesMass & Energy Balances by DR Hilmi Mukhtar, FichemeSyukri ShahNo ratings yet
- CDB 1064 Principles of Chemical EngineeringDocument17 pagesCDB 1064 Principles of Chemical EngineeringluckyluckNo ratings yet
- Rad UnitsDocument1 pageRad Unitsmuayad73No ratings yet
- 1.1 WaveDocument87 pages1.1 WavePeggy Esther YongNo ratings yet
- Reference Book: Elements of X-Ray DiffractionDocument14 pagesReference Book: Elements of X-Ray Diffractiondtu epNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument132 pagesHSC Physics Chapterwise Important Questionstusharsuryawanshi320No ratings yet
- 4.2.3 Simple Harmonic Oscillations BDocument7 pages4.2.3 Simple Harmonic Oscillations BotookofialexNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesDocument6 pagesSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesMsLiewNo ratings yet
- 10 Wave OpticsDocument5 pages10 Wave OpticsSimon PradeepNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer (Laura Cardoso)Document4 pagesHeat Transfer (Laura Cardoso)Laura CardosoNo ratings yet
- Bphe-101 Phe-01 - EngDocument5 pagesBphe-101 Phe-01 - EngLONE SAAHILNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Acoustics by Crocker, Malcolm J. PDFDocument1,398 pagesHandbook of Acoustics by Crocker, Malcolm J. PDFExrtra Terrestrial100% (1)
- Cdna102013ac 001Document202 pagesCdna102013ac 001Fernando HoyoNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow PDFDocument90 pagesCompressible Flow PDFOmer TokhNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature and RadiationDocument39 pagesDual Nature and RadiationWedger RealmeNo ratings yet
- Poynting VectorDocument3 pagesPoynting Vectorpadmavathy2kNo ratings yet
- Catalog of Labor Scientific (Smallsize)Document94 pagesCatalog of Labor Scientific (Smallsize)alfayha sciNo ratings yet
- The Sun Shadows Presentation FreebieDocument7 pagesThe Sun Shadows Presentation Freebie8lu3dzNo ratings yet
- Microshade Datasheet: Type: MS-X LeavesDocument5 pagesMicroshade Datasheet: Type: MS-X Leavesstefan cirlanaruNo ratings yet
- Group 3 WavesDocument61 pagesGroup 3 WavesCE-Velasquez, AndreaNo ratings yet
- MCQ OscillationsDocument3 pagesMCQ OscillationsYoussef HassanNo ratings yet
- FB60-18 2023 Understanding Reflected Solar Energy Glazing Systems BuildingsDocument8 pagesFB60-18 2023 Understanding Reflected Solar Energy Glazing Systems BuildingsLEONARDONo ratings yet
- Energy Balance and The Greenhouse EffectDocument6 pagesEnergy Balance and The Greenhouse Effectsteph wallNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Classical Mechanics-IIDocument1 pageAssignment # 1 Classical Mechanics-IIMaqsood Khan KhattakNo ratings yet
- 314 ch1Document70 pages314 ch1Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fourier OpticsDocument28 pagesFourier OpticsVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Space EnvironmentDocument250 pagesIntroduction To Space EnvironmentIKOROMILOS100% (1)
- Wave Transmission in CrystalsDocument11 pagesWave Transmission in CrystalsRichard Simon KisituNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument5 pagesIndustrial Training Reportpravesh1992No ratings yet
- HS Earth Science Chapter 20 Power PointDocument36 pagesHS Earth Science Chapter 20 Power PointMichael McPeakNo ratings yet
- List of Physics Terms and Terminology Chapter One (Introduction To Physics) Item Meaning / DefinitionDocument11 pagesList of Physics Terms and Terminology Chapter One (Introduction To Physics) Item Meaning / DefinitionsmileshaNo ratings yet
Thermodynamics 14 Weeks of Hell
Thermodynamics 14 Weeks of Hell
Uploaded by
seirphenyo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesOriginal Title
Thermodynamics 14 weeks of hell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesThermodynamics 14 Weeks of Hell
Thermodynamics 14 Weeks of Hell
Uploaded by
seirphenyoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
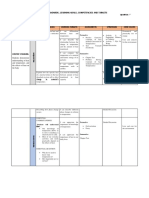
Week 1: Themes Learning Unit 1 Assessment criteria Media / resources
Objectives for this unit
Introduction to Understand the Classify Learner guide
thermodynamics Module Content, thermodynamic
Learning outcomes Lectures
systems systems
and Assessment Text Book
Derive energy
Criteria
equation Illustrative
Understand Define heat and work examples
classification of
Explain pressure and
thermodynamic Library research
systems, the temperature
properties and state measurement
of a system
Understand
pressure and
temperature
measurements
Understand heat
and work and the
derivation of the
Energy Equation
Week 2: Themes Learning Unit 2 Assessment criteria Media / resources
Objectives for this unit
Laws of Understand laws of Define the laws of Lectures
thermodynamics thermodynamics, thermodynamics
Text Book
their limitations
Explain the
and applications Illustrative
limitations and
examples
Understand applications of
maximum thermal thermodynamic laws Library research
efficiency
Determine maximum
Understand thermal efficiency of
coefficient of an engine
performance for Determine the
refrigerator and maximum coefficient
heat pump. of performance of a
refrigeration plant
and a heat pump
Week 3: Themes Learning Unit 3 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Properties of Understand laws of Define the laws of Lectures
perfect gases perfect gases perfect gases
Text Book
Understand general Derive the general
gas equation and gas equation Illustrative
characteristic gas examples
Apply characteristic
equation
gas equation to Library research
Understand specific specific problems
heat at constant
Define heat capacity
pressure and at
of a gas at constant
constant volume
pressure and at
and the
constant volume
relationships
between them. Derive the relation
between specific
Understand internal
heats
energy and
enthalpy Determine specific
heats, change in
internal energy,
change in enthalpy,
heat transferred and
work done for a
process
Week 4: Themes Learning Unit 4 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Thermodynamic Understand Differentiate between Lectures
processes of perfect classification of thermodynamic
Text Book
gases. thermodynamic processes
processes Illustrative
Use process
examples
Understand work equations and non-
done for a non-flow flow energy Library research
process equations to
evaluate the final
Understand non-
properties of a
flow energy
constant volume,
equation
constant pressure or
Understand constant
constant volume temperature
process process.
Understand Determine the heat
constant transferred, work
temperature done and change in
process internal energy for
Understand the above three
processes
constant pressure
process
Week 5: Themes Learning Unit 5 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Understand
Thermodynamic Calculate heat Lectures
adiabatic process
processes of transferred, work
Text Book
perfect gases. Understand done and change in
polytropic process internal energy for Illustrative
adiabatic and examples
Understand
polytropic processes Library research
pressure volume
temperature Determine the
relationships for polytropic index for
adiabatic and a polytropic process
polytropic
Explain the free
processes
expansion process
Understand free
Summarise the
expansion (or
equations for non-
unresisted
flow reversible
expansion) process
processes for
perfect gases
Week 6: Themes Learning Unit 6 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Understand flow
Thermodynamic Differentiate between Lectures
processes
processes of steady flow and
Understand the Text Book
perfect gases. unsteady flow
application of the Illustrative
processes
first law of examples
thermodynamics Apply the steady flow
energy equation Library research
to a steady flow
process Determine work done
Understand work in a various steady
done in a steady flow processes
flow process
Explain the throttling
Understand
process
Throttling process
Understand the Apply steady flow
application of energy equation to
steady state engineering systems
energy equation
to engineering
systems
Week 7: Themes Learning Unit 7 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Entropy of perfect Understand Explain the Lectures
gases entropy relationship
Text Book
between heat and
Understand the
entropy Illustrative
derivation of the
examples
general expression Derive the general
for change in expression for Library research
entropy for a change in entropy
perfect gas
Determine the
Understand the change in entropy
change in entropy for constant volume,
of a perfect gas for constant pressure
constant volume, and constant
constant pressure temperature
and constant processes
temperature
processes
Week 8: Themes Learning Unit 8 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Entropy of perfect Understand the Determine the Lectures
gases change in entropy change in entropy
Text Book
of a perfect gas for for an adiabatic and
an adiabatic and a polytropic process Illustrative
polytropic process examples
Summarize the
change in entropy of Library research
a perfect gas for all
processes
Week 9: Themes Learning Unit 4 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Thermodynamic air Understand Differentiate between Lectures
cycles assumptions made reversible and
Text Book
when investigating irreversible cycles
air cycle and the Illustrative
Describe the working
classification of examples
of an ideal engine
thermodynamic Library research
cycles Describe the
processes of a
Understand
Carnot cycle
reversible and
irreversible Evaluate the missing
processes properties at all
state points and the
Understand terms
thermal efficiency
used in
for the Carnot cycle
thermodynamic
cycles and the Determine the work
efficiency of a cycle done per cycle and
the heat supplied
Understand Carnot
and rejected for the
cycle
two cycles
Week 10: Themes Learning Unit 5 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Thermodynamic air Understand Stirling Describe the Lectures
cycles cycle processes of Stirling
Text Book
cycle
Understand Joule’s
Illustrative
cycle Describe the
examples
processes of Joule’s
cycle Library research
Evaluate the missing
properties at all state
points and the
thermal efficiency for
the above cycles
Determine the work
done per cycle and
the heat supplied
and rejected for the
above cycles
Week 11: Themes Learning Unit 5 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Thermodynamic Understand Diesel Describe the Lectures
air cycles cycle processes of Diesel
Text Book
cycle
Understand Dual
Illustrative
combustion cycle Describe the
examples
processes of Dual
combustion cycle Library research
Evaluate the missing
properties at all state
points and the
thermal efficiency for
the above cycles
Determine the work
done per cycle and
the heat supplied
and rejected for the
above cycles
Week 12: Themes Learning Unit 6 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Fuels and their Understand types of Classify fuels Learner guide
properties fuels.
Explain the Lectures
Understand the advantages and
Tutorial book
calorific value of disadvantages of
fuels different types of fuel Illustrative
examples
Understand the Define calorific value
experimental of fuels Library research
determination of
Determine calorific
Higher Calorific
value of fuels
value
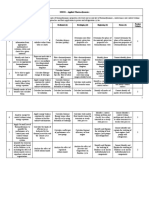
Week 13: Themes Learning Unit 6 Assessment Criteria Media / Resources
Objectives for this unit
Combustion of Understand basic Apply combustion Learner
fuels combustion equations to guide
equations and determine theoretical
Lectures
products of volume of air required
combustion for complete Tutorial book
combustion Illustrative
Understand
theoretical and Convert the examples
minimum mass volumetric analysis of Library
required for flue gases to research
complete gravimetric analysis
combustion
Determine the
Understand the theoretical mass of air
conversion of supplied per kg of fuel
volumetric analysis and evaluate the
into gravimetric actual mass of air
analysis supplied to the
combustion
Understand the
excess air supplied Determine the air to
fuel ratio for known
fuel composition and
measured flue gas
composition
You might also like
- Viscous Fluid Flow Frank M White Third Edition - Compress PDFDocument4 pagesViscous Fluid Flow Frank M White Third Edition - Compress PDFDenielNo ratings yet
- Astm E473-03 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm E473-03 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTA100% (1)
- DP 1 Unit Planner 3Document10 pagesDP 1 Unit Planner 3Mona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bits f111 Thermodynamics Ho 2019Document3 pagesBits f111 Thermodynamics Ho 2019avriolopes1308No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)Document2 pagesFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)Shubhash JoshiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument8 pagesThermodynamics SyllabusCarlo BensurtoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan CHE433 150914 3Document8 pagesLesson Plan CHE433 150914 3Mohd Hafiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic-Thermodynamics KLS PDFDocument6 pagesBasic-Thermodynamics KLS PDFAnonymous 5HYsyrddpNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Science 10 B PhysicsDocument4 pagesCourse Syllabus Science 10 B PhysicsNard EmsocNo ratings yet
- Defense Engineering College Department of Motor Vehicle TechnologyDocument5 pagesDefense Engineering College Department of Motor Vehicle TechnologyGODNo ratings yet
- CHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedDocument24 pagesCHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedJULLIE MAE SAULON100% (1)
- Grade 10 Physics - Term 3Document8 pagesGrade 10 Physics - Term 3Trevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusTMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Course Code: 3350505Document5 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Course Code: 3350505Arpit vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Unit Standards, Learning Goals, Competencies and Targets: 8 HeatDocument4 pagesUnit Standards, Learning Goals, Competencies and Targets: 8 HeatRevilyn WonNo ratings yet
- PhyCompulsory & Elective Part-Revised Curriculum-20151211 PDFDocument29 pagesPhyCompulsory & Elective Part-Revised Curriculum-20151211 PDFonlineyykNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument6 pagesCourse OutlineanleyedemeNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusTMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusDocument4 pagesBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusKrish RobertsNo ratings yet
- Physics XIIDocument255 pagesPhysics XIIQulb e AbbasNo ratings yet
- BITS F111 1004 UpdatedDocument6 pagesBITS F111 1004 UpdatedSUGEET SOODNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesSyllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsGautam GunjanNo ratings yet
- 2015.462984.mechanical Engineering TextDocument545 pages2015.462984.mechanical Engineering Textcaserisimo hechoconamorNo ratings yet
- Thermal Science 2ndDocument2 pagesThermal Science 2ndSyh TfkNo ratings yet
- Department Dept. Code Course Title Course Code Pre-Requisite(s) Credit Hours Course Objective No. Assigned Program Learning Outcome (PLO) Level ToolDocument4 pagesDepartment Dept. Code Course Title Course Code Pre-Requisite(s) Credit Hours Course Objective No. Assigned Program Learning Outcome (PLO) Level ToolShahzad AsifNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 10 - Q4Document32 pagesDLL - Science 10 - Q4Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Definitions, and PrinciplesDocument65 pagesChapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Definitions, and PrinciplesPrincess Oria-ArebunNo ratings yet
- Astm e 473 Rev A 2006 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm e 473 Rev A 2006 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- MEF 217 Applied ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesMEF 217 Applied ThermodynamicsAmbarish ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Atd Course HandoutDocument5 pagesAtd Course Handoutmaaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document17 pagesUnit 1wartha10000No ratings yet
- Course Outline SKF1013Document4 pagesCourse Outline SKF1013Munir EffendyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Combustion: Fundamental Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics and Combustion: Fundamental Concepts of ThermodynamicsVineeth SivarajNo ratings yet
- First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesFirst Law of ThermodynamicsewannnkobaNo ratings yet
- Me201 - Applied Thermodynamics: National University of Computer & Emerging Sciences, Fast-NuDocument2 pagesMe201 - Applied Thermodynamics: National University of Computer & Emerging Sciences, Fast-NuHamzaNo ratings yet
- ME201 - Rubrics v.00.00.01 2017-8-27Document2 pagesME201 - Rubrics v.00.00.01 2017-8-27Shahzad AsifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Document36 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Ng Kee NainNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Pilani Campus AUGS/AGSR DivisionDocument6 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani: Pilani Campus AUGS/AGSR DivisionAmanNo ratings yet
- Course Guide in Thermodynamics 1Document2 pagesCourse Guide in Thermodynamics 1mansang.mc62No ratings yet
- Bits F111 1004 20230811181755Document6 pagesBits F111 1004 20230811181755Sourabh KumarNo ratings yet
- C FakepathBasics Chemical Thermodinamics SyllabusDocument4 pagesC FakepathBasics Chemical Thermodinamics Syllabusxz4wvhpks6No ratings yet
- Thermalphysics (3403)Document7 pagesThermalphysics (3403)Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- 9202 International Gcse Chemistry Scheme of WorkDocument84 pages9202 International Gcse Chemistry Scheme of WorklxyshjphoebeNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University Chemical EngineeringDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University Chemical EngineeringNeel ShelatNo ratings yet
- Bits F111-Course HandoutDocument3 pagesBits F111-Course HandoutPPNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument1 pageFlow ChartJP SaunarNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: by The End of Chapter 1, Students Should Be Able ToDocument10 pagesObjectives:: by The End of Chapter 1, Students Should Be Able ToAbdulrahman DesoukyNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Scheme of Work: Dtopic SubtopicDocument6 pagesTeacher'S Scheme of Work: Dtopic SubtopicAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Syllabus On CHE ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesSyllabus On CHE ThermodynamicsJannineNo ratings yet
- TABIANAN Major Requirement - 2 Curriculum Plan - PDF - PDFDocument6 pagesTABIANAN Major Requirement - 2 Curriculum Plan - PDF - PDFJeramy BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Week 30 RPH Physics F4Document2 pagesWeek 30 RPH Physics F4Mohamad Shahir Ismail100% (1)
- Che 205Document7 pagesChe 205Moyin OlaoyeNo ratings yet
- FE - 16 ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesFE - 16 ThermodynamicsRizki FebrianNo ratings yet
- XE SampleDocument31 pagesXE SampleJerome HarinaNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 TermoDocument23 pagesBab 1 TermoChella YuanharNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMICS - Course OutlineDocument2 pagesTHERMODYNAMICS - Course OutlineNduati JohnNo ratings yet
- Mass & Energy Balances by DR Hilmi Mukhtar, FichemeDocument12 pagesMass & Energy Balances by DR Hilmi Mukhtar, FichemeSyukri ShahNo ratings yet
- CDB 1064 Principles of Chemical EngineeringDocument17 pagesCDB 1064 Principles of Chemical EngineeringluckyluckNo ratings yet
- Rad UnitsDocument1 pageRad Unitsmuayad73No ratings yet
- 1.1 WaveDocument87 pages1.1 WavePeggy Esther YongNo ratings yet
- Reference Book: Elements of X-Ray DiffractionDocument14 pagesReference Book: Elements of X-Ray Diffractiondtu epNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument132 pagesHSC Physics Chapterwise Important Questionstusharsuryawanshi320No ratings yet
- 4.2.3 Simple Harmonic Oscillations BDocument7 pages4.2.3 Simple Harmonic Oscillations BotookofialexNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesDocument6 pagesSt. Anthony's Canossian Secondary School Sec 4E Science (Physics) Chapter 14 Sound NotesMsLiewNo ratings yet
- 10 Wave OpticsDocument5 pages10 Wave OpticsSimon PradeepNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer (Laura Cardoso)Document4 pagesHeat Transfer (Laura Cardoso)Laura CardosoNo ratings yet
- Bphe-101 Phe-01 - EngDocument5 pagesBphe-101 Phe-01 - EngLONE SAAHILNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Acoustics by Crocker, Malcolm J. PDFDocument1,398 pagesHandbook of Acoustics by Crocker, Malcolm J. PDFExrtra Terrestrial100% (1)
- Cdna102013ac 001Document202 pagesCdna102013ac 001Fernando HoyoNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow PDFDocument90 pagesCompressible Flow PDFOmer TokhNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature and RadiationDocument39 pagesDual Nature and RadiationWedger RealmeNo ratings yet
- Poynting VectorDocument3 pagesPoynting Vectorpadmavathy2kNo ratings yet
- Catalog of Labor Scientific (Smallsize)Document94 pagesCatalog of Labor Scientific (Smallsize)alfayha sciNo ratings yet
- The Sun Shadows Presentation FreebieDocument7 pagesThe Sun Shadows Presentation Freebie8lu3dzNo ratings yet
- Microshade Datasheet: Type: MS-X LeavesDocument5 pagesMicroshade Datasheet: Type: MS-X Leavesstefan cirlanaruNo ratings yet
- Group 3 WavesDocument61 pagesGroup 3 WavesCE-Velasquez, AndreaNo ratings yet
- MCQ OscillationsDocument3 pagesMCQ OscillationsYoussef HassanNo ratings yet
- FB60-18 2023 Understanding Reflected Solar Energy Glazing Systems BuildingsDocument8 pagesFB60-18 2023 Understanding Reflected Solar Energy Glazing Systems BuildingsLEONARDONo ratings yet
- Energy Balance and The Greenhouse EffectDocument6 pagesEnergy Balance and The Greenhouse Effectsteph wallNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Classical Mechanics-IIDocument1 pageAssignment # 1 Classical Mechanics-IIMaqsood Khan KhattakNo ratings yet
- 314 ch1Document70 pages314 ch1Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fourier OpticsDocument28 pagesFourier OpticsVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Space EnvironmentDocument250 pagesIntroduction To Space EnvironmentIKOROMILOS100% (1)
- Wave Transmission in CrystalsDocument11 pagesWave Transmission in CrystalsRichard Simon KisituNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training ReportDocument5 pagesIndustrial Training Reportpravesh1992No ratings yet
- HS Earth Science Chapter 20 Power PointDocument36 pagesHS Earth Science Chapter 20 Power PointMichael McPeakNo ratings yet
- List of Physics Terms and Terminology Chapter One (Introduction To Physics) Item Meaning / DefinitionDocument11 pagesList of Physics Terms and Terminology Chapter One (Introduction To Physics) Item Meaning / DefinitionsmileshaNo ratings yet