Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amines - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Amines - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Uploaded by
dptrtfn879Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Example 10.3 For The System Methanol (1) / Methyl AcetateDocument2 pagesExample 10.3 For The System Methanol (1) / Methyl Acetatepanalopee50% (2)
- Consumer Chemistry Module 1 Day 1 PDFDocument8 pagesConsumer Chemistry Module 1 Day 1 PDFPrincess Loraine Duyag100% (2)
- Arihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers ChemistryDocument466 pagesArihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers ChemistryKrishna K75% (8)
- O'Level Organic Chemistry Brief NotesDocument5 pagesO'Level Organic Chemistry Brief NotesHassan Daud Khalid100% (3)
- A New Introduction To Organic Chemistry by G.I. BrownDocument193 pagesA New Introduction To Organic Chemistry by G.I. Brownkiddho100% (1)
- Several New Aspects of Indigo ChemistryDocument34 pagesSeveral New Aspects of Indigo ChemistryAnonymous hkDxd8L0% (1)
- AMINESDocument17 pagesAMINESRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- Amines 01 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023Document4 pagesAmines 01 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023dptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Nitrogen Containing CompoundsDocument15 pagesNitrogen Containing CompoundsSHIVI DwivediNo ratings yet
- 2610 Amine Chem 30307WMD261021306Document8 pages2610 Amine Chem 30307WMD261021306miranpathan2424No ratings yet
- Aakash Chapter - 13 (Xii) AminesDocument10 pagesAakash Chapter - 13 (Xii) AminesCartoons WorldNo ratings yet
- Amine DPP 02Document4 pagesAmine DPP 02Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- 14 - The Reimer-Tiemann ReactionDocument5 pages14 - The Reimer-Tiemann Reactionmayank.kr.jha.19.01No ratings yet
- 5 Poll Chemistry Question PartDocument3 pages5 Poll Chemistry Question PartMag GamingNo ratings yet
- AITS-03 12th Ass - Chemistry - Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAITS-03 12th Ass - Chemistry - Practice Sheetyashpatil17.2906No ratings yet
- Amines 02 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023Document4 pagesAmines 02 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023dptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Grignard 28Document7 pagesGrignard 28Oshi JainNo ratings yet
- Amines - Exercise-1 and 2Document28 pagesAmines - Exercise-1 and 2Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Amine DPP 01Document3 pagesAmine DPP 01Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives and Organic Hydroxy CompoundsDocument18 pagesHalogen Derivatives and Organic Hydroxy CompoundsEvery Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- 62da56649ec58d0011abeedb - ## - Alcohol, Phenol & Ether - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03)Document6 pages62da56649ec58d0011abeedb - ## - Alcohol, Phenol & Ether - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03)Prarabdh TiwariNo ratings yet
- CPP AminesDocument13 pagesCPP AminesDivyansh purohitNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds - UnlockedDocument5 pagesCarbonyl Compounds - UnlockedHuda ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives Practice Problems 2024Document24 pagesHalogen Derivatives Practice Problems 2024Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 06Document2 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 06shaanmukherjee2020No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument15 pagesHydrocarbonChandrika AnchanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AminesDocument8 pagesChemistry AminesVanshika LudhaniNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 2Document1 pageHaloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 2Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Halogen+Compound+ +Ex+I+by+PC+SirDocument8 pagesHalogen+Compound+ +Ex+I+by+PC+SirSuraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 02Document6 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 02shaanmukherjee2020No ratings yet
- Amines - IDocument13 pagesAmines - IDarkSlayerNo ratings yet
- XI-Chemistry Chapter Test-13-HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesXI-Chemistry Chapter Test-13-Hydrocarbonscakof67215No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons 1Document7 pagesHydrocarbons 1shalika42598No ratings yet
- Resonance Booklet of Nitrogen Containig CompoundDocument3 pagesResonance Booklet of Nitrogen Containig CompoundAlok pandeyNo ratings yet
- Amines NEET QuestionDocument13 pagesAmines NEET Questionmahi.nitukNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPPDocument18 pagesHydrocarbon DPPtemp93630No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 1 61Document18 pagesHydrocarbon 1 61Oshi JainNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument15 pagesHydrocarbonzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- Amines 03 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023Document4 pagesAmines 03 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023dptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry MergeDocument397 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mergekd79329No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes HaloarnesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes Haloarneshareharanbt22No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon _ DPP 01 __ Lakshya JEE 2025-merged (1)Document8 pagesHydrocarbon _ DPP 01 __ Lakshya JEE 2025-merged (1)deepakjat4356No ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenDocument9 pagesOrganic Compounds Containing NitrogenAUM S. PATELNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 5Document2 pagesHaloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 5Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-02 For AIATS-04: ChemistryDocument13 pagesPractice Test-02 For AIATS-04: ChemistrySiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPPDocument24 pagesHydrocarbon DPPitsbladderNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPP1234Document24 pagesHydrocarbon DPP1234Saanvi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic AcidDocument20 pagesAldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic AcidRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- Halogen+Compound+ +PYQ+by+PC+SirDocument4 pagesHalogen+Compound+ +PYQ+by+PC+SirSuraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument12 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & EtherssiddharthchillapwarNo ratings yet
- Amines: Fact / Definition Type QuestionsDocument16 pagesAmines: Fact / Definition Type QuestionsBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 09Document4 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 09shaanmukherjee2020No ratings yet
- Aromatic - 1, 2, 3, 4Document5 pagesAromatic - 1, 2, 3, 4Rajdeep BiswasNo ratings yet
- 10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentDocument6 pages10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentalarmbarbarNo ratings yet
- Exersice PDFDocument24 pagesExersice PDFharsh mishraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 2 58Document13 pagesHydrocarbon 2 58Oshi JainNo ratings yet
- Mathongo Jee Main 2015Document28 pagesMathongo Jee Main 2015rishithhr rajeevNo ratings yet
- Test - 10 (B) - Nomenclature & Isomerism + Reaction Mechanism I & II and Hydrocarbon (Paper)Document5 pagesTest - 10 (B) - Nomenclature & Isomerism + Reaction Mechanism I & II and Hydrocarbon (Paper)rahulkaushikNo ratings yet
- DPP 21Document10 pagesDPP 21sudhanshu.maluNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Containing Compuonds-03 - Assignments (New)Document20 pagesNitrogen Containing Compuonds-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 7 SET 2 Chapter 13Document32 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 7 SET 2 Chapter 13Rohit Pal100% (2)
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ethers 02 - Practice Sheet & SolutionDocument4 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Ethers 02 - Practice Sheet & Solutiondptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Parishram (2024) : Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument3 pagesParishram (2024) : Alcohol, Phenol and Etherbiswajitttt8No ratings yet
- Lakshya JEE (2024) : Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument4 pagesLakshya JEE (2024) : Haloalkanes and HaloarenesPRITAM KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Organic Reactions 1Document23 pagesMechanism of Organic Reactions 1Suresh Vedpathak100% (2)
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Multiple Choice QuestionsYASH PRANESHNo ratings yet
- CPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDocument5 pagesCPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- عضوية كامل PDFDocument201 pagesعضوية كامل PDFfdghhNo ratings yet
- Documents - Tips - Fundamentals of Epoxy Formulation PDFDocument5 pagesDocuments - Tips - Fundamentals of Epoxy Formulation PDFnanoNo ratings yet
- AlkylHalideClassTests 11Document2 pagesAlkylHalideClassTests 11GabyMendiola_No ratings yet
- 1,3-Butadiene Polymerization by 2009Document2 pages1,3-Butadiene Polymerization by 2009mayamaruguerraNo ratings yet
- Week 11Document4 pagesWeek 11sam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Organic Acids & Organic BasesDocument20 pagesOrganic Acids & Organic BasesCheng KathyNo ratings yet
- WORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryDocument28 pagesWORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryTikeshwar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Applications of Heterobifunctional Poly (Ethylene Oxide) OligomersDocument29 pagesSynthesis and Applications of Heterobifunctional Poly (Ethylene Oxide) OligomersFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Sophorolipids ThesisDocument8 pagesSophorolipids ThesisBuyAPaperForCollegeElgin100% (1)
- Communications: Dehydrogenative CouplingDocument5 pagesCommunications: Dehydrogenative CouplingLakshay KathuriaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes ClassDocument27 pagesAlkanes ClassRyan JamesNo ratings yet
- Frustrated Lewis PairsDocument18 pagesFrustrated Lewis PairsBaloch SamNo ratings yet
- Sodium Borohydride DigestDocument212 pagesSodium Borohydride DigestDmitry67% (3)
- Nazarov CyclizationDocument17 pagesNazarov CyclizationAtul YelpaleNo ratings yet
- 8 Formyl 7 Hydroxy 4 MethylcoumarinDocument8 pages8 Formyl 7 Hydroxy 4 Methylcoumarinrakeshtalele007No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Compounds With NitrogenDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes Compounds With NitrogenNosiphesihle ShanduNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument26 pagesCarbohydrates BiochemReimond VinceNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidIqbal A Mir100% (1)
- Amidine SynthesisDocument4 pagesAmidine SynthesisHalohydrinNo ratings yet
- Quiz Chemical Bonding: 1. The Hybridisation of Cationic Part in CL O (A) SP (B) SP (C) SP (D) SP D Ans. (B)Document4 pagesQuiz Chemical Bonding: 1. The Hybridisation of Cationic Part in CL O (A) SP (B) SP (C) SP (D) SP D Ans. (B)Emraan EmmiNo ratings yet
- Conformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3Document56 pagesConformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3swastikNo ratings yet
Amines - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Amines - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Uploaded by
dptrtfn879Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amines - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Amines - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Uploaded by
dptrtfn879Copyright:
Available Formats
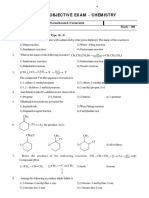
1
Safal 2.0
Amines
1. Hybridisation of nitrogen in amino group is: 8. Primary, secondary and tertiary amines can be
(1) sp (2) dsp2 separated by using:
(3) sp3 (4) None of these (1) Iodoform
(2) Ethyl bromide
(3) Benzene sulphonyl chloride
2. C3H9N represents (4) Tollen's reagent
(1) Primary amine (2) Secondary amine
(3) Tertiary amine (4) All of these 9. For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic
KOH and:
NaOBr
(1) Any primary amine and chloroform
3. Reaction CH3CONH2 gives : (2) Chloroform and silver powder
(1) CH3Br (2) CH4 (3) A primary amine and an alkyl halide
(4) A monoalkylamine and trichloromethane
(3) CH3OBr (4) CH3NH2
10. A primary amine can be converted to an alcohol by
4. Which among the given amides will give ethylamine the action of
on reaction with sodium hypobromide? (1) Alkali (2) Nitrous acid
(1) Butanamide (2) Propanamide (3) Reducing agent (4) Oxidising agent
(3) Acetamide (4) None of these
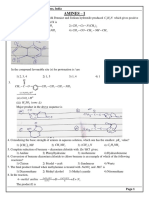
11. An organic compound A with molecular formula
C3H5N hydrolysis forms an acid which reduces
5. Which of the following reactions does not yield on Fehling's solution The compound can be
amine? (1) Ethanenitrile (2) Ethyl carbylamine
(1) R X NH3 (3) Methoxyethane (4) Propanenitrile
(2) R CH NOH H NaNO2 /H Cu 2 CN 2
Na
C3H5OH 12. C6 H5 NH 2 X
H
(3) R CN H 2O H O/H
Y
2
Z; Z is :
(4) R CONH2 4 H
LiAlH4
(1) C6H5 – NH – CH3
(2) C6H5 – COOH
(3) C6H5 – CH2NH2
6. Which one of the following on reduction with lithium
(4) C6H5 – CH2 – COOH
aluminium hydride yields a secondary amine?
(1) Methyl isocyanide 13. Which of the following compounds will not undergo
(2) Acetamide azo coupling reaction with benzene diazonium
(3) Methyl cyanide chloride?
(4) Nitroethane
(1) Aniline (2) Phenol
7. The correct order of boiling points of the following (3) Anisole (4) Nitrobenzene
isomeric amines is:
ArB2 Cl
Cu/HCl
C4H9NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2H5N(CH3)2 14. ArCl N2 CuCl
(1) C2H5N(CH3)2 > (C2H5)2NH > C4H9NH2
Above reaction is known as:
(2) (C2H5)2NH > C2H5N(CH3)2 > C4H9NH2
(1) Sandmeyer reaction
(3) C4H9NH2 > (C2H5)2 NH > C2H5N(CH3)2
(2) Gatterman reaction
(4) None of these
(3) Etard chloride
(4) Carbylamine reaction
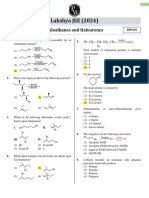
2
18. The correct sequence of reaction to be performed to
15. convert benzene into m-bromoaniline is:
(1) Nitration, reduction, bromination
(2) Bromination, nitration, reduction
The product ‘S’ in the above sequence of reactions is:
(3) Nitration, bromination, reduction
(1) 2, 4, 6-Tribromofluorobenzene (4) Reduction, nitration, bromination
(2) Fluorobenzene
(3) p-Bromofluorobenzene NaNO HCl CuCN H /H O
19. C6 H5 NH 2
2
A B
2
C
(4) Tribromobenzene 273K Boil
The compound ‘C’ in the above reaction is:
16. Azo-dyes are prepared from: (1) C6H5CN (2) C6H5CH3
(3) C6H5COOH (4) C6H5CH2NH2
(1) Aniline (2) Salicylic acid
(3) Benzaldehyde (4) Chlorobenzene 20. Consider the following compounds:
(i) p-Methyl aniline
17. Benzenediazonium chloride reacts with phenol to (ii) N, N-dimethylaniline
give p-hydroxy azobenzene, an orange dye. This (iii) N-ethyl aniline
reaction is known as: (iv) N-ethyl-N-methyl aniline
(1) Coupling reaction The compounds which do not form diazonium salt
(2) Carbylamine reaction with ice-cold NaNO2 and HCl are:
(3) Gattermann reaction (1) (i), (ii) and (iii) (2) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(4) Hinsberg's reaction (3) (i), (iii) and (iv) (4) (ii) and (iv)
3
Answer Key
1. (3) 11. (2)
2. (4) 12. (2)
3. (4) 13. (4)
4. (2) 14. (2)
15. (1)
5. (3)
16. (1)
6. (1)
17. (1)
7. (3)
18. (3)
8. (3)
19. (3)
9. (1)
20. (2)
10. (2)
PW Web/App - https://smart.link/7wwosivoicgd4
Library- https://smart.link/sdfez8ejd80if
You might also like
- Example 10.3 For The System Methanol (1) / Methyl AcetateDocument2 pagesExample 10.3 For The System Methanol (1) / Methyl Acetatepanalopee50% (2)
- Consumer Chemistry Module 1 Day 1 PDFDocument8 pagesConsumer Chemistry Module 1 Day 1 PDFPrincess Loraine Duyag100% (2)
- Arihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers ChemistryDocument466 pagesArihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers ChemistryKrishna K75% (8)
- O'Level Organic Chemistry Brief NotesDocument5 pagesO'Level Organic Chemistry Brief NotesHassan Daud Khalid100% (3)
- A New Introduction To Organic Chemistry by G.I. BrownDocument193 pagesA New Introduction To Organic Chemistry by G.I. Brownkiddho100% (1)
- Several New Aspects of Indigo ChemistryDocument34 pagesSeveral New Aspects of Indigo ChemistryAnonymous hkDxd8L0% (1)
- AMINESDocument17 pagesAMINESRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- Amines 01 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023Document4 pagesAmines 01 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023dptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Nitrogen Containing CompoundsDocument15 pagesNitrogen Containing CompoundsSHIVI DwivediNo ratings yet
- 2610 Amine Chem 30307WMD261021306Document8 pages2610 Amine Chem 30307WMD261021306miranpathan2424No ratings yet
- Aakash Chapter - 13 (Xii) AminesDocument10 pagesAakash Chapter - 13 (Xii) AminesCartoons WorldNo ratings yet
- Amine DPP 02Document4 pagesAmine DPP 02Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- 14 - The Reimer-Tiemann ReactionDocument5 pages14 - The Reimer-Tiemann Reactionmayank.kr.jha.19.01No ratings yet
- 5 Poll Chemistry Question PartDocument3 pages5 Poll Chemistry Question PartMag GamingNo ratings yet
- AITS-03 12th Ass - Chemistry - Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAITS-03 12th Ass - Chemistry - Practice Sheetyashpatil17.2906No ratings yet
- Amines 02 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023Document4 pagesAmines 02 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023dptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Grignard 28Document7 pagesGrignard 28Oshi JainNo ratings yet
- Amines - Exercise-1 and 2Document28 pagesAmines - Exercise-1 and 2Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Amine DPP 01Document3 pagesAmine DPP 01Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives and Organic Hydroxy CompoundsDocument18 pagesHalogen Derivatives and Organic Hydroxy CompoundsEvery Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- 62da56649ec58d0011abeedb - ## - Alcohol, Phenol & Ether - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03)Document6 pages62da56649ec58d0011abeedb - ## - Alcohol, Phenol & Ether - DPP 02 (Of Lec 03)Prarabdh TiwariNo ratings yet
- CPP AminesDocument13 pagesCPP AminesDivyansh purohitNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds - UnlockedDocument5 pagesCarbonyl Compounds - UnlockedHuda ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives Practice Problems 2024Document24 pagesHalogen Derivatives Practice Problems 2024Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]No ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 06Document2 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 06shaanmukherjee2020No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument15 pagesHydrocarbonChandrika AnchanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AminesDocument8 pagesChemistry AminesVanshika LudhaniNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 2Document1 pageHaloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 2Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Halogen+Compound+ +Ex+I+by+PC+SirDocument8 pagesHalogen+Compound+ +Ex+I+by+PC+SirSuraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 02Document6 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 02shaanmukherjee2020No ratings yet
- Amines - IDocument13 pagesAmines - IDarkSlayerNo ratings yet
- XI-Chemistry Chapter Test-13-HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesXI-Chemistry Chapter Test-13-Hydrocarbonscakof67215No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons 1Document7 pagesHydrocarbons 1shalika42598No ratings yet
- Resonance Booklet of Nitrogen Containig CompoundDocument3 pagesResonance Booklet of Nitrogen Containig CompoundAlok pandeyNo ratings yet
- Amines NEET QuestionDocument13 pagesAmines NEET Questionmahi.nitukNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPPDocument18 pagesHydrocarbon DPPtemp93630No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 1 61Document18 pagesHydrocarbon 1 61Oshi JainNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument15 pagesHydrocarbonzohaibsalamNo ratings yet
- Amines 03 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023Document4 pagesAmines 03 - DPP & Solution - Sankalp 2023dptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry MergeDocument397 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mergekd79329No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes HaloarnesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes Haloarneshareharanbt22No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon _ DPP 01 __ Lakshya JEE 2025-merged (1)Document8 pagesHydrocarbon _ DPP 01 __ Lakshya JEE 2025-merged (1)deepakjat4356No ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenDocument9 pagesOrganic Compounds Containing NitrogenAUM S. PATELNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 5Document2 pagesHaloalkane and Haloarenes DPP 5Dharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-02 For AIATS-04: ChemistryDocument13 pagesPractice Test-02 For AIATS-04: ChemistrySiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPPDocument24 pagesHydrocarbon DPPitsbladderNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPP1234Document24 pagesHydrocarbon DPP1234Saanvi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic AcidDocument20 pagesAldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic AcidRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- Halogen+Compound+ +PYQ+by+PC+SirDocument4 pagesHalogen+Compound+ +PYQ+by+PC+SirSuraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument12 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & EtherssiddharthchillapwarNo ratings yet
- Amines: Fact / Definition Type QuestionsDocument16 pagesAmines: Fact / Definition Type QuestionsBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 09Document4 pagesHaloalkane & Haloarene _ DPP 09shaanmukherjee2020No ratings yet
- Aromatic - 1, 2, 3, 4Document5 pagesAromatic - 1, 2, 3, 4Rajdeep BiswasNo ratings yet
- 10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentDocument6 pages10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentalarmbarbarNo ratings yet
- Exersice PDFDocument24 pagesExersice PDFharsh mishraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 2 58Document13 pagesHydrocarbon 2 58Oshi JainNo ratings yet
- Mathongo Jee Main 2015Document28 pagesMathongo Jee Main 2015rishithhr rajeevNo ratings yet
- Test - 10 (B) - Nomenclature & Isomerism + Reaction Mechanism I & II and Hydrocarbon (Paper)Document5 pagesTest - 10 (B) - Nomenclature & Isomerism + Reaction Mechanism I & II and Hydrocarbon (Paper)rahulkaushikNo ratings yet
- DPP 21Document10 pagesDPP 21sudhanshu.maluNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Containing Compuonds-03 - Assignments (New)Document20 pagesNitrogen Containing Compuonds-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 7 SET 2 Chapter 13Document32 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 7 SET 2 Chapter 13Rohit Pal100% (2)
- Alcohol, Phenol and Ethers 02 - Practice Sheet & SolutionDocument4 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Ethers 02 - Practice Sheet & Solutiondptrtfn879No ratings yet
- Parishram (2024) : Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument3 pagesParishram (2024) : Alcohol, Phenol and Etherbiswajitttt8No ratings yet
- Lakshya JEE (2024) : Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument4 pagesLakshya JEE (2024) : Haloalkanes and HaloarenesPRITAM KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Organic Reactions 1Document23 pagesMechanism of Organic Reactions 1Suresh Vedpathak100% (2)
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Multiple Choice QuestionsYASH PRANESHNo ratings yet
- CPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDocument5 pagesCPT Rasi Xi Che NeetDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- عضوية كامل PDFDocument201 pagesعضوية كامل PDFfdghhNo ratings yet
- Documents - Tips - Fundamentals of Epoxy Formulation PDFDocument5 pagesDocuments - Tips - Fundamentals of Epoxy Formulation PDFnanoNo ratings yet
- AlkylHalideClassTests 11Document2 pagesAlkylHalideClassTests 11GabyMendiola_No ratings yet
- 1,3-Butadiene Polymerization by 2009Document2 pages1,3-Butadiene Polymerization by 2009mayamaruguerraNo ratings yet
- Week 11Document4 pagesWeek 11sam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Organic Acids & Organic BasesDocument20 pagesOrganic Acids & Organic BasesCheng KathyNo ratings yet
- WORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryDocument28 pagesWORK BOOK - Exercise in ChemistryTikeshwar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Applications of Heterobifunctional Poly (Ethylene Oxide) OligomersDocument29 pagesSynthesis and Applications of Heterobifunctional Poly (Ethylene Oxide) OligomersFranciscoNo ratings yet
- Sophorolipids ThesisDocument8 pagesSophorolipids ThesisBuyAPaperForCollegeElgin100% (1)
- Communications: Dehydrogenative CouplingDocument5 pagesCommunications: Dehydrogenative CouplingLakshay KathuriaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes ClassDocument27 pagesAlkanes ClassRyan JamesNo ratings yet
- Frustrated Lewis PairsDocument18 pagesFrustrated Lewis PairsBaloch SamNo ratings yet
- Sodium Borohydride DigestDocument212 pagesSodium Borohydride DigestDmitry67% (3)
- Nazarov CyclizationDocument17 pagesNazarov CyclizationAtul YelpaleNo ratings yet
- 8 Formyl 7 Hydroxy 4 MethylcoumarinDocument8 pages8 Formyl 7 Hydroxy 4 Methylcoumarinrakeshtalele007No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Compounds With NitrogenDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes Compounds With NitrogenNosiphesihle ShanduNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument26 pagesCarbohydrates BiochemReimond VinceNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Solomon Periodic AcidIqbal A Mir100% (1)
- Amidine SynthesisDocument4 pagesAmidine SynthesisHalohydrinNo ratings yet
- Quiz Chemical Bonding: 1. The Hybridisation of Cationic Part in CL O (A) SP (B) SP (C) SP (D) SP D Ans. (B)Document4 pagesQuiz Chemical Bonding: 1. The Hybridisation of Cationic Part in CL O (A) SP (B) SP (C) SP (D) SP D Ans. (B)Emraan EmmiNo ratings yet
- Conformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3Document56 pagesConformational Analysis: Carey & Sundberg: Part A Chapter 3swastikNo ratings yet