Professional Documents
Culture Documents
History Timeline PDF
History Timeline PDF
Uploaded by
Abdur Rahman Yadgar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views11 pagesO'level Pakistan studies history timeline from section 1 till section 3. Highlighting important events from O'level syllabus
Original Title
History Timeline pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentO'level Pakistan studies history timeline from section 1 till section 3. Highlighting important events from O'level syllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views11 pagesHistory Timeline PDF
History Timeline PDF
Uploaded by
Abdur Rahman YadgarO'level Pakistan studies history timeline from section 1 till section 3. Highlighting important events from O'level syllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
O’ level Pakistan Studies
History Timeline
Section 1-3
Date Event Focus points
• EIC landed at Surat in India for trade, but were
1606
British enter India rejected by Jahangir
1612 • Later Shah Jehan gave permission for trade
1703 Birth of Shah Wali-Ullah • A Religious reformer, born in Delhi
• Initiated the decline of Mughal Empire as
1707 Death of Aurangzeb successors fought & no capable ruler came.
• Persian Ruler Nadir Shah invaded India and took
1738 Invasion of Nadir Shah peacock throne
• Attack on Fort William by Nawab Siraj-ud-Daula
1757 Battle of Plassey • Mir Jaffar met with Robert Clive & Siraj-ud-Daula
was defeated
• Ahmed Shah Abdali invaded India and defeated
1761 3rd Battle of Panipat Marathas
• Combined forces of Mir Qasim (Nawab of Bengal)
Shuja-ud-daulah (Nawab of Oudh) and the Shah Alam II
1764 Battle of Buxar (Mughal Emperor)
• Set the foundations of British political rule in India
• Born in Faridpur (Bengal)
1781 Haji Shariat Ullah • He launched Faraizi movement
• This act made the position of Governor General a
1784 Pits India Act royal appointment. Lord Cornwallis was appointed
to this position in 1786
1786 Syed Ahmed Shaheed • Born in Rai Barelvi (near lucknow)
Barelvi • He started Jihad movement
• After series of Anglo-Mysore wars, British captured
1799 Defeat of Tipu Sultan Mysore & defeated Tipu Sultan
• British captured Delhi after it became part of
1803 British capture Delhi Maratha Empire
• Muslim reformer
• laid foundations to Ali Garh movement
1817 Birth of Sir Syed • provided two nation theory
• Removed misunderstandings between Muslims and
British
Maratha wars with • Maratha lost the Battle in Hyderabad
1818 •
British Last obstacle was removed to rule over India
• Under this policy if the landowner did not have the
1852 Agrarian Policy documents of the land, the land would be
confiscated by british
• Under this policy, if the landlord did not have a
1852 Doctrine of Lapse male heir to be in charge of the land after he died,
the land would be confiscated by british
• Indians against British
• Started from Meerut by Mungal sepoy
1857 War of Independence • Officially ended in 1858 & marked the end of
Mughal Empire
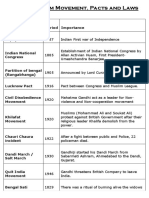
Indian National Congress (INC) • First political party for Indians made by Allen
1885:
formed Octavian Hume
1905 Partition of Bengal • Viceroy Lord Curzon partitioned Bengal
Shimla • Muslim delegation under the leadership of sir Agha
1906 Khan went to meet Lord Minto
Deputation/Delegation
All India Muslim League
1906 • Muslim League was formed in Dhakka
(AIML) formed
• 1st Reform by British to transfer power to Indians
1909 Morley Minto Reforms step by step
• They planned to bring reforms after every 10 years
Reversal of partition of • Due to Hindus violent actions & an attempt to
1911 assassinate Lord Minto
Bengal
• Both INC & AIML held their annual session to sign
1916 Lucknow Pact an agreement and work together
• It was Jinnah who brought both parties
• 2nd Reform by British in response to Morley Minto
Montague Chelmsford
1919 Reforms
Reforms • Minor powers were given
• A committee was formed to study the revolutionary
activities under Justice Rowlatt and the act passed
1917 Rowlatt Act in 1919
• Public gatherings were banned & others
• Muslims, Hindus & Sikhs ghathered for peaceful
Amritsar demonstration
1919 Massacre/Jallianwala • General Dyer opened fire and killed 400 Indians.
Bagh incident Later he was found guilty, he was removed from
service and sent to England
• Indians fought alongside British
1914-1918 World war 1 • Abolishment of Ottoman Empire in 1920 started
Khilafat movement (1919-1924)
• A meeting was held to send a delegation to
1919 (Nov) 1st Khilafat conference England, pursuing British not to abolish Khilafat
• Khilafat movement & Non-cooperation movement
1919 (Dec) 2nd Khilafat conference were merged
• M. Ali Johar lead the delegation to meet PM Lolyd
1920 Khilafat delegation George, but was refused to accept any proposals of
the Khilafat
• Military services were termed “HARAM”
1920 3rd Khilafat conference • Indians boycotted British schools, government jobs
and products
• Jinnah called Muslim leaders to discuss future
1927 Delhi Proposals constitutional reforms
• 3rd Reform was passed two years earlier as
1927 Simon commission government was changing in England
• In response to Simon commission all parties were
called
• The report allinated Muslim rights and Jinnah
1928 Nehru Report proposed 3 amendments which were also refused.
This marked the end of any future cooperation
between both parties
• They were in response to Simon commission and
1929 14 points of Jinnah Nehru report. They were also issued to protect the
rights of Muslims
• Idea of separate homeland was presented by Iqbal
1930 Allahabad address in AIML’s annual session
1st Round table • All parties attended the conference except Congress
1930 as they wanted Nehru report to be enforced
conference
2nd Round table • Gandhi refused to accept minority rights and kept
1931 rude behavior throughout the conference
conference
• Muslims accepted the award as it was favorable for
1932 Communal award them
3rd Round table
1932 • It was just a formality
conference
• British concluded Simon commission & RTC’s
1935 Government of India Act main talks and framed the law
• Both parties rejected it
• Congress gain victory over 5 provinces & forming
1936 Elections coalition in 4 provinces
• AIML lost their majority areas
• Cruelties with Muslims
1937-1939 Congress rule • Bande Matram (Hindu national poem)
• Wardha Scheme (Spinning of cotton)
• Congress resigned from ministeries, so on Jinnah’s
1939 Day of Deliverance advice, Muslims observed it as getting rid of
injustices by Congress rule
• On 22nd Mar, Jinnah chaired the meeting to have a
1940 Pakistan Resolution separate state for Muslims
• British wanted Indians to participate in World war 2
and assured to transfer power after war
1940 August offer • AIML wanted separate state & Congress wanted
immediate transfer of power
• 4th Reform by British to give dominion status to
1942 Cripps mission India after war
• Both parties rejected
• Congress passed a civil disobedience in response to
Cripps mission
1942 Quit India Movement • British arrested all prominent leaders of Congress
and AIML stayed neutral
• It was the last biggest Satyagraha by Gandhi
• Both leaders held meetings at Jinnah’s house in
1944 Gandhi-Jinnah talks Bombay from 9-27 Sep
• Jinnah refused to accept Gandhi’s demands
• British invited all parties from India after the war to
1945 Shimla conference leave India peacefully
• Conference failed
145-1946 Elections • AIML & Congress won in their majority areas
• A delegation was sent to frame the future
1946 Cabinet mission constitution
• Cabinet mission was rejected by Congress, so
1946 Direct action day AIML asked Muslims for strike and show their
strength for a separate homeland
• Lor Mountbatten (last viceroy) was sent to form a
solution. After it was approved by British it was
1947 3rd June plan announced on 3rd June
• It approved separation of India & Pakistan
• Approved on 15th July
1947 Independence act • Government of India act would be used as
temporary constitution
• On 16th Aug, sir Cyril Radcliffe announced the
Radcliffe Award
1947 boundaries of both states.
(boundary Commission) • Muslim Majority areas were given to India
• 1st Governor General
1947-1948 Quaid-e-Azam • Pakistan became part of UNO
• Faced early problems after partition
• 2nd Governor General
• Objectives resolution
1948-1951 Khuaja Nazim-ud-Din • Basic principle committee
• PRODA (disqualification act)
• Liaquat-Nehru pact signed in 1950
• 3rd Governor General
1951-1955 Malik Ghulam • Strikes to declare Ahmadis as non-Muslims
• 6 year economic plan
• Dismissed Khuaja Nazimuddin
• In Aug 1955 fell ill and resigned
• 4th Governor General
• Introduced One-unit scheme
• He made Pakistan’s 1st constitution
• He dismissed five prime minsters and appointed
1955-1958 Iskandar Mirza Ayub khan
• Due to economic crises, he imposed 1st martial law
and later Ayub khan forced him to resign and leave
Pakistan
• Capital shift to Islamabad
• Indus water treaty signed in 1960
• U2 spy plane incident
1958-1969 Ayub Khan • 1965 war
• Tashkent declaration signed in 1966
• Sheikh Mujeeb’s six points in 1966
• 1st General elections in 1970
1969-1971 Yahya Khan • War of 1971
• Separation of East Pakistan
• Shimla agreement signed with India & POW
1971-1977 Zulfiquar Ali Bhutto returned to Pakistan
• New constitution was enforced on 14th Aug 1973
• 2nd OIC held in Lahore in 1974
• Nationalization policy
• Execution of Bhutto in 1977
• Soviet-Afghan war in 19179
• Movement of Restoration of Democracy
• National referendum on Islamization in 1984
1977-1988 Zia-ul-Haq • Martial law lifted and Constitution of 1973 restored
in 1984
• Ojhri camp disaster in 1988
• Zia’s plane crash on 17th Aug 1988
1988-1990 Benazir’s 1st Tenure • Visited U.S.A and acquired 60 F-16 planes in 1989
• In 19991, Shariat bill was passed
• Cooperative societies scandal
1990-1993 Nawaz’s 1st Tenure • BCCI scandal in 1991
• Klashankov culture
• Pressler amendment was removed
• Pakistan sent 5000 soilders to Somalia by UN
1993-1996 Benazir’s 2nd Tenure • Train march by Nawaz
• Murtaza Bhutto killed at his residency in 1993 in a
police ambush
1997-1999 Nawaz’s 2nd Tenure • 8th amendment repealed
• In 1997, he was accused of corruption charges and a
mob stormed into the court during hearing
• Series of Nuclear tests carried out in 1998
• Pervaz Musharraf started war at Kargil
• Nawaz orders to replace Musharraf, but was exiled
to Saudia Arabia
You might also like
- Inglorious Empire: what the British did to IndiaFrom EverandInglorious Empire: what the British did to IndiaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Villasis Week 1 LMT - Poli PDFDocument9 pagesVillasis Week 1 LMT - Poli PDFKristinaCastellanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Decline of Muslim Rule in India and Arrival of BritishDocument23 pagesLecture 4 Decline of Muslim Rule in India and Arrival of Britishaiman nazeerNo ratings yet
- Modern IndiaDocument14 pagesModern IndiaShahidNo ratings yet
- L1 - Revolt of 1857 and INC SessionsDocument10 pagesL1 - Revolt of 1857 and INC Sessionsabhijeetdas164No ratings yet
- Khilafat MovementDocument8 pagesKhilafat Movementabdullah khalilNo ratings yet
- 4 Marks Q Grade 9Document6 pages4 Marks Q Grade 9Techno GamerNo ratings yet
- Political and Constitutional Developments in British India 1911-1929Document27 pagesPolitical and Constitutional Developments in British India 1911-1929osama iqbalNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument31 pagesEast India Companyomarali.office4877No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document12 pagesPresentation 1NitishNo ratings yet
- HIS-103 Lecture-4: Govt. of India Act 1919, Non-Cooperation Movement and The Khilafat MovementDocument27 pagesHIS-103 Lecture-4: Govt. of India Act 1919, Non-Cooperation Movement and The Khilafat MovementTaef Hossain 1531416630No ratings yet
- List of ViceroysDocument4 pagesList of ViceroysaishasiddiqbakhshNo ratings yet
- Making National Movement Part 3Document12 pagesMaking National Movement Part 3Machhindra DahifaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Causes & Effects of War of Independence 1857Document8 pagesLecture 05 Causes & Effects of War of Independence 1857Hamza ShahNo ratings yet
- List of Viceroys in IndiaDocument3 pagesList of Viceroys in IndiaRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chronology of Important Events Leading To Creation ofDocument27 pagesChronology of Important Events Leading To Creation ofWaqas MazharNo ratings yet
- 4 Marks Q Grade 9Document7 pages4 Marks Q Grade 9rizwanejazascNo ratings yet
- Pak Stud. Handouts Unit 1.3Document12 pagesPak Stud. Handouts Unit 1.3Liye MemonNo ratings yet
- Work of Viceroys of IndiaDocument4 pagesWork of Viceroys of Indiajkl manNo ratings yet
- Koonj 3467 19693 5 W2apsDocument13 pagesKoonj 3467 19693 5 W2apscontactbeselfhealthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-16 - British Rule Before 1857.pdf-72Document5 pagesChapter-16 - British Rule Before 1857.pdf-72Shivanand KamatarNo ratings yet
- HUM111 Slides Lecture06Document39 pagesHUM111 Slides Lecture06Sumaya KhalidNo ratings yet
- 1857 RevoltDocument7 pages1857 RevoltashaNo ratings yet
- Governor General/Viceroy Period Points To RememberDocument5 pagesGovernor General/Viceroy Period Points To Rememberkittu_sivaNo ratings yet
- 1857-1947 Pak StudyDocument30 pages1857-1947 Pak StudyAreeb UrNo ratings yet
- Tribal RevoltsDocument3 pagesTribal RevoltspeersaqibislamNo ratings yet
- History NotesDocument15 pagesHistory Notesceleste nixonNo ratings yet
- British ExpansionDocument31 pagesBritish ExpansionSamantha JonesNo ratings yet
- First They Ignore You Then They Laugh at You Then They Fight You Then You WinDocument37 pagesFirst They Ignore You Then They Laugh at You Then They Fight You Then You WinkiNo ratings yet
- The 1857 RevoltDocument7 pagesThe 1857 RevoltAzeeza ShaikNo ratings yet
- 1,2,3Document13 pages1,2,3dua latifNo ratings yet
- List of Viceroys in IndiaDocument4 pagesList of Viceroys in IndiaKiranNo ratings yet
- Advent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalDocument15 pagesAdvent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalFarhana Faruquee 1812059615No ratings yet
- Environmental Studies: Grade 5Document19 pagesEnvironmental Studies: Grade 5chethan_438784378No ratings yet
- India and China in The Age of ImperialismDocument7 pagesIndia and China in The Age of ImperialismKayeden CubacobNo ratings yet
- History 1Document41 pagesHistory 1juberNo ratings yet
- Governor General of India Upsc Note 59Document25 pagesGovernor General of India Upsc Note 59Naeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Time Line 2Document8 pagesTime Line 2Danial KashifNo ratings yet
- Historic Wars - IndiaDocument2 pagesHistoric Wars - IndiaSingh JiNo ratings yet
- List of Viceroys of India Upsc Notes 29Document7 pagesList of Viceroys of India Upsc Notes 29palisettiajay0No ratings yet
- Historical Background of PakistanDocument27 pagesHistorical Background of PakistanSameel AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Indian Freedom MOVEMENT (1857-1947) : Himani Jain Shift-Ii Div - A'Document17 pagesPresentation On Indian Freedom MOVEMENT (1857-1947) : Himani Jain Shift-Ii Div - A'Himani JainNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Studies P1 Crash NotesDocument16 pagesPakistan Studies P1 Crash Noteskazim.sohail110No ratings yet
- Nationalism in India NotesDocument28 pagesNationalism in India NotesradianceclassesdbgNo ratings yet
- Viceroys of IndiaDocument10 pagesViceroys of IndiaDr. Prashan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- 4.the Great Revolt of 1857Document3 pages4.the Great Revolt of 1857BaroNo ratings yet
- Military Institute of Science and Technology: Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering DepartmentDocument24 pagesMilitary Institute of Science and Technology: Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering DepartmentMuhammad Ashiqur Rahaman NoorNo ratings yet
- List of Viceroys of IndiaDocument3 pagesList of Viceroys of IndiaAbdul Hakeem100% (2)
- Safari - 16-Feb-2023 at 9:35 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 16-Feb-2023 at 9:35 PM10D Joel Alfred IsraelNo ratings yet
- Viceroys of IndiaDocument4 pagesViceroys of IndiaShyam SundarNo ratings yet
- Section IDocument62 pagesSection IFahad HussainNo ratings yet
- Hisotry Ncer - Theme 3 - Class 12 - Important PointersDocument3 pagesHisotry Ncer - Theme 3 - Class 12 - Important PointersAMSNo ratings yet
- Nationalism in India PDFDocument50 pagesNationalism in India PDFAshwin .R100% (2)
- CH 9 The Making of The National Movement 1870-1947 2Document24 pagesCH 9 The Making of The National Movement 1870-1947 2HENA AJAYAKUMAR100% (1)
- Chap 2 NotesDocument11 pagesChap 2 Notesumais kamranNo ratings yet
- History ProjectDocument12 pagesHistory ProjectRAJ SAHANo ratings yet
- The Great Uprising of 1857Document28 pagesThe Great Uprising of 1857ANAND GUPTANo ratings yet
- How Did EIC Start?Document21 pagesHow Did EIC Start?Ammar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Gandhi: "We Must Be The Change We Wish To See in The World"Document14 pagesMohandas Gandhi: "We Must Be The Change We Wish To See in The World"Kanna Rajesh DhanekulaNo ratings yet
- Modern History TimelineDocument2 pagesModern History TimelineDeepika JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Modern History of Bihar 41 PDFDocument21 pagesModern History of Bihar 41 PDFHago KrNo ratings yet
- Proposed Rape Kit Law - SB0014Document2 pagesProposed Rape Kit Law - SB0014FOX 17 News Digital StaffNo ratings yet
- English Diary 2021Document166 pagesEnglish Diary 2021Akash guptaNo ratings yet
- Sectarianism & Civil Society: 3 Parts of CocDocument3 pagesSectarianism & Civil Society: 3 Parts of CocDawoodNo ratings yet
- DSKH Villa Ecolake Binh Duong 154Document23 pagesDSKH Villa Ecolake Binh Duong 154Ti TanNo ratings yet
- Affordable CebuDocument19 pagesAffordable CebuNicko TanteNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Vivo Mobile India Private LimitedDocument1 pageTax Invoice: Vivo Mobile India Private LimitedRaghav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Virtue Ethics in NursingDocument4 pagesVirtue Ethics in NursingChubs Riego100% (1)
- Reportable: Ramgopal & Anr. ..... Appellant(s) Versus The State of Madhya Pradesh ..... RespondentDocument20 pagesReportable: Ramgopal & Anr. ..... Appellant(s) Versus The State of Madhya Pradesh ..... RespondentKARTHIKEYAN MNo ratings yet
- Notice To Brisk Intl. (PKG-9) SargodhaDocument2 pagesNotice To Brisk Intl. (PKG-9) Sargodhamuhammad ihtisham khanNo ratings yet
- State v. MariasDocument7 pagesState v. MariasSamuel RichardsonNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - 01 BBUN2103 CVR & CPDocument349 pagesMicrosoft Word - 01 BBUN2103 CVR & CPviosvario579No ratings yet
- National Highways Excellence Awards - Winners2019Document2 pagesNational Highways Excellence Awards - Winners2019Amit Kumar ChandaNo ratings yet
- 20-10-06 Epic Games v. Apple Case Scheduling and Pretrial OrderDocument3 pages20-10-06 Epic Games v. Apple Case Scheduling and Pretrial OrderFlorian MuellerNo ratings yet
- Unsettling Partition Jill DidurDocument212 pagesUnsettling Partition Jill Diduralifblog.orgNo ratings yet
- Spot Report Ra 9208 & Ra 8484Document2 pagesSpot Report Ra 9208 & Ra 8484Jack NapierNo ratings yet
- Outsource ProcedureDocument8 pagesOutsource Procedurejogender kumarNo ratings yet
- Enter The Body Makeover Challenge CompetitionDocument2 pagesEnter The Body Makeover Challenge CompetitionbmapiraNo ratings yet
- Republic of Kenya: County Government of BusiaDocument94 pagesRepublic of Kenya: County Government of BusiaSolidr ArchitectsNo ratings yet
- Sano V SBMADocument10 pagesSano V SBMAMara ClaraNo ratings yet
- ULAB 6100 SEMESTER II, 2018/2019 Critical Reading Test Author'S Purpose & Tone Due Date: 23 DECDocument4 pagesULAB 6100 SEMESTER II, 2018/2019 Critical Reading Test Author'S Purpose & Tone Due Date: 23 DECErik AidenNo ratings yet
- Using Statutory and Case Law, Discuss in Details The Principle of Relevancy. (25 Marks)Document7 pagesUsing Statutory and Case Law, Discuss in Details The Principle of Relevancy. (25 Marks)Brian Abaga100% (2)
- General Clauses Act, 1897Document24 pagesGeneral Clauses Act, 1897avniNo ratings yet
- Summary - Civil DisobedienceDocument3 pagesSummary - Civil DisobedienceQueenNo ratings yet
- Garcia Vs VazquezDocument1 pageGarcia Vs VazquezAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Ass No. 3Document2 pagesAss No. 3Ako C. IvanNo ratings yet
- Hse ManualDocument10 pagesHse ManualJkNo ratings yet
- Civics and Ethics Education For Grade 9 Chapter 12Document3 pagesCivics and Ethics Education For Grade 9 Chapter 12Moa Army100% (1)
- Policy Instrument Choice - HowlettDocument18 pagesPolicy Instrument Choice - HowlettChristin ChatrinNo ratings yet
- Violence As (De) Civilizing Process in Fight ClubDocument13 pagesViolence As (De) Civilizing Process in Fight ClubAnastasija OrlovaNo ratings yet