Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measurement
Measurement
Uploaded by
Cassandra Kate GuerreroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measurement
Measurement
Uploaded by
Cassandra Kate GuerreroCopyright:
Available Formats
Measurement is the basic concept in the study of Mathematics and Science.
Measurement
quantifies the characteristics of an object or event, which we can compare with other things or
events. Measurement is the most commonly used word, whenever we deal with the division of a
quantity. Also, in taking a certain amount of things to accomplish a particular task. In our daily
existence, we often come across different measurement types for length, weight, times, etc. In this
article, you will learn the meaning and definitions of measurement, along with types of measurement
and examples.
Types of Measurement
● Time
● Length
● Weight
● Volume
● Temperature
Measurement Units
Time: Units for expressing time include seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, years, etc.
Length: Units for measuring length include millimetres, centimetres, meters, kilometres, etc.
Weight: Units for expressing the weight of certain objects include grams, kilograms, tons, etc.
Volume: Units for expressing volume include cm3, m3, litres, etc.
Temperature: The major units of temperature include centigrade and fahrenheit.
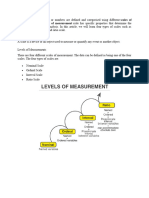
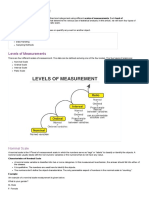
Measurement and Scaling
Nominal measurement: The nominal measurement scale is the first level of measurement scale in
which the numbers serve as titles or labels to categorise or recognise the objects. This scaling
usually deals with non-numeric variables or objects with no value.
Ordinal measurement: The ordinal measurement scale is the second level of measurement that
declares the ordering and ranking of data without designating the degree of variation among them.
Ordinal symbolises the “order.” Ordinal data is referred to as qualitative or categorical data, and this
data can be grouped and named also can be ranked.
Interval measurement: The interval measurement scale is the third level of measurement scale.
This scaling is a quantitative measurement scale in which we can express the difference between
any two variables.
Ratio measurement: The ratio measurement scale is the fourth level of measurement scale, which
is quantitative. The ratio scaling has a unique feature: it possesses the origin or zero points
character.
You might also like
- GebeDocument2 pagesGebeGebeyaw DemekeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document25 pagesUnit 3Yash SonkarNo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDocument2 pagesScales of Measurement - Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and RatioDESHRAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement Unit 4Document4 pagesScales of Measurement Unit 4sanju BarmanNo ratings yet
- M8-Research MethodologyDocument21 pagesM8-Research MethodologyLarissa Rodrigues GCHSNo ratings yet
- M7-Research MethodologyDocument20 pagesM7-Research MethodologyLarissa Rodrigues GCHSNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument70 pagesMeasurement and ScalingRitik ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument13 pagesMeasurement and ScalingARUNSANKAR NNo ratings yet
- Statistics Lecture Notes - UNIT 1Document8 pagesStatistics Lecture Notes - UNIT 1mphephubono9No ratings yet
- Engineering Stats Lecture NotesDocument143 pagesEngineering Stats Lecture NotesFatsoNo ratings yet
- ME 362: Instrumentation and Measurement Sessional: Lecture 1: The Process of MeasurementDocument14 pagesME 362: Instrumentation and Measurement Sessional: Lecture 1: The Process of Measurementদুর্জয় দুর্বারNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument11 pagesMeasurementRidhima jainNo ratings yet
- Standardized Measurement and AssessmentDocument6 pagesStandardized Measurement and AssessmentWalter MarquezNo ratings yet
- SBDnotes BFIA1BDocument4 pagesSBDnotes BFIA1BChetan SinghNo ratings yet
- Discussion 6Document2 pagesDiscussion 6Alexia Lesley LaxaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Statistics 02032021 122551amDocument3 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Statistics 02032021 122551amHafsa TanveerNo ratings yet
- Dimensions and UnitsDocument4 pagesDimensions and UnitsSadia BatoolNo ratings yet
- Measurement ToolDocument30 pagesMeasurement ToolLekhnath SubediNo ratings yet
- Research-Copmputing MUMBAIDocument43 pagesResearch-Copmputing MUMBAIAdelekan sodiqNo ratings yet
- Sta 301Document6 pagesSta 301bc210402586 HAFIZA ANIQA IRFANNo ratings yet
- Godfrey Summary Accounting Theory Chapter 5 MeasurementDocument7 pagesGodfrey Summary Accounting Theory Chapter 5 MeasurementEggie Auliya HusnaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probablity Note For EngineersDocument79 pagesStatistics and Probablity Note For EngineerstasheebedaneNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1Document91 pagesCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1Onetwothree Tube100% (1)
- Data and Its TypesDocument32 pagesData and Its TypesHassan Shah72No ratings yet
- Research Methodology: Tushar Sawant Rohit SinghaniaDocument26 pagesResearch Methodology: Tushar Sawant Rohit SinghaniaAmruta ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Level of MeasurementDocument4 pagesLevel of Measurementpegtimaryjoy091No ratings yet
- Measurement-Grade 7Document26 pagesMeasurement-Grade 7a.gayle1998No ratings yet
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note (For Engineering) - 1Document93 pagesCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note (For Engineering) - 1tazeb AbebeNo ratings yet
- 1 Units and Sig DigitsDocument20 pages1 Units and Sig DigitsSurendran NagiahNo ratings yet
- Scales of MeasurementDocument12 pagesScales of MeasurementXyrene Keith MedranoNo ratings yet
- Measurement and ScalingDocument14 pagesMeasurement and ScalingabcdNo ratings yet
- Numbers and NumDocument12 pagesNumbers and NumHarley MendesNo ratings yet
- Fba 324 Research SeminarDocument7 pagesFba 324 Research SeminarEMMANUEL LEKANNo ratings yet
- Stats Module 1Document6 pagesStats Module 1Mary Rose BioNo ratings yet
- SharewDocument3 pagesSharewgaroasenti44No ratings yet
- Measurement Theory: Ikhtisar Materi Kuliah Teori AkuntansiDocument13 pagesMeasurement Theory: Ikhtisar Materi Kuliah Teori AkuntansihaikalNo ratings yet
- Faryal NisarDocument7 pagesFaryal NisarSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Data & The Scales of Measurement: Data at The Highest Level: Qualitative and QuantitativeDocument7 pagesTypes of Data & The Scales of Measurement: Data at The Highest Level: Qualitative and QuantitativeSanthosh K SNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument3 pagesMeasurementMiguelThaxNo ratings yet
- Scales of MeasurementsDocument18 pagesScales of Measurementsuzma azamNo ratings yet
- 1.measurement and ScalingDocument44 pages1.measurement and ScalingGaganNo ratings yet
- Measurement - MetalworksDocument41 pagesMeasurement - MetalworksStyrich Nyl AbayonNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Mathematics Week 1 Lesson 1 - 2021 - Term 3Document5 pagesGrade 6 Mathematics Week 1 Lesson 1 - 2021 - Term 3MARK DEFREITASNo ratings yet
- Remaining NotesDocument13 pagesRemaining Notesparasharsamiksha0208No ratings yet
- Accounting Theory Chapter 5Document3 pagesAccounting Theory Chapter 5nabila IkaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BRM PDFDocument6 pagesUnit 3 BRM PDFvarshneypalak0No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Statistics RefresherDocument32 pagesLesson 2 Statistics RefresherEric PaderNo ratings yet
- Scales of Measurement: By-Yukti SharmaDocument15 pagesScales of Measurement: By-Yukti SharmaYukti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2-Skala Pengukuran Dan Ukuran DataDocument96 pagesPertemuan 2-Skala Pengukuran Dan Ukuran DataRestu BisnisNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis - WikipediaDocument75 pagesDimensional Analysis - WikipediaThawdar TunNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument9 pagesMeasurement ScalesAsim KhanNo ratings yet
- Continues VariablesDocument7 pagesContinues Variablesjuanelx2023No ratings yet
- CH 4 MeasurementDocument10 pagesCH 4 Measurementlenalena123100% (2)
- CH 7 Data MeasurementDocument17 pagesCH 7 Data MeasurementShoyeab Rahman AbirNo ratings yet
- Quantity. The Result of The Measurement Is A Numeric Value With Certain Units. We CanDocument1 pageQuantity. The Result of The Measurement Is A Numeric Value With Certain Units. We CanJubelle Mae Batalla RentuzaNo ratings yet
- EDUM 541 - Research: Ivy Leah P. Santillan - Maed IDocument27 pagesEDUM 541 - Research: Ivy Leah P. Santillan - Maed IMeriam Gornez TorresNo ratings yet
- Four Different Levels of MeasurementDocument2 pagesFour Different Levels of MeasurementMaria Isabella RuaYanaNo ratings yet
- GEM 804 - Advance Engineering Statistic: Types of Variable and Level of MeasurementDocument14 pagesGEM 804 - Advance Engineering Statistic: Types of Variable and Level of MeasurementLeah Ann ManuelNo ratings yet
- Variables We Wish To Study. A Variable Is Something That Can Change or Vary. For Example, A Variable ofDocument6 pagesVariables We Wish To Study. A Variable Is Something That Can Change or Vary. For Example, A Variable ofLisa FerraroNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankFrom EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Research TitlesDocument11 pagesGroup 2 Research TitlesCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- ED 5 Report TopicsDocument6 pagesED 5 Report TopicsCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- The Shift of Educational Focus From Content To Learning OutcomesDocument2 pagesThe Shift of Educational Focus From Content To Learning OutcomesCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Jean Piaget and Cognitive LearningDocument25 pagesJean Piaget and Cognitive LearningCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Aproaches and Methods in Teaching Ap in The Intermediate LevelDocument3 pagesAproaches and Methods in Teaching Ap in The Intermediate LevelCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Report ExplanationDocument2 pagesReport ExplanationCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- The Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts 1Document16 pagesThe Self in Western and Eastern Thoughts 1Cassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet