Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes
Enzymes
Uploaded by
Vedant SinghCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes
Enzymes
Uploaded by
Vedant SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes | IGCSE Biology and GCSE Biology Revision
Save My Exams
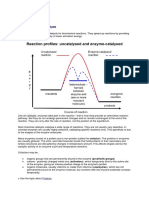
An enzyme is a biological catalyst, which means it speeds up chemical
reactions without being used up in the process. Enzymes are important
in living organisms because they allow reactions to occur at lower
temperatures than would normally be possible without a catalyst.
Enzymes play a role in various metabolic processes such as respiration,
photosynthesis, and digestion. They are called biological catalysts
because they are made from proteins, which are composed of amino
acids held together by bonds. However, these bonds can break under
certain conditions, such as changes in temperature and pH, causing the
enzyme to lose its shape and become denatured.
The lock and key model is a way to describe how enzymes function. The
reactant, known as the substrate, has a specific shape that fits into the
enzyme's active site, similar to how a key fits into a lock. When the
substrate binds to the active site, the reaction occurs. Enzyme specificity
refers to the fact that each enzyme can only catalyse reactions with the
correct shaped substrate. This means that each enzyme typically
catalyses only one type of reaction.
It's important to note that the enzyme and substrate are not the same
shape; rather, they are complementary in shape to each other. Enzymes
and substrates are in constant motion due to their kinetic energy.
Sometimes, they collide and the substrate binds to the enzyme's active
site, forming an enzyme-substrate complex. The reaction then takes
place, converting the substrate into a product. After the product is
formed, it detaches from the enzyme and diffuses away, allowing the
enzyme to catalyze another reaction.
In summary, enzymes are biological catalysts that bind to substrates at
their active sites to catalyze reactions. The lock and key model illustrates
how the enzyme's active site acts as a lock, joining with the substrate,
which is the key. Most enzymes are specific to only one type of reaction.
The enzyme and substrate move around due to their kinetic energy, and
when they collide, the enzyme-substrate complex forms, leading to the
reaction and product formation. Afterward, the product detaches from
the enzyme and diffuses away, making the enzyme available for another
reaction.
You might also like
- Enzyme NotesDocument4 pagesEnzyme NotesPreethaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymessashi bNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation: EnzymesDocument7 pagesProtein Denaturation: EnzymescharlesNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: E E E EDocument15 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: E E E EFarhana MuradNo ratings yet
- Inhibition and RegulationDocument28 pagesInhibition and RegulationRoyal MindNo ratings yet
- Sameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureDocument5 pagesSameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureSameer ButtNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument23 pagesEnzymessamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Lecture On EnzymesDocument26 pagesLecture On EnzymesDAVIE MATIASNo ratings yet
- Enzyme StructureDocument17 pagesEnzyme Structureام احمدNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document6 pagesEnzymes 1zarszNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymeskhadija92sara32No ratings yet
- Jessica Lee Enzyme LabDocument15 pagesJessica Lee Enzyme LabAshalee JonesNo ratings yet
- GCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME NoteDocument11 pagesGCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME Notengnicole090607No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Function and StructureDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Function and Structuretiyf mojaleedNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - Doc Version 1Document7 pagesEnzymes - Doc Version 1LALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Bio IgcseDocument7 pagesChap 5 Bio Igcseananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument41 pagesBiology ProjectGanesan Siva67% (12)
- GEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesGEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam ReviewerVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanDocument11 pagesEnzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- Enzyme, A Substance That Acts As ADocument5 pagesEnzyme, A Substance That Acts As Amuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Role of Enzymes in MetabolismDocument6 pagesRole of Enzymes in MetabolismJett Matthew AquinoNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab Theory DiscussionDocument4 pagesEnzyme Lab Theory DiscussionQuade FrancesNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Inorganic Chemistry AssignmentDocument17 pagesEnzyme: Inorganic Chemistry AssignmentAakash ShahNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Enzymes AreDocument11 pagesEnzyme: Enzymes ArePiyush BhallaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Principles of BiologyDocument18 pagesEnzymes: Principles of BiologyNaskar SouvikNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Chapter 3 - EnzymesDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY Chapter 3 - Enzymeschelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 5Document6 pagesVIII Biology HO 5aditiroy201208No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Mechanism of Enzymatic ActionDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Mechanism of Enzymatic ActionMoon PhạmNo ratings yet
- Jontong Harvey (Enzymes)Document6 pagesJontong Harvey (Enzymes)Harvey Q. JontongNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and The Active SiteDocument23 pagesEnzymes and The Active SiteLaura GambaNo ratings yet
- 34Document1 page34abiudonsare1No ratings yet
- 34Document1 page34abiudonsare1No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Keshav Vashistha (Associate Professor, M.G.C.P.S., Jaipur)Document7 pagesEnzymes: Keshav Vashistha (Associate Professor, M.G.C.P.S., Jaipur)KeshavVashisthaNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesii15021No ratings yet
- Week 6 EnzymessDocument49 pagesWeek 6 EnzymessRechell Mae DaclesNo ratings yet
- Module 11: EnzymesDocument3 pagesModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariNo ratings yet
- Enzymes FinalDocument1 pageEnzymes FinalAlyssa Katrina SitoyNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12Document7 pagesEnzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12almira garciaNo ratings yet
- 4-C1.1 Enzymes and MetabolismDocument42 pages4-C1.1 Enzymes and Metabolismmakaya02No ratings yet
- Lesson #8 - EnzymesDocument29 pagesLesson #8 - EnzymesMaya AwadNo ratings yet
- Scienze e Rapporto Uomo NaturaDocument2 pagesScienze e Rapporto Uomo NaturaEmilia EspositoNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (HL)Document26 pagesMetabolism (HL)Sapreen KaurNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument1 pageEnzymesKarim El NefeidiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes in Food IndustryDocument67 pagesEnzymes in Food Industryamrutha tkNo ratings yet
- Genes & Inheritance SeriesDocument58 pagesGenes & Inheritance SeriesKim HoangNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ClassificationDocument8 pagesEnzyme ClassificationR.KRISHNA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Enzymes: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme RegulationDocument16 pagesEnzyme RegulationnadimbioinformaticsNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument9 pagesEnzymes42h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 EnzymesDocument4 pagesCh-5 EnzymesMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument31 pagesEnzymemiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Lesson, The Learners Shall Be Able ToDocument5 pagesAt The End of The Lesson, The Learners Shall Be Able ToYenzy Dariel Cabrillos AurelioNo ratings yet
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDocument26 pagesEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesAyesha JamilNo ratings yet
- KavetaDocument2 pagesKavetaDoc_Neurologist8478No ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The PH ScaleDocument2 pagesThe PH ScaleVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument1 pageArtificial IntelligenceVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.1.4 Features of OrganismsDocument41 pages1.1.4 Features of OrganismsVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 - Programming Companion Python-If SatementsDocument9 pages4 - Programming Companion Python-If SatementsVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.6. Representing Images, Sound and Other DataDocument8 pages5.6. Representing Images, Sound and Other DataVedant SinghNo ratings yet