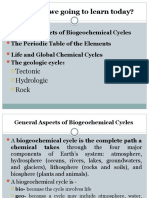
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrosphere
Hydrosphere
Uploaded by
igor.janickiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Environmental HydrologyDocument60 pagesEnvironmental HydrologyAbelNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Water Distribution On EarthDocument2 pagesHydrology Water Distribution On EarthgkkumarrajNo ratings yet
- Environmental HydrologyDocument88 pagesEnvironmental HydrologyTigist TameneNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering PDFDocument259 pagesWater Resources Engineering PDFEfraim PablacioNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument6 pagesHydrologyRaman LuxNo ratings yet
- Environment 2Document2 pagesEnvironment 2Sahil SoodNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester NoteDocument40 pages2nd Semester NoteAbinash Mardi100% (1)
- HydrosphereDocument1 pageHydrosphereJinn Allan LuañaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of HydrogeologyDocument3 pagesConcepts of HydrogeologyT N Roland BourgeNo ratings yet
- Water On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDocument1 pageWater On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDoung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Environmental SystemsDocument5 pagesEnvironmental SystemsMehwishNo ratings yet
- The EarthDocument1 pageThe EarthJhon AlcoyNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CR Hr. 3: Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Dire Dawa UniversityDocument42 pagesCourse Code: CR Hr. 3: Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Dire Dawa UniversityAbdisadebele BedaneNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Environment: Overview of LectureDocument18 pagesL1 Introduction To Environment: Overview of LectureFardeen KhanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 1Document41 pagesHydrology 1hazelanncabinianNo ratings yet
- Ecohydrology Ecohydrology (from Greek οἶκος, oikos, "house (hold) "; ὕδωρ,Document14 pagesEcohydrology Ecohydrology (from Greek οἶκος, oikos, "house (hold) "; ὕδωρ,annisaNo ratings yet
- Ce 324 Updated LectureDocument32 pagesCe 324 Updated LectureCharles William ValentonNo ratings yet
- Journal Topics 4-6 - CRUZ YSADocument2 pagesJournal Topics 4-6 - CRUZ YSAYSA JANELLE CRUZNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument38 pagesHydrologyMelannie ArgenteraNo ratings yet
- Subject Matter of Physical GeographyDocument3 pagesSubject Matter of Physical GeographyAl Sakib RahmanNo ratings yet
- 101 PresentationDocument31 pages101 PresentationIbrahim IslamNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTDocument12 pagesENVIRONMENTrakesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Constituents of Environment: Physical or Abiotic EnvironmentDocument6 pagesConstituents of Environment: Physical or Abiotic EnvironmentAvvai VijayaNo ratings yet
- Realms of Earth GeographyDocument2 pagesRealms of Earth GeographyNeha Khalid02No ratings yet
- Hydrology and Climatology For BSC Forestry StudentsDocument83 pagesHydrology and Climatology For BSC Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment: Unit Processes of Secondary TreatmentDocument9 pagesWastewater Treatment: Unit Processes of Secondary TreatmentMarco Ramos JacobNo ratings yet
- Envi. Sci-BuayaDocument1 pageEnvi. Sci-BuayaRochelle MaeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies: - Shaik TouseefDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Studies: - Shaik TouseefindianNo ratings yet
- Hydrology AssignmentDocument20 pagesHydrology AssignmentMannat DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- SummarizeDocument7 pagesSummarizesaturinas.136539142065No ratings yet
- Docs 1Document2 pagesDocs 1Jobelle RafaelNo ratings yet
- BCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Document29 pagesBCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Philip TibenderanaNo ratings yet
- Env 107-5Document13 pagesEnv 107-5Avishek PaulNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Class 01 24 2023Document2 pagesHydrology Class 01 24 2023Kamii Ryu DumpNo ratings yet
- Major Domains of The Earth: Posted On: Mar 19,2010Document2 pagesMajor Domains of The Earth: Posted On: Mar 19,2010rbanandNo ratings yet
- Evs Unit 1Document40 pagesEvs Unit 1Aryan PawarNo ratings yet
- SignificaceDocument1 pageSignificaceisaakongtamadNo ratings yet
- FC Unit III EcologyDocument110 pagesFC Unit III EcologyMahiman pandyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Is The Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality ofDocument8 pagesHydrology Is The Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality ofkamdemonnNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Introduction PDFDocument16 pagesChap 1 - Introduction PDFRezaul KarimNo ratings yet
- Ce322 AssignmentDocument2 pagesCe322 AssignmentAloysius LaparaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Subsystem of The Earth - 102842Document12 pagesLesson 2 Subsystem of The Earth - 102842Marian Evangelista MoralesNo ratings yet
- Bcom 210Document77 pagesBcom 210groy43682No ratings yet
- Materi 1 Hidrologi 2022Document49 pagesMateri 1 Hidrologi 2022Diva AnandaNo ratings yet
- Intro. To Env. SystemsDocument14 pagesIntro. To Env. SystemsJohn SimwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument19 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- Types of EnvironmentDocument13 pagesTypes of EnvironmentNayeema khanNo ratings yet
- Water 5Document5 pagesWater 5Rey Jr. Cobel CababasadaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 1 (Introduction - The - Hydrologic - and - Carbon - Cycle)Document29 pagesHydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 1 (Introduction - The - Hydrologic - and - Carbon - Cycle)joelkyeswa97No ratings yet
- WaterDocument1 pageWaterPedro MiguelNo ratings yet
- Imran AssignmentDocument23 pagesImran Assignmentmahek shaikhNo ratings yet
- Evs - Final Unit 1 - IntroductionDocument96 pagesEvs - Final Unit 1 - IntroductionJay Guruprasad KanitkarNo ratings yet
- Emp 316.2, Complete-Note, 2023Document53 pagesEmp 316.2, Complete-Note, 2023uc211heNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Co1Document27 pagesHydrology Co1Jeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Hydrologic CycleDocument63 pagesChapter 1 Hydrologic CyclesubxaanalahNo ratings yet
- ENVI SCI NOTES 1 EcosystemDocument7 pagesENVI SCI NOTES 1 EcosystemabiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Water Resources EngineeringDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Water Resources EngineeringMayolites100% (1)
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
Hydrosphere
Hydrosphere
Uploaded by
igor.janickiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrosphere
Hydrosphere
Uploaded by
igor.janickiCopyright:
Available Formats
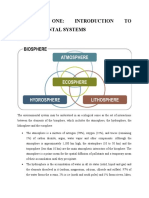
Definition: The hydrosphere refers to all the water on Earth's surface, including oceans, seas, rivers,
lakes, glaciers, groundwater, and atmospheric water vapor.
Water Distribution: Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by water, with the majority
(about 97%) found in oceans and seas. The remaining 3% is freshwater, found in glaciers, rivers, lakes,
and groundwater.
Importance: The hydrosphere plays a crucial role in supporting life on Earth. It regulates the climate,
influences weather patterns, provides habitat for diverse aquatic ecosystems, and is essential for human
survival, agriculture, industry, and transportation.
Oceanography: Oceanography is the scientific study of the oceans and is a multidisciplinary field that
encompasses various branches of science, including biology, chemistry, physics, geology, and
meteorology.
Water Cycle: The hydrosphere is interconnected with other Earth systems through the water cycle, also
known as the hydrological cycle. This continuous process involves the movement of water between the
atmosphere, land, and oceans through processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation,
runoff, infiltration, and transpiration.
Global Water Crisis: Despite the abundance of water on Earth, access to clean freshwater is a pressing
global issue. Population growth, urbanization, industrialization, pollution, climate change, and
unsustainable water management practices have led to water scarcity, pollution, and environmental
degradation in many regions.
Conservation and Management: Sustainable management of the hydrosphere is essential for ensuring
water security, protecting aquatic ecosystems, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Conservation efforts, water recycling, desalination, watershed management, and international
cooperation are among the strategies employed to address water-related challenges.
Understanding the hydrosphere and its dynamics is critical for addressing global water issues, promoting
environmental sustainability, and safeguarding the planet's ecosystems and resources.
You might also like
- Environmental HydrologyDocument60 pagesEnvironmental HydrologyAbelNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Water Distribution On EarthDocument2 pagesHydrology Water Distribution On EarthgkkumarrajNo ratings yet
- Environmental HydrologyDocument88 pagesEnvironmental HydrologyTigist TameneNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering PDFDocument259 pagesWater Resources Engineering PDFEfraim PablacioNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument6 pagesHydrologyRaman LuxNo ratings yet
- Environment 2Document2 pagesEnvironment 2Sahil SoodNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester NoteDocument40 pages2nd Semester NoteAbinash Mardi100% (1)
- HydrosphereDocument1 pageHydrosphereJinn Allan LuañaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of HydrogeologyDocument3 pagesConcepts of HydrogeologyT N Roland BourgeNo ratings yet
- Water On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDocument1 pageWater On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDoung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Environmental SystemsDocument5 pagesEnvironmental SystemsMehwishNo ratings yet
- The EarthDocument1 pageThe EarthJhon AlcoyNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CR Hr. 3: Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Dire Dawa UniversityDocument42 pagesCourse Code: CR Hr. 3: Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Dire Dawa UniversityAbdisadebele BedaneNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction To Environment: Overview of LectureDocument18 pagesL1 Introduction To Environment: Overview of LectureFardeen KhanNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 1Document41 pagesHydrology 1hazelanncabinianNo ratings yet
- Ecohydrology Ecohydrology (from Greek οἶκος, oikos, "house (hold) "; ὕδωρ,Document14 pagesEcohydrology Ecohydrology (from Greek οἶκος, oikos, "house (hold) "; ὕδωρ,annisaNo ratings yet
- Ce 324 Updated LectureDocument32 pagesCe 324 Updated LectureCharles William ValentonNo ratings yet
- Journal Topics 4-6 - CRUZ YSADocument2 pagesJournal Topics 4-6 - CRUZ YSAYSA JANELLE CRUZNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument38 pagesHydrologyMelannie ArgenteraNo ratings yet
- Subject Matter of Physical GeographyDocument3 pagesSubject Matter of Physical GeographyAl Sakib RahmanNo ratings yet
- 101 PresentationDocument31 pages101 PresentationIbrahim IslamNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTDocument12 pagesENVIRONMENTrakesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Constituents of Environment: Physical or Abiotic EnvironmentDocument6 pagesConstituents of Environment: Physical or Abiotic EnvironmentAvvai VijayaNo ratings yet
- Realms of Earth GeographyDocument2 pagesRealms of Earth GeographyNeha Khalid02No ratings yet
- Hydrology and Climatology For BSC Forestry StudentsDocument83 pagesHydrology and Climatology For BSC Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment: Unit Processes of Secondary TreatmentDocument9 pagesWastewater Treatment: Unit Processes of Secondary TreatmentMarco Ramos JacobNo ratings yet
- Envi. Sci-BuayaDocument1 pageEnvi. Sci-BuayaRochelle MaeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies: - Shaik TouseefDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Studies: - Shaik TouseefindianNo ratings yet
- Hydrology AssignmentDocument20 pagesHydrology AssignmentMannat DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- SummarizeDocument7 pagesSummarizesaturinas.136539142065No ratings yet
- Docs 1Document2 pagesDocs 1Jobelle RafaelNo ratings yet
- BCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Document29 pagesBCE 3102 Hydrology and Hydraulics - Lecture 2 (The Hydrologic and Carbon Cycle)Philip TibenderanaNo ratings yet
- Env 107-5Document13 pagesEnv 107-5Avishek PaulNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Class 01 24 2023Document2 pagesHydrology Class 01 24 2023Kamii Ryu DumpNo ratings yet
- Major Domains of The Earth: Posted On: Mar 19,2010Document2 pagesMajor Domains of The Earth: Posted On: Mar 19,2010rbanandNo ratings yet
- Evs Unit 1Document40 pagesEvs Unit 1Aryan PawarNo ratings yet
- SignificaceDocument1 pageSignificaceisaakongtamadNo ratings yet
- FC Unit III EcologyDocument110 pagesFC Unit III EcologyMahiman pandyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Is The Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality ofDocument8 pagesHydrology Is The Study of The Movement, Distribution, and Quality ofkamdemonnNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Introduction PDFDocument16 pagesChap 1 - Introduction PDFRezaul KarimNo ratings yet
- Ce322 AssignmentDocument2 pagesCe322 AssignmentAloysius LaparaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Subsystem of The Earth - 102842Document12 pagesLesson 2 Subsystem of The Earth - 102842Marian Evangelista MoralesNo ratings yet
- Bcom 210Document77 pagesBcom 210groy43682No ratings yet
- Materi 1 Hidrologi 2022Document49 pagesMateri 1 Hidrologi 2022Diva AnandaNo ratings yet
- Intro. To Env. SystemsDocument14 pagesIntro. To Env. SystemsJohn SimwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument19 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionAbdanur JihadNo ratings yet
- Types of EnvironmentDocument13 pagesTypes of EnvironmentNayeema khanNo ratings yet
- Water 5Document5 pagesWater 5Rey Jr. Cobel CababasadaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 1 (Introduction - The - Hydrologic - and - Carbon - Cycle)Document29 pagesHydraulics and Hydrology - Lecture 1 (Introduction - The - Hydrologic - and - Carbon - Cycle)joelkyeswa97No ratings yet
- WaterDocument1 pageWaterPedro MiguelNo ratings yet
- Imran AssignmentDocument23 pagesImran Assignmentmahek shaikhNo ratings yet
- Evs - Final Unit 1 - IntroductionDocument96 pagesEvs - Final Unit 1 - IntroductionJay Guruprasad KanitkarNo ratings yet
- Emp 316.2, Complete-Note, 2023Document53 pagesEmp 316.2, Complete-Note, 2023uc211heNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Co1Document27 pagesHydrology Co1Jeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Hydrologic CycleDocument63 pagesChapter 1 Hydrologic CyclesubxaanalahNo ratings yet
- ENVI SCI NOTES 1 EcosystemDocument7 pagesENVI SCI NOTES 1 EcosystemabiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Water Resources EngineeringDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Water Resources EngineeringMayolites100% (1)
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet