Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PR 1st Sem Prelims
PR 1st Sem Prelims
Uploaded by
Daligdig, Queen DuqueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PR 1st Sem Prelims
PR 1st Sem Prelims
Uploaded by
Daligdig, Queen DuqueCopyright:
Available Formats
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2 1ST SEM PRELIMS September 19 2023 7:20 - 8:00
COVERAGE: KINDS OF QR DESIGN, QR ACROSS DIFF. FIELDS, VARIABLES 11C Salinas, Lizbeth Lhen L.
Practical Research 2
INTERRUPTED TIME SERIES DESIGN
Employs multiple measures before and after the
experimental intervention
Kinds of QR Design It differs from the single-group pre-experiment that
has only one pretest and one posttest
Users of this design assume that the time threats
NOTE: QR = Quantitative Research
such as history or maturation appear as regular
RESEARCH DESIGN changes in the measures prior to the intervention.
The overall strategy that you choose in order to
integrate the different components of the study in PRE-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
a coherent and logical way, thereby ensuring you A designs with the least internal validity
will effectively address the research problem. One type of pre-experiment, the single group, pre-
test-post-test design, measures the group two
times, before and after the intervention.
NON-EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
External variables are introduced.
The variables are not deliberately manipulated nor
is the setting controlled
Researchers collect data without making changes or
introducing treatments
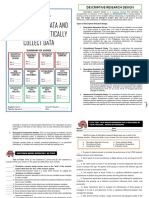
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH DESCRIPTIVE DESIGN
Allows the researcher to control the situation Main purpose is to observe, describe and
It allows the researcher to answer the question, document aspects of a situation as it naturally
"What causes something to occur?" occurs and sometimes to serve as a starting point
Allows the researcher to identify cause and effect for hypothesis generation or theory development
relationships between variables and to distinguish TYPES OF DESCRIPTIVE RESEARCH DESIGN
placebo effects from treatment effects. SURVEY
Creswell, 2003 - used when the researcher intends
CLASSES OF EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH to provide a quantitative or numeric description of
TRUE EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN trends, attitudes or opinions of a population by
Controls for both time-related and group-related studying a sample of that population
threats.
Two or more differently treated groups and random BIVARIATE CORRELATIONAL STUDIES
assignment to these groups. Obtain scores from two variables for each subject,
The researchers have control over the experimental then use them to calculate a correlation coefficient.
treatment and the power to place subjects in The term bivariate implies that the two variables
groups are correlated (variables are selected because they
are believed to be related).
QUASI-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
The researcher can collect more data, either by PREDICTION STUDIES
scheduling more observations or finding more Use correlation co-efficient to show how one
existing measures. variable (the predictor variable) predicts another
TYPES OF QUASI-EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN (the criterion variable).
NON-EQUIVALENT CONTROL GROUP DESIGN
the chance failure of random assignment to MULTIPLE REGRESSION PREDICTION STUDIES
equalize the conditions by converting a true The over-all prediction in an equation that adds
experiment into this kind of design, for purposes of together the predictive power of each identified
analysis. variable.
Pakisabi po if may mali. Thank you and do well ! 1/3
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2 1ST SEM PRELIMS September 19 2023 7:20 - 8:00
COVERAGE: KINDS OF QR DESIGN, QR ACROSS DIFF. FIELDS, VARIABLES 11C Salinas, Lizbeth Lhen L.
EX-POST FACTO RESEARCH DESIGN BEHAVIORAL SCIENCES
Used to investigate causal relationships. They The output of this research focuses on how human
examine whether one or more pre- existing behavior relates with another people and also the
conditions could possibly have caused subsequent individual differences that may affect human
differences in groups of subjects. relations.
COMPARATIVE DESIGN EDUCATION AND PSYCHOLOGY
involves comparing and contrasting two or more Many educational principles in understanding
samples of study subjects on one or more variables, human behavior are the offshoot of this research
often at a single point of time.
Specifically, this design is used to compare two SOCIAL SCIENCE
distinct groups on the basis of selected attributes The method employed in this type of quantitative
such as knowledge level, perceptions, and social research are mostly typically the survey and
attitudes, physical or psychological symptoms. the experiment.
Variables
EVALUATE RESEARCH
seeks to assess or judge in some way providing
information about something other than might be A characteristics or attribute of an individual or an
gleaned in mere observation or investigation of organization that can be measured or observed and
relationships. that varies among people or organization being
studied.
METHODOLOGICAL
the implementation of a variety of methodologies
THE NATURE OF VARIABLES AND DATA
forms a critical part of achieving the goal of NOMINAL VARIABLES
developing a scale-matched approach, where data Represents categories that cannot be ordered in
from different disciplines can be integrated any particular way.
These are variables whose data are non-numeric
QR Across Diff. labels that do not reflect quantitative information
Fields ORDINAL VARIABLES
ANTHROPOLOGY Represents categories that can be ordered from
Many discoveries in this field like human behavior smallest to greatest.
in the society, racial conflicts and human evolution It refers to variables where there is a meaningful
have given enormous contributions to the order or categories but there is no measurable
improvement of human life. distance between categories
COMMUNICATION INTERVAL VARIABLES
Researchers are often interested in how an Values that lie along an evenly dispersed range of
understanding of a particular communication numbers.
phenomena might be generalized to a larger It is a variable whose data values are ranged in a
population. real interval and can be as large as from negative
infinity to positive infinity.
MEDICINE
This tends to be predominantly observational RATIO VARIABLES
research based on surveys or correlational studies. Have values that lie along an evenly dispersed
Experimental research designs may enhance the range of numbers when there is an absolute zero.
quality of medical education.
Pakisabi po if may mali. Thank you and do well ! 2/3
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2 1ST SEM PRELIMS September 19 2023 7:20 - 8:00
COVERAGE: KINDS OF QR DESIGN, QR ACROSS DIFF. FIELDS, VARIABLES 11C Salinas, Lizbeth Lhen L.
KINDS OF VARIABLES
INDEPENDENT VARIABLES
Those that probably cause influence or affect
outcomes.
They are invariably called treatment, manipulated,
antecedent or predictor variables
DEPENDENT VARIABLES
Those that depend on the independent variables;
they are the outcomes of the influence of the
independent variable.
INTERVENING OR MEDIATING VARIABLES
“stand between” the independent and dependent
variables and they show the effects of the
independent variable on the dependent variable.
CONTROL VARIABLES
Special type of independent variables that are
measured in a study because they influence the
dependent variable.
Researchers use statistical procedures (analysis of
covariance [ANCOVA]) to control these variables
CONDOUNDING VARIABLES
Those that are not actually measured or observed
in a study. They exist but their influence cannot be
directly detected in a study.
EXAMPLES OF VARIABLES RELATED TO A
PHENOMENON
• Phenomenon: Climate Change
• Examples of variables related to climate change:
1. Sea level
2. temperature
3. The amount of carbon emission
4. the amount of rainfall
Pakisabi po if may mali. Thank you and do well ! 3/3
You might also like
- Customer Satisfaction Towards McDonald'sDocument50 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Towards McDonald'sChandan Srivastava75% (4)
- Types of Quantitative ResearchDocument26 pagesTypes of Quantitative Researchakira terushimaNo ratings yet
- Finaldocument-Visa Interview Questions Date06122010Document15 pagesFinaldocument-Visa Interview Questions Date06122010WorkNo ratings yet
- Research Ii PartDocument62 pagesResearch Ii PartPrecilla C. StephenNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Quantitative Research DesignsDocument3 pagesKinds of Quantitative Research DesignsAnalie CabanlitNo ratings yet
- Types - of - Quantitative - Research - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''Types of Quantitative ResearchDocument16 pagesTypes - of - Quantitative - Research - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''Types of Quantitative ResearchCris VillarNo ratings yet
- PR ReviwerDocument5 pagesPR ReviwerMichelle CailaNo ratings yet
- App 2 Finals - Quanti MethodsDocument3 pagesApp 2 Finals - Quanti MethodsBryle GarayNo ratings yet
- Prac - Res m1 8 Lesson ReviewerDocument6 pagesPrac - Res m1 8 Lesson ReviewerShinra ValdemothNo ratings yet
- PR For PTDocument3 pagesPR For PTAbbyjane MadlangsakayNo ratings yet
- PR Research DesignsDocument11 pagesPR Research DesignsJulienne BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map FinalDocument1 pageMind Map FinalGinielle Gem Atim BelarminoNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument36 pagesPractical ResearchGeline De Jesus MarquezNo ratings yet
- Focuses On Gathering Numerical Data: QuantitativeDocument8 pagesFocuses On Gathering Numerical Data: QuantitativeCHIELOU MARIE T. POGOYNo ratings yet
- Correlational & Quasi Experimental DesignsDocument52 pagesCorrelational & Quasi Experimental DesignsFerdinand PagaranNo ratings yet
- 3 Kinds of Quantitaive Researh DesignDocument30 pages3 Kinds of Quantitaive Researh DesignKitchie Dianne BejarinNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchCortado, Jeffer SolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5.readingsDocument3 pagesLesson 5.readingsCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument48 pagesMethodologybarbie robertsNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Quantitative Research DesignsDocument1 pageKinds of Quantitative Research DesignsRic SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1 Characteristics StrenDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1 Characteristics StrenDonna CasillaNo ratings yet
- Main Goals of Research Quasi-Experimental Research DesignDocument8 pagesMain Goals of Research Quasi-Experimental Research DesignseanakkigNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Research 2Document5 pagesHandouts in Research 2nona yamutNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 ReviewerMaria Christine OgenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Activities With LessonsDocument24 pagesUnit 4 Activities With LessonsAndrea Serrano100% (1)
- DR - Maheswari Jaikumar: VariableDocument36 pagesDR - Maheswari Jaikumar: VariableRomulo Dumala BalendoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 RevDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 RevChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Lessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative ResearchDocument17 pagesLessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative Researchjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument12 pagesResearch DesignDennis S. AgudoNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument16 pagesThe Nature of Inquiry and ResearchElenear De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Lesson 1Document3 pagesPractical Research 2 Lesson 1Pepito ManlolokoNo ratings yet
- Formulation of The Research TitleDocument14 pagesFormulation of The Research TitleSeizashino AkiyamaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Research 2Document8 pagesModule 1 - Research 2Jayvee Ken Celis RocillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchDocument8 pagesLesson 1: The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchAlma Cecilia Quiao100% (1)
- PR 2 - Lesson 2Document15 pagesPR 2 - Lesson 2Ilonah Jean Benito VivencioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Research Design 1 PDFDocument43 pagesLesson 5 Research Design 1 PDFjhonel ballerasNo ratings yet
- Laguna State Polytechnic University: Los Baños Campus Los Baños, LagunaDocument8 pagesLaguna State Polytechnic University: Los Baños Campus Los Baños, LagunaAnthonyAlinsodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Writing MethodologyDocument31 pagesLesson 4 - Writing MethodologyLloyd PawaonNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerKit DyNo ratings yet
- 4 211 A&E Mills & Gay. 2016. Glossary MERAH 11th Eds. Educational - Research - Competencies - For - Analysis - and - ApplicationsDocument12 pages4 211 A&E Mills & Gay. 2016. Glossary MERAH 11th Eds. Educational - Research - Competencies - For - Analysis - and - ApplicationsNur ShiraNo ratings yet
- Resesarch ReviewerDocument3 pagesResesarch ReviewerMa Jollie Mae BereNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignsDocument16 pagesQuantitative Research Designsapi-339611548100% (15)
- Research DesignDocument4 pagesResearch DesignKhushiNo ratings yet
- PR 2Document24 pagesPR 2Adrian BisqueraNo ratings yet
- 2.o Methods of ResearchDocument72 pages2.o Methods of ResearchgangejuneNo ratings yet
- 3B Research Combined MidtermsDocument160 pages3B Research Combined MidtermsCHRISTIAN ASHLEY PASCUANo ratings yet
- Research Final Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesResearch Final Exam ReviewerRhanessa Banacia NordanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Mid TermDocument9 pagesStudy Guide For Mid Term455.lorenzoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter PR 2 REVIEWERDocument5 pages2nd Quarter PR 2 REVIEWERReggie AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 and Pr2Document8 pagesLesson 11 and Pr2Jama BustamanteNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT NO.2 Research ApproachDocument5 pagesHANDOUT NO.2 Research ApproachHazel MarananNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ReviewerGabby GargantosNo ratings yet
- Unit 02 Word Wall - Research MethodsDocument23 pagesUnit 02 Word Wall - Research MethodsJayNo ratings yet
- Understanding Academic Research Its Design and Methods ALUNA March 29 2021Document73 pagesUnderstanding Academic Research Its Design and Methods ALUNA March 29 2021Elmalyn BernarteNo ratings yet
- PR2 (Note - Reviewer)Document9 pagesPR2 (Note - Reviewer)Woxi BedineNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignDocument51 pagesQuantitative Research DesignFarah BasemNo ratings yet
- QuanDocument6 pagesQuanstrongzhongliNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentDocument5 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core Contentenojosa nhoelNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Rizwoods Colleges IncDocument7 pagesSenior High School: Rizwoods Colleges IncJoji Ann Tibay EsganaNo ratings yet
- Research: Exploring HorizonsDocument196 pagesResearch: Exploring HorizonsTata MumuNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Management and School Effectiveness in Government Technical Secondary and High Schools in CameroonDocument13 pagesHuman Resources Management and School Effectiveness in Government Technical Secondary and High Schools in CameroonEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- The ISO/IEC 27001 Information Security Management Standard: Literature Review and Theory-Based Research AgendaDocument31 pagesThe ISO/IEC 27001 Information Security Management Standard: Literature Review and Theory-Based Research AgendaJosue OuattaraNo ratings yet
- Operation Management ThesisDocument96 pagesOperation Management ThesisTpow giftNo ratings yet
- Chambers 1993Document26 pagesChambers 1993ayuduNo ratings yet
- Parental Involvement 2022Document27 pagesParental Involvement 2022Dainielle BianzonNo ratings yet
- FS2 Epi19 PontejosDocument4 pagesFS2 Epi19 PontejosPontejos Princess Dianne G.100% (1)
- Social Studies DefinedDocument6 pagesSocial Studies DefinedSaidu abu100% (1)
- Teaching by PrinciplesDocument4 pagesTeaching by PrinciplesKelemen Maria Magdolna100% (1)
- Sample Doctoral Dissertation in TheologyDocument5 pagesSample Doctoral Dissertation in TheologyDoMyPaperUK100% (1)
- Report FinalDocument48 pagesReport FinalSantosh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A STUDY ON SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT OF Dairy ProductsDocument18 pagesA STUDY ON SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT OF Dairy ProductsUpadhayayAnkurNo ratings yet
- Plaquette Advanced Finance AccountingDocument2 pagesPlaquette Advanced Finance AccountingmeriiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Lea 122Document7 pagesSyllabus - Lea 122rubie rubioNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Technical Research PaperDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Technical Research PaperRia DumapiasNo ratings yet
- Walidd Score, A New Tool To Diagnose Dysmenorrhea and Predict Medical Leave in University StudentsDocument11 pagesWalidd Score, A New Tool To Diagnose Dysmenorrhea and Predict Medical Leave in University Studentsxavi5_5No ratings yet
- Cultural and Linguistic Adaptations of Early Language Interventions Recommendations For Advancing Research and PracticeDocument24 pagesCultural and Linguistic Adaptations of Early Language Interventions Recommendations For Advancing Research and PracticeGintarė AmalevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- BataDocument58 pagesBataParth MalhotraNo ratings yet
- RDL Layout SampleDocument136 pagesRDL Layout SampleDanielle Therese IsaisNo ratings yet
- Loan Prediction SystemDocument5 pagesLoan Prediction SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A7 - Chapter I 3-13-11Document11 pagesA7 - Chapter I 3-13-11Makil SellarimNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Menstrual Hygiene Among Nursing Students in Vivekananda College of Nursing, LucknowDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Menstrual Hygiene Among Nursing Students in Vivekananda College of Nursing, LucknowEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Educational PsychologyDocument28 pagesEducational PsychologysyedmirsyedNo ratings yet
- Reading and Understanding Research Third EditionDocument234 pagesReading and Understanding Research Third EditionGhulam JailanNo ratings yet
- Youth JFASDocument13 pagesYouth JFASJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- International Self-Report Delinquency Questionnaire 3 (ISRD-3)Document27 pagesInternational Self-Report Delinquency Questionnaire 3 (ISRD-3)Mike Angelo Vellesco CabsabaNo ratings yet
- DHTM MKTDocument155 pagesDHTM MKTSim HamimNo ratings yet
- Literature REVIEW: LOCAL PLANDocument10 pagesLiterature REVIEW: LOCAL PLANAizuddinHakimBennyNo ratings yet
- Edited Action Research Proposal Project UsbsDocument10 pagesEdited Action Research Proposal Project UsbsSONY JOY QUINTONo ratings yet