Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsHisto Lec 3 - The Nucleus
Histo Lec 3 - The Nucleus
Uploaded by
jkthmsvtchCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Basic radiobiology: fractionation, 5 Rs, α/β ratio, QUANTEC: ESO Masterclass in Oncology Basics for BeginnersDocument32 pagesBasic radiobiology: fractionation, 5 Rs, α/β ratio, QUANTEC: ESO Masterclass in Oncology Basics for BeginnersAji PatriajatiNo ratings yet
- Calamba, Micah Lou C. MD1: Phase, This Is Where The Cells PhysicallyDocument3 pagesCalamba, Micah Lou C. MD1: Phase, This Is Where The Cells PhysicallyKaykie CalambaNo ratings yet
- Q2 L2 Mitosis Cell CycleDocument26 pagesQ2 L2 Mitosis Cell CycleReese DeborahNo ratings yet
- Gafa6w0sr MITOSISDocument21 pagesGafa6w0sr MITOSISsmahlikNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceDocument11 pagesMitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Foz Lec M3Document9 pagesFoz Lec M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document9 pagesBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNo ratings yet
- L1 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument39 pagesL1 - Cell Cycle and MitosisTahmina MaryamNo ratings yet
- Cell DevisionDocument13 pagesCell DevisionNeha PurohitNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division22-50863No ratings yet
- Biology Assessment Task 2Document8 pagesBiology Assessment Task 2akshishree23No ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRAlfer JaoNo ratings yet
- Block 1 Lecture 2 Cell CycleDocument34 pagesBlock 1 Lecture 2 Cell CycleNahome YebassewNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and Mitosis PDFDocument77 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Mitosis PDFRonzie EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & MitosisDocument42 pagesCell Cycle & Mitosismariam yahiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle - RSJ - 2020 - FINALDocument53 pagesCell Cycle - RSJ - 2020 - FINALArmy JmNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument8 pagesMitosisMilongy JavierNo ratings yet
- BIODocument7 pagesBIOREYES, Kyla Marie M.No ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 7Document40 pagesBIOL223-Lab 7chicken fries100% (2)
- 5 Cell-CycleDocument13 pages5 Cell-CycleKyzenNo ratings yet
- Cell-3 0Document17 pagesCell-3 0rhyshryroch royerasNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 MitosisDocument11 pagesGenbio1 MitosisJessie Katrisha TayagNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle To MeiosisDocument13 pagesCell Cycle To MeiosisSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Class Rules School Education InfographicDocument3 pagesClass Rules School Education InfographicStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- CellDocument63 pagesCellCharlize Jeneah MedinaNo ratings yet
- Cellular ReproductionDocument15 pagesCellular ReproductionShermay Dela Serna GranitoNo ratings yet
- 7) 1 - 14 Cell CycleDocument19 pages7) 1 - 14 Cell CycleDawar Aziz MemonNo ratings yet
- GENB4Document5 pagesGENB4Azeleah Nosil VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesLecture 3 Cell DivisionSalim HudheifaNo ratings yet
- Bio M3Document17 pagesBio M3Zen ShuziNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleCharmaine AngaraNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument44 pagesCellsRuthie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument28 pagesCell DivisionPalagiri MadhuNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell CycleDocument43 pagesMitosis and Cell CycleKavindu MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell CycleDocument7 pagesMitosis and Cell CycleMahmoud HeshamNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis OnlyDocument56 pagesCell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis Onlymarimay.lumabanNo ratings yet
- L3 - Cellular DivisionDocument33 pagesL3 - Cellular DivisionTiffany LimNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 2Document10 pagesBiology - Module 2ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument18 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisMohammed Ridzuwan0% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cancer 1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesCancer 1 ReviewerPimpamNo ratings yet
- GB2 Asexual ReproductionDocument23 pagesGB2 Asexual Reproductionsja254677No ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument120 pagesCell Cycle & Cell DivisionGanesh Patil100% (1)
- Bio LectureDocument4 pagesBio LectureAbegail TaarNo ratings yet
- ىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاDocument9 pagesىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاعبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument3 pagesCell CyclerueNo ratings yet
- Xii Semana - El Nucleo InterfasicoDocument67 pagesXii Semana - El Nucleo Interfasicofiorella pahuachonNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideDocument41 pagesThe Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideSeleneblueNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 (Bio)Document10 pagesCHP 10 (Bio)Serena BautistaNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesDocument4 pages10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesWrestling Communication100% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Microbiology & Parasitology Module 1 Part 2Document7 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology Module 1 Part 2BARRERAS Aubrey Eden Faye G.No ratings yet
- Organisms Can Be Classified Based On Physical Similarities.: Key ConceptDocument46 pagesOrganisms Can Be Classified Based On Physical Similarities.: Key ConceptMUHAMMAD ARGANo ratings yet
- Real Quant PCRDocument48 pagesReal Quant PCRu77No ratings yet
- Natural Selection Simulation - BasicDocument2 pagesNatural Selection Simulation - BasicImeeNo ratings yet
- 9700 s16 QP 42Document24 pages9700 s16 QP 42Lavender KawodzaNo ratings yet
- Virulence Factor of E. ColiDocument26 pagesVirulence Factor of E. ColiNazii Baig100% (1)
- 12 - Molecular Evolution Notes 2015Document8 pages12 - Molecular Evolution Notes 2015Melissa GarciaNo ratings yet
- LG Cell Growth and ReproductioDocument52 pagesLG Cell Growth and ReproductioNiezl Mae Dimzon DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Medical Incubator 1Document6 pagesMedical Incubator 1Yan YanNo ratings yet
- Whole Life Sciences GlossaryDocument108 pagesWhole Life Sciences Glossaryramakrishnansatish100% (4)
- Meiosis NotesDocument2 pagesMeiosis Notesapi-505203040No ratings yet
- Ihc Staining MethodsDocument218 pagesIhc Staining MethodsBing Noid100% (1)
- Human and Social Biology Lesson 1Document26 pagesHuman and Social Biology Lesson 1alferoz zabarNo ratings yet
- (Roche) Scanner Ms200 Brochure 2009-12-22Document12 pages(Roche) Scanner Ms200 Brochure 2009-12-22Luong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Uganda Guidelines For Marketing Authorization of A Pharmaceutical Product For Human Use R1Document250 pagesUganda Guidelines For Marketing Authorization of A Pharmaceutical Product For Human Use R1Shivraj ParmarNo ratings yet
- s41586 020 2798 3 - Reference PDFDocument16 pagess41586 020 2798 3 - Reference PDFYudi AriefNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov-2: Empowers To Live WellDocument2 pagesSars-Cov-2: Empowers To Live WellAkhil KNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q2-M24 Genetic EngineeringDocument3 pagesEarth and Life Science Q2-M24 Genetic EngineeringTheo John CruzNo ratings yet
- 4 RazzaqueDocument10 pages4 RazzaquesanNo ratings yet
- Certificat EU VaccinareDocument2 pagesCertificat EU VaccinareAlina ComanNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Preparing Kinnex Libraries From 16S rRNA AmpliconsDocument22 pagesProcedure Checklist Preparing Kinnex Libraries From 16S rRNA Ampliconslinqin029No ratings yet
- Microbiology (HBM 531)Document5 pagesMicrobiology (HBM 531)panther795No ratings yet
- Presentation RAPDDocument30 pagesPresentation RAPDLita MeilinaNo ratings yet
- Building Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project HopeDocument18 pagesBuilding Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project Hopesusy kusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Quatum DotsDocument9 pagesQuatum DotssherlyNo ratings yet
- 2021 22363 AuthorDocument28 pages2021 22363 AuthorGeorge LaliotisNo ratings yet
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- 05 Twin Studies ContextsDocument5 pages05 Twin Studies ContextsAnh LeutharNo ratings yet
- Birth of Earth Video WorksheetDocument2 pagesBirth of Earth Video Worksheetquirmche70No ratings yet
Histo Lec 3 - The Nucleus
Histo Lec 3 - The Nucleus
Uploaded by
jkthmsvtch0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesHisto Lec 3 - The Nucleus
Histo Lec 3 - The Nucleus
Uploaded by
jkthmsvtchCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
MT2213: HUMAN HISTOLOGY| LECTURE – PRELIM
Lesson 3: The Nucleus
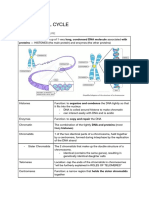
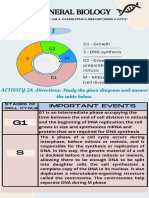
THE NUCLEUS CELL CYCLE
INTRODUCTION — This refers to the sequence of events that
controls cell growth and division.
— The NUCLEUS is the membrane-enclosed
organelle within a cell that contains the DIVIDED INTO SEVERAL PHASES:
chromosomes.
• G1 PHASE (FIRST GAP) – the stage where
— The nucleus contains the code for all of a cell’s
cell is preparing to divide, the cell grows larger,
enzyme and other proteins.
copies organelles, and makes the molecular
— It functions as a command center of the cell building block.
and function as the machinery to replicate the
• S PHASE (DNA SYNTHESIS) – the stage
DNA and to synthesize and process all types of
where cell copies all the DNA in its nucleus.
RNA.
• G2 PHASE (SECOND GAP) – the stage where
the cells grows more and makes proteins and
COMPONENTS OF THE NUCLEUS organelles, the stage where DNA starts to
condense and prepares for division.
NUCLEAR ENVELOPE
• MITOSIS – the stage where the cell divides its
— Forms a selective permeable barrier copied DNA and cytoplasm to make TWO new
between the nuclear and cytoplasmic cells.
components.
— This also provides structural framework of the
nucleus.
CHROMATIN
— Is consist of DNA and all of the associated
proteins that form the chromosomes and is
involved in the organization and function of
DNA.
— In human, each cell’s chromatin is divided
among 46 CHROMOSOMES (23 pairs).
— After DNA replication, each chromosome is
consist of 2 identical chromatin units called
CHROMATIDS MITOSIS PHASE
NUCLEOLUS • INTERPHASE – G1, synthesis, G2
• PROPHASE – when chromosomes condense,
— Is the largest nuclear organelle and is the the nuclear envelope disassembles and the
primary site of ribosome subunit biogenesis in microtubular spindles forms.
eukaryotic cells. • METAPHASE – when chromosomes are
— Appears to be spherical, highly basophilic aligned.
subdomain of nuclei in cells actively engaged • ANAPHASE – when chromosomes begin to
in protein synthesis. separate toward the two centrosomes.
• TELOPHASE – when nuclear envelope re-
forms around the separated chromosomes.
• CYTOKINESIS
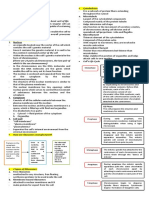
APOPTOSIS
— Aka process of PROGRAMMED CELL DEATH
— It happens during early development to
eliminate unwanted cells.
— Apoptosis is used to rid of body cells that have
been damaged beyond repair.
— This also plays a role in preventing cancer.
— Cells that die as a result of acute injury typically
swell and burst.
— They spill their contents all over their neighbors
(cell necrosis) causing a potentially damaging
inflammatory response.
— When a cell dies neatly (w/o damaging its
neighbor) the cell shrinks and condenses; the
cytoskeleton collapses, the nuclear envelope
disassembles, and the nuclear DNA breaks up
into fragments.
You might also like
- Basic radiobiology: fractionation, 5 Rs, α/β ratio, QUANTEC: ESO Masterclass in Oncology Basics for BeginnersDocument32 pagesBasic radiobiology: fractionation, 5 Rs, α/β ratio, QUANTEC: ESO Masterclass in Oncology Basics for BeginnersAji PatriajatiNo ratings yet
- Calamba, Micah Lou C. MD1: Phase, This Is Where The Cells PhysicallyDocument3 pagesCalamba, Micah Lou C. MD1: Phase, This Is Where The Cells PhysicallyKaykie CalambaNo ratings yet
- Q2 L2 Mitosis Cell CycleDocument26 pagesQ2 L2 Mitosis Cell CycleReese DeborahNo ratings yet
- Gafa6w0sr MITOSISDocument21 pagesGafa6w0sr MITOSISsmahlikNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceDocument11 pagesMitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Foz Lec M3Document9 pagesFoz Lec M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document9 pagesBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNo ratings yet
- L1 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument39 pagesL1 - Cell Cycle and MitosisTahmina MaryamNo ratings yet
- Cell DevisionDocument13 pagesCell DevisionNeha PurohitNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division22-50863No ratings yet
- Biology Assessment Task 2Document8 pagesBiology Assessment Task 2akshishree23No ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRAlfer JaoNo ratings yet
- Block 1 Lecture 2 Cell CycleDocument34 pagesBlock 1 Lecture 2 Cell CycleNahome YebassewNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and Mitosis PDFDocument77 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Mitosis PDFRonzie EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & MitosisDocument42 pagesCell Cycle & Mitosismariam yahiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle - RSJ - 2020 - FINALDocument53 pagesCell Cycle - RSJ - 2020 - FINALArmy JmNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument8 pagesMitosisMilongy JavierNo ratings yet
- BIODocument7 pagesBIOREYES, Kyla Marie M.No ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 7Document40 pagesBIOL223-Lab 7chicken fries100% (2)
- 5 Cell-CycleDocument13 pages5 Cell-CycleKyzenNo ratings yet
- Cell-3 0Document17 pagesCell-3 0rhyshryroch royerasNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 MitosisDocument11 pagesGenbio1 MitosisJessie Katrisha TayagNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle To MeiosisDocument13 pagesCell Cycle To MeiosisSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Class Rules School Education InfographicDocument3 pagesClass Rules School Education InfographicStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- CellDocument63 pagesCellCharlize Jeneah MedinaNo ratings yet
- Cellular ReproductionDocument15 pagesCellular ReproductionShermay Dela Serna GranitoNo ratings yet
- 7) 1 - 14 Cell CycleDocument19 pages7) 1 - 14 Cell CycleDawar Aziz MemonNo ratings yet
- GENB4Document5 pagesGENB4Azeleah Nosil VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesLecture 3 Cell DivisionSalim HudheifaNo ratings yet
- Bio M3Document17 pagesBio M3Zen ShuziNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleCharmaine AngaraNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument44 pagesCellsRuthie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument28 pagesCell DivisionPalagiri MadhuNo ratings yet
- Cell Division MitosisDocument7 pagesCell Division MitosisAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell CycleDocument43 pagesMitosis and Cell CycleKavindu MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Cell CycleDocument7 pagesMitosis and Cell CycleMahmoud HeshamNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis OnlyDocument56 pagesCell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis Onlymarimay.lumabanNo ratings yet
- L3 - Cellular DivisionDocument33 pagesL3 - Cellular DivisionTiffany LimNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 2Document10 pagesBiology - Module 2ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument18 pagesChapter 6: Cell Division: 6.2: Cell Cycle and MitosisMohammed Ridzuwan0% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cancer 1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesCancer 1 ReviewerPimpamNo ratings yet
- GB2 Asexual ReproductionDocument23 pagesGB2 Asexual Reproductionsja254677No ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument120 pagesCell Cycle & Cell DivisionGanesh Patil100% (1)
- Bio LectureDocument4 pagesBio LectureAbegail TaarNo ratings yet
- ىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاDocument9 pagesىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاعبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument3 pagesCell CyclerueNo ratings yet
- Xii Semana - El Nucleo InterfasicoDocument67 pagesXii Semana - El Nucleo Interfasicofiorella pahuachonNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideDocument41 pagesThe Cell Cycle and How Cells DivideSeleneblueNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 (Bio)Document10 pagesCHP 10 (Bio)Serena BautistaNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesDocument4 pages10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesWrestling Communication100% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Microbiology & Parasitology Module 1 Part 2Document7 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology Module 1 Part 2BARRERAS Aubrey Eden Faye G.No ratings yet
- Organisms Can Be Classified Based On Physical Similarities.: Key ConceptDocument46 pagesOrganisms Can Be Classified Based On Physical Similarities.: Key ConceptMUHAMMAD ARGANo ratings yet
- Real Quant PCRDocument48 pagesReal Quant PCRu77No ratings yet
- Natural Selection Simulation - BasicDocument2 pagesNatural Selection Simulation - BasicImeeNo ratings yet
- 9700 s16 QP 42Document24 pages9700 s16 QP 42Lavender KawodzaNo ratings yet
- Virulence Factor of E. ColiDocument26 pagesVirulence Factor of E. ColiNazii Baig100% (1)
- 12 - Molecular Evolution Notes 2015Document8 pages12 - Molecular Evolution Notes 2015Melissa GarciaNo ratings yet
- LG Cell Growth and ReproductioDocument52 pagesLG Cell Growth and ReproductioNiezl Mae Dimzon DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Medical Incubator 1Document6 pagesMedical Incubator 1Yan YanNo ratings yet
- Whole Life Sciences GlossaryDocument108 pagesWhole Life Sciences Glossaryramakrishnansatish100% (4)
- Meiosis NotesDocument2 pagesMeiosis Notesapi-505203040No ratings yet
- Ihc Staining MethodsDocument218 pagesIhc Staining MethodsBing Noid100% (1)
- Human and Social Biology Lesson 1Document26 pagesHuman and Social Biology Lesson 1alferoz zabarNo ratings yet
- (Roche) Scanner Ms200 Brochure 2009-12-22Document12 pages(Roche) Scanner Ms200 Brochure 2009-12-22Luong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Uganda Guidelines For Marketing Authorization of A Pharmaceutical Product For Human Use R1Document250 pagesUganda Guidelines For Marketing Authorization of A Pharmaceutical Product For Human Use R1Shivraj ParmarNo ratings yet
- s41586 020 2798 3 - Reference PDFDocument16 pagess41586 020 2798 3 - Reference PDFYudi AriefNo ratings yet
- Sars-Cov-2: Empowers To Live WellDocument2 pagesSars-Cov-2: Empowers To Live WellAkhil KNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q2-M24 Genetic EngineeringDocument3 pagesEarth and Life Science Q2-M24 Genetic EngineeringTheo John CruzNo ratings yet
- 4 RazzaqueDocument10 pages4 RazzaquesanNo ratings yet
- Certificat EU VaccinareDocument2 pagesCertificat EU VaccinareAlina ComanNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Preparing Kinnex Libraries From 16S rRNA AmpliconsDocument22 pagesProcedure Checklist Preparing Kinnex Libraries From 16S rRNA Ampliconslinqin029No ratings yet
- Microbiology (HBM 531)Document5 pagesMicrobiology (HBM 531)panther795No ratings yet
- Presentation RAPDDocument30 pagesPresentation RAPDLita MeilinaNo ratings yet
- Building Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project HopeDocument18 pagesBuilding Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project Hopesusy kusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Quatum DotsDocument9 pagesQuatum DotssherlyNo ratings yet
- 2021 22363 AuthorDocument28 pages2021 22363 AuthorGeorge LaliotisNo ratings yet
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- 05 Twin Studies ContextsDocument5 pages05 Twin Studies ContextsAnh LeutharNo ratings yet
- Birth of Earth Video WorksheetDocument2 pagesBirth of Earth Video Worksheetquirmche70No ratings yet