Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment No. 3: Answer
Assignment No. 3: Answer
Uploaded by
tech.anand2211Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment No. 3: Answer
Assignment No. 3: Answer
Uploaded by
tech.anand2211Copyright:
Available Formats
Assignment No.
3
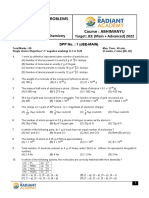
1. Number of gold atoms in 300 mg of a gold ring of 20 carat gold (pure gold is 24 carat) are :
(A) 4.5 × 1020 (B) 6.8 × 1015 (C) 7.6 × 1020 (D) 9.5 × 1020
2. From a container having 64 g Oxygen, 11.2 L Oxygen gas at S.T.P. and 6.022 × 1023 Oxygen atoms are
removed. Find the mass of the oxygen gas left :
(A) zero (B) 32 g (C) 16 g (D) none
3. Column-I Column-II
(A) 32 g each of O2 and S (p) 2 moles of Fe
(B) 2 gram-molecules of K3[Fe(CN)6] (q) 3 moles of ozone molecule
(C) 144 g of Oxygen atom (r) one mole of given unit
(D) From 168 g of iron, 6.022 × 1023 atoms (s) 12 moles of carbon atoms
of iron are removed, then the iron left
4. If a sample of Ferric sulphate Fe2(SO4)3 contains 7.2 moles of O-atoms, then the number of S-atoms in the
given sample are :
(A) 1.8 NA (B) 1.2 NA (C) 1.6 NA (D) 1.4 NA
5. 10 moles of CO2 do not contain :
(A) 120 g of C (B) 6.022 × 1024 atoms of O
(C) 10 NA molecules of CO2 (D) 20 gram-atoms of O.
6. A compound has the molecular formula X4O6. If 11 g of X4O6 has 6.2 g of X, then atomic mass of X is :
(A) 31 amu (B) 37 amu (C) 42 amu (D) 98 amu
7. A sample of CaCO3 has Ca = 40%, C = 12% and O = 48% by mass. If the law of constant proportions is
true, then the mass of Ca in 5 g of CaCO3 from another source will be:
(A) 2 g (B) 0.2 g (C) 0.02 g (D) 20 g
8. In compound A, 1 g nitrogen combine with 0.57 g oxygen. In compound B, 2 g nitrogen combine with
2.28 g oxygen and in compound C, 3 g nitrogen combine with 5.13 g oxygen. These results obey the law of:
(A) multiple proportions (B) constant proportions
(C) mixed proportions (D) none of these
9. The respective ratio of weight of oxygen in samples of pure CuO and Cu2O, if both samples contain the
same mass of copper, is :
(A) 1 : 2 (B) 1 : 1 (C) 2 : 1 (D) none of these
10. Find the relative density of SO3 gas with respect to methane.
11. The density of air at STP is 0.001287 g mL–1. Its vapour density is :
(A) 143 (B) 14.3 (C) 1.43 (D) 0.143
[Hint : Divide with the density of hydrogen at STP, i.e., 0.00009 g mL–1]
12. The atomic mass of a metal is 27. If its valency is 3, the vapour density of the volatile metal chloride will be:
(A) 66.75 (B) 6.675 (C) 667.5 (D) 81
ANSWER
1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (A – r ; B – p, s ; C – q ; D – p). 4.
(A)
5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (C)
10. 5. 11. (B) 12. (A)
Assignment No. 4
1.* 11.2 L of a gas at STP weighs 14 g The gas could be :
(A) N2O (B) NO2 (C) N2 (D) CO
2. A compound of Mg contains 6% of Mg by mass. If the minimum molar mass of the compound is n × 102 g/
mol then determine value of ‘n’.
3. A sample of a compound contains 9.75 g Zn, 1.8 × 1023 atoms of Cr and 0.6 gram-atoms of O. What is
empirical formula of compound ? (Atomic Mass Zn = 65)
(A) ZnCrO4 (B) ZnCr2O4 (C) Zn2CrO4 (D) ZnCr2O2
4. An organic compound on analysis was found to contain 0.032% of sulphur by mass. The molecular mass
of the compound, if its one molecule contains two sulphur atoms, is :
(A) 100000 u (B) 10000 u (C) 20000 u (D) 200000 u
5. Column - I Column - II
(A) A compound containing 5 g ‘S’ and 5 g oxygen (p) Empirical formula is CH2
600
(B) A hydrocarbon containing % ‘C’ by mass (q) Molecular formula is C2H4
7
300 800
(C) A compound containing % of ‘C’ and % of ‘O’ by mass (r) Empirical formula is SO2
11 11
100
(D) A hydrocarbon containing % H by mass (Molecular mass = 28) (s) Empirical formula is CO2
7
6. 0.1 mole of a carbohydrate with empirical formula CH2O contains 1 g of hydrogen. What is its molecular
formula?
(A) C5H10O5 (B) C6H12O6 (C) C4H8O4 (D) C3H6O3
7. The number of moles of oxygen obtained by the electrolytic decomposition of 90 g water is :
elec .
(2H2O 2H2 + O2)
(A) 2.5 (B) 5 (C) 7.5 (D) 10
8.* In a gaseous reaction of type :
xA(g) + yB(g) pC(g) + qD(g)
where x, y, p and q are stoichiometric coefficients.
Which of the following statements is/are correct :
(A) At STP, x litre of A combine with y litre of B to give C and D
(B) x mole of A combine with y mole of B to give C and D
(C) x g of A combine with y g of B to give C and D.
(D) x molecules of A combine with y molecules of B to give C and D.
ANSWER
1.* (C,D) 2. 4 3. (B) 4. (D)
5. [A — r] ; [B — p] ; [C — s] ; [D — p, q]. 6. (A) 7. (A) 8.* (A,B,D)
You might also like
- 八大題型全攻略Document32 pages八大題型全攻略Jeff Suck100% (1)
- Mole Concept IDocument8 pagesMole Concept ISohil Paudel100% (2)
- SPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsDocument64 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Module On The Basicskent_tam611980% (5)
- CHM-1025 Syllabus Summer 2019 (2) (1) (1) - 2Document11 pagesCHM-1025 Syllabus Summer 2019 (2) (1) (1) - 2459872305datNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry - DPP-05Document3 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry - DPP-05aswineekumar200No ratings yet
- Total Success Mole Concept and RedoxDocument8 pagesTotal Success Mole Concept and RedoxVengefulNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Advanced Questions PDFDocument14 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Advanced Questions PDFAditya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemistry A0x49QVl3BT5Ko2KDocument20 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemistry A0x49QVl3BT5Ko2Krineeth22745No ratings yet
- Mole CPP Combine PDFDocument13 pagesMole CPP Combine PDFPiyushNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document14 pagesChemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020johnNo ratings yet
- Mole-1 JEE Advanced Level MCQsDocument8 pagesMole-1 JEE Advanced Level MCQswhoeverNo ratings yet
- Sicmyb - DPP Mole ConceptDocument6 pagesSicmyb - DPP Mole ConceptBorn to fightNo ratings yet
- DPP 01Document2 pagesDPP 01urmomNo ratings yet
- Final 01 A Some Basic Concept of Chemistry PDFDocument22 pagesFinal 01 A Some Basic Concept of Chemistry PDFSwastik TripathiNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course Assig - Mole ConceptsDocument2 pagesBridge Course Assig - Mole ConceptsSubs BadaoNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Test ..,..Document3 pagesMole Concept Test ..,..bajajnamish130No ratings yet
- Fiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Chemistry - CPMDocument2 pagesFiitjee Coimbatore Centre: 10 - Chemistry - CPMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry - DPP-1 - Without Ans & Sol.Document4 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry - DPP-1 - Without Ans & Sol.Vaibhav RAJ KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Full Chapter Practice Sheet - 220627 - 1 - 220627 - 155952Document7 pagesMole Concept Full Chapter Practice Sheet - 220627 - 1 - 220627 - 1559522005anushkasharmaNo ratings yet
- × 10 Atoms × 10 × 10Document8 pages× 10 Atoms × 10 × 10Sahil PalNo ratings yet
- DPT-2 Chem & Zoo Neet 29.12.2023Document8 pagesDPT-2 Chem & Zoo Neet 29.12.2023pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- 1001-Class XI - C-232.Mole Concept Assignment - 1Document5 pages1001-Class XI - C-232.Mole Concept Assignment - 1The GentlemanNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Exercise-1Document10 pagesMole Concept Exercise-1Game TechNo ratings yet
- 2 A - 2 A - 2 A - 2 A - 2 A - 2 ADocument2 pages2 A - 2 A - 2 A - 2 A - 2 A - 2 ArajeshNo ratings yet
- Mole DPPDocument3 pagesMole DPPnams0% (2)
- Mole Concept Sheet (Exercise)Document26 pagesMole Concept Sheet (Exercise)hppavilion597No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry - DPP-04Document2 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry - DPP-04aswineekumar200No ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Book Back Questions New BookDocument38 pages11th Chemistry Book Back Questions New BookNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY - II ALTAF SIR CHEMISTRY FinallllDocument3 pagesSOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY - II ALTAF SIR CHEMISTRY Finallllcupcat196No ratings yet
- Test 001 Mole Concept and Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesTest 001 Mole Concept and Atomic StructureDarsh ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- DPP 02Document2 pagesDPP 02urmomNo ratings yet
- JR Chemistry Sat-1 05-04-2024Document3 pagesJR Chemistry Sat-1 05-04-2024k.akhilmurthyNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Worksheet 2 PDFDocument7 pagesMole Concept Worksheet 2 PDFKripa DeviNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept DPP-3 - 501352Document1 pageMole Concept DPP-3 - 501352Vatsal BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept 11 PDFDocument26 pagesMole Concept 11 PDFSamyak Jha100% (1)
- Cnhemistry 11 em Book Back One Mark Reduced SyllabusDocument14 pagesCnhemistry 11 em Book Back One Mark Reduced Syllabuselavarasannatesan0No ratings yet
- Vol1-20220120120129414437 231117 000554Document67 pagesVol1-20220120120129414437 231117 000554Abhirama Bhat U RNo ratings yet
- Ths 6 X 5 Ye Urudmq QSGSPDDocument7 pagesThs 6 X 5 Ye Urudmq QSGSPDrudrakumbhar2005No ratings yet
- Yti 45 Tu VD0 QKJ Beh Ekm LDocument46 pagesYti 45 Tu VD0 QKJ Beh Ekm LAradhana GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mole Reactions and Stoichiometry MultipleDocument25 pagesMole Reactions and Stoichiometry MultiplelinaNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept DPP-2 - 501352Document1 pageMole Concept DPP-2 - 501352Vatsal BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument7 pagesMole ConceptTahir Raj BhasinNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesMole Concept Worksheet PDFKripa DeviNo ratings yet
- (SK) 11th PaperDocument8 pages(SK) 11th PaperChemistry classes by Dr.AshokNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet 1.2Document7 pagesPractice Sheet 1.2daya nandNo ratings yet
- Dpp-Mole ConceptDocument2 pagesDpp-Mole ConceptPratibhasthali IndoreNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry, SPLDocument6 pagesStoichiometry, SPLaneekdofficialNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1,2,3,4Document29 pagesCh. 1,2,3,4Kankana ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- DPP 01 Mole Concept JH Sir-3571Document8 pagesDPP 01 Mole Concept JH Sir-3571PrädunmaChoudhury100% (3)
- DPP - 01-11 - PH. CHEM - Abhimanyu (SC)Document23 pagesDPP - 01-11 - PH. CHEM - Abhimanyu (SC)Rohan VayaNo ratings yet
- Test Paper - 1 (Arihant)Document7 pagesTest Paper - 1 (Arihant)kumarsanu2905No ratings yet
- Moleconcept (E L)Document3 pagesMoleconcept (E L)ramanji1021No ratings yet
- Paper I 11Document5 pagesPaper I 11master aexpeckNo ratings yet
- IX Chem Mole Concept Kailash Khatwani FinalDocument8 pagesIX Chem Mole Concept Kailash Khatwani FinalAditya ParuiNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Revision Assignment For Test 1Document9 pages1st Year Chemistry Revision Assignment For Test 1Syed Moeen NaqviNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument8 pagesMole ConceptMohit GargNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document2 pagesWorksheet 1keerthana deviNo ratings yet
- Mole and Stoichiometric CalculationDocument18 pagesMole and Stoichiometric CalculationSajjad MiraniNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concept of Chemistry: Chapter - 01Document7 pagesSome Basic Concept of Chemistry: Chapter - 01MidhunNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesFrom EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 Mole and Chemical CompositionDocument36 pagesChap 7 Mole and Chemical CompositionAnthony AraizaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Q and ADocument5 pagesExercise 1 Q and AJames WongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Atomic StructureDocument22 pagesChapter 02 Atomic StructureAndy Rei Kou100% (2)
- CH 3. Mass Relations in Chemistry - StoichiometryDocument12 pagesCH 3. Mass Relations in Chemistry - Stoichiometryewewwe weweweweNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument31 pagesMole ConceptApex Institute50% (4)
- Laboratory Manual: Bacis Physical ChemistryDocument30 pagesLaboratory Manual: Bacis Physical ChemistryNurul SafwahNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Grade 9Document3 pages2nd Quarter Exam Grade 9Ma. Lourdes CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Final Revision-STEM Fayoum Chemistry ClubDocument48 pagesFinal Revision-STEM Fayoum Chemistry Clubromaehab201912No ratings yet
- Gas Laws Worksheet 2024Document4 pagesGas Laws Worksheet 2024nourlina200020No ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry Chapter 3 - StoichiometryDocument31 pagesCIE Chemistry Chapter 3 - StoichiometryIt's futfutiNo ratings yet
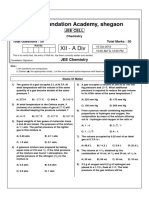
- Nand Foundation Academy, Shegaon: Xii - A DivDocument9 pagesNand Foundation Academy, Shegaon: Xii - A DivSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry: Summer Bridging WorkDocument40 pagesA Level Chemistry: Summer Bridging WorkOabile 14kNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry Atoms First 5Th Edition Russo Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesIntroductory Chemistry Atoms First 5Th Edition Russo Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJodyArcherdkco100% (10)
- Gulf International School: in Pursuit of ExcellenceDocument93 pagesGulf International School: in Pursuit of Excellencemohz.122007No ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Class 12 Important QuestionsDocument32 pagesImportant Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Class 12 Important QuestionsTharun VasuNo ratings yet
- Use The Mole Concept To Express Mass of Substances (S9Mt-Iii-19)Document4 pagesUse The Mole Concept To Express Mass of Substances (S9Mt-Iii-19)ChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Anderson's Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesAnderson's Practice ProblemsJeff TongNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8 ClassDocument36 pagesWorksheet 8 ClassKerimberdiNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises (Molality) PDFDocument11 pagesPractice Exercises (Molality) PDFKenneth Roy MatuguinaNo ratings yet
- 12 Osmotic PressureDocument44 pages12 Osmotic PressureShinwha Y. FuentesNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - SampleDocument22 pagesCHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - Sampleviswajithv66No ratings yet
- Skema Kimia K123 Trial SPM SBP 2019 PDFDocument39 pagesSkema Kimia K123 Trial SPM SBP 2019 PDFSiti Hajar Abd Hamid100% (1)
- Mcqs and Solved Short Questions Applied ChemistryDocument25 pagesMcqs and Solved Short Questions Applied ChemistryShahbaz Ahmed RanaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 120 1109 Test2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesCHEM 120 1109 Test2 SolutionsasdaasdNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Study Guide ChemistryDocument15 pagesYear 9 Study Guide Chemistryreem halawiNo ratings yet
- F321 CalculationsDocument21 pagesF321 CalculationsDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Chemistry Form 4 2020Document38 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Chemistry Form 4 2020Liana JalilNo ratings yet