Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsBDGS
BDGS
Uploaded by
nahiyan.khan.siyanaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Advent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalDocument39 pagesAdvent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalAfrin AnwarNo ratings yet
- The Arrival of The British: Bangladesh Studies Grade-9Document26 pagesThe Arrival of The British: Bangladesh Studies Grade-9azmain prantoNo ratings yet
- Advent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalDocument15 pagesAdvent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalFarhana Faruquee 1812059615No ratings yet
- Military Institute of Science and Technology: Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering DepartmentDocument24 pagesMilitary Institute of Science and Technology: Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering DepartmentMuhammad Ashiqur Rahaman NoorNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument31 pagesEast India Companymahnoorimran100% (1)
- Battle of Plassey (1757)Document19 pagesBattle of Plassey (1757)Nomani FoundationNo ratings yet
- British RajDocument8 pagesBritish RajLakshmi KsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Week II - Roots of BangladeshDocument28 pagesWeek II - Roots of BangladeshMusfirat Ahmed Sajin 2131571630No ratings yet
- Super Class Midterm 2019 Presentation WA Grade 9Document39 pagesSuper Class Midterm 2019 Presentation WA Grade 9AmmarNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document12 pagesPresentation 1NitishNo ratings yet
- History 2Document17 pagesHistory 2Good Anony7No ratings yet
- British RajDocument8 pagesBritish RajLakshmi KsrinivasNo ratings yet
- How Did EIC Start?Document21 pagesHow Did EIC Start?Ammar QureshiNo ratings yet
- British EmpireDocument8 pagesBritish Empirenicoleta.cNo ratings yet
- Quiz - 1 - Lecture-2 - Early Impacts of British ImperialismDocument11 pagesQuiz - 1 - Lecture-2 - Early Impacts of British ImperialismMohasin Niloy Ahmed 2121497642No ratings yet
- History 1Document41 pagesHistory 1juberNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 NotesDocument11 pagesChap 2 Notesumais kamranNo ratings yet
- Module 05 PDFDocument14 pagesModule 05 PDFIndigo CupcakeNo ratings yet
- Modern History of Bihar 41 PDFDocument21 pagesModern History of Bihar 41 PDFHago KrNo ratings yet
- India and China in The Age of ImperialismDocument7 pagesIndia and China in The Age of ImperialismKayeden CubacobNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument192 pagesEast India CompanyFIZA SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- Revolt of 1857Document9 pagesRevolt of 1857Zanetta SuriNo ratings yet
- British Colonialism in Greater IndiaDocument59 pagesBritish Colonialism in Greater IndiaRafia TasnimNo ratings yet
- British Raj: India in The Colonial Period Under The BritishDocument18 pagesBritish Raj: India in The Colonial Period Under The BritishJericho BautistaNo ratings yet
- India Act 1919Document22 pagesIndia Act 1919Mohasin Niloy Ahmed 2121497642No ratings yet
- Bengal To Bangladesh: Tracing Its Historical Roots: HIS 103 Lecture-1Document15 pagesBengal To Bangladesh: Tracing Its Historical Roots: HIS 103 Lecture-1Taef Hossain 1531416630No ratings yet
- Decline NotesDocument4 pagesDecline NotesHarry ShawNo ratings yet
- East India Company ShowDocument19 pagesEast India Company ShowAyushman Dubey100% (2)
- UP Buxar: Unit 8 The British - Iw Eastern India TODocument9 pagesUP Buxar: Unit 8 The British - Iw Eastern India TOAnjali AroraNo ratings yet
- The British in IndiaDocument1 pageThe British in Indiam1kuuuNo ratings yet
- British Colonialism in Greater India (Lec 4)Document59 pagesBritish Colonialism in Greater India (Lec 4)arid zeusNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 Enter The British Notes (Questions)Document6 pagesChap-2 Enter The British Notes (Questions)Rahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Arrival of British in IndiaDocument24 pagesArrival of British in IndiaAyesha KhadijaNo ratings yet
- Political Background of Colonial Rule in India: Dr. Mohammad Humayun KabirDocument26 pagesPolitical Background of Colonial Rule in India: Dr. Mohammad Humayun Kabirabdullah islamNo ratings yet
- East India Company ShowDocument19 pagesEast India Company ShowrazwanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Colonial Rule in BengalDocument4 pagesImpact of Colonial Rule in BengalShahanaj Akther TamannaNo ratings yet
- 03 The British East India ComapnyDocument22 pages03 The British East India ComapnydhruvaNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument31 pagesEast India Companyomarali.office4877No ratings yet
- Arrival of The BritishDocument9 pagesArrival of The BritishMuhammad Asad AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 History o LevelDocument4 pagesChapter 2 History o LevelAbdul WasayNo ratings yet
- Battle of PlasseyDocument10 pagesBattle of PlasseyAashana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- East India Companythe Organization That Changed Teh WorldDocument35 pagesEast India Companythe Organization That Changed Teh WorldMohammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Do Britain Owe Reparations To India?Document2 pagesDo Britain Owe Reparations To India?ashwini patilNo ratings yet
- What Was The East India Company (Eng-Bng)Document14 pagesWhat Was The East India Company (Eng-Bng)dhruvaNo ratings yet
- EIC NotesDocument25 pagesEIC Notesbulldozer100% (1)
- Mughal Rule in Sub-ContinentDocument45 pagesMughal Rule in Sub-Continentʍʊɦǟʍʍǟɖ ֆɦʊǟɨɮNo ratings yet
- 025 Day 24 European Penetration of IndiaDocument29 pages025 Day 24 European Penetration of IndiaMohit SuaradkarNo ratings yet
- Company Rule in Bengal (Modern History)Document18 pagesCompany Rule in Bengal (Modern History)nahopa9788No ratings yet
- The East India CompanyDocument24 pagesThe East India CompanyHareem Sattar100% (1)
- Modern HistoryDocument156 pagesModern HistoryPrashant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Modern IndiaDocument14 pagesModern IndiaShahidNo ratings yet
- G8 From Trade To Territory Flow Chart PDFDocument2 pagesG8 From Trade To Territory Flow Chart PDFSonia100% (2)
- History Part 1Document70 pagesHistory Part 1arunNo ratings yet
- Chapter-16 - British Rule Before 1857.pdf-72Document5 pagesChapter-16 - British Rule Before 1857.pdf-72Shivanand KamatarNo ratings yet
- Mughal Empire of IndiaDocument5 pagesMughal Empire of IndiaMESSAOUD MADNINo ratings yet
- 7-Economic Policies of The EastDocument15 pages7-Economic Policies of The Eastafi12gNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies: Grade 5Document19 pagesEnvironmental Studies: Grade 5chethan_438784378No ratings yet
- Colonial History of BengalDocument32 pagesColonial History of BengalRamishaNo ratings yet
- HIS103 Chapter 1Document4 pagesHIS103 Chapter 1shifatNo ratings yet
- HY Result Class 7Document1 pageHY Result Class 7nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- BDGS Chap-6Document18 pagesBDGS Chap-6nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- BDGS Chap-8Document7 pagesBDGS Chap-8nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Much Ado About Nothing William ShakespeareDocument3 pagesMuch Ado About Nothing William Shakespearenahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Lit 2Document2 pagesLit 2nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book NotesDocument9 pagesCambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book Notesnahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book NotesDocument5 pagesCambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book Notesnahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
BDGS
BDGS
Uploaded by
nahiyan.khan.siyana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views11 pagesBDGS
BDGS
Uploaded by
nahiyan.khan.siyanaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Chap-1
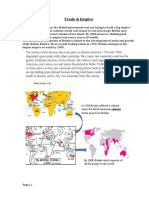
Bengal as a bridgehead of the British emperor
Economic decline in Eastern Bengal
• The arrival of European -15 century
• This arrival coincide the decline of Mughal
• The subcontinent became an arena of struggle
(Among indigenous and other Europeans)
Arrival of British east Indian Company
• By 1600s Mughal Emperor had culminated strong
power, dominance, resources , culture etc.
British East India company
• A private company Formed 1600 ( under Queen
Elizabeth l )
• During Mughal emperor
• Establish factory 1650, Hooghly ( Bengal)
• Founded City of Kolkata (1690) Massive expansion
started
• 1690 started political dominance
British India 1914
• Governor of Bengal Sah Suja the English to trade in
Bengal without any customs duty
• With immense profit it was becoming a ruling
enterprise
• The company took advantages of the political
fragmentation of and internal conspiracy Mughal
Rulers.
• In 1757, Siraj-Ud-Doula ( last Nawab of Bengal) was
defeated in Battle of Plassey ( Polasi) by Robert
Clive
• Granted the title of Diwani in Bangla, Bihar, Orissa
making t he supreme governing power
Robert Clive
Early impact of the British
• Because of extreme drought and flood lack of
cultivation, unrestricted profiteering grain markets let
to a feminine between 1769-1773 ( in Bengali 1176-
1180)
• Commonly known as Chiyattorer Monantor
• One third of Bengal's population starved to death
Chhiyattorer Monontar
• The permanent Settlement and the Bengal Peasantry
• In late 18 century India stared developing with the
power of East India company. Still it found loss because
of
1. Corruption of officers
2. Massive military expenditure
3. Famine of 1770
• Company transformed into an implement of British
foreign policy
Warren Hastings
First Govornor General
Lord Charles Cornwallis
2nd Govornor General
Large-scale export oriented cash cropping
• Bengal was already producing the following ( offten
exported)
• Cotton
• Rice
• Sugarcane
• Mulberry
• Silk and spices were also very precious and attractive
products of India.
You might also like
- Advent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalDocument39 pagesAdvent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalAfrin AnwarNo ratings yet
- The Arrival of The British: Bangladesh Studies Grade-9Document26 pagesThe Arrival of The British: Bangladesh Studies Grade-9azmain prantoNo ratings yet
- Advent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalDocument15 pagesAdvent of Colonial Rule and Annexation of BengalFarhana Faruquee 1812059615No ratings yet
- Military Institute of Science and Technology: Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering DepartmentDocument24 pagesMilitary Institute of Science and Technology: Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering DepartmentMuhammad Ashiqur Rahaman NoorNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument31 pagesEast India Companymahnoorimran100% (1)
- Battle of Plassey (1757)Document19 pagesBattle of Plassey (1757)Nomani FoundationNo ratings yet
- British RajDocument8 pagesBritish RajLakshmi KsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Week II - Roots of BangladeshDocument28 pagesWeek II - Roots of BangladeshMusfirat Ahmed Sajin 2131571630No ratings yet
- Super Class Midterm 2019 Presentation WA Grade 9Document39 pagesSuper Class Midterm 2019 Presentation WA Grade 9AmmarNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document12 pagesPresentation 1NitishNo ratings yet
- History 2Document17 pagesHistory 2Good Anony7No ratings yet
- British RajDocument8 pagesBritish RajLakshmi KsrinivasNo ratings yet
- How Did EIC Start?Document21 pagesHow Did EIC Start?Ammar QureshiNo ratings yet
- British EmpireDocument8 pagesBritish Empirenicoleta.cNo ratings yet
- Quiz - 1 - Lecture-2 - Early Impacts of British ImperialismDocument11 pagesQuiz - 1 - Lecture-2 - Early Impacts of British ImperialismMohasin Niloy Ahmed 2121497642No ratings yet
- History 1Document41 pagesHistory 1juberNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 NotesDocument11 pagesChap 2 Notesumais kamranNo ratings yet
- Module 05 PDFDocument14 pagesModule 05 PDFIndigo CupcakeNo ratings yet
- Modern History of Bihar 41 PDFDocument21 pagesModern History of Bihar 41 PDFHago KrNo ratings yet
- India and China in The Age of ImperialismDocument7 pagesIndia and China in The Age of ImperialismKayeden CubacobNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument192 pagesEast India CompanyFIZA SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- Revolt of 1857Document9 pagesRevolt of 1857Zanetta SuriNo ratings yet
- British Colonialism in Greater IndiaDocument59 pagesBritish Colonialism in Greater IndiaRafia TasnimNo ratings yet
- British Raj: India in The Colonial Period Under The BritishDocument18 pagesBritish Raj: India in The Colonial Period Under The BritishJericho BautistaNo ratings yet
- India Act 1919Document22 pagesIndia Act 1919Mohasin Niloy Ahmed 2121497642No ratings yet
- Bengal To Bangladesh: Tracing Its Historical Roots: HIS 103 Lecture-1Document15 pagesBengal To Bangladesh: Tracing Its Historical Roots: HIS 103 Lecture-1Taef Hossain 1531416630No ratings yet
- Decline NotesDocument4 pagesDecline NotesHarry ShawNo ratings yet
- East India Company ShowDocument19 pagesEast India Company ShowAyushman Dubey100% (2)
- UP Buxar: Unit 8 The British - Iw Eastern India TODocument9 pagesUP Buxar: Unit 8 The British - Iw Eastern India TOAnjali AroraNo ratings yet
- The British in IndiaDocument1 pageThe British in Indiam1kuuuNo ratings yet
- British Colonialism in Greater India (Lec 4)Document59 pagesBritish Colonialism in Greater India (Lec 4)arid zeusNo ratings yet
- Chap-2 Enter The British Notes (Questions)Document6 pagesChap-2 Enter The British Notes (Questions)Rahat RizwanNo ratings yet
- Arrival of British in IndiaDocument24 pagesArrival of British in IndiaAyesha KhadijaNo ratings yet
- Political Background of Colonial Rule in India: Dr. Mohammad Humayun KabirDocument26 pagesPolitical Background of Colonial Rule in India: Dr. Mohammad Humayun Kabirabdullah islamNo ratings yet
- East India Company ShowDocument19 pagesEast India Company ShowrazwanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Colonial Rule in BengalDocument4 pagesImpact of Colonial Rule in BengalShahanaj Akther TamannaNo ratings yet
- 03 The British East India ComapnyDocument22 pages03 The British East India ComapnydhruvaNo ratings yet
- East India CompanyDocument31 pagesEast India Companyomarali.office4877No ratings yet
- Arrival of The BritishDocument9 pagesArrival of The BritishMuhammad Asad AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 History o LevelDocument4 pagesChapter 2 History o LevelAbdul WasayNo ratings yet
- Battle of PlasseyDocument10 pagesBattle of PlasseyAashana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- East India Companythe Organization That Changed Teh WorldDocument35 pagesEast India Companythe Organization That Changed Teh WorldMohammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Do Britain Owe Reparations To India?Document2 pagesDo Britain Owe Reparations To India?ashwini patilNo ratings yet
- What Was The East India Company (Eng-Bng)Document14 pagesWhat Was The East India Company (Eng-Bng)dhruvaNo ratings yet
- EIC NotesDocument25 pagesEIC Notesbulldozer100% (1)
- Mughal Rule in Sub-ContinentDocument45 pagesMughal Rule in Sub-Continentʍʊɦǟʍʍǟɖ ֆɦʊǟɨɮNo ratings yet
- 025 Day 24 European Penetration of IndiaDocument29 pages025 Day 24 European Penetration of IndiaMohit SuaradkarNo ratings yet
- Company Rule in Bengal (Modern History)Document18 pagesCompany Rule in Bengal (Modern History)nahopa9788No ratings yet
- The East India CompanyDocument24 pagesThe East India CompanyHareem Sattar100% (1)
- Modern HistoryDocument156 pagesModern HistoryPrashant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Modern IndiaDocument14 pagesModern IndiaShahidNo ratings yet
- G8 From Trade To Territory Flow Chart PDFDocument2 pagesG8 From Trade To Territory Flow Chart PDFSonia100% (2)
- History Part 1Document70 pagesHistory Part 1arunNo ratings yet
- Chapter-16 - British Rule Before 1857.pdf-72Document5 pagesChapter-16 - British Rule Before 1857.pdf-72Shivanand KamatarNo ratings yet
- Mughal Empire of IndiaDocument5 pagesMughal Empire of IndiaMESSAOUD MADNINo ratings yet
- 7-Economic Policies of The EastDocument15 pages7-Economic Policies of The Eastafi12gNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies: Grade 5Document19 pagesEnvironmental Studies: Grade 5chethan_438784378No ratings yet
- Colonial History of BengalDocument32 pagesColonial History of BengalRamishaNo ratings yet
- HIS103 Chapter 1Document4 pagesHIS103 Chapter 1shifatNo ratings yet
- HY Result Class 7Document1 pageHY Result Class 7nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- BDGS Chap-6Document18 pagesBDGS Chap-6nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- BDGS Chap-8Document7 pagesBDGS Chap-8nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Much Ado About Nothing William ShakespeareDocument3 pagesMuch Ado About Nothing William Shakespearenahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Lit 2Document2 pagesLit 2nahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book NotesDocument9 pagesCambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book Notesnahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book NotesDocument5 pagesCambridge Lower Secondary Learners Book Notesnahiyan.khan.siyanaNo ratings yet