Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9
9
Uploaded by
dennyherdanathaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9
9
Uploaded by
dennyherdanathaCopyright:
Available Formats
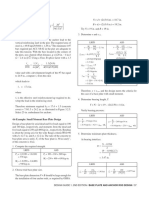
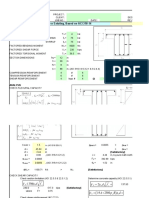
8.
Check beam shear capacity: M 43
f1 = = = 0.9 kip.in.
Allowable V = 0.4Fy (A) = 0.4(36)(18.35 × 0.45 + S w 48
6(1)) = 205 kip. 14.4
f2 = = 0.6 kip in.
Since 205 kip exceeds the actual shear of 14.4 kip, 24
the member is OK in this regard. (Shear is hardly ever
critical in lifting beams.) f w = f 1 + f 2 = 0.9 + 0.6 = 15
. kip in.
9. Check for beam bending capacity: 5
16 -in. fillet weld → 4.6 kip/in. > 1.5 OK
20,000 20,000 In order to keep the weather out, use an all around
Lc = = = 172 < 12( 30) (AISC Spec. F1.1)
d A f ( Fy ) 3.22( 36) weld. The hole is made 1½ in. dia. to accept the 1 in.
dia. pin. The corner of the plate is lopped off to
therefore a reduced Fb must be calculated (AISC formula
accommodate the inside length of the shackle minus the
F1-8 governs).
line diameter.
12,000 A f 12,000(7.59)(.75) Min. a = 0.5(d) = 0.5(1.5) = 0.75 in. < 3 – 0.75 OK
Fb = = = 10.34 ksi
ld 30(12)(18.35) Min. e = 0.67(d) = 0.67(1.5) = 1.0 in. < 2.25 OK
Check for dishing:
Allowable M = FbS = 10.34(142) = 1468 kip-in. = 122
kip-ft > 108 OK Min. t = 0.25(d) = 0.375 in. < 1.25 OK
10. Torsion is not a problem in this example, as stated Check for tension tearing at sides of hole:
previously. Ultimate Load Pu = 2atFu = 2(2.25)(1.25)58 = 326 kip
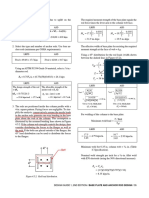
11. Select shackle size for upper slings: Apply factor of safety of 5.
From Fig. 13C the maximum line load is 14.4 × Design P = 326/5 = 65 kip > 15 OK
1.414 = 20.4 kip when angle θ is at the 90° limit.
A 12-ton shackle is selected (see Fig. 5). The jaw Check for lug tearout:
width is 2¼ in., pin diameter is 1 38 in., flange diameter . Fb te 2 167
167 . )(3 − 0.75) 2
. (24)(125
Allowable P = =
is 3 in., and inside length is 4 1116 in. Select shackle size d 15
.
for lower slings: referring to Fig. 13B the load is 14.4 = 169 kip > 20.4 OK
kip and a 8½-ton shackle would be in order. For Fig. 13C 13. Design of bottom lugs:
the load is 28.8 kip and a 17-ton shackle will suffice. Instead of individual lugs, it was decided previously
to use a continuous plate with holes at 1 ft 0 in. on
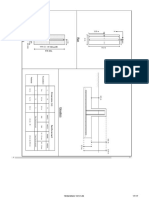
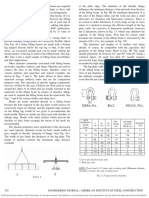
12. Design top lug: center. The assumed thickness of 1 in. easily
A trial lug plate thickness of 1¼ in. is chosen to be accommodates the jaws of the 8½-ton shackle. The holes
compatible with the 12-ton shackle. A trial size is shown will be made 1½-in. dia. to accept the 1 18 -in. dia. pin or
in Fig. 16A with the dimensions picked to accommodate
a larger pin, if desired. (If it is anticipated that the beam
the 12-ton shackle. The work line of the diagonal load is
will be used as in Fig. 4B, the center hole should be
made to intersect the center of the weld when the load is
made 1¾-in. dia. to accept the 1 58 -in. dia. pin of the 17-
at its maximum practical angle of 45°. At this angle the
load is 20.4 kip. ton shackle.)
20.4
Requird weld = = 0.85 kip in .
2(12)
To meet AISC Specification Table J2.4, a minimum
size fillet weld of 516 in. is required.
Check the weld requirements for a vertical pull of
14.4 kip:
Using the Line Method (Omer Blodgett, Design of
Welded Structures, pages 7.4-62).
d 2 12 2
Sw = = = 48in.2
3 3
M = 3(14.4) = 43 kip-in. Figure 16.
FOURTH QUARTER / 1991 157
© 2003 by American Institute of Steel Construction, Inc. All rights reserved. This publication or any part thereof must not be reproduced in any form without the written permission of the publisher.
You might also like
- Advanced Diagnostics Ford Manual-FordDocument55 pagesAdvanced Diagnostics Ford Manual-FordAnonymous 8To07bJFa71% (7)
- Ibong Tiririt (MDSP 1) Machine Design and Shop Practice ProblemsDocument173 pagesIbong Tiririt (MDSP 1) Machine Design and Shop Practice ProblemsRoss AlteaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Frequency Response of BJT & MosfetDocument54 pagesChapter 9 Frequency Response of BJT & Mosfetshubhankar palNo ratings yet
- Bottom Failure - Annex K - en 14015 - Rev 3Document3 pagesBottom Failure - Annex K - en 14015 - Rev 3KP SahuNo ratings yet
- Aisc 2Document5 pagesAisc 2CyrilNo ratings yet
- AlterationDocument37 pagesAlterationkrishimaNo ratings yet
- Pilecap DesignDocument7 pagesPilecap DesignEngr Zin Myo MinNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt Design For Shear and TensionDocument2 pagesAnchor Bolt Design For Shear and Tensionk.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- A Bolts Aci318 05Document6 pagesA Bolts Aci318 05RnD2013No ratings yet
- ATC4Document1 pageATC4Aek JanNo ratings yet
- ..Document22 pages..Ghiffa Syauqiyya Harahap 1707113714No ratings yet
- Slab Design:: Two Way Concrete Floor SystemDocument3 pagesSlab Design:: Two Way Concrete Floor SystemArpan SahaNo ratings yet
- Mstrip-Base Plate QueryDocument2 pagesMstrip-Base Plate QueryPANKAJ TAMBAKHENo ratings yet
- ATC5Document1 pageATC5Aek JanNo ratings yet
- Machine Design - INHOUSE 3Document28 pagesMachine Design - INHOUSE 3Pia May Torres PablicoNo ratings yet
- Alternate Beam DesignDocument14 pagesAlternate Beam DesignLandel SmithNo ratings yet
- Composite Floor Beam With CantileverDocument6 pagesComposite Floor Beam With CantileverprasNo ratings yet
- SA LAB - Singly Reinforced BeamDocument8 pagesSA LAB - Singly Reinforced BeamAjayNo ratings yet
- Assignment-7 1Document6 pagesAssignment-7 1Md. Kibria FerdousNo ratings yet
- Slab - Continous One WayDocument6 pagesSlab - Continous One WayAyitehek 99No ratings yet
- Bobcat S100 - Skid Steer - SlabCalcs - GOODDocument28 pagesBobcat S100 - Skid Steer - SlabCalcs - GOODKailin JuNo ratings yet
- Deep Beam Design Based On ACI 318-19: Input DataDocument1 pageDeep Beam Design Based On ACI 318-19: Input Datajorge01No ratings yet
- Base Plate & Bolt DesignDocument2 pagesBase Plate & Bolt DesigndovermanNo ratings yet
- Computation of The Results of Isolated Footings For Proposed BuildingDocument3 pagesComputation of The Results of Isolated Footings For Proposed BuildingKendrickNo ratings yet
- Design of Plate Girder: Faculty of Engineering Technology and ResearchDocument15 pagesDesign of Plate Girder: Faculty of Engineering Technology and ResearchDhruv ShahNo ratings yet
- Screw ProblemsDocument40 pagesScrew ProblemsanthonyNo ratings yet
- Shear Connections Notes: (1) The Beams Considered With Coped ConditionDocument9 pagesShear Connections Notes: (1) The Beams Considered With Coped ConditionSrikanth SikhaNo ratings yet
- 970119rev0 Breakout Torque 900HP ECI Toque TrackDocument12 pages970119rev0 Breakout Torque 900HP ECI Toque TrackProyectil De ProyectoNo ratings yet
- Flexural Design Reinforced Concrete T Beams ACI 318 14Document19 pagesFlexural Design Reinforced Concrete T Beams ACI 318 14alufuq companyNo ratings yet
- Composite Beam Design With Verco Floor Deck Based On AISC Manual 9thDocument6 pagesComposite Beam Design With Verco Floor Deck Based On AISC Manual 9thridho ziskaNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap Design For 3-Piles Pattern Based On ACI 318-05Document8 pagesPile Cap Design For 3-Piles Pattern Based On ACI 318-05PatyNo ratings yet
- Shear - Strength - of - Concrete - Slabs - With - Openings - ACI 318-14Document17 pagesShear - Strength - of - Concrete - Slabs - With - Openings - ACI 318-14AzlanNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1Anwaraime RadzakNo ratings yet
- RC Example ES-EN Code-1Document17 pagesRC Example ES-EN Code-1Firomsa EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures: Time: 4 HRS.) (Marks: 100Document20 pagesDesign of Steel Structures: Time: 4 HRS.) (Marks: 100Bhumika YadavNo ratings yet
- Desing of SlabDocument40 pagesDesing of SlabJohn Ajish100% (1)
- Typical Slab DesignDocument3 pagesTypical Slab DesignArpan SahaNo ratings yet
- Corbel For Bottom Slab of Water Tank Design of Corbel at El+18.266Document2 pagesCorbel For Bottom Slab of Water Tank Design of Corbel at El+18.266mathuNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument44 pagesPile DesignEr Navneet JassiNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument44 pagesPile DesignEr Navneet JassiNo ratings yet
- Crack WidthDocument4 pagesCrack WidthAmmarNo ratings yet
- Moment Connection Design For Beam To Weak Axis Column Based On AISC 360-10/16Document4 pagesMoment Connection Design For Beam To Weak Axis Column Based On AISC 360-10/16gyanwapiNo ratings yet
- PileCaps Important Calculation (SI Units)Document8 pagesPileCaps Important Calculation (SI Units)Kaushal RautNo ratings yet
- HW #3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesHW #3 SolutionsLuis AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Aisc 28Document4 pagesAisc 28mirfanjpcgmailcomNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap Design For 3-Piles Pattern Based On ACI 318-19Document6 pagesPile Cap Design For 3-Piles Pattern Based On ACI 318-19Vivian Guadalupe Pérez HernándezNo ratings yet
- Concrete 003 PDFDocument25 pagesConcrete 003 PDFStevieNo ratings yet
- Simpson SMF Beam DesignDocument11 pagesSimpson SMF Beam DesignQuốc KhánhNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Composite BeamDocument5 pagesEnhanced Composite BeamgalatiansNo ratings yet
- 22 Singly Reinforced BeamDocument8 pages22 Singly Reinforced Beamabdullah rahmanNo ratings yet
- Design Steps For SRBDocument3 pagesDesign Steps For SRBKhajaNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document76 pagesCH 10Sky 6794No ratings yet
- Timesaving TorsionDesign IADocument22 pagesTimesaving TorsionDesign IAzhengwenyi4No ratings yet
- BOX Sec-Beam-Column-AiscDocument6 pagesBOX Sec-Beam-Column-AiscWintun73No ratings yet
- Beam Design DD2Document1 pageBeam Design DD2Emdadul HuqNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Clip Angle ConnectionDocument8 pagesMathcad - Clip Angle ConnectionShobanBaabu ArumugamNo ratings yet
- External Applied Torque: Applying, We: A B A BDocument1 pageExternal Applied Torque: Applying, We: A B A BJuan BlanquicettNo ratings yet
- Concrete BeamDocument40 pagesConcrete BeamJoshua NideaNo ratings yet
- Deep BeamDocument1 pageDeep BeamAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument188 pagesFoundationARUNKUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Crane Bridge Box+4l100Document5 pagesCrane Bridge Box+4l100Wintun73No ratings yet
- General PS4Document1 pageGeneral PS4dennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- Temporary Support CheckDocument1 pageTemporary Support CheckdennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument1 pageExampledennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
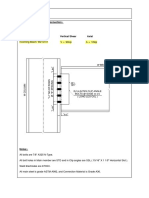
- Two Leg Bridle Slings: Single Rope Legs, Oblong Link. Eye-Hoist HooksDocument1 pageTwo Leg Bridle Slings: Single Rope Legs, Oblong Link. Eye-Hoist HooksdennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5dennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4dennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Lifting Beams: David T. Ricker Is A Structural Engineer in Payson, AZDocument1 pageDesign and Construction of Lifting Beams: David T. Ricker Is A Structural Engineer in Payson, AZdennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
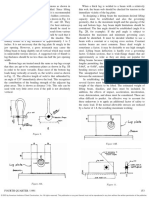
- Torsion Analysis of Steel Members,: Strength Is 6 Times The Safe Working Load. Fig. 5. Forged Anchor ShacklesDocument1 pageTorsion Analysis of Steel Members,: Strength Is 6 Times The Safe Working Load. Fig. 5. Forged Anchor ShacklesdennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slab CheckDocument2 pagesConcrete Slab CheckdennyherdanathaNo ratings yet
- 8&9-High Voltage KitDocument7 pages8&9-High Voltage KitMinh VienNo ratings yet
- Developmental Counseling Form: The Leader's Facts and Observations Prior To The Counseling.)Document3 pagesDevelopmental Counseling Form: The Leader's Facts and Observations Prior To The Counseling.)Anonymous EpKfz0LNo ratings yet
- User Manual EG8245Q EG8247Q 4065149Document13 pagesUser Manual EG8245Q EG8247Q 4065149Claudio Carrasco NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Blues Scales - Euphonium (Bass Clef) - LexcerptsDocument2 pagesBlues Scales - Euphonium (Bass Clef) - LexcerptsLexcerptsNo ratings yet
- PHILIPS SLS15 Bulb 14 WATTS 120 VOLTS $ 28.08Document1 pagePHILIPS SLS15 Bulb 14 WATTS 120 VOLTS $ 28.08Dustin GriffithNo ratings yet
- B031910499 - Students Who Study Abroad Achieve Greater SuccessDocument9 pagesB031910499 - Students Who Study Abroad Achieve Greater SuccessIsrat DibaNo ratings yet
- Swithmail V 2.0: Usage and General How-ToDocument6 pagesSwithmail V 2.0: Usage and General How-ToDaniel AraújoNo ratings yet
- Trust CasesDocument5 pagesTrust CasesRevina EstradaNo ratings yet
- AllDocument2 pagesAllamarkiran vinayakNo ratings yet
- Informe Semana 11Document4 pagesInforme Semana 11LILI JHOVANITA SALDAÑA MANOSALVANo ratings yet
- Share Capital Materials-1 (Theory and Framework)Document18 pagesShare Capital Materials-1 (Theory and Framework)Joydeep DuttaNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report Arun KabraDocument53 pagesSummer Internship Report Arun KabraGuruNo ratings yet
- AFV - Modeller July-Aug 2016Document68 pagesAFV - Modeller July-Aug 2016Prplknite100% (5)
- PLC Lader LogicDocument53 pagesPLC Lader LogicKamaraju DaviliNo ratings yet
- Conservative Political TheoryDocument1 pageConservative Political TheoryOpenLearner0% (1)
- Surge Arrester - GIS ELK-04CDocument4 pagesSurge Arrester - GIS ELK-04CCbdtxd PcbtrNo ratings yet
- L6 - Shear and Moment DiagramsDocument11 pagesL6 - Shear and Moment DiagramsSuman BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Structure Gad DrawingsDocument56 pagesStructure Gad Drawingsdheeraj sehgalNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarms PDFDocument5 pagesFire Alarms PDFSaulangel CruzNo ratings yet
- Health Economics 2Document4 pagesHealth Economics 2Rira Fauziah INo ratings yet
- Classification of MSME in IndiaDocument7 pagesClassification of MSME in Indiaaishu patilNo ratings yet
- SEM-3 - Business Process Integration (BPI)Document20 pagesSEM-3 - Business Process Integration (BPI)Hee ManNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Uti Mutual Fund With Reliance Mutual FundDocument64 pagesAnalysis of Uti Mutual Fund With Reliance Mutual FundSanjayNo ratings yet
- Non-Current Asset Held For Sale - NotesDocument4 pagesNon-Current Asset Held For Sale - NotesMARCUAP Flora Mel Joy H.No ratings yet
- Anhang Amel 55Document12 pagesAnhang Amel 55frankNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Part 1 PPEDocument64 pagesModule 5. Part 1 PPElord kwantoniumNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Foundations of Mobile Radio Engineering First Edition Yacoub Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Foundations of Mobile Radio Engineering First Edition Yacoub Online Ebook All Chapter PDFarturo.williams321100% (13)
- URS R404aDocument1 pageURS R404aironiteNo ratings yet