Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3
3
Uploaded by
Siow Shi XianCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3
3
Uploaded by
Siow Shi XianCopyright:
Available Formats
3/6/24, 8:41 AM Platform | Study Fetch
Protein Structure and Function
Amino Acids and Peptide Bonds (Fig. 2.17b,c)
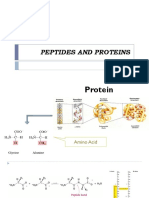
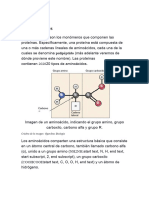
- Amino acids contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group that determines the amino acid type
- At physiological pH, the amino group is positively charged (NH3+) and the carboxyl group is negatively
charged (COO-)
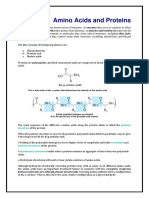
- Amino acids link together through peptide bonds between the carboxyl carbon and amino nitrogen of adjacent
amino acids
- Peptide bond formation involves the loss of a water molecule from the carboxyl oxygen and amino hydrogens
Amino Acid Properties
- There are 20 standard amino acids that make up cellular proteins
- Amino acids can be classified based on properties of their R groups
Protein Structure Determines Function
- The sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its 3D structure through folding
- A protein's 3D structure dictates its specific function in the cell
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
Nucleotide Composition
- Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides containing phosphate, sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and nitrogenous
base groups
Genetic Information Storage
- The sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids encodes genetic information much like letters in an alphabet (Fig.
2.17c)
- Nucleic acids are informational molecules that carry chemical information in their nucleotide sequence
DNA and RNA
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are two major classes of nucleic acids
- DNA stores and transmits genetic information to guide synthesis of RNA and proteins
- RNA has several roles in protein synthesis including mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
https://www.studyfetch.com/platform/studyset/65e7b8ed25d36a738a282618/material/65e7b9483971f34235635cba/document 1/1
You might also like
- 4Document1 page4Siow Shi XianNo ratings yet
- LO Week 4Document11 pagesLO Week 4Matthew ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino Acids: F. FerdinalDocument110 pagesProteins and Amino Acids: F. FerdinalfeliciaivdNo ratings yet
- 5 4 Huremovic - 2Document22 pages5 4 Huremovic - 2haurathyaNo ratings yet
- Visualization of Protein Structures Use of Pymol Software: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesVisualization of Protein Structures Use of Pymol Software: ObjectivesArpan GhoshNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Chemiccal ComponentDocument12 pages2.0 Chemiccal ComponentmiftahNo ratings yet
- Peptide Bond Formation of Polypeptides and ProteinDocument11 pagesPeptide Bond Formation of Polypeptides and ProteinSusana N peNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Bio-Molecules: 9 2. Proteins 13Document62 pagesStructure and Function of Bio-Molecules: 9 2. Proteins 13Alex-Mihai CiubaraNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument5 pagesContentsVasile CuprianNo ratings yet
- Aji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Document81 pagesAji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Gandhes Cintya DewiNo ratings yet
- Aji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Document81 pagesAji Sutrisno Food Science and Technology Universitas Brawijaya (Ub)Nirma MardinitaNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument51 pagesProteins and Amino AcidsAlbert TandyNo ratings yet
- Learning Targets Unit 1Document3 pagesLearning Targets Unit 1api-522789883No ratings yet
- Biomolecules of Life (Part 2) - ProteinsDocument34 pagesBiomolecules of Life (Part 2) - ProteinsNiharika GuptaNo ratings yet
- 28.01 - Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pages28.01 - Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsMarch SamNo ratings yet
- Proteins & Amino Acid 2016Document106 pagesProteins & Amino Acid 2016ririnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Amino Acids - ProteinsDocument81 pagesChemistry of Amino Acids - ProteinsgurmroadNo ratings yet
- 2.09 ProteinsDocument7 pages2.09 ProteinsMarsXplorerNo ratings yet
- SLG Chem 3 LG 5.3 Structure of Amino Acids and Levels of Protein StructureDocument9 pagesSLG Chem 3 LG 5.3 Structure of Amino Acids and Levels of Protein StructurefranzachilleslindayagNo ratings yet
- Protein StructureDocument42 pagesProtein StructureronojoysenguptaNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5Siow Shi XianNo ratings yet
- 03 - Intro UNIT 2Document24 pages03 - Intro UNIT 2Elena OlmedoNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryDocument77 pagesLehninger Principles of BiochemistryShivya BansalNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins 2018Document70 pagesAmino Acids, Peptides and Proteins 2018georgeNo ratings yet
- AminoácidosDocument5 pagesAminoácidoscarlosNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Macromolecules: 2.2.1 Carbohydrates-The Energy GiversDocument12 pagesStructure and Function of Macromolecules: 2.2.1 Carbohydrates-The Energy GiversSteven BanksNo ratings yet
- BiotinDocument12 pagesBiotinvasanthg.2.2002No ratings yet
- Asam Amino, Peptida Dan Protein: Oleh: Syaiful BahriDocument35 pagesAsam Amino, Peptida Dan Protein: Oleh: Syaiful BahriMita SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules PDFDocument11 pagesMacromolecules PDFChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- BasicDocument2 pagesBasicapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Their Structure: Cooh-Ch-Nh2 - RDocument12 pagesAmino Acids and Their Structure: Cooh-Ch-Nh2 - RRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecule:: Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pagesOrganic Molecule:: Nucleic AcidsCharles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- B1. Amino Acid Analysis and Chemical SequencingDocument4 pagesB1. Amino Acid Analysis and Chemical SequencinganiNo ratings yet
- Iejmd 2006 5 0237Document11 pagesIejmd 2006 5 0237aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Department of Industrial Chemistry: Bahir Dar UniversityDocument25 pagesDepartment of Industrial Chemistry: Bahir Dar UniversityFikere'ab HabtamuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of MicroorganismsDocument35 pagesChemistry of MicroorganismsJisan RaihanNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Physical Science - Grade 11 Quarter 3 - Module 10: Macromolecules: Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesLesson: Physical Science - Grade 11 Quarter 3 - Module 10: Macromolecules: Proteins and Nucleic AcidsJAY BALLESTEROSNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument17 pagesPROTEINSAbhijat Jha100% (1)
- Biochemistry ProteinDocument71 pagesBiochemistry Proteinurooj ilyasNo ratings yet
- Full download Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry (Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Series) 7th Edition, (Ebook PDF) file pdf all chapter on 2024Document41 pagesFull download Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry (Lippincott Illustrated Reviews Series) 7th Edition, (Ebook PDF) file pdf all chapter on 2024matuscatitaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 PPT (Laboratory) BiochemDocument16 pagesWeek 2 PPT (Laboratory) BiochemHumphrey SubitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Proteins and AminoacidsDocument37 pagesChapter 7. Proteins and AminoacidsMuhammad Adil Farhan Bin Ramlan E19A0157No ratings yet
- Proteins: Presented By: Deepika Kaithal M.Sc. Semester Iv Department of Applied PhysicsDocument23 pagesProteins: Presented By: Deepika Kaithal M.Sc. Semester Iv Department of Applied PhysicsasifNo ratings yet
- Overview of Protein StructureDocument3 pagesOverview of Protein StructureAnas JamshedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Protein Structure: B: Probing Composition, Sequence, and ConformationDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Protein Structure: B: Probing Composition, Sequence, and ConformationMona ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules ProteinsDocument13 pagesBiomolecules Proteinszaydharoon419No ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 08/03/2018Document33 pagesBio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 08/03/2018Atif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Generation of Random SequencesDocument80 pagesGeneration of Random SequencesHemant BetalaNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidDocument17 pagesAmino AcidAnonymous E4Rbo2sNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical Compomsotion of The Cell: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesChapter 4: Chemical Compomsotion of The Cell: ObjectivesHazim AziziNo ratings yet
- 03 Proteins Structure and FunctionsDocument57 pages03 Proteins Structure and FunctionsJohn bryan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Bioinfo Notes PDFDocument21 pagesBioinfo Notes PDFsaurav choudharyNo ratings yet
- 5.nucleic AcidDocument24 pages5.nucleic AcidAzizi ZainodinNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument16 pagesLec 2 - Amino Acids and ProteinsBishal SahNo ratings yet
- Essential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsDocument36 pagesEssential Idea: Proteins Have A Very Wide Range of Functions in Living OrganismsMike BevanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineDocument16 pagesAmino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 7 Structures and Functions of Proteins I-2020Document43 pagesBiochemistry Week 7 Structures and Functions of Proteins I-2020Karen 3No ratings yet
- Bionanocomposites: Integrating Biological Processes for Bioinspired NanotechnologiesFrom EverandBionanocomposites: Integrating Biological Processes for Bioinspired NanotechnologiesCarole AiméNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Web-Based Search Engines for Analyzing Biological MacromoleculesFrom EverandUtilizing Web-Based Search Engines for Analyzing Biological MacromoleculesNo ratings yet