Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Uploaded by
sharmabeefarms1992Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Uploaded by
sharmabeefarms1992Copyright:
Available Formats
Dual Nature Of Radiation and Matter
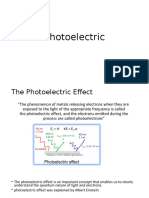
Photoelectric Effect Photoelectric Equation
The phenomenon of emission of electrons Where ф0 = Work function
from a metal surface when an electromagnetic E = Kmax + ф0 E = energy of incident light
wave of suitable frequency is incident on it is Kmax = maximum K.E of electron
called photoelectric effect.
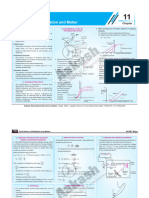
Photocell
electron Incident light
Light rays emission
Anode
Cathode
Photocell
Experimental Study Of Photoelectric Effect
• At constant frrequency v and potential V,
photocurrent ip α I (intensity) Intensity
Current I1
• At constant frequency and intensity, the I2
minimum negative potential at which the I3
photocurrent becomes zero is called stopping I3> I2>I1
potential (V0)
• At stopping potential V0, Kmax of electron = eV0 -V0 Voltage
• For a given frequency of the incident radiation,
the V0 is independent of I.
Emax Current
V1
V2
V3> V2>V1
V3
0 Ve(3) Ve(2) Ve(1) Retarding Potential
V0 V
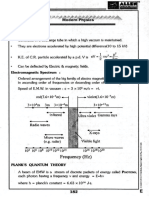
Davisson And Germer Experiment
• Intensity of scattered electrons depends on
scattering angle ф.
• A kink occurs in graph at ф = 50º for 54 eV beam.
• The intensity is maximum at accelerating voltage
54 eV. After this voltage, intensity starts decreasing.
54 V
de Broglie Wavelength
Scattered electrons
Intensity
h
λ= —
p
Where p is the momentum of the particle.
• For electron having K.E(K),
0 5 10 15 20 25 h
Accelerating voltage λ=
2mK
de Borglie Hypothesis • For ea charged particle accelerated by
potential V,
A particle in motion also possess wave-like h
λ=
properties. These waves are called matter wave. 2qmV
You might also like
- LMS Solutions QuantumDocument260 pagesLMS Solutions QuantumMartin SeungWhan Kim86% (7)
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument36 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matterggle82338No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of MatterDocument16 pagesDual Nature of Mattermahima sunilNo ratings yet
- 11 Photoelectric Effect Dual Nature of Matter RadiationsDocument12 pages11 Photoelectric Effect Dual Nature of Matter RadiationsHusaina zoebNo ratings yet
- Dual & Atomic NucliusDocument20 pagesDual & Atomic NucliussouravNo ratings yet
- 17 Dual-Nature-of-Matter-and-RadiationDocument19 pages17 Dual-Nature-of-Matter-and-RadiationDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Day 31Document10 pagesDay 31g.sathyanarayanan252008No ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument45 pagesPhotoelectric EffectdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: By: Louisa, Angelica, CalistaDocument17 pagesQuantum Physics: By: Louisa, Angelica, Calistaahmad fatoniNo ratings yet
- Particle Wave DualityDocument24 pagesParticle Wave DualityIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- Dual NatureDocument15 pagesDual NatureJinshy VinodNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationsDocument21 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationsVishesh SheraNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: IgureDocument27 pagesQuantum Physics: Igurep_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect: Day Thirty TwoDocument9 pagesPhotoelectric Effect: Day Thirty TwoPrayas RaneNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric NewDocument20 pagesPhotoelectric NewJun Hong TeeNo ratings yet
- 07 QuantumMechanicsDocument22 pages07 QuantumMechanicsĐăng NguyênNo ratings yet
- Photoelectricity HN 2023Document13 pagesPhotoelectricity HN 2023si siamNo ratings yet
- Electron and PhotonDocument20 pagesElectron and Photonnitin100% (2)
- Topic 1:: Particle DualityDocument15 pagesTopic 1:: Particle DualityAzelia PuteriNo ratings yet
- 01 - Properties SafetyDocument50 pages01 - Properties SafetyAnonymous yFUhyy3No ratings yet
- Photoelectric and Compton EffectDocument17 pagesPhotoelectric and Compton EffectRitam DattaNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Determining Plank's Constant Counter Voltage MethodDocument6 pagesAtomic and Nuclear Physics: Determining Plank's Constant Counter Voltage MethodSurafel akeleNo ratings yet
- X Ray NotesDocument5 pagesX Ray NotesCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Photoelectric Effect: Summary From Last TimeDocument6 pagesThe Photoelectric Effect: Summary From Last TimeNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dual NatureDocument87 pagesDual Naturemeow meowNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Electrostatics: You May Download All The Class Lectures From The Following BlogDocument43 pagesLecture 2: Electrostatics: You May Download All The Class Lectures From The Following Blogamiteetumtech2013No ratings yet
- JC Chapter 2 HandoutDocument4 pagesJC Chapter 2 Handoutxie gruNo ratings yet
- 30 34Document37 pages30 34Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Determining Planck's ConstantDocument4 pagesAtomic and Nuclear Physics: Determining Planck's ConstantAlejandra AwimbaweNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument13 pagesPhotoelectric EffectEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument6 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Mattersub100% (1)
- Electric CurrentDocument41 pagesElectric Currentnorhazli ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Expt. 3 Planck's ConstantDocument10 pagesExpt. 3 Planck's ConstantSandeepNo ratings yet
- DUAL - NATURE - OF - MATTER - RADIATION OneDocument25 pagesDUAL - NATURE - OF - MATTER - RADIATION OneLEGEND GAMINGNo ratings yet
- HV WH (V-V: E Energy of PhotonDocument1 pageHV WH (V-V: E Energy of PhotonNitin RanaNo ratings yet
- Module22-Lesson 1 Model of WavesDocument18 pagesModule22-Lesson 1 Model of Wavesdodoch2005No ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect XI A1Document15 pagesPhotoelectric Effect XI A14kcb48pgdsNo ratings yet
- L1 Basic Circuit Theory PDFDocument65 pagesL1 Basic Circuit Theory PDFKushal ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation MatterDocument4 pagesDual Nature of Radiation MatterPranshu PatelNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 1 A Particle Model of WavesDocument32 pagesCA Lesson 1 A Particle Model of Wavesc9kyyrcrt9No ratings yet
- 01-39 Dual Nature of Radiation MatterDocument39 pages01-39 Dual Nature of Radiation MatterStockPlusIndiaNo ratings yet
- Narayana Physics ADV Material - 1Document32 pagesNarayana Physics ADV Material - 1Sri VarshiniNo ratings yet
- Quantization of LightDocument12 pagesQuantization of LightPRIYAA A/P JAYASANKAR / UPMNo ratings yet
- 02.dual Nature of MatterDocument32 pages02.dual Nature of MatterSurya teja cvNo ratings yet
- PE Compton and X RaysDocument110 pagesPE Compton and X RaysShishir Babu RijalNo ratings yet
- Reflex Klystron PDFDocument23 pagesReflex Klystron PDFDr. Sudhansu Kumar Pati100% (1)
- 7 Electricity SDocument45 pages7 Electricity SNor ShuhadaNo ratings yet
- Smart Revision Quantum PhysicsDocument18 pagesSmart Revision Quantum PhysicsZAIHASRA BINTI AHMAD KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 141 MergedDocument5 pagesPHYSICS 141 Mergeds10668389No ratings yet
- Dual Nature Matter and RadiationDocument8 pagesDual Nature Matter and RadiationNITINMAGIC100% (1)
- 02a MI MEBiom XraysDocument54 pages02a MI MEBiom XraysRoshi_11No ratings yet
- Group Presentation: Quantum TunnellingDocument14 pagesGroup Presentation: Quantum TunnellingdeepakNo ratings yet
- Shri JalDocument29 pagesShri JalPrakhar MohnaniNo ratings yet
- Tube High by 1: Cathode RavsDocument12 pagesTube High by 1: Cathode RavsJasteg SinghNo ratings yet
- Quantum LecturesDocument117 pagesQuantum LecturesAman KaushikNo ratings yet
- The Interaction of Light and Matter: And: Refractive IndexDocument33 pagesThe Interaction of Light and Matter: And: Refractive IndexSiddharth RajamohananNo ratings yet
- 656018ce13ff95001940db17 ## Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument2 pages656018ce13ff95001940db17 ## Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterprincipaltamannaNo ratings yet
- 19 Quantum Physics Summary PDFDocument2 pages19 Quantum Physics Summary PDFabdul halimNo ratings yet
- PHY 102: Quantum Physics: Topic 1 The Nature of LightDocument42 pagesPHY 102: Quantum Physics: Topic 1 The Nature of LightsgmdhussainNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument34 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDisney DoreamonNo ratings yet
- Probing Matter: Where, λ is the wavelength of the particle h is the plack's constant p is the momentum of the particleDocument2 pagesProbing Matter: Where, λ is the wavelength of the particle h is the plack's constant p is the momentum of the particleTrials SartajNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Eugene MerzbacherDocument670 pagesQuantum Mechanics THIRD EDITION Eugene MerzbachersplouvrosNo ratings yet
- DiffractionDocument13 pagesDiffractiontimtailieu2010No ratings yet
- The Wave Like Nature of LightDocument6 pagesThe Wave Like Nature of LightChathumi LelwalaNo ratings yet
- Physics SyllabusDocument16 pagesPhysics SyllabusReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- PHYS 1003 Physics 1 (Technological) 2007: Quantum Physics - Assignment 6 and Tutorial QuestionsDocument20 pagesPHYS 1003 Physics 1 (Technological) 2007: Quantum Physics - Assignment 6 and Tutorial QuestionsFrancisco OlveraNo ratings yet
- 12 markscheme-HL-paper1Document42 pages12 markscheme-HL-paper1Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit 1 SEM II 2021-2022Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Unit 1 SEM II 2021-2022Sanat NarangNo ratings yet
- Duel Nature of MatterDocument46 pagesDuel Nature of MatterSheik Dawood Kadhar100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument7 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MatterKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sybsc Sem IV Paper IIDocument13 pagesSybsc Sem IV Paper IISayantan DeyNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument5 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Mattercopadag753No ratings yet
- Waves and Particles: Basic Concepts of Quantum Mechanics: Physics Dep., University College CorkDocument33 pagesWaves and Particles: Basic Concepts of Quantum Mechanics: Physics Dep., University College Corkjainam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit V Quantum Mechanics PPT PH101Document11 pagesUnit V Quantum Mechanics PPT PH101Kripanshu Kumar100% (1)
- MATTER-WAVe Exercise 1 - 4Document14 pagesMATTER-WAVe Exercise 1 - 4Karlssën DreyarNo ratings yet
- Tut SheetDocument9 pagesTut SheetramparkNo ratings yet
- Syllabus R13Document118 pagesSyllabus R13Eliezer BenjaminNo ratings yet
- 1.1.6 Einstein Coefficients - 1: Rate EquationDocument15 pages1.1.6 Einstein Coefficients - 1: Rate Equationshouravme2k11No ratings yet
- PHY110 Unit IV PDFDocument73 pagesPHY110 Unit IV PDFAnsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Physics March2019 B E Withcredits RegularJune-2018PatternFE DDF3F8EFDocument2 pagesPhysics March2019 B E Withcredits RegularJune-2018PatternFE DDF3F8EFvishalmahale647No ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument38 pagesQuantum MechanicsSoumyadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry ExamDocument12 pagesPhysical Chemistry ExamBreyonnaMorganNo ratings yet
- IAS Previous Year Test PapersDocument4 pagesIAS Previous Year Test PapersRavinder Singh100% (2)
- EEE R07 SyllabusDocument85 pagesEEE R07 SyllabusHima Chandu KakiNo ratings yet
- EP Mid-1 Question Papers and Mid-3Document3 pagesEP Mid-1 Question Papers and Mid-3Sonu GoudNo ratings yet
- Final LAS Science 9 Q2 W1Document19 pagesFinal LAS Science 9 Q2 W1Melogen Labrador100% (1)
- Pattern Printing in CDocument20 pagesPattern Printing in CAMIT KUMAR PRADHANNo ratings yet