Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leeband
Leeband
Uploaded by
samoha.businessOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leeband
Leeband
Uploaded by
samoha.businessCopyright:
Available Formats
# Class Notes on Space
## Introduction to Space
- **Definition**: Space, also known as outer space, is the vast expanse that exists beyond
Earth's atmosphere. It is where everything, including stars, planets, and galaxies, exists.
## Characteristics of Space
- **Vacuum**: Space is a near-perfect vacuum, meaning it has extremely low pressure and
density. There are only a few hydrogen atoms per cubic meter of space.
- **Temperature**: The temperature in space can vary dramatically. In sunlight, temperatures
can reach 250 degrees Fahrenheit, and in shadow, temperatures can drop to minus 250
degrees Fahrenheit.
## Components of the Universe
1. **Stars**: Massive celestial bodies made of hydrogen and helium that produce light and
heat through nuclear fusion.
2. **Planets**: Bodies that orbit stars, including the eight planets in our solar system.
3. **Moons**: Natural satellites that orbit planets.
4. **Comets and Asteroids**: Smaller celestial bodies; comets are made of ice and dust,
while asteroids are composed of metals and rocky material.
5. **Galaxies**: Large systems of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. The Milky
Way is our home galaxy.
## The Solar System
- **Structure**: Consists of the Sun, eight planets, their moons, and other celestial bodies
like dwarf planets and asteroids.
- **Inner Planets**: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars - rocky and smaller.
- **Outer Planets**: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune - larger and mostly gaseous.
## Exploration of Space
- **Telescopes**: Devices that allow us to observe distant planets, stars, and galaxies.
Notable examples include the Hubble Space Telescope.
- **Manned Spaceflights**: Human missions to space, such as the Apollo moon landings.
- **Unmanned Missions**: Spacecrafts and probes sent to explore the far reaches of our
solar system and beyond. Examples include the Voyager probes and the Mars Rovers.
## Theories and Concepts
- **Big Bang Theory**: The leading explanation about how the universe began; suggests that
the universe was once compacted into a small point that then expanded rapidly.
- **Relativity**: Einstein's theory explaining the relationship between space and time.
## Importance of Space Exploration
- **Scientific Knowledge**: Helps us understand the universe and our place in it.
- **Technology and Innovation**: Advances in space technology often lead to innovations on
Earth, such as satellite communications and GPS.
- **Inspiration and Curiosity**: Fuels curiosity and inspires future generations of scientists
and engineers.
These notes should provide a fundamental overview of space and its characteristics,
suitable for an introductory lecture or as a starting point for more in-depth study.
You might also like
- Electricity, Magnetism, and LightDocument789 pagesElectricity, Magnetism, and LightJasharatNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1. Universe and Solar SystemDocument7 pagesUNIT 1. Universe and Solar SystemtissusesNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument30 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemAngelie Fey OngNo ratings yet
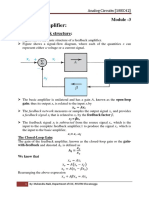
- ANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 (Module - 3)Document33 pagesANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 (Module - 3)mahendra naik71% (14)
- Clamp Meter - Mastering The Art of Measurement - EN.r00Document65 pagesClamp Meter - Mastering The Art of Measurement - EN.r00Carl SundbergNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument2 pagesSolar Systemava.bonettiiNo ratings yet
- Asteroid ADocument6 pagesAsteroid AIMade Adi WiadnyanaNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1يحي المهذبيNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 2Document1 pageAstronomy Notes 2SaraNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Wonders of PlanetsDocument3 pagesExploring The Wonders of PlanetsANNooonynmousNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Formation of The UniverseDocument29 pagesLesson 1 - Formation of The UniverseNovee Claire Peregrino SuarezNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes 1Document2 pagesAstronomy Notes 1SaraNo ratings yet
- Solar SystemDocument2 pagesSolar Systemfilipzdzierak535No ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar System - Early TheoriesDocument8 pagesOrigin of The Solar System - Early TheoriesCharles CaraigNo ratings yet
- Origin of The Solar SystemDocument12 pagesOrigin of The Solar SystemdhonaNo ratings yet
- Comets, Meteors and AsteroidsDocument40 pagesComets, Meteors and Asteroidsjocelyn.matigaNo ratings yet
- Comets, Asteroids, Meteoroids and MeteoritesDocument30 pagesComets, Asteroids, Meteoroids and Meteoriteskim hanaNo ratings yet
- SpaceDocument2 pagesSpaceAsror KurosakiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 9 10Document64 pagesLecture 8 9 10itzzharry5No ratings yet
- A Brief Overview On Nature and SpaceDocument3 pagesA Brief Overview On Nature and Spaceanshgupta91580No ratings yet
- PlanetsDocument2 pagesPlanetsMartin KissNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Science: Todays Topic Is About: AstronomyDocument35 pagesSeminar in Science: Todays Topic Is About: AstronomyJhosenette M NavarroNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Geology AssignmentDocument52 pagesEarth Science Geology AssignmentChristine MaeNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The UniverseDocument67 pagesThe Origin of The Universeorioluna00No ratings yet
- The Universe 5º EPODocument1 pageThe Universe 5º EPOdenebolapuerto2021No ratings yet
- Module 3Document33 pagesModule 3GracielaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 The Origin and Structure of The Solar System and The Earth System (1st Part)Document21 pagesCh1 The Origin and Structure of The Solar System and The Earth System (1st Part)Nedal MagarangNo ratings yet
- Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument25 pagesOrigin and Structure of The EarthArlyn TapisNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 8 - Comets Asteroids and MeteoroidsDocument90 pagesQ2 Week 8 - Comets Asteroids and MeteoroidsJohn ForteNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - The Solar System Up CloseDocument7 pagesTopic 7 - The Solar System Up Closeapi-208538578No ratings yet
- 645a226fe4b0146031629fa6 OriginalDocument6 pages645a226fe4b0146031629fa6 OriginalMAHADEV BHAKTINo ratings yet
- 02 - Universe and The Solar System (Part 2) PDFDocument41 pages02 - Universe and The Solar System (Part 2) PDFZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Formation of The Solar System PowerpointDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Formation of The Solar System PowerpointJoshua Manalili0% (1)
- Els SHS GR11Document6 pagesEls SHS GR11daughterofhades029No ratings yet
- Formation and Evolution of The Solar SystemDocument17 pagesFormation and Evolution of The Solar SystemjyoprasadNo ratings yet
- How Things Work in Space-1 - 240121 - 154547Document1 pageHow Things Work in Space-1 - 240121 - 154547anjalisolanke01No ratings yet
- GNR649 Lecture31 CometsDocument23 pagesGNR649 Lecture31 CometsR KumarNo ratings yet
- Exploring The UniverseDocument40 pagesExploring The Universeapi-243736913No ratings yet
- Science: Form 3Document17 pagesScience: Form 3akamNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science PowerPointDocument53 pagesEarth and Life Science PowerPointAlthea Mae DuqueNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth ScienceKC KayeNo ratings yet
- Earth EvolutionDocument37 pagesEarth Evolutionkrish_mplNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 8Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 8Racquel De Chavez MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Comets Meteors and AsteroidsDocument56 pagesComets Meteors and AsteroidsJeal Amyrrh Caratiquit100% (2)
- Planetary NebulaDocument19 pagesPlanetary NebulaAbraxazNo ratings yet
- Notes - The Big Bang Theory, The Solar System, THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTHDocument6 pagesNotes - The Big Bang Theory, The Solar System, THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTHShravani KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science NotesDocument21 pagesEarth Science NotesHannah May AquinoNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Comets, Meteors, and AsteroidsDocument28 pagesCompare and Contrast Comets, Meteors, and Asteroidsehlie canlas100% (1)
- Earthscie ReviewerDocument14 pagesEarthscie ReviewerAechey Frando100% (2)
- Comets Asteroids and Meteors FINAL PDFDocument41 pagesComets Asteroids and Meteors FINAL PDFluke perezNo ratings yet
- All About Comets! - 20240421 - 075833 - 0000Document21 pagesAll About Comets! - 20240421 - 075833 - 0000Axestetikriey HalesNo ratings yet
- Adithya l1 Mission HemaDocument21 pagesAdithya l1 Mission Hemaonesh.raju.2006No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Text QuestionsDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Text QuestionsTori HubbardNo ratings yet
- Griffith Observatory ReportDocument5 pagesGriffith Observatory Reportapi-295396070100% (1)
- Module 3: Comet, Asteroid and Meteor: Comets, Asteroids, and MeteorsDocument54 pagesModule 3: Comet, Asteroid and Meteor: Comets, Asteroids, and MeteorsLovely Reianne Rosita ManigbasNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Week 1Document8 pagesEarth and Life Week 1Jericho CunananNo ratings yet
- Earth Science HandoutsDocument7 pagesEarth Science HandoutsAnnie VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Comet Asteroid Meteor HandoutDocument1 pageComet Asteroid Meteor HandoutWHWHWHWHWWH WWGHWHGWGHWNo ratings yet
- What Is A Comet Made Of?: RelatedDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Comet Made Of?: RelatedClaChristinaNo ratings yet
- RocketsDocument3 pagesRocketsbkt.mysaNo ratings yet
- The Fascinating World of MeteorsDocument3 pagesThe Fascinating World of MeteorsANNooonynmousNo ratings yet
- Properties of PZT-Based PiezoelectricDocument28 pagesProperties of PZT-Based PiezoelectricAndres Felipe Cordoba PachecoNo ratings yet
- On The Role of Spatial Phase and Phase Correlation in Vision, Illusion, and CognitionDocument14 pagesOn The Role of Spatial Phase and Phase Correlation in Vision, Illusion, and Cognitiondw wwNo ratings yet
- Catalog Burner, Model H440X PDFDocument3 pagesCatalog Burner, Model H440X PDFHưng QuangNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter08Document1 pageRing Design Chapter08ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- 400 RRDocument20 pages400 RRjimmy barusNo ratings yet
- Flow in ConduitsDocument29 pagesFlow in ConduitsEngr Sabiul AlamNo ratings yet
- 7sj61 ManualDocument29 pages7sj61 Manualpaari506No ratings yet
- Session 1 - Speed-Time GraphDocument7 pagesSession 1 - Speed-Time GraphSelvenNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Solved QuestionsDocument18 pagesStates of Matter Solved QuestionsAryan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 3311071.017 DometicRooftopACMechanicalComfortSingleZoneControl SVM AMER (En) 2012 01Document63 pages3311071.017 DometicRooftopACMechanicalComfortSingleZoneControl SVM AMER (En) 2012 01Adrian LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 302 Heat and CalorimetryDocument2 pagesExperiment 302 Heat and CalorimetryJasmin DionisioNo ratings yet
- Ippe Round 1Document21 pagesIppe Round 1twometersNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids Unit 3 Fluid DynamicDocument59 pagesMechanics of Fluids Unit 3 Fluid DynamicĐạt Vũ HữuNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power Supply: APS 300 S-3DDocument4 pagesRegulated DC Power Supply: APS 300 S-3DUno DosNo ratings yet
- C1212857-1015-18awg-16-0.254bc-Tew Baoh01Document2 pagesC1212857-1015-18awg-16-0.254bc-Tew Baoh01HugoSpktNo ratings yet
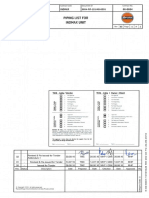
- 6684-PIP-101-MB-0001 - 000 - 02 - Piping List For Indmax UnitDocument17 pages6684-PIP-101-MB-0001 - 000 - 02 - Piping List For Indmax UnitMuthu AlaguRajNo ratings yet
- EDITED STE Electronics Q1M6 ApoderadoCorazon SMNHSDocument29 pagesEDITED STE Electronics Q1M6 ApoderadoCorazon SMNHSwetlog lolololim100% (1)
- Special Section: Karst: - Fort Worth BasinDocument20 pagesSpecial Section: Karst: - Fort Worth Basincunin12No ratings yet
- CE11P2E Set1Document17 pagesCE11P2E Set1Hmt1167 HoNo ratings yet
- VRF VS Chiller: Technical ManagerDocument38 pagesVRF VS Chiller: Technical ManagerJhon Lewis Pino100% (2)
- EE3005: Electromagnetic Theory: Section: A, B, C (Fall 2021)Document3 pagesEE3005: Electromagnetic Theory: Section: A, B, C (Fall 2021)I190845 Samana NayyabNo ratings yet
- Alexandria Higher Institute of Engineering & Technology: 2020/2021 Sheet (2) Spring ElementsDocument6 pagesAlexandria Higher Institute of Engineering & Technology: 2020/2021 Sheet (2) Spring Elementskhaled mohamed0% (1)
- Table of Specification 9.4Document2 pagesTable of Specification 9.4Promise SalvatieraNo ratings yet
- Kuchipudi DanceDocument13 pagesKuchipudi DanceArmaandeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- Energy IsolamentoDocument24 pagesEnergy IsolamentoArtur KinalNo ratings yet
- FDOT BB978 RPTDocument14 pagesFDOT BB978 RPTirfanquadriNo ratings yet
- 40QBG QBU CatalogDocument4 pages40QBG QBU CatalogKhun WunNo ratings yet