Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's Equations
Uploaded by
Nagai KumaresanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's Equations
Uploaded by
Nagai KumaresanCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT IV
5. Write short notes on self induction and mutual induction
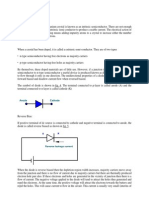
Self Inductance:
According to Faradays law, whenever the flux linking with a coil changes, the
voltage is induced in it. The magnitude of this induced voltage is proportional to the rate
of change of flux linkage.
V d(N)/dt = - N d/dt ------------------(1)
In terms of current we can write,
V = - N (d/dt) (di/di) = - N (d/di) (di/dt) ------------------(2)
But, (d/di) = L = Self inductance
V = - NL(di/dt) volts -------------------(3)
Here,
V = Number of turns of the coil
L = Self inductance
V = Voltage of Self inductance
(di/dt) = Rate of change of current
Mutual Inductance:
Considering two coils A and B, placed very close to each other. Let N 1 be the
number of turns of coil A and let N 2 be the number of turns of coil B. All the flux
produced by coil A will link with coil B. If the flux through coil A changed then this will
induce voltage in coil A. This is called self inductance. The change in flux also induces
voltage in coil B which is called as mutual inductance.
The voltage induced in coil B is given by,
V2 = -N2d12/dt -----------------------(1)
The inductance is defined as the ratio of flux linkage to the current (N/I). The voltage of
mutual inductance in coil B is given by,
M12 = N212/I1 -----------------------(2)
Where,
N2 = Numbers of turns of coil B
12 = Magnetic flux induced in coil B, due to current in I1 coil A
I1 = Current passing through coil A
You might also like
- Single Phase TransformerDocument10 pagesSingle Phase Transformerঅন্বেষা সেনগুপ্তNo ratings yet
- Basic Elec Chapter FourDocument17 pagesBasic Elec Chapter FourNebiyou KorraNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (IV) (IV) : (Chapter 9)Document35 pagesSinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (IV) (IV) : (Chapter 9)Phan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Solution - Assignment 2 - PN JN & DiodesDocument6 pagesSolution - Assignment 2 - PN JN & Diodesshirsodey21No ratings yet
- 10 InductanceDocument16 pages10 InductanceAde Nur HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - PHY121 - Magnetic Field - InductionDocument8 pagesCh4 - PHY121 - Magnetic Field - Inductionrhrazz6No ratings yet
- ECL NotesDocument57 pagesECL Notesvamsee007No ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits PDFDocument21 pagesMagnetically Coupled Circuits PDFOrlando100% (1)
- Resistors in Series:: Resistor CombinationsDocument7 pagesResistors in Series:: Resistor CombinationsKeith E SproatNo ratings yet
- Syllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Document82 pagesSyllabus:Network Theory (3-1-0)Hassan SayedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document11 pagesChapter 1Dhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- EM InductionDocument21 pagesEM InductionSatheshNo ratings yet
- UNIT1 Question Bank EDDocument7 pagesUNIT1 Question Bank EDsuganya1190No ratings yet
- Ciruit Theory-Eee-Part A Univ - QuestionsDocument43 pagesCiruit Theory-Eee-Part A Univ - QuestionsnavaneethangcebNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Coupled CircuitsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Coupled CircuitsAmitava Biswas100% (2)
- Ee 8251 Circuit TheoryDocument43 pagesEe 8251 Circuit TheorynavaneethangcebNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - PHY301 Handouts Lecture 32Document4 pagesCircuit Theory - PHY301 Handouts Lecture 32Samman ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitsDocument6 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitsSreejith VaneryNo ratings yet
- ECE320 Chapter 3 PDFDocument23 pagesECE320 Chapter 3 PDFAhsan NisarNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument22 pagesDiode정대영No ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDocument11 pagesChapter 1 (A) DC Circuits Class 2: Ohm'S LawDhanashree ParanjapeNo ratings yet
- Modul Praktikum Elda Satu Semester 5 FinalDocument29 pagesModul Praktikum Elda Satu Semester 5 FinalZdSentono ChannelNo ratings yet
- Bucking Coils Produce Energy Gain2Document6 pagesBucking Coils Produce Energy Gain2KONSTANTINOS TOMAZISNo ratings yet
- Electro-Magnetic Induction: HE Xperiments of Araday and EnryDocument10 pagesElectro-Magnetic Induction: HE Xperiments of Araday and Enryphysicskn92No ratings yet
- 4 1 Formulae Electromagnetic InductionDocument6 pages4 1 Formulae Electromagnetic InductionNathanianNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitDocument28 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitKhuram Shahzad KhalidNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - SolutionDocument99 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - SolutionSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuits or Uncontrolled Rectifier: EE 435-Electric Drives Dr. Ali M. EltamalyDocument21 pagesDiode Circuits or Uncontrolled Rectifier: EE 435-Electric Drives Dr. Ali M. EltamalyNaga Surya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Mutual and Self InductanceDocument53 pagesMutual and Self InductanceTrungpv PhamNo ratings yet
- Emi AcDocument6 pagesEmi ActhinkiitNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic InductionDocument3 pagesElectro Magnetic Inductionadnankhannomanpathan100No ratings yet
- Buck and Boost Converters With Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesBuck and Boost Converters With Transmission LinesVisu TamilNo ratings yet
- Class de Inverters and Rectifiers For DC-DC ConversiondDocument8 pagesClass de Inverters and Rectifiers For DC-DC ConversiondRon HuangNo ratings yet
- Pe 08 Ee17Document33 pagesPe 08 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitDocument83 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitRonmark AbinoNo ratings yet
- Solution - Assignment 3 - Diode CircuitsDocument12 pagesSolution - Assignment 3 - Diode Circuitsshirsodey21No ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument9 pagesElectrical Circuitsمسلم محمودNo ratings yet
- MIT8 02SC Notes25Document42 pagesMIT8 02SC Notes25asdf12322No ratings yet
- Magnetically Coupled CircuitDocument38 pagesMagnetically Coupled CircuitAlfred MoresNo ratings yet
- 1transformer VkmehtaDocument5 pages1transformer VkmehtadtrhNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Theory 1 YearDocument13 pagesElectrical and Electronic Theory 1 YearJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- Computing Average Resistor Power: Voltage Is Defined As The Voltage That Is As Effective AsDocument26 pagesComputing Average Resistor Power: Voltage Is Defined As The Voltage That Is As Effective AsSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- EC&ED QB For CIE2Document10 pagesEC&ED QB For CIE2bhardamuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering - Principles & Applications, Global EditionDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering - Principles & Applications, Global Editionmohammedashlab.n2023No ratings yet
- 3.magnetically Coupled CircuitDocument38 pages3.magnetically Coupled CircuitRamanjaneyulu Anji Yadav100% (1)
- Magnetic Coupling CircuitDocument37 pagesMagnetic Coupling CircuitCHAYANIN AKETANANUNNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Coupling CircuitDocument37 pagesMagnetic Coupling CircuitCHAYANIN AKETANANUNNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic InductionAdverse codingNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Coupling CircuitDocument37 pagesMagnetic Coupling CircuitCHAYANIN AKETANANUNNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 DC CircuitsDocument45 pagesUnit 1 DC CircuitsKaju KatliNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - ECELXM1L - Lab01Document8 pagesGroup 8 - ECELXM1L - Lab01Hannah VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- UNIT 1 Elec FieldDocument59 pagesUNIT 1 Elec FieldNagai KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Course Outcomes Rmkcet - EmfDocument1 pageCourse Outcomes Rmkcet - EmfNagai KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Magneto StaticsDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Magneto StaticsNagai KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Boundary ConditionsDocument2 pagesBoundary ConditionsNagai KumaresanNo ratings yet