Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsFractures and Dislocations
Fractures and Dislocations
Uploaded by
mtlqhsn78Document
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Gerontological Possible QuestionDocument48 pagesGerontological Possible QuestionNur Sanaani90% (10)
- Open Reduction Internal Fixation PPT With Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesOpen Reduction Internal Fixation PPT With Nursing ResponsibilitiesMiciola Mitch Tanquiamco100% (2)
- SplintsDocument55 pagesSplintsanon_406346371No ratings yet
- Stress - The Different Kinds of StressDocument4 pagesStress - The Different Kinds of StressbogdanNo ratings yet
- Yeast Connection (Candida Albicans)Document4 pagesYeast Connection (Candida Albicans)ngranadosg100% (1)
- Therapeutic EquivalenceDocument2 pagesTherapeutic EquivalenceyuppierajNo ratings yet
- 10 - Musculoskeletal InjuriesDocument8 pages10 - Musculoskeletal InjuriesEastern SamarNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan University Philippines: FracturesDocument21 pagesWesleyan University Philippines: Fracturesjeneva029No ratings yet
- Bone Joint and Muscle Injuries SplintingDocument30 pagesBone Joint and Muscle Injuries SplintingHesedh Jireh MartinNo ratings yet
- Facture/Dislocation: R I C EDocument23 pagesFacture/Dislocation: R I C EKrishnamurti KambleNo ratings yet
- Malambut, Sahani S. - Closed FractureDocument6 pagesMalambut, Sahani S. - Closed FractureSahani MalambutNo ratings yet
- Fracture Management: Anthony SafiDocument14 pagesFracture Management: Anthony SafiAnthony safiNo ratings yet
- FIX - Fracture and DislocationDocument80 pagesFIX - Fracture and DislocationWildan Hilmi AnsoriNo ratings yet
- Fracture 140717081851 Phpapp02Document63 pagesFracture 140717081851 Phpapp02Jaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument7 pagesFractureAbigail MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Fracture: Presented By: Ms. Durga Joshi M. SC NursingDocument63 pagesFracture: Presented By: Ms. Durga Joshi M. SC NursingSanjaya PutraNo ratings yet
- Penanganan FrakturDocument78 pagesPenanganan FrakturelizabethmargarethNo ratings yet
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument3 pagesNeurologic ExaminationDap Dap DogelioNo ratings yet
- Fracture 190706114534Document61 pagesFracture 190706114534Precious BlessingNo ratings yet
- 6-Fractures and Joints Dislocations ManagementDocument91 pages6-Fractures and Joints Dislocations ManagementMUGISHA GratienNo ratings yet
- Fracture: SGC Technical Vocational DepartmentDocument14 pagesFracture: SGC Technical Vocational DepartmentPrecious Ann Gonzales ReyesNo ratings yet
- FIrst Aid For Crush InjuriesDocument14 pagesFIrst Aid For Crush InjuriesGoldenMaidenNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Aurang ZebDocument73 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders: Aurang ZebMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Maja Musculo Sceletal-NovaDocument18 pagesMaja Musculo Sceletal-NovaLuka KoloskiNo ratings yet
- Principle of FractureDocument56 pagesPrinciple of Fracturefahim ahamedNo ratings yet
- Fractures & DislocationsDocument36 pagesFractures & DislocationsMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- A Closed Fracture Does Not Penetrate The SkinDocument5 pagesA Closed Fracture Does Not Penetrate The SkinIvan Liquiran Avenado100% (1)
- Sprain: Strain: Dislocation: FractureDocument3 pagesSprain: Strain: Dislocation: Fracturemitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- Injuries To Muscles and BonesDocument24 pagesInjuries To Muscles and BonesbrentupdegraffNo ratings yet
- Immobilization ExtricationDocument75 pagesImmobilization ExtricationJohn Britto100% (3)
- Bones, Joints, & Muscle InjuriesDocument14 pagesBones, Joints, & Muscle InjuriesAngela YlaganNo ratings yet
- Inroduction To AmputationDocument67 pagesInroduction To AmputationAlfred JacksonNo ratings yet
- First Aid Broken BoneDocument11 pagesFirst Aid Broken BoneRodo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument2 pagesPhysical EducationAlexia SamonteNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sores: AssessmentDocument7 pagesPressure Sores: AssessmentXyzelle Kim Monteilo OrtizNo ratings yet
- Fracture and Dislocation: Raditya Bagus Parama BambieDocument102 pagesFracture and Dislocation: Raditya Bagus Parama Bambieherdinata sudiartanaNo ratings yet
- 1-Fracture Definition and ClassificationDocument77 pages1-Fracture Definition and Classificationk8hxrn5ddbNo ratings yet
- Principles Fracture ManagementDocument88 pagesPrinciples Fracture ManagementYauffa Hanna Elt MisykahNo ratings yet
- Ms. Elizabeth D. Cruz E.N., M.A.N.: 9.1 PathophysiologyDocument20 pagesMs. Elizabeth D. Cruz E.N., M.A.N.: 9.1 PathophysiologyAlfadz AsakilNo ratings yet
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)Document13 pagesOpen Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)Miciola Mitch Tanquiamco67% (3)
- Fractures and Low Back Pain: Dr. Lubna DwerijDocument49 pagesFractures and Low Back Pain: Dr. Lubna DwerijNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- First Aid and ParamedicsDocument4 pagesFirst Aid and ParamedicsshubhmNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic 1Document161 pagesOrthopedic 1avisajames7No ratings yet
- Fracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013Document32 pagesFracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013aqel605859No ratings yet
- Orthopedic: Clinical Features of FracturesDocument6 pagesOrthopedic: Clinical Features of FracturesDrAyyoub AbboodNo ratings yet
- Nur Rachmat Lubis: Divisi Orthopaedi Dept Bedah FK UNSRI/ RS Dr. M. Hoesin PalembangDocument38 pagesNur Rachmat Lubis: Divisi Orthopaedi Dept Bedah FK UNSRI/ RS Dr. M. Hoesin Palembangsoleha09la solehaNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Trauma Principle Management - Dr. FannyDocument43 pagesOrthopaedic Trauma Principle Management - Dr. FannyMurtini TintinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Fracture-1Document18 pagesNursing Care of Fracture-1sutajiNo ratings yet
- Fractures, Dislocations and Soft Tissue Injuries: BandagingDocument8 pagesFractures, Dislocations and Soft Tissue Injuries: BandagingmakananlezatNo ratings yet
- 5 Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument102 pages5 Musculoskeletal TraumaMaria Lynne Parambita100% (1)
- Traumatic InjuryDocument64 pagesTraumatic InjuryDYRAH GRACE COPAUSNo ratings yet
- Forearm Fracture and DiathermyDocument66 pagesForearm Fracture and DiathermyJoel ChongNo ratings yet
- Fracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013Document32 pagesFracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013ahmadNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID and BANDAGINGDocument36 pagesFIRST AID and BANDAGINGAlzeia Presto Agas100% (1)
- Skill Lab AtlsDocument50 pagesSkill Lab AtlsApriyani Supia DewiNo ratings yet
- Smiths FractureDocument4 pagesSmiths FractureDyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Elearning Surgery 1Document100 pagesElearning Surgery 1daniyfondoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Fractures - Appley (PROF RPT)Document62 pagesPrinciple of Fractures - Appley (PROF RPT)Fuad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 29 - Dr. TRI - Fracture Treatment For Primary Care PDFDocument33 pages29 - Dr. TRI - Fracture Treatment For Primary Care PDFfaruuukNo ratings yet
- CRI 089 Midterm NotesDocument39 pagesCRI 089 Midterm Notesdebroah280No ratings yet
- PHT204-Ortho Lecture 3 PRINICIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENTDocument31 pagesPHT204-Ortho Lecture 3 PRINICIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENTDean WillemseNo ratings yet
- Fracture: Prepared By: Jamito, Anisa A. & Mauna, AlaysaDocument37 pagesFracture: Prepared By: Jamito, Anisa A. & Mauna, AlaysaBella DonnaNo ratings yet
- Management of FractureDocument20 pagesManagement of FractureHitesh RohitNo ratings yet
- Sprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Orientation To Pharmacy-1Document46 pagesOrientation To Pharmacy-1mtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Revision On PharmacognosyDocument17 pagesRevision On Pharmacognosymtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- ShockDocument10 pagesShockmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Capsules ٠٦١٧٢٣Document34 pagesCapsules ٠٦١٧٢٣mtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Vital Body SignsDocument32 pagesVital Body Signsmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- UnconsciousnessDocument23 pagesUnconsciousnessmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- PharmaceuticsDocument13 pagesPharmaceuticsmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Semisolids+Supp+Powders ٠٦١٧٣٦Document71 pagesSemisolids+Supp+Powders ٠٦١٧٣٦mtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Real Time Health Monitoring System Through Iot Using SensorsDocument6 pagesReal Time Health Monitoring System Through Iot Using Sensorsقابوس الليثيNo ratings yet
- Republic of Iraq: Medical DevicesDocument5 pagesRepublic of Iraq: Medical Devicesالحارث فخري فياض احمدNo ratings yet
- Medicalcertificate: Locsin ST, Molo, Iloilo City, 5000 Iloilo TelDocument1 pageMedicalcertificate: Locsin ST, Molo, Iloilo City, 5000 Iloilo TelMixedTvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Components of Physical FitnessDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Components of Physical FitnessMerynette Pangilinan VillaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Umilical CordDocument12 pagesDisorders of The Umilical CordNabilah Hanun MudjahidahNo ratings yet
- 3i T3 Implant Surgical Manual - CATMT3 - ENDocument67 pages3i T3 Implant Surgical Manual - CATMT3 - ENSalem RawashdahNo ratings yet
- The Social Impact of Covid-19Document1 pageThe Social Impact of Covid-19Trisha MaguikayNo ratings yet
- Uspi LomotilDocument8 pagesUspi LomotilhaiduvnNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Treatment Potential Therapy DiseasesDocument11 pagesStem Cells Treatment Potential Therapy DiseasesNOVO Cellular Medicine InstituteNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document9 pagesCase Study 1andry natanel tonyNo ratings yet
- Maternity MOH 333 PDFDocument4 pagesMaternity MOH 333 PDFMajivaNo ratings yet
- Courtney Connolly Critical Elements For Health Assessment Documentation HistoryDocument4 pagesCourtney Connolly Critical Elements For Health Assessment Documentation HistorycourtneyNo ratings yet
- Table of Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesTable of Genetic DisordersEli100% (1)
- Antibiotic Selection GuideDocument37 pagesAntibiotic Selection GuideAbanoub Nabil100% (1)
- The Beatles - The Noble PrizeDocument7 pagesThe Beatles - The Noble PrizeJuanitaNo ratings yet
- All Things MoringaDocument40 pagesAll Things MoringaAnjee SugatriNo ratings yet
- Nursing ResumeDocument1 pageNursing Resumeapi-383929607No ratings yet
- Product Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721Document5 pagesProduct Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721JoaoNo ratings yet
- Difference: Making ADocument24 pagesDifference: Making AlonmtNo ratings yet
- Patient 1 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPatient 1 Drug StudyCharlyn JenselNo ratings yet
- Depression: Juan David Caldon Rojas Oral Communication Libert Alonso Vergara National UniversityDocument11 pagesDepression: Juan David Caldon Rojas Oral Communication Libert Alonso Vergara National UniversityJuan David Caldon RojasNo ratings yet
- EHS Groin Hernia ClassificationDocument4 pagesEHS Groin Hernia ClassificationbogdanotiNo ratings yet
- Management of Preoperative Anemia: Laura Mendez-Pino,, Andrés Zorrilla-Vaca,, David L. HepnerDocument9 pagesManagement of Preoperative Anemia: Laura Mendez-Pino,, Andrés Zorrilla-Vaca,, David L. HepneryenuginNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument21 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemiasammi83No ratings yet
- COVID CONCEPTS - CBQ - Dr. GragedaDocument4 pagesCOVID CONCEPTS - CBQ - Dr. GragedaKonstantin KonstantiusNo ratings yet
- SAFETY Manual HandlingDocument2 pagesSAFETY Manual HandlingerharsinghNo ratings yet
Fractures and Dislocations
Fractures and Dislocations
Uploaded by
mtlqhsn780 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views27 pagesDocument
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDocument
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views27 pagesFractures and Dislocations
Fractures and Dislocations
Uploaded by
mtlqhsn78Document
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 27
Fractures and dislocations
By
Dr. Khalil Abdulqawi El-Aajam
PhD. M.Sc. B.Sc
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
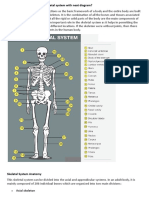
Fractures
• A fracture is a break in the continuity of bone.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Types of Fractures
1. Complete fracture involves a break across the entire cross-section
of the bone and is frequently displaced (removed from normal
position).
2. Incomplete fracture (eg, greenstick fracture), the break occurs
through only part of the cross-section of the bone.
3. Comminuted fracture is one that produces several bone fragments.
4. Closed fracture(simple fracture) is one that does not cause a break
in the skin.
5. Open fracture (compound, or complex, fracture) is one in which the
skin or mucous membrane wound extends to the fractured bone.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Clinical Manifestations
a. Pain
b. loss of function
c. Deformity
d. shortening of the extremity
e. local swelling
f. discoloration
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a fracture is based on the patient’s symptoms, the
physical signs, and the x-ray.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Urgent Management of Fractures
1. Immediately immobilize affected limb. If movement is required
before splinting, support limb above and below fracture.
2. Unless there is bleeding apply splints and padding (above and
below fracture site) directly over the clothing. If bleeding is
present visualization may be necessary before pressure can
be applied where bleeding is originating. Keep patient
covered to preserve body heat.
3. If the fractured extremity is a leg bone, the unaffected
extremity can be used as a splint by bandaging both legs
together. An arm can be bandaged to the chest or put into a
sling to minimize further tissue damage.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
4. Assess color, warmth, circulation, and movement (CWCM) of the
limb distal to the fracture.
5. Open fractures require the protruding bone be covered with a
clean (sterile preferred) dressing.
6. Do not attempt to “straighten” the fractured extremity. Move
the affected limb as little as necessary.
7. Transport to an emergency department as soon as possible.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
• Medical Management of Fractures
1. Reduction
a. Closed reduction
b. Open reduction
2. Immobilization
3. Regaining of normal function
4. Strength through rehabilitation
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Splints and Bandages
• Bandage:- is strip or roll of material that is wrapped around a body
part to support or immobilize a body part, or to secure a dressing.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Kinds of bandages:
• Gauze is use for bandages because it is light and porous and
conforms to body parts, inexpensive and can be discarded after one
use.
• Elastic bandages adhere to the skin providing support and pressure
and conforms to body parts.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Principles of Application of Bandages
1. Elevate extremity for several seconds prior to application to reduce
venous congestion.
2. Always wrap from distal to proximal direction (towards the heart to
promote venous return)
3. Each rotation should overlap previous lap by one half
4. Use an equal amount of tension for each turn
5. Following application, check distal body parts (hands, fingers, feet &
toes) for numbness, pale or cyanotic color, absence of pulse to
determine if bandage is too tight)
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Complications
• Complications of fractures fall into two categories—
a) Early complications include shock, fat embolism, compartment
syndrome, deep vein thrombosis, thromboembolism (pulmonary
embolism), and infection.
b) Delayed complications include delayed union and nonunion,
necrosis of bone.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Dislocations
• Dislocations are a common injury in which the ends of the bones are
forced from their normal position.
• They are usually caused by trauma as in falls or contact sports or a
disease such as rheumatoid arthritis. Any joint large or small may
become dislocated.
• Severe pain along with lost range of motion of the joint and joint
deformity occurs.
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
Medical intervention
• Immediate medical treatment is required to preserve function.
• Splint the extremity as it is found, apply ice, and seek help.
• Do not move the extremity as blood vessels, muscles, and nerves
could be damaged..
Dr. Khalil El-Aajam
You might also like
- Gerontological Possible QuestionDocument48 pagesGerontological Possible QuestionNur Sanaani90% (10)
- Open Reduction Internal Fixation PPT With Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument13 pagesOpen Reduction Internal Fixation PPT With Nursing ResponsibilitiesMiciola Mitch Tanquiamco100% (2)
- SplintsDocument55 pagesSplintsanon_406346371No ratings yet
- Stress - The Different Kinds of StressDocument4 pagesStress - The Different Kinds of StressbogdanNo ratings yet
- Yeast Connection (Candida Albicans)Document4 pagesYeast Connection (Candida Albicans)ngranadosg100% (1)
- Therapeutic EquivalenceDocument2 pagesTherapeutic EquivalenceyuppierajNo ratings yet
- 10 - Musculoskeletal InjuriesDocument8 pages10 - Musculoskeletal InjuriesEastern SamarNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan University Philippines: FracturesDocument21 pagesWesleyan University Philippines: Fracturesjeneva029No ratings yet
- Bone Joint and Muscle Injuries SplintingDocument30 pagesBone Joint and Muscle Injuries SplintingHesedh Jireh MartinNo ratings yet
- Facture/Dislocation: R I C EDocument23 pagesFacture/Dislocation: R I C EKrishnamurti KambleNo ratings yet
- Malambut, Sahani S. - Closed FractureDocument6 pagesMalambut, Sahani S. - Closed FractureSahani MalambutNo ratings yet
- Fracture Management: Anthony SafiDocument14 pagesFracture Management: Anthony SafiAnthony safiNo ratings yet
- FIX - Fracture and DislocationDocument80 pagesFIX - Fracture and DislocationWildan Hilmi AnsoriNo ratings yet
- Fracture 140717081851 Phpapp02Document63 pagesFracture 140717081851 Phpapp02Jaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument7 pagesFractureAbigail MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Fracture: Presented By: Ms. Durga Joshi M. SC NursingDocument63 pagesFracture: Presented By: Ms. Durga Joshi M. SC NursingSanjaya PutraNo ratings yet
- Penanganan FrakturDocument78 pagesPenanganan FrakturelizabethmargarethNo ratings yet
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument3 pagesNeurologic ExaminationDap Dap DogelioNo ratings yet
- Fracture 190706114534Document61 pagesFracture 190706114534Precious BlessingNo ratings yet
- 6-Fractures and Joints Dislocations ManagementDocument91 pages6-Fractures and Joints Dislocations ManagementMUGISHA GratienNo ratings yet
- Fracture: SGC Technical Vocational DepartmentDocument14 pagesFracture: SGC Technical Vocational DepartmentPrecious Ann Gonzales ReyesNo ratings yet
- FIrst Aid For Crush InjuriesDocument14 pagesFIrst Aid For Crush InjuriesGoldenMaidenNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Aurang ZebDocument73 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders: Aurang ZebMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Maja Musculo Sceletal-NovaDocument18 pagesMaja Musculo Sceletal-NovaLuka KoloskiNo ratings yet
- Principle of FractureDocument56 pagesPrinciple of Fracturefahim ahamedNo ratings yet
- Fractures & DislocationsDocument36 pagesFractures & DislocationsMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- A Closed Fracture Does Not Penetrate The SkinDocument5 pagesA Closed Fracture Does Not Penetrate The SkinIvan Liquiran Avenado100% (1)
- Sprain: Strain: Dislocation: FractureDocument3 pagesSprain: Strain: Dislocation: Fracturemitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- Injuries To Muscles and BonesDocument24 pagesInjuries To Muscles and BonesbrentupdegraffNo ratings yet
- Immobilization ExtricationDocument75 pagesImmobilization ExtricationJohn Britto100% (3)
- Bones, Joints, & Muscle InjuriesDocument14 pagesBones, Joints, & Muscle InjuriesAngela YlaganNo ratings yet
- Inroduction To AmputationDocument67 pagesInroduction To AmputationAlfred JacksonNo ratings yet
- First Aid Broken BoneDocument11 pagesFirst Aid Broken BoneRodo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument2 pagesPhysical EducationAlexia SamonteNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sores: AssessmentDocument7 pagesPressure Sores: AssessmentXyzelle Kim Monteilo OrtizNo ratings yet
- Fracture and Dislocation: Raditya Bagus Parama BambieDocument102 pagesFracture and Dislocation: Raditya Bagus Parama Bambieherdinata sudiartanaNo ratings yet
- 1-Fracture Definition and ClassificationDocument77 pages1-Fracture Definition and Classificationk8hxrn5ddbNo ratings yet
- Principles Fracture ManagementDocument88 pagesPrinciples Fracture ManagementYauffa Hanna Elt MisykahNo ratings yet
- Ms. Elizabeth D. Cruz E.N., M.A.N.: 9.1 PathophysiologyDocument20 pagesMs. Elizabeth D. Cruz E.N., M.A.N.: 9.1 PathophysiologyAlfadz AsakilNo ratings yet
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)Document13 pagesOpen Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)Miciola Mitch Tanquiamco67% (3)
- Fractures and Low Back Pain: Dr. Lubna DwerijDocument49 pagesFractures and Low Back Pain: Dr. Lubna DwerijNoor MajaliNo ratings yet
- First Aid and ParamedicsDocument4 pagesFirst Aid and ParamedicsshubhmNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic 1Document161 pagesOrthopedic 1avisajames7No ratings yet
- Fracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013Document32 pagesFracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013aqel605859No ratings yet
- Orthopedic: Clinical Features of FracturesDocument6 pagesOrthopedic: Clinical Features of FracturesDrAyyoub AbboodNo ratings yet
- Nur Rachmat Lubis: Divisi Orthopaedi Dept Bedah FK UNSRI/ RS Dr. M. Hoesin PalembangDocument38 pagesNur Rachmat Lubis: Divisi Orthopaedi Dept Bedah FK UNSRI/ RS Dr. M. Hoesin Palembangsoleha09la solehaNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Trauma Principle Management - Dr. FannyDocument43 pagesOrthopaedic Trauma Principle Management - Dr. FannyMurtini TintinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Fracture-1Document18 pagesNursing Care of Fracture-1sutajiNo ratings yet
- Fractures, Dislocations and Soft Tissue Injuries: BandagingDocument8 pagesFractures, Dislocations and Soft Tissue Injuries: BandagingmakananlezatNo ratings yet
- 5 Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument102 pages5 Musculoskeletal TraumaMaria Lynne Parambita100% (1)
- Traumatic InjuryDocument64 pagesTraumatic InjuryDYRAH GRACE COPAUSNo ratings yet
- Forearm Fracture and DiathermyDocument66 pagesForearm Fracture and DiathermyJoel ChongNo ratings yet
- Fracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013Document32 pagesFracture PP Ahmad Aqel 2013ahmadNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID and BANDAGINGDocument36 pagesFIRST AID and BANDAGINGAlzeia Presto Agas100% (1)
- Skill Lab AtlsDocument50 pagesSkill Lab AtlsApriyani Supia DewiNo ratings yet
- Smiths FractureDocument4 pagesSmiths FractureDyah AyuNo ratings yet
- Elearning Surgery 1Document100 pagesElearning Surgery 1daniyfondoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Fractures - Appley (PROF RPT)Document62 pagesPrinciple of Fractures - Appley (PROF RPT)Fuad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 29 - Dr. TRI - Fracture Treatment For Primary Care PDFDocument33 pages29 - Dr. TRI - Fracture Treatment For Primary Care PDFfaruuukNo ratings yet
- CRI 089 Midterm NotesDocument39 pagesCRI 089 Midterm Notesdebroah280No ratings yet
- PHT204-Ortho Lecture 3 PRINICIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENTDocument31 pagesPHT204-Ortho Lecture 3 PRINICIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENTDean WillemseNo ratings yet
- Fracture: Prepared By: Jamito, Anisa A. & Mauna, AlaysaDocument37 pagesFracture: Prepared By: Jamito, Anisa A. & Mauna, AlaysaBella DonnaNo ratings yet
- Management of FractureDocument20 pagesManagement of FractureHitesh RohitNo ratings yet
- Sprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Orientation To Pharmacy-1Document46 pagesOrientation To Pharmacy-1mtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Revision On PharmacognosyDocument17 pagesRevision On Pharmacognosymtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- ShockDocument10 pagesShockmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Capsules ٠٦١٧٢٣Document34 pagesCapsules ٠٦١٧٢٣mtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Vital Body SignsDocument32 pagesVital Body Signsmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- UnconsciousnessDocument23 pagesUnconsciousnessmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- PharmaceuticsDocument13 pagesPharmaceuticsmtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Semisolids+Supp+Powders ٠٦١٧٣٦Document71 pagesSemisolids+Supp+Powders ٠٦١٧٣٦mtlqhsn78No ratings yet
- Real Time Health Monitoring System Through Iot Using SensorsDocument6 pagesReal Time Health Monitoring System Through Iot Using Sensorsقابوس الليثيNo ratings yet
- Republic of Iraq: Medical DevicesDocument5 pagesRepublic of Iraq: Medical Devicesالحارث فخري فياض احمدNo ratings yet
- Medicalcertificate: Locsin ST, Molo, Iloilo City, 5000 Iloilo TelDocument1 pageMedicalcertificate: Locsin ST, Molo, Iloilo City, 5000 Iloilo TelMixedTvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Components of Physical FitnessDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Components of Physical FitnessMerynette Pangilinan VillaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Umilical CordDocument12 pagesDisorders of The Umilical CordNabilah Hanun MudjahidahNo ratings yet
- 3i T3 Implant Surgical Manual - CATMT3 - ENDocument67 pages3i T3 Implant Surgical Manual - CATMT3 - ENSalem RawashdahNo ratings yet
- The Social Impact of Covid-19Document1 pageThe Social Impact of Covid-19Trisha MaguikayNo ratings yet
- Uspi LomotilDocument8 pagesUspi LomotilhaiduvnNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Treatment Potential Therapy DiseasesDocument11 pagesStem Cells Treatment Potential Therapy DiseasesNOVO Cellular Medicine InstituteNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document9 pagesCase Study 1andry natanel tonyNo ratings yet
- Maternity MOH 333 PDFDocument4 pagesMaternity MOH 333 PDFMajivaNo ratings yet
- Courtney Connolly Critical Elements For Health Assessment Documentation HistoryDocument4 pagesCourtney Connolly Critical Elements For Health Assessment Documentation HistorycourtneyNo ratings yet
- Table of Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesTable of Genetic DisordersEli100% (1)
- Antibiotic Selection GuideDocument37 pagesAntibiotic Selection GuideAbanoub Nabil100% (1)
- The Beatles - The Noble PrizeDocument7 pagesThe Beatles - The Noble PrizeJuanitaNo ratings yet
- All Things MoringaDocument40 pagesAll Things MoringaAnjee SugatriNo ratings yet
- Nursing ResumeDocument1 pageNursing Resumeapi-383929607No ratings yet
- Product Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721Document5 pagesProduct Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721JoaoNo ratings yet
- Difference: Making ADocument24 pagesDifference: Making AlonmtNo ratings yet
- Patient 1 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPatient 1 Drug StudyCharlyn JenselNo ratings yet
- Depression: Juan David Caldon Rojas Oral Communication Libert Alonso Vergara National UniversityDocument11 pagesDepression: Juan David Caldon Rojas Oral Communication Libert Alonso Vergara National UniversityJuan David Caldon RojasNo ratings yet
- EHS Groin Hernia ClassificationDocument4 pagesEHS Groin Hernia ClassificationbogdanotiNo ratings yet
- Management of Preoperative Anemia: Laura Mendez-Pino,, Andrés Zorrilla-Vaca,, David L. HepnerDocument9 pagesManagement of Preoperative Anemia: Laura Mendez-Pino,, Andrés Zorrilla-Vaca,, David L. HepneryenuginNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument21 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemiasammi83No ratings yet
- COVID CONCEPTS - CBQ - Dr. GragedaDocument4 pagesCOVID CONCEPTS - CBQ - Dr. GragedaKonstantin KonstantiusNo ratings yet
- SAFETY Manual HandlingDocument2 pagesSAFETY Manual HandlingerharsinghNo ratings yet