Professional Documents
Culture Documents
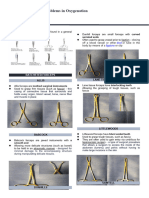
Medical Equipments 1. Scalpel Handle: 4. Bandage Scissors: 7. Deaver
Medical Equipments 1. Scalpel Handle: 4. Bandage Scissors: 7. Deaver
Uploaded by
Phoebe CosteloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical Equipments 1. Scalpel Handle: 4. Bandage Scissors: 7. Deaver
Medical Equipments 1. Scalpel Handle: 4. Bandage Scissors: 7. Deaver
Uploaded by
Phoebe CosteloCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDICAL EQUIPMENTS 4. Bandage Scissors: 7.
Deaver:
- Lister bandage scissors are used for - handheld retractor commonly used to hold
1. Scalpel handle: dressings, drapes. back the abdominal wall during abdominal
- used to firmly hold the surgical blade in order - the blunt tip of the scissor helps to lift the or thoracic procedures.
to puncture or cut the tissues bandage from the skin safely for easy - used to move or hold organs away from
dressing and safe bandage removal. the surgical site.
2. Scalpel:
- a bladed surgical instrument used to make cuts
into the body. 5. Army Navy Retractor: 8. Gut Basin:
- used to expose surface layers of skin and - it is used to hold the OS.
also most often used in orthopedic
surgeries.
3. Towel clamp/clip: 9. Richardson Retractor:
- used to secure the drapes to the patient and 6. Bladder retractor: - used to expose, retract, or push tissues,
ancillary equipment to the drapes to achieve a - urological surgical instruments used for organs, muscles, and bones during
sterile field. exposing surgical sites by retracting surgeries.
- tips are curved to improve visibility and allow bladder tissue, skin, and muscles. - used in various surgical procedures,
the handles to lie flat on the patient. - used for cystectomy and prostate including gynecological, urological, and
enucleation to tumor removal. abdominal surgeries.
10. Kelly Forceps (Straight): 15. Allis:
- used during surgery to compress the - used to hold and grip tissues and are often
artery, clamp and seal small to medium known as Allis Clamps.
size blood vessels or hold the artery out of - have finger-ring grips, sharp edges, and a
the way. ratcheted handle.
- used to snatch fascia and ligaments,
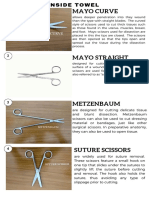
13. Mayo Scissors (Straight): including the breast and bowel tissues.
- to cut thick tissues such as those found in
the uterus, muscles, breast, and foot.
11. Kelly Forceps (Curve):
- used during surgery to compress the
artery, clamp and seal small to medium
16. Tissue Forceps:
size blood vessels or hold the artery out of
- manipulate tissues.
the way. 14. Babcock:
- support tissues while making incisions, and
- Is a finger ring, ratcheted, non-perforating
suturing. retract tissues to improve
forceps used to grasp delicate tissue.
exposure.
- frequently used with intestinal and
laparotomy procedures.
12. Metzembaum “metz”:
- use in performing blunt dissections and
cutting delicate and fine tissues.
- Surgeons use these dissecting scissors for
incising the deep rib bed periosteal layer.
17. Thumb Forceps: 19. Ovum Forceps: 21. Debakey Forceps:
- used with thumb and forefinger's - to properly remove pieces of placenta or - holding and manipulating delicate tissues,
compression. products of conception from the uterus to especially in cardiovascular procedures.
- suitable for grasping, holding, and prevent infection.
manipulating body tissues. - flat blades are serrated and hollow to
- used for holding, grasping, and firmly grasp the tissue to be removed.
manipulating body tissues.
22. Mixters Forceps:
20. Weitlaner Retractor: - used to clamp blood vessels, control
18. Needle Holder:
- used to hold soft tissues apart during bleeding, and manipulate tissues during
- used to hold a suturing needle during
surgical procedures to give the surgeon surgery.
surgical procedures.
access to the site.
PRINCIPLES OF ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE TYPES OF ANESTHESIA 10 GOLDEN RULES DURING DRUG ADMINISTRATION
1. Right Patient
1. Only sterile items are used within sterile field. 1. Regional
2. Right Medication
2. Sterile persons are gowned and gloved. 2. Local
3. Right Dosage
3. Tables are sterile only at the table level. 3. General
4. Right Route
4. Sterile persons touch only sterile items/areas.
TYPES OF SURGERY ACC. TO: 5. Right Time
Unsterile persons touch only unsterile
1. Risk 6. Right Documentation
items/areas.
2. Purpose 7. Right Client Education
5. Sterile persons avoid leaning over unsterile
8. Right to refuse
areas. LAYERS OF TISSUE
9. Right Assessment
Unsterile persons avoid reaching over sterile 1. Skin
10. Right Evaluation
field. 2. Subcutaneous
6. Edges of anything that encloses sterile content 3. Fascia
are considered unsterile. 4. Muscle
7. Unsterile persons avoid sterile areas. 5. Peritoneum
8. Sterile field is created as close as possible to
the time of use. PARTS OF SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS
9. Sterile areas are continuously kept in view. 1. Tips
10. Sterile persons keep within sterile area. 2. Jaws
11. Sterile persons keep contact with sterile areas 3. Box lock pin
to a minimum. 4. Box lock
12. Microorganisms must be kept to irreducible 5. Shank
minimum. 6. Ratchet
13. Destruction of integrity of microbial barriers 7. Ring holder
result to contamination.
PHASES OF SURGERY
1. Preoperative Phase
2. Intraoperative Phase
3. Post-operative Phase
You might also like
- Operative Dictations in OphthalmologyFrom EverandOperative Dictations in OphthalmologyEric D. RosenbergNo ratings yet
- Instruments by RcogDocument18 pagesInstruments by RcoglinaNo ratings yet
- Bungaku Shoujo Volume 6Document274 pagesBungaku Shoujo Volume 6beall231No ratings yet
- Surgery Alaa NotesDocument59 pagesSurgery Alaa NotesBaraa Kassis100% (3)
- Instrument Function Picture Cutting and Dissecting InstrumentsDocument10 pagesInstrument Function Picture Cutting and Dissecting InstrumentsNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- List of InstrumentsDocument7 pagesList of Instruments11loeychanNo ratings yet
- Common or InstrumentsDocument16 pagesCommon or InstrumentsCosmic PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Major & Minor Surgical Instrument: ScalpelDocument7 pagesMajor & Minor Surgical Instrument: Scalpeledgar malupengNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Activity 3A Surgical Instruments: Mayo StraightDocument9 pagesNCM 112 Activity 3A Surgical Instruments: Mayo StraightJustine Simeon lagunzadNo ratings yet
- Retractors 2. Grasping / HoldingDocument5 pagesRetractors 2. Grasping / HoldingJanelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A. Cutting or Dissecting Instruments: Basic Instruments in The Operating RoomDocument5 pagesA. Cutting or Dissecting Instruments: Basic Instruments in The Operating Roomcatsclaw13No ratings yet
- 20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErDocument8 pages20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErMelissa GoNo ratings yet
- 20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErDocument8 pages20 Common Surgical Instruments in ErMelissa GoNo ratings yet
- b5 Notebook 1Document19 pagesb5 Notebook 1fontanilla.rioangeli.tNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument63 pagesSurgical InstrumentsSohaily DalumaNo ratings yet
- Study The Following Instruments. Be Able To Identify and Know Its UsesDocument2 pagesStudy The Following Instruments. Be Able To Identify and Know Its UsesJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument3 pagesSurgical Instrumentslaarns.manalo04No ratings yet
- Surgical Instrumentation: Iii. Grasping and HoldingDocument37 pagesSurgical Instrumentation: Iii. Grasping and Holdingkaren carpioNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument8 pagesSurgical InstrumentsSharmaine Simon91% (11)
- 312 or - Instrumentation, Sutures, Principles of Aseptic TechniquesDocument5 pages312 or - Instrumentation, Sutures, Principles of Aseptic TechniquesasdfjvNo ratings yet
- Dilation and CurettageDocument4 pagesDilation and CurettageFernandez, Florence NicoleNo ratings yet
- Basic Surgical Instruments Print BPDocument6 pagesBasic Surgical Instruments Print BPkrischaniNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy CareDocument6 pagesTracheostomy CareBern NerquitNo ratings yet
- Peri Op InstrumentsDocument16 pagesPeri Op Instruments3S BOTE, SEAN CARLLO T.No ratings yet
- SurgicalzDocument6 pagesSurgicalzkrischaniNo ratings yet
- Common Surgical Instruments (Autorecovered)Document6 pagesCommon Surgical Instruments (Autorecovered)Princess AntivoNo ratings yet
- Mayo CurveDocument6 pagesMayo CurveDanielle Marie SimoraNo ratings yet
- Basic Instruments in The Operating RoomDocument6 pagesBasic Instruments in The Operating RoomAbegail M. TolosaNo ratings yet
- Or InstrumentsDocument5 pagesOr InstrumentsDenise CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Normal Delivery Instrument SetsDocument14 pagesNormal Delivery Instrument SetsFrances Kaye Sta. CruzNo ratings yet
- Or InstrumentDocument4 pagesOr InstrumentMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument7 pagesSurgical InstrumentsCarmelita SaltNo ratings yet
- Common Surgical InstrumentsDocument23 pagesCommon Surgical InstrumentsCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument4 pagesSurgical InstrumentsWafa L. Abdulrahman100% (2)
- NCMB312 RLE OR Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic Techniques PDFDocument70 pagesNCMB312 RLE OR Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic Techniques PDFwokorow100% (1)
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument6 pagesSurgical InstrumentsSis CrezylNo ratings yet
- 10 Basic InstrumentsDocument2 pages10 Basic InstrumentsIsaac papicaNo ratings yet
- Peri-Op 1,2&3Document12 pagesPeri-Op 1,2&3nhmae gcabNo ratings yet
- I. Cutting and DissectingDocument10 pagesI. Cutting and DissectingApple MaeNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTATIONDocument9 pagesINSTRUMENTATIONkesNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument7 pagesSurgical InstrumentsElaiza Angela Atido RoqueNo ratings yet
- OR InstrumentsDocument56 pagesOR Instrumentssellyna SaidinNo ratings yet
- Surgical IntrumentsDocument5 pagesSurgical IntrumentsMa. Kristina Cazandra IbañezNo ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument4 pagesInstrumentationDaniel SottoNo ratings yet
- NCMB312 RLE or Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic TechniquesDocument70 pagesNCMB312 RLE or Instrumentation Sutures Principles of Aseptic TechniquesNine SoleilNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentDocument7 pagesSurgical InstrumentLabinnah MoresNo ratings yet
- Maternal RLE - InstrumentationDocument3 pagesMaternal RLE - InstrumentationMark VincentNo ratings yet
- Or InstrumentDocument23 pagesOr InstrumenttabiNo ratings yet
- Surgical Sutures: A Practical Guide of Surgical Knots and Suturing Techniques Used in Emergency Rooms, Surgery, and General MedicineFrom EverandSurgical Sutures: A Practical Guide of Surgical Knots and Suturing Techniques Used in Emergency Rooms, Surgery, and General MedicineRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersFrom EverandA Manual of the Operations of Surgery: For the Use of Senior Students, House Surgeons, and Junior PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology Taping Guide Effects of Kinesiotape on Lower LimbsFrom EverandKinesiology Taping Guide Effects of Kinesiotape on Lower LimbsNo ratings yet
- How to Apply StarkTape Kinesiology Tape. Best Kinesiology Taping TechniquesFrom EverandHow to Apply StarkTape Kinesiology Tape. Best Kinesiology Taping TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyFrom EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- GIT Pathology Lecture 2005Document161 pagesGIT Pathology Lecture 2005api-3700579100% (5)
- Basic Guide To Fire Alarm InstallationDocument12 pagesBasic Guide To Fire Alarm InstallationCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- Cha 2Document13 pagesCha 2jayachandranNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Paper 4: Listening: Part 1 (Questions 1-8)Document24 pagesTest 1 Paper 4: Listening: Part 1 (Questions 1-8)Trần Anh KiệtNo ratings yet
- LEVOXIN eDocument1 pageLEVOXIN ejim_corbet1211No ratings yet
- Omm 1106eDocument84 pagesOmm 1106eDedy setiawanNo ratings yet
- Porn and Sex Education Porn As Sex EducationDocument13 pagesPorn and Sex Education Porn As Sex EducationMathilde MoureauNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Document1 pageToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarterly Examination-Earth-and-Life-Science-2022-2023Document7 pages1st Quarterly Examination-Earth-and-Life-Science-2022-2023Maryjul Ramos Ranay100% (4)
- Individual Practice With Peer EvaluationDocument1 pageIndividual Practice With Peer EvaluationFatima TreviñoNo ratings yet
- K K A C D W K P S K T: Eteraturan Unjungan Ntenatal ARE I Ilayah Erja Uskesmas Lawi Abupaten EgalDocument6 pagesK K A C D W K P S K T: Eteraturan Unjungan Ntenatal ARE I Ilayah Erja Uskesmas Lawi Abupaten EgalSelly MonicaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Transport and StorageDocument34 pagesLipid Transport and StorageGuru Kiran C KNo ratings yet
- Investigating Transformer FailuresDocument54 pagesInvestigating Transformer Failureslbk50100% (2)
- Documment Number (Rev.) Comments: Project: PETROBRAS 78 (P-78)Document4 pagesDocumment Number (Rev.) Comments: Project: PETROBRAS 78 (P-78)Sumit MishraNo ratings yet
- 60 - Sensor TriggerDocument9 pages60 - Sensor TriggerP SmithNo ratings yet
- Arogya Sanjeevani - One PagerDocument1 pageArogya Sanjeevani - One Pagernaval730107No ratings yet
- Toyota TercelDocument29 pagesToyota TercelAbdon Reyes100% (1)
- CH 19035Document7 pagesCH 19035Abdul GhaffarNo ratings yet
- EIA Envt Impact Assessment Report On Myitsone Dam BurmeseDocument13 pagesEIA Envt Impact Assessment Report On Myitsone Dam BurmesePugh JuttaNo ratings yet
- 52369.Đề ôn thi lớp 10Document5 pages52369.Đề ôn thi lớp 10Phương LinhNo ratings yet
- Child-Friendly School SurveyDocument8 pagesChild-Friendly School SurveyOscar Jr Dejarlo MatelaNo ratings yet
- Region 4-ADocument22 pagesRegion 4-Aapi-251414497No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Managing IT in A Digital WorldDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Managing IT in A Digital WorldliamdrlnNo ratings yet
- English Persuasive SpeechDocument3 pagesEnglish Persuasive SpeechEve HustonNo ratings yet
- 2008-11-14 Service Manual - General - Multi V Plus II Outdoor Unit - mfl50459503 - 20120105122839 PDFDocument134 pages2008-11-14 Service Manual - General - Multi V Plus II Outdoor Unit - mfl50459503 - 20120105122839 PDFBudi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- FEI Quanta 400 FEG - FEI CompanyDocument2 pagesFEI Quanta 400 FEG - FEI CompanyGrégory PezzattiNo ratings yet
- TenBoom EbookDocument366 pagesTenBoom EbookZinedine Benaia HernandezNo ratings yet
- Grade 6Document6 pagesGrade 6People of BadiangNo ratings yet