Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quadratic Functions and Equations
Quadratic Functions and Equations
Uploaded by
idlanhakimi159Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quadratic Functions and Equations
Quadratic Functions and Equations
Uploaded by
idlanhakimi159Copyright:
Available Formats
Quadratic Functions
and Equations in One
Variable
Quadratic Functions and Equations
Definition
A quadratic expression in one variable is
an algebraic expression that has the
highest power variable is two.
The basic form of a quadratic
expression is ax2 + bx + c, which is
a, b and c is a constant and a = 0, x is
a variable.
a is the coefficient of x2 , b is the
coefficient of x and c is a constant
Examples
x2 + 5x − 1
−y 2 + 3y
2m2 + 7
Tips
Besides x, other letters can be used to
represents variables
Relationship between a quadratic function
and many-to-one relation
Quadratic function, f (x) = ax2 + bx + c
All quadratic functions have the
same image for two different
images
Many-to-one relation
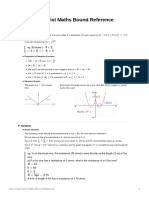
Have two shapes of graph
Shapes of the graph, f (x) = ax2 + bx +
c, a
=0
For the graph a < 0, (x1 , y1 ) is
known as maximum point
For the graph a > 0, (x2 , y2 ) is known
as minimum point
Tips
The curved shape of the graph of a
quadratic function is called a parabola
Axis of symmetry of the graph of a
quadratic function
Explanation
Definition: A straight line that is parallel to
the y−axis and divides the graph into two
parts of the same size and shape
The axis of symmetry will pass
through the maximum and
minimum point of the graph of the
function as shown in the diagram
below
b
Equation axis of symmetry , x =−
2a
Effects of changing the values of a, b, and c
on graphs of quadratic functions, f (x) =
ax2 + bx + c
The value of a determines the shape of
the graph
The value of b determines the position
of the axis of symmetry
The value of c determines the position
of the y−intercept
Forming a quadratic equation based on a
situation
A quadratic function is written in the
form of f (x) = ax2 + bx + c while a
quadratic equation is written in the
general form ax2 + bx + c = 0
Roots of a quadratic equation
The root of a quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0 are the values of the
variables, x which satisfy the equation.
Relationship between the roots of a
quadratic equation and the positions of the
roots.
The roots of equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are
the points of intersection of the graph of the
quadratic functions f (x) = ax2 + bx + c
and the x−axis which are also knowns as
the x−intercepts.
Determine the roots of a quadratic equation
by using factorisation method
Tips
A quadratic equation needs to be written
in the form of ax2 + bx + c = 0 before we
carry out factorisation
Example
Determine the roots of this quadratic
equations by using factorisation method
x2 − 5x + 6 = 0.
Solution:
x2 − 5x + 6 = 0
(x − 3)(x − 2) = 0
x = 3 or x = 2.
Determine the roots of a quadratic equation
by using graphical method
The roots of a quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0 can be obtained by
using a graphical method by reading
the values of x which are the points of
intersections of the graph
Chapter : Function and Quadratic Equation
in One Variable
Topic : Quadratic Functions and Equations
Form 4 Mathematics
Related notes
Number Bases
Statements
Arguments
Intersection of Sets
Union of Sets
Combined Operations on Sets
Chapter 5: Network in Graph Theory
Network
Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
Systems of Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
Report this note
Homework Help
Get your homework done
with live tutors’ help
Learn more
Register for a free Pandai account now
©Quiz
2024 Pandai.org All Rights
View video m ViewReserved
note m Account
You might also like
- Quadratic Functions and EquationsDocument4 pagesQuadratic Functions and Equationslweisheng669No ratings yet
- Quadratics PDFDocument9 pagesQuadratics PDFRafena MustaphaNo ratings yet
- The Quadratic FunctionDocument4 pagesThe Quadratic FunctionCharalampidis DimitrisNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2Document8 pagesCaie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2ballersNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2Document7 pagesCaie Igcse Additional Mathematics 0606 Theory v2965161191No ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Add Maths 0606 Theory v1Document8 pagesCaie Igcse Add Maths 0606 Theory v1vivianlangzhaoNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation For Class 10Document6 pagesQuadratic Equation For Class 10abhayaps975No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsDocument18 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsZlata OsypovaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument20 pagesQuadratic FunctionsSalmizam IzamNo ratings yet
- Znotes - TheoryDocument8 pagesZnotes - TheoryThar Lon Lin HtetNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument32 pagesMathsnour mohammedNo ratings yet
- Different Forms of Quadratic FunctionsDocument3 pagesDifferent Forms of Quadratic FunctionsCharalampidis Dimitris0% (1)
- Introduction To Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Linear EquationsJami MendozaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Review FunctionsDocument12 pages3.0 Review Functionsummu***No ratings yet
- Quadratics Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesQuadratics Lecture NotesKaness Mathz100% (1)
- Unit 9 Lesson NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 9 Lesson Notesapi-291793268No ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionDocument13 pagesQuadratic FunctionJasmine Marie Padilla LimsonNo ratings yet
- Functions and Equations PracticeDocument2 pagesFunctions and Equations PracticeHarveen Kaur AnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii. Linear Equations in Two Variables: at The End of This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument3 pagesChapter Iii. Linear Equations in Two Variables: at The End of This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToJonathan PidoNo ratings yet
- International A Level Maths Spec Issue3Document3 pagesInternational A Level Maths Spec Issue3Atef BawabNo ratings yet
- Parabola Worksheets For StudentsDocument5 pagesParabola Worksheets For StudentsWickedFan!!!!No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quad Functions and Polynomisl Functions of Higher DegreeDocument59 pagesLesson 3 Quad Functions and Polynomisl Functions of Higher DegreeMa. Consuelo Melanie Cortes IIINo ratings yet
- 2 5 ST LineDocument9 pages2 5 ST LineAudrey LeeNo ratings yet
- MAT 1320 Calculus I Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesMAT 1320 Calculus I Lecture NotestwinlensNo ratings yet
- 11 Mathematics Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pages11 Mathematics Quadratic Equationsjethalal worldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument60 pagesChapter 3 PDFBrishti AroraNo ratings yet
- AUSTRIA Cathline M Graphing and Factoring Quadratic EquationsDocument33 pagesAUSTRIA Cathline M Graphing and Factoring Quadratic EquationsJudy Ann BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Algebraiic Expressions, Equations and Quadratic EquationsDocument37 pagesAlgebraiic Expressions, Equations and Quadratic EquationsNaomi NyambasoNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Functions & GraphsDocument93 pagesCh1 Functions & GraphsBen SmithNo ratings yet
- Calc II ReviewDocument7 pagesCalc II ReviewPablo KhilopNo ratings yet
- Middle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This ClassDocument9 pagesMiddle School Mathematics: 1 Introduction of This Class01. ZUENo ratings yet
- M2 - Lesson 6Document8 pagesM2 - Lesson 6alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- MEI AS Mathematics: Quadratic Functions: Section 1: Quadratic Graphs and EquationsDocument8 pagesMEI AS Mathematics: Quadratic Functions: Section 1: Quadratic Graphs and Equationsbobjeffords687No ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasAmir MustakimNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsDocument16 pagesQuadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsGGy Joe YeeNo ratings yet
- VCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceDocument17 pagesVCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceMikiNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument42 pagesPolynomialsapi-296824694No ratings yet
- Bab 1Document8 pagesBab 1jak92No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument30 pagesQuadratic EquationsChandra Vamsi AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument88 pagesIlovepdf MergedRudransh PawarNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged MergedDocument132 pagesIlovepdf Merged MergedRudransh PawarNo ratings yet
- Solving Polynomial Equations L-1Document5 pagesSolving Polynomial Equations L-1Rohinish DeyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Quadratic EquationiiiDocument9 pagesWorksheet Quadratic EquationiiiKartik AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Equations of Lines Slope of A Line (p.68) : y M (X yDocument9 pages2.1 Equations of Lines Slope of A Line (p.68) : y M (X yAila Elocin PalmasNo ratings yet
- Makalah Quadratic Function in EconomicsDocument25 pagesMakalah Quadratic Function in EconomicsFashihahNo ratings yet
- Linear Law QuestionDocument13 pagesLinear Law QuestionFardeena DaniaNo ratings yet
- Quardatic Equation-01 - TheoryDocument17 pagesQuardatic Equation-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasLuis Fernando De AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Continuity Functions and Continuity Functions and Continuity Functions and ContinuityDocument22 pagesFunctions and Continuity Functions and Continuity Functions and Continuity Functions and ContinuityUmesh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Maths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Document34 pagesMaths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Sam Scheding0% (1)
- LHSBMath9 Q1 Lesson 1Document9 pagesLHSBMath9 Q1 Lesson 1Adrienne BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument57 pagesQuadratic EquationNIKHIL MITTALNo ratings yet
- 3 Quadratic FunctionDocument12 pages3 Quadratic FunctionTANG PEI PEI100% (10)
- C1 Graphs of Functions QuestionsDocument6 pagesC1 Graphs of Functions QuestionsChaterine AdiwinotoNo ratings yet
- Quick Review Chap 4Document2 pagesQuick Review Chap 4Zaid BabarNo ratings yet
- Add Maths F4 Topical Test 3 (E)Document3 pagesAdd Maths F4 Topical Test 3 (E)HANIFAH50% (2)
- Linear Equation in Two VariablesDocument9 pagesLinear Equation in Two Variablesuser-309594No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- General Knowledge Question Answers For Bank PO ExamsDocument37 pagesGeneral Knowledge Question Answers For Bank PO Examsnilesh_manakikarNo ratings yet
- BJ S C, USA: Doug LehrDocument12 pagesBJ S C, USA: Doug LehrBalkis FatihaNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Energy Consumption ModellingDocument20 pagesElectric Vehicle Energy Consumption ModellingRohanNo ratings yet
- Mcdonald's - Group 5Document57 pagesMcdonald's - Group 5Thanh Trà100% (1)
- Table Tennis ActivityDocument2 pagesTable Tennis ActivityCristopher JhanrieNo ratings yet
- Action Plan - Science Dept 2022-2023Document4 pagesAction Plan - Science Dept 2022-2023KIM MARLON GANOBNo ratings yet
- 123Document10 pages123Aryan SanezNo ratings yet
- ECGBiometricsMACS13 Sumair v5 ResearchGateDocument7 pagesECGBiometricsMACS13 Sumair v5 ResearchGatearlikaNo ratings yet
- BSR 231 Grouping Assignment FinaleDocument149 pagesBSR 231 Grouping Assignment FinaleMUHAMMAD FARIS IQBAL BIN RIDUANNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Activity 3Document6 pagesFS 1 Activity 3Nilda EStradaNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers Story of A SeagullDocument5 pagesQuestions and Answers Story of A SeagullScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- NHIDCL Project Status As On 30.09.2023 For Uploading On PortalDocument24 pagesNHIDCL Project Status As On 30.09.2023 For Uploading On PortalChris PresleyNo ratings yet
- Fundamental and Derived PositionDocument47 pagesFundamental and Derived PositionAmbusam Anita100% (1)
- Bronchiectasis in nonCF in ChildrenDocument9 pagesBronchiectasis in nonCF in ChildrenathaNo ratings yet
- CXA 1238 DatasheetDocument58 pagesCXA 1238 DatasheetHoan TranNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Computer and Communication Networks 2 e Nader F MirDocument35 pagesSolution Manual For Computer and Communication Networks 2 e Nader F Mirconcreteprimula2ppwr100% (17)
- IT0007-Laboratory-Exercise-7 - Incident HandlingDocument5 pagesIT0007-Laboratory-Exercise-7 - Incident HandlingDenise JaoNo ratings yet
- Marie Rochelle - Dangerous BetDocument4 pagesMarie Rochelle - Dangerous BetPaulette Jones50% (2)
- Financial Institution Failure Prediction Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference Systems: Evidence From The East Asian Economic CrisisDocument2 pagesFinancial Institution Failure Prediction Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference Systems: Evidence From The East Asian Economic CrisisHannan KüçükNo ratings yet
- Red Hat System Administration I 3.4 PracticeDocument9 pagesRed Hat System Administration I 3.4 PracticestefygrosuNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Introduction To BiostatisticsDocument18 pagesLecture1 Introduction To BiostatisticsIdiAmadouNo ratings yet
- p9-13 PDF Rev2Document5 pagesp9-13 PDF Rev2Moi le Sage100% (2)
- Flashcards - Topic 6.1 6.4 - Microbiology - Edexcel IAL Biology A LevelDocument49 pagesFlashcards - Topic 6.1 6.4 - Microbiology - Edexcel IAL Biology A LevelULFANo ratings yet
- EUNIC Culture Report, 2014Document103 pagesEUNIC Culture Report, 2014Bernd ReiterNo ratings yet
- QA Lead Position Interview Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesQA Lead Position Interview Questions and AnswersAkshay KhotNo ratings yet
- Music Link Investigation 1 & 2 Chhairatanak Huy PDFDocument27 pagesMusic Link Investigation 1 & 2 Chhairatanak Huy PDFChay HuyNo ratings yet
- Explain FOUR Measures Which Governments Can Use To Encourage Entrepreneurial Activities in The Caribbean Region.Document2 pagesExplain FOUR Measures Which Governments Can Use To Encourage Entrepreneurial Activities in The Caribbean Region.Bridget SequeaNo ratings yet
- Highlights of Netbeans Ide 7.0 Keyboard Shortcuts & Code TemplatesDocument2 pagesHighlights of Netbeans Ide 7.0 Keyboard Shortcuts & Code TemplatesJOSEPH DAVID CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalog: 6 WG 200 (555/5) Material Number: 4644.026.333 Current Date: 27.02.2020Document74 pagesSpare Parts Catalog: 6 WG 200 (555/5) Material Number: 4644.026.333 Current Date: 27.02.2020GeorgiNo ratings yet
- Nvod Na Pouitvirtuoso II LINET EN Id192pdfDocument35 pagesNvod Na Pouitvirtuoso II LINET EN Id192pdfrobertoNo ratings yet